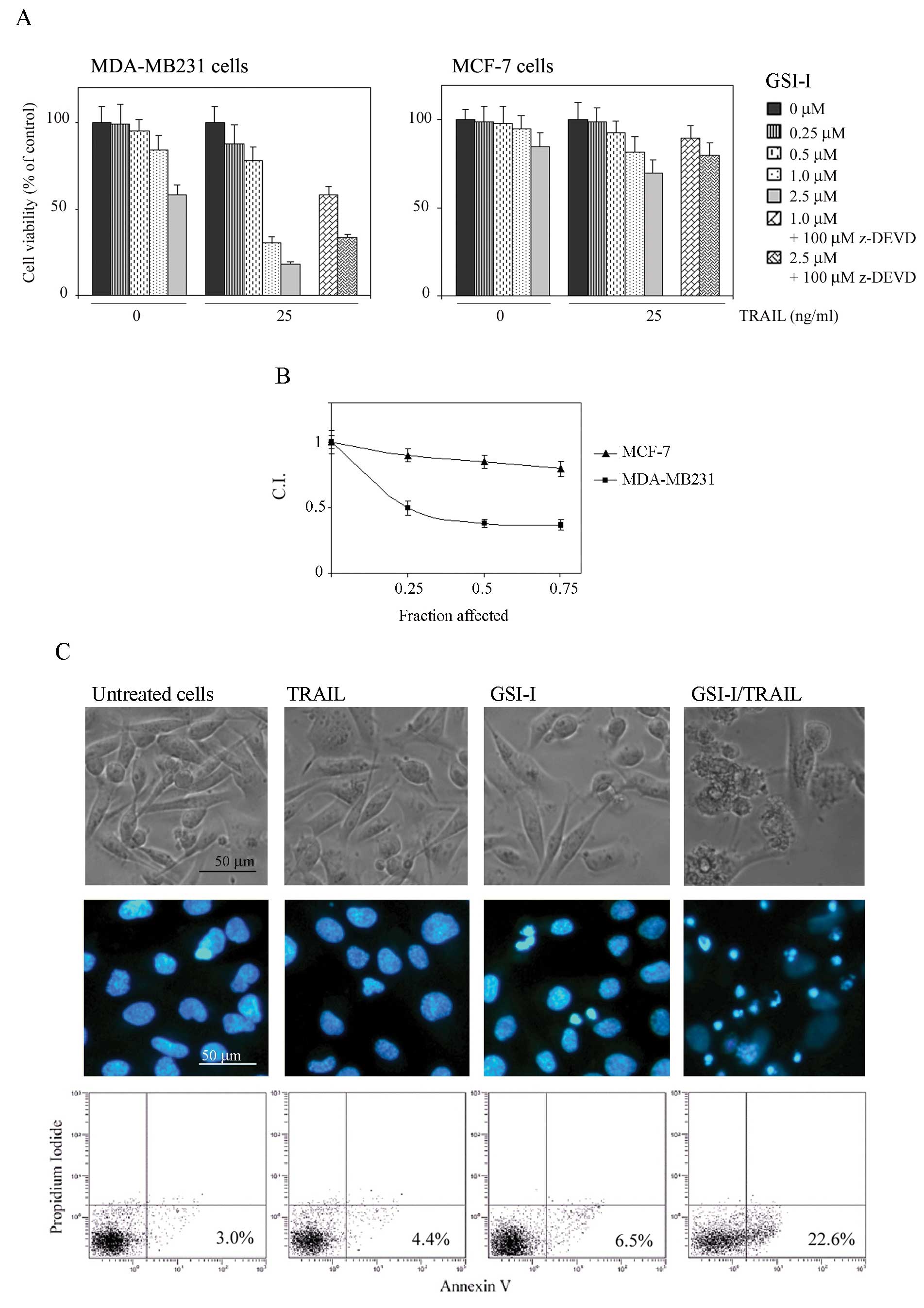
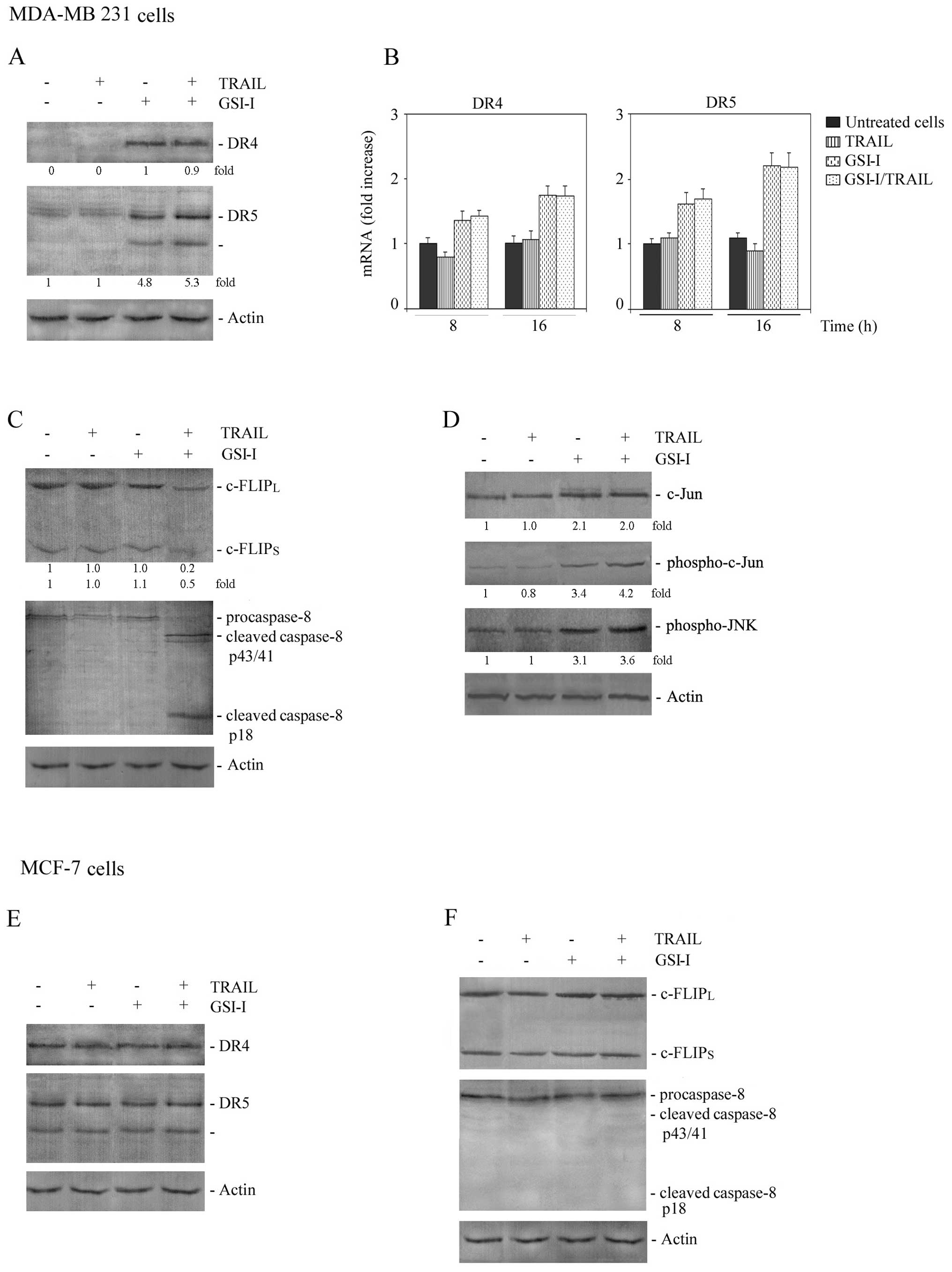
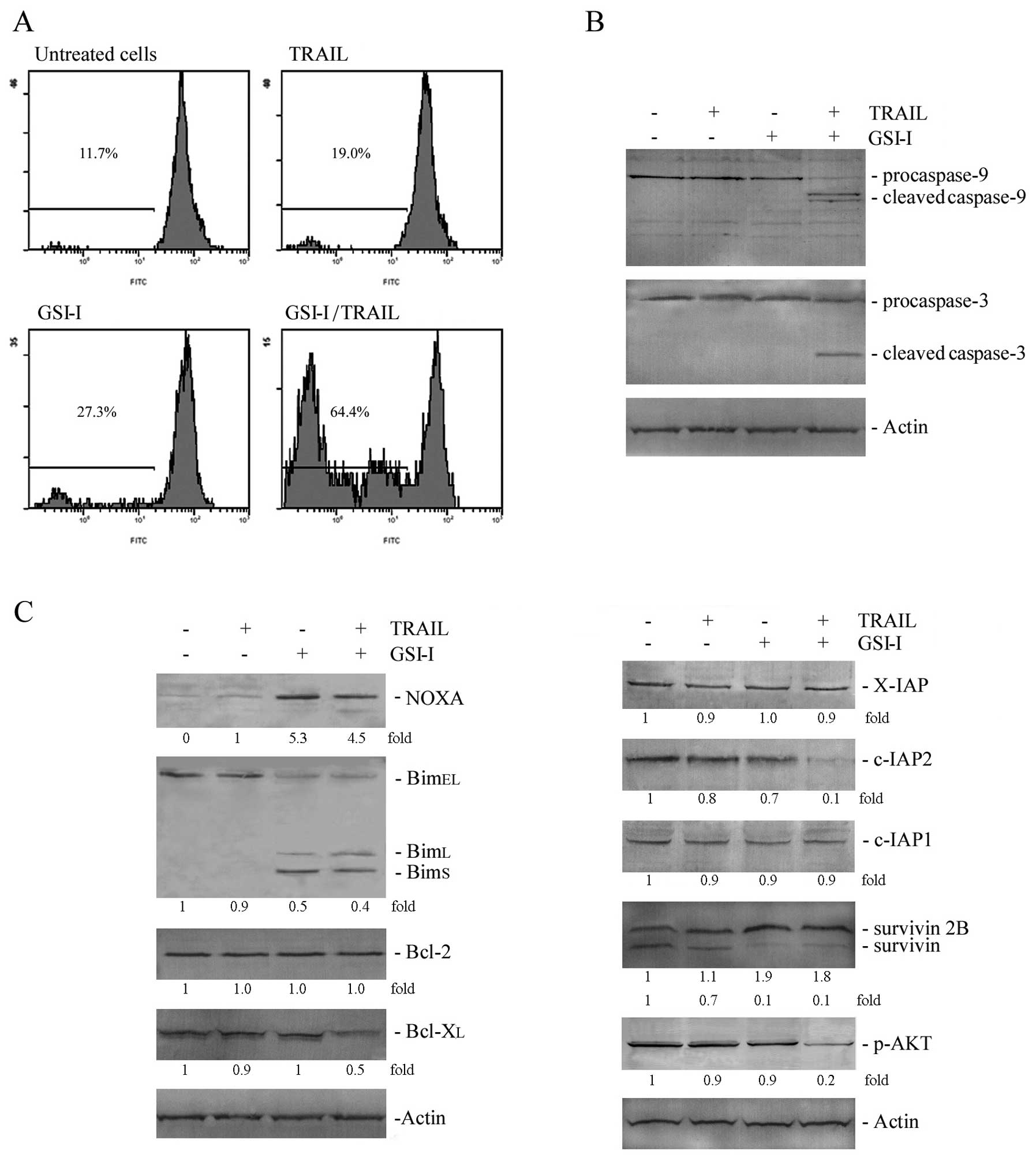
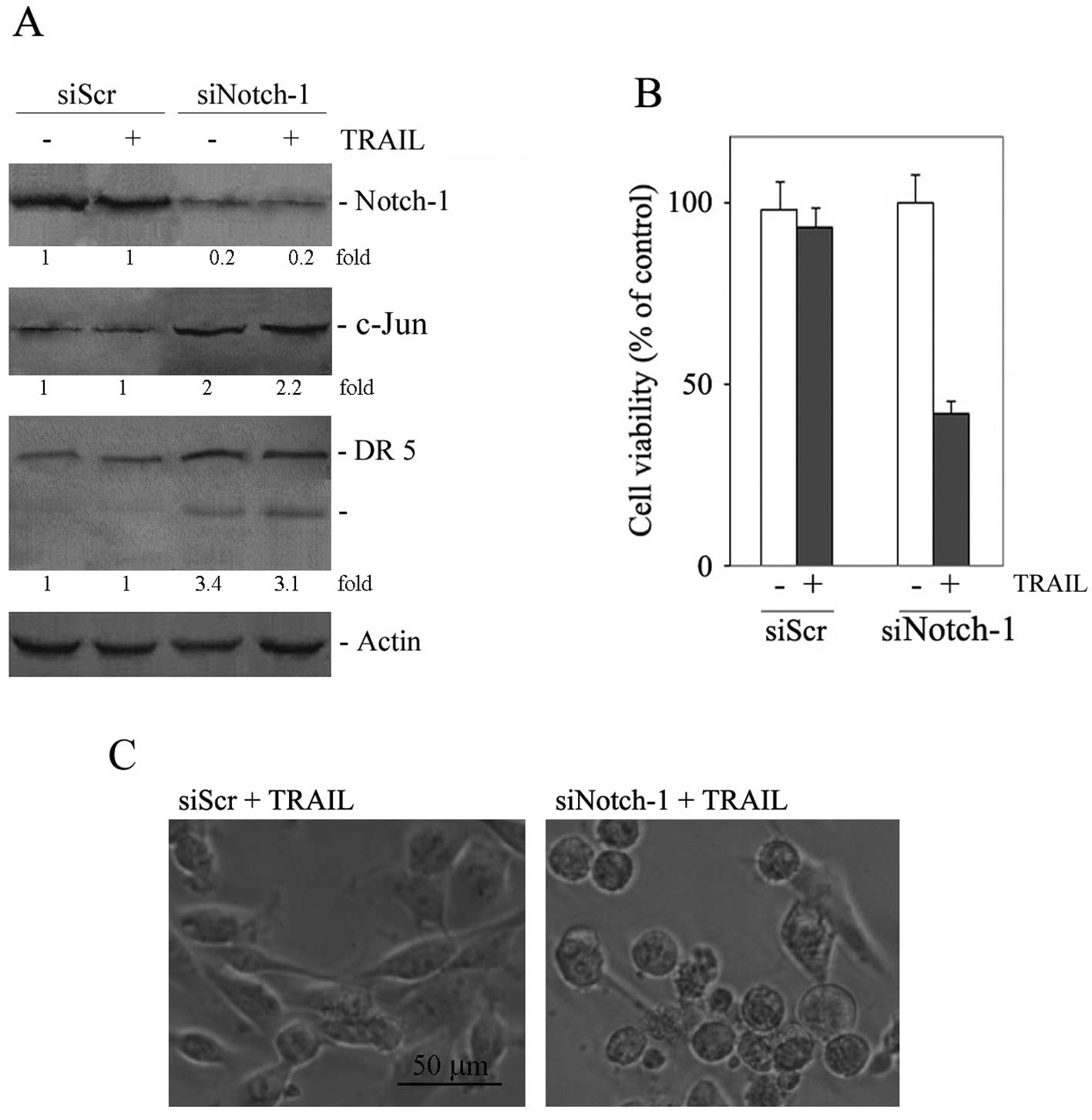
|
1.
|
Dotto GP: Notch tumor suppressor function.
Oncogene. 27:5115–5123. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Fortini ME: Notch signaling: the core
pathway and its post-translational regulation. Dev Cell.
16:633–647. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Miele L, Miao H and Nickoloff BJ: Notch
signaling as a novel cancer therapeutic target. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 6:313–323. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Zardawi SJ, O’Toole SA, Sutherland RL and
Musgrove EA: Dysregulation of Hedgehog, Wnt and Notch signaling
pathways in breast cancer. Histol Histopathol. 24:385–398.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Sonoshita M, Aoki M, Fuwa H, Aoki K,
Hosogi H, Sakai Y, Hashida H, Takabayashi A, Sasaki M, Robine S,
Itoh K, Yoshioka K, Kakizaki F, Kitamura T, Oshima M and Taketo MM:
Suppression of colon cancer metastasis by Aes through inhibition of
Notch signaling. Cancer Cell. 19:125–137. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Wang Z, Li Y, Ahmad A, Banerjee S, Azmi
AS, Kong D, Wojewoda C, Miele L and Sarkar FH: Down-regulation of
Notch-1 is associated with Akt and FoxM1 in inducing cell growth
inhibition and apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. J Cell Biochem.
