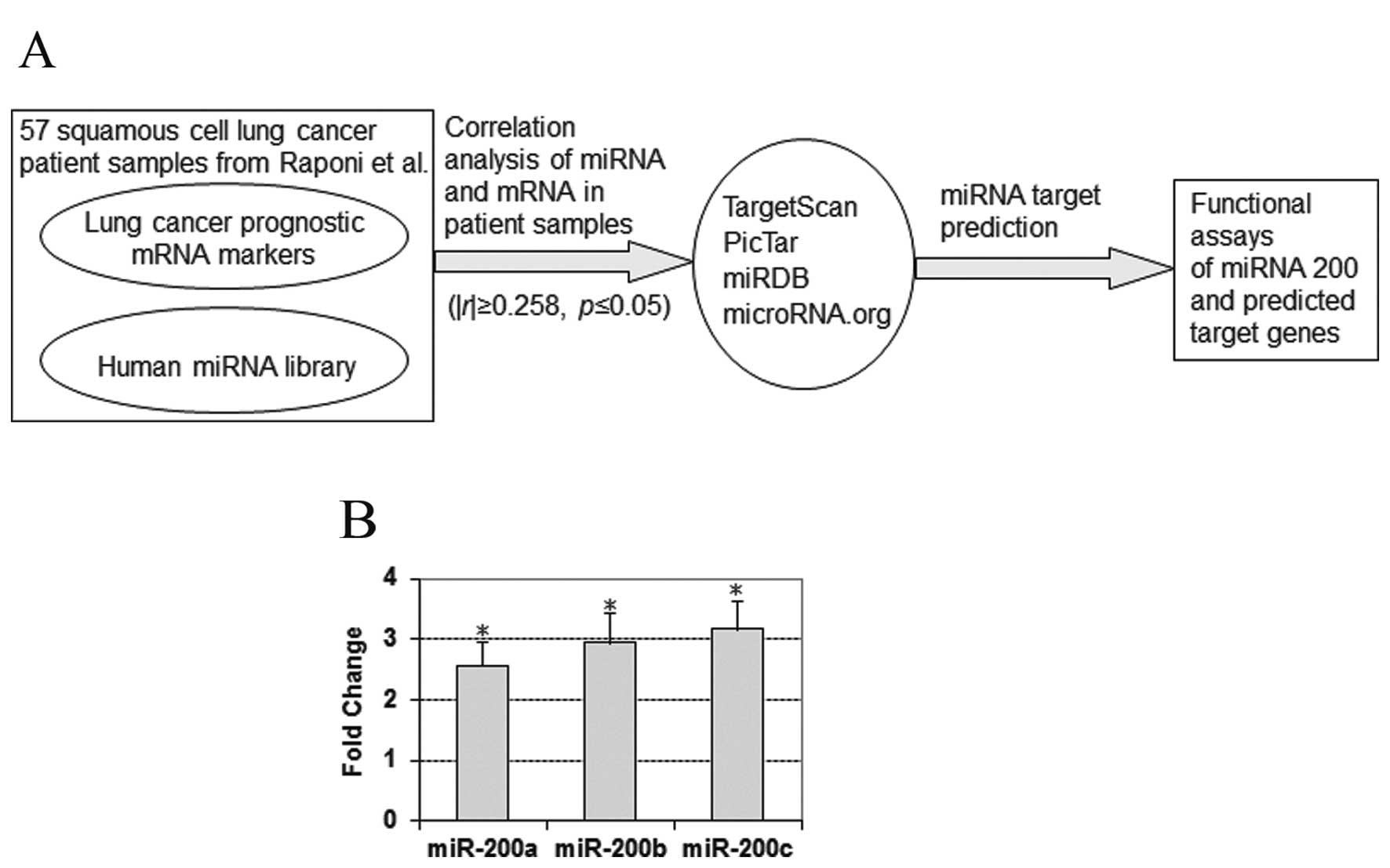
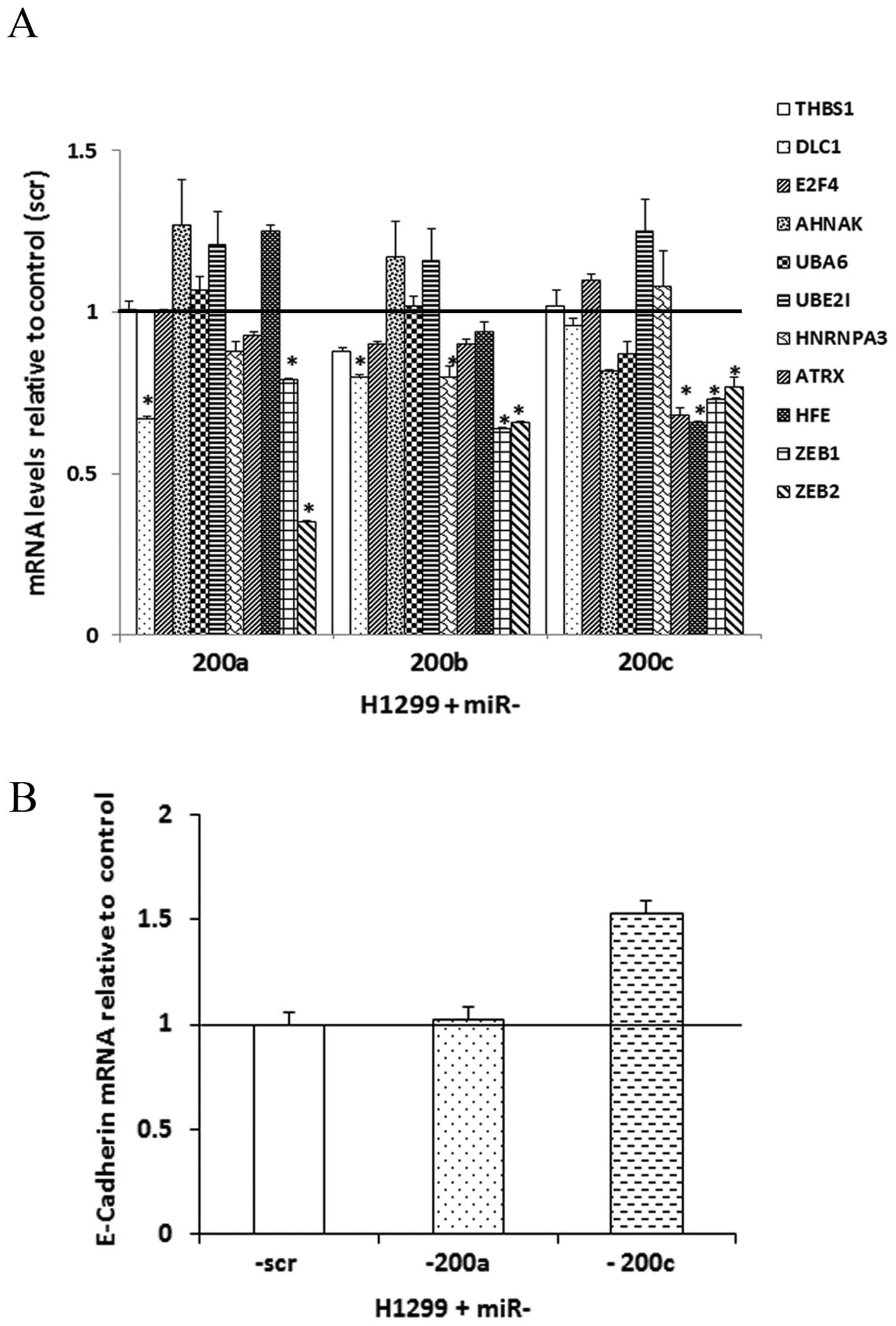
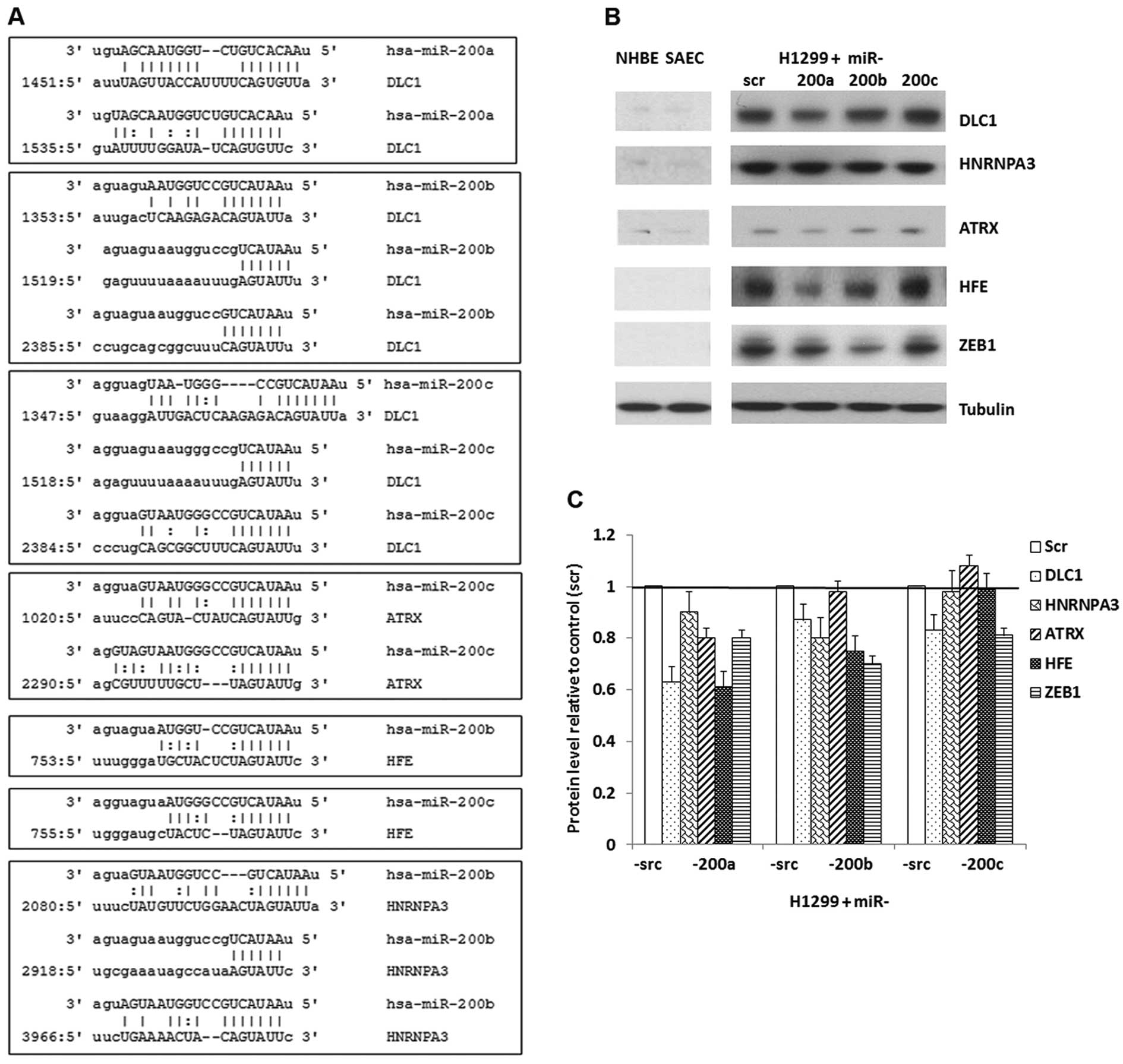
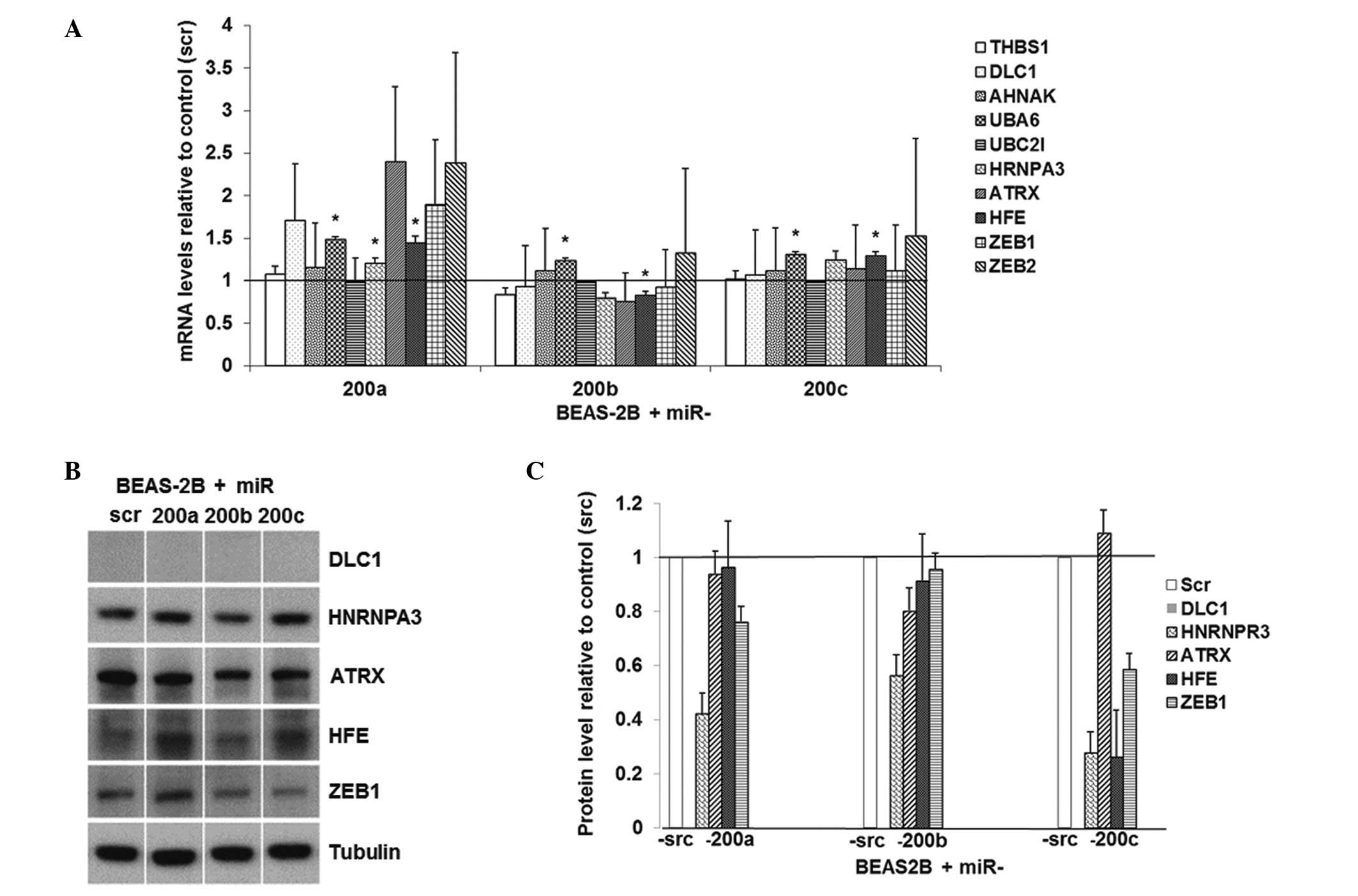
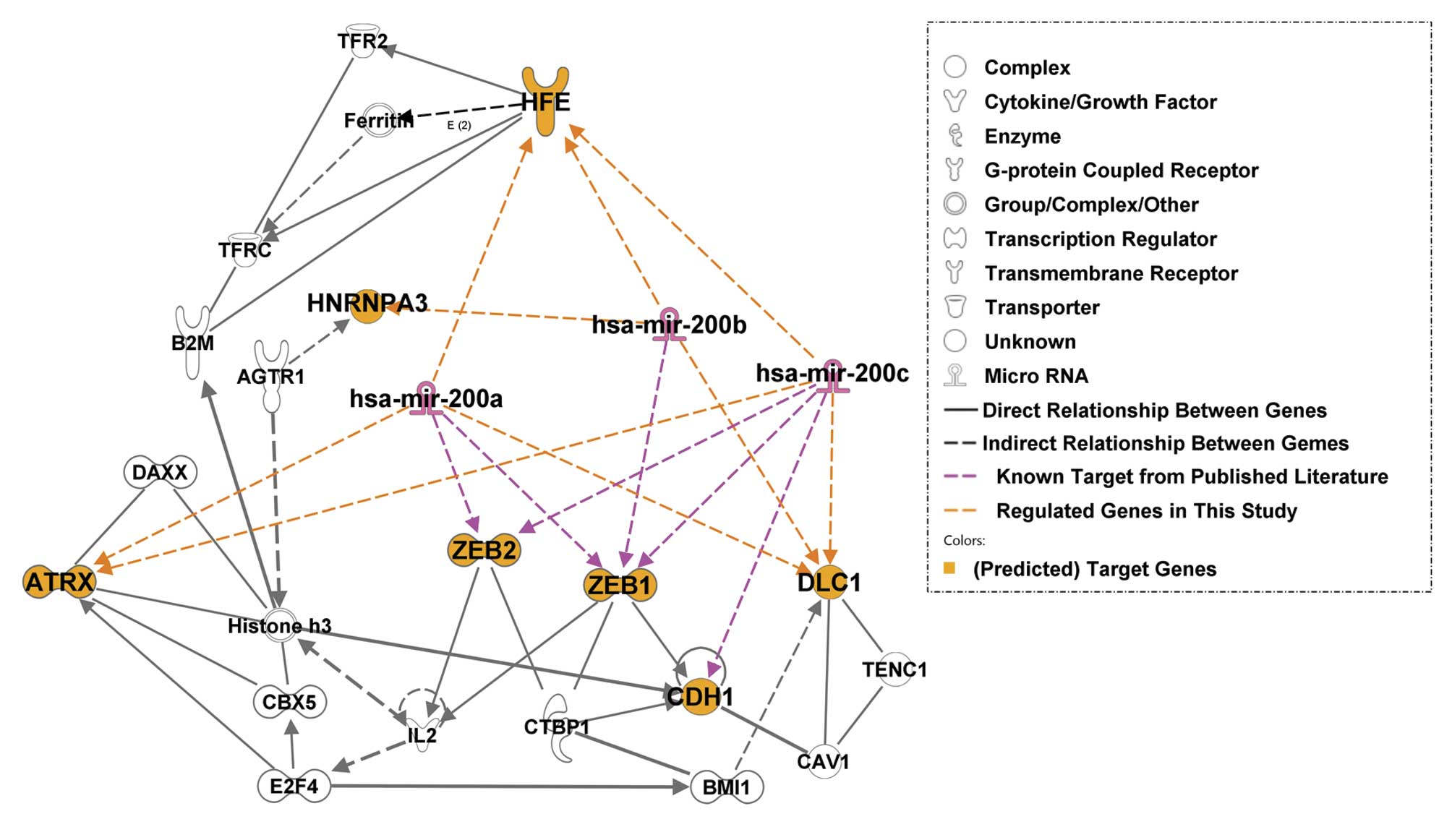
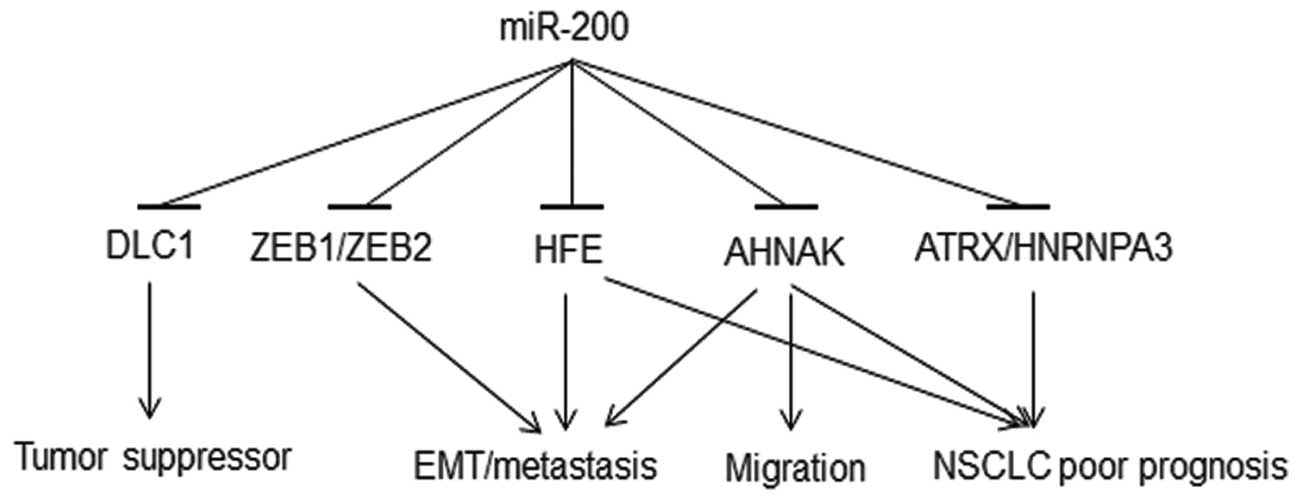
|
1.
|
Mirshahidi HR and Hsueh CT: Updates in
non-small cell lung cancer - insights from the 2009 45th annual
meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J Hematol
Oncol. 3:182010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Monteiro J and Fodde R: Cancer stemness