112:78–88. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Bedogni B, Warneke JA, Nickoloff BJ,
Giaccia AJ and Powell MB: Notch1 is an effector of Akt and hypoxia
in melanoma development. J Clin Invest. 118:3660–3670. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Aster JC, Blacklow SC and Pear WS: Notch
signaling in T-cell lymphoblastic leukaemia/lymphoma and other
haematological malignancies. J Pathol. 223:262–273. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Wang Z, Li Y, Banerjee S and Sarkar FH:
Exploitation of the Notch signaling pathway as a novel target for
cancer therapy. Anticancer Res. 28:3621–3630. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Bergmans BA and De Strooper B:
Gamma-secretase: from cell biology to therapeutic strategies.
Lancet Neurol. 9:215–226. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Panza F, Frisardi V, Imbimbo BP, Capurso
C, Logroscino G, Sancarlo D, Seripa D, Vendemiale G, Pilotto A and
Solfrizzi V: γ-secretase inhibitors for the treatment of
Alzheimer’s disease: the current state. CNS Neurosci Ther.
16:272–284. 2010.
|
|
12.
|
Lin J, Zhang XM, Yang JC, Ye YB and Luo
SQ: γ-secretase inhibitor-I enhances radiosensitivity of
glioblastoma cell lines by depleting CD133+ tumor cells.
Arch Med Res. 41:519–529. 2010.
|
|
13.
|
Wang S and El-Deiry WS: TRAIL and
apoptosis induction by TNF-family death receptors. Oncogene.
22:8628–8633. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Zhang XD, Nguyen T, Thomas WD, Sanders JE
and Hersey P: Mechanisms of resistance of normal cells to TRAIL
induced apoptosis vary between different cell types. FEBS Lett.
482:193–199. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Zhang L and Fang B: Mechanisms of
resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in cancer. Cancer Gene Ther.
12:228–237. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Kischkel FC, Lawrence DA, Chuntharapai A,
Schow P, Kim KJ and Ashkenazi A: Apo2L/TRAIL-dependent recruitment
of endogenous FADD and caspase-8 to death receptors 4 and 5.
Immunity. 12:611–620. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Van Geelen CM, Pennarun B, Le PT, De Vries
EG and De Jong S: Modulation of TRAIL resistance in colon carcinoma
cells: different contributions of DR4 and DR5. BMC Cancer.
11:39–51. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Pellerito O, Calvaruso G, Portanova P, De
Blasio A, Santulli A, Vento R, Tesoriere G and Giuliano M: The
synthetic cannabinoid WIN 55,212-2 sensitizes hepatocellular
carcinoma cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis by activating p8/CCAAT/enhancer
binding protein homologous protein (CHOP)/death receptor 5 (DR5)
axis. Mol Pharmacol. 77:854–863. 2010.
|
|
19.
|
Kahana S, Finniss S, Cazacu S, Xiang C,
Lee HK, Brodie S, Goldstein RS, Roitman V, Slavin S, Mikkelsen T
and Brodie C: Proteasome inhibitors sensitize glioma cells and
glioma stem cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by PKCε-dependent
down-regulation of AKT and XIAP expressions. Cell Signal.
23:1348–1357. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Lauricella M, Ciraolo A, Carlisi D, Vento
R and Tesoriere G: SAHA/TRAIL combination induces detachment and
anoikis of MDA-MB231 and MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Biochimie.
94:287–299. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Barten DM, Meredith JE Jr, Zaczek R,
Houston JG and Albright CF: Gamma-secretase inhibitors for
Alzheimer’s disease: balancing efficacy and toxicity. Drugs RD.
7:87–97. 2006.
|
|
22.
|
Okuhashi Y, Itoh M, Nara N and Tohda S:
Effects of combination of notch inhibitor plus hedgehog inhibitor
or Wnt inhibitor on growth of leukemia cells. Anticancer Res.
31:893–896. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Chen F, Pisklakova A, Li M, Baz R,
Sullivan DM and Nefedova Y: Gamma-secretase inhibitor enhances the
cytotoxic effect of bortezomib in multiple myeloma. Cell Oncol
(Dordr). 34:545–551. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Giuliano M, Pellerito O, Portanova P,
Calvaruso G, Santulli A, De Blasio A, Vento R and Tesoriere G:
Apoptosis induced in HepG2 cells by the synthetic cannabinoid WIN:
involvement of the transcription factor PPARgamma. Biochimie.