and metastasis: therapeutic consequences and perspectives. Eur J
Cancer. 46:1198–1203. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelialmesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Dohadwala M, Yang SC, Luo J, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2-dependent regulation of E-cadherin: prostaglandin
E(2) induces transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and snail in non-small
cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 66:5338–5345. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Kasinski AL and Slack FJ: MicroRNAs en
route to the clinic: progress in validating and targeting microRNAs
for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:849–864. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Edwards JK, Pasqualini R, Arap W and Calin
GA: MicroRNAs and ultraconserved genes as diagnostic markers and
therapeutic targets in cancer and cardiovascular diseases. J
Cardiovasc Transl Res. 3:271–279. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Fabbri M: miRNAs as molecular biomarkers
of cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 10:435–444. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Krek A, Grun D, Poy MN, et al:
Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet. 37:495–500.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Nicoloso MS, Spizzo R, Shimizu M, Rossi S
and Calin GA: MicroRNAs - the micro steering wheel of tumour
metastases. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:293–302. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Kozomara A and Griffiths-Jones S: miRBase:
integrating microRNA annotation and deep-sequencing data. Nucleic
Acids Res. 39:D152–D157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Gregory PA, Bracken CP, Bert AG and
Goodall GJ: MicroRNAs as regulators of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Cell Cycle. 7:3112–3118. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, et al:
The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 10:593–601.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Park SM, Gaur AB, Lengyel E and Peter ME:
The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer
cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes
Dev. 22:894–907. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Guarino M, Rubino B and Ballabio G: The
role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer pathology.