91:457–465. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Calvaruso G, Giuliano M, Portanova P,
Pellerito O, Vento R and Tesoriere G: Hsp72 controls
bortezomib-induced HepG2 cell death via interaction with
pro-apoptotic factors. Oncol Rep. 18:447–450. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Rizzo P, Miao H, D’Souza G, Osipo C, Song
LL, Yun J, Zhao H, Mascarenhas J, Wyatt D, Antico G, Hao L, Yao K,
Rajan P, Hicks C, Siziopikou K, Selvaggi S, Bashir A, Bhandari D,
Marchese A, Lendahl U, Qin JZ, Tonetti DA, Albain K, Nickoloff BJ
and Miele L: Cross-talk between Notch and the estrogen receptor in
breast cancer suggest novel therapeutic approaches. Cancer Res.
68:5226–5235. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Chou TC and Talalay P: Quantitative
analysis of dose effect relationship: the combined effect of
multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul. 22:27–55.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
LeBlanc HN and Ashkenazi A: Apo2L/TRAIL
and its death and decoy receptors. Cell Death Differ. 10:66–75.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Zou W, Liu X, Yue P, Zhou Z, Sporn MB,
Lotan R, Khuri FR and Sun SY: c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-mediated
up-regulation of death receptor 5 contributes to induction of
apoptosis by the novel synthetic triterpenoid
methyl-2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1, 9-dien-28-oate in human lung
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 64:7570–7578. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30.
|
Day TW, Huang S and Safa AR: c-FLIP
knockdown induces ligand-independent DR5-, -FADD-, caspase-8-, and
caspase-9-dependent apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Biochem
Pharmacol. 76:1694–1704. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
O’Connor L, Strasser A, O’Reilly LA,
Hausmann G, Adams JM, Cory S and Huang DC: Bim: a novel member of
the Bcl-2 family that promotes apoptosis. EMBO J. 17:384–395.
1998.
|
|
33.
|
Li F: Role of survivin and its splice
variants in tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer. 92:212–216. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Ryan B, O’Donovan N, Browne B, O’Shea C,
Crown J, Hill AD, McDermott E, O’Higgins N and Duffy MJ: Expression
of surviving and its splice variants surviving-2B and surviving-Ex3
in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 92:120–124. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Ghayad SE and Cohen PA: Inhibitors of the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway: new hope for breast cancer patients. Recent
Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 5:29–57. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Carnero A: The PKB/AKT pathway in cancer.
Curr Pharm Des. 16:34–44. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Tenzer A, Zingg D, Rocha S, Hemmings B,
Fabbro D, Glanzmann C, Schubiger PA, Bodis S and Pruschy M: The
phosphatidylinositide 3′-kinase/Akt survival pathway is a target
for the anticancer and radiosensitizing agent PKC412, an inhibitor
of protein kinase C. Cancer Res. 61:8203–8210. 2001.
|
|
38.
|
Chen JQ and Russo J: ERalpha-negative and
triple negative breast cancer: molecular features and potential
therapeutic approaches. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1796:162–175.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Borggrefe T and Oswald F: The Notch
signaling pathway: transcriptional regulation at Notch target
genes. Cell Mol Life Sci. 66:1631–1646. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Chu J, Jeffties S, Norton JE, Capobianco
AJ and Bresnick EH: Repression of activator protein-1 mediated
transcriptional activation by the Notch-1 intracellular domain. J
Biol Chem. 277:7587–7597. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Kim JW, Kim MJ, Kim KJ, Yun HJ, Chae JS,
Hwang SG, Chang TS, Park HS, Lee KW, Han PL, Cho SG, Kim TW and
Choi EJ: Notch interferes with the scaffold function of
JNK-interacting protein 1 to inhibit the JNK signaling pathway.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:14308–14313. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Han J, Ma I, Hendzel MJ and
Allalunis-Turner J: The cytotoxicity of gamma-secretase inhibitor I
to breast cancer cells is mediated by proteasome inhibition, not by
gamma-secretase inhibition. Breast Cancer Res. 11:R572009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Lee CW, Raskett CM, Prudovsky I and
Altieri DC: Molecular dependence of estrogen receptor-negative
breast cancer on a notch-survivin signaling axis. Cancer Res.
68:5273–5281. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Wang C, Qi R, Li N, Wang Z, An H, Zhang Q,
Yu Y and Cao X: Notch1 signaling sensitizes tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis in human
hepato-cellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting Akt/Hdm2-mediated p53
degradation and up-regulating p53-dependent DR5 expression. J Biol
Chem. 284:16183–16190. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|