Pathology. 39:305–318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Cochrane DR, Howe EN, Spoelstra NS and
Richer JK: Loss of miR-200c: a marker of aggressiveness and
chemoresistance in female reproductive cancers. J Oncol.
2010:8217172010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Guo L, Ma Y, Ward R, et al: Constructing
molecular classifiers for the accurate prognosis of lung
adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 12:3344–3354. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Guo NL, Wan YW, Tosun K, et al:
Confirmation of gene expression-based prediction of survival in
non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 14:8213–8220. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Wan YW, Sabbagh E, Raese R, et al: Hybrid
models identified a 12-gene signature for lung cancer prognosis and
chemoresponse prediction. PLoS One. 5:e122222010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Shedden K, Taylor JM, Enkemann SA, et al:
Gene expression-based survival prediction in lung adenocarcinoma: a
multi-site, blinded validation study. Nat Med. 14:822–827. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Raponi M, Zhang Y, Yu J, et al: Gene
expression signatures for predicting prognosis of squamous cell and
adenocarcinomas of the lung. Cancer Res. 66:7466–7472. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Raponi M, Dossey L, Jatkoe T, et al:
MicroRNA classifiers for predicting prognosis of squamous cell lung
cancer. Cancer Res. 69:5776–5783. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Chen K and Rajewsky N: Natural selection
on human microRNA binding sites inferred from SNP data. Nat Genet.
38:1452–1456. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Betel D, Wilson M, Gabow A, Marks DS and
Sander C: The microRNA.orgurisimplemicroRNA.org resource: targets
and expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 36:D149–D153. 2008.
|
|
27.
|
Papadopoulos GL, Reczko M, Simossis VA,
Sethupathy P and Hatzigeorgiou AG: The database of experimentally
supported targets: a functional update of TarBase. Nucleic Acids
Res. 37:D155–D158. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Jan CH, Friedman RC, Ruby JG and Bartel
DP: Formation, regulation and evolution of Caenorhabditis
elegans 3′UTRs. Nature. 469:97–101. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Elson-Schwab I, Lorentzen A and Marshall
CJ: MicroRNA-200 family members differentially regulate
morphological plasticity and mode of melanoma cell invasion. PLoS
One. 5:e131762010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Ceppi P, Mudduluru G, Kumarswamy R, et al:
Loss of miR-200c expression induces an aggressive, invasive, and
chemoresistant phenotype in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer
Res. 8:1207–1216. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Takeyama Y, Sato M, Horio M, et al:
Knockdown of ZEB1, a master epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
(EMT) gene, suppresses anchorage-independent cell growth of lung
cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 296:216–224. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Hoffman PC, Mauer AM and Vokes EE: Lung
cancer. Lancet. 355:479–485. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Naruke T, Goya T, Tsuchiya R and Suemasu
K: Prognosis and survival in resected lung carcinoma based on the
new international staging system. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
96:440–447. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Shields TH, LoCicero J, Reed CE and Feins
RH: General Thoracic Surgery. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins;
Philadelphia, PA: 2009
|
|
35.
|
Burk U, Schubert J, Wellner U, et al: A
reciprocal repression between ZEB1 and members of the miR-200
family promotes EMT and invasion in cancer cells. EMBO Rep.
9:582–589. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Bracken CP, Gregory PA, Kolesnikoff N, et
al: A double-negative feedback loop between ZEB1-SIP1 and the
microRNA-200 family regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Cancer Res. 68:7846–7854. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Sulzer MA, Leers MP, van Noord JA, Bollen
EC and Theunissen PH: Reduced E-cadherin expression is associated
with increased lymph node metastasis and unfavorable prognosis in
non-small cell lung cancer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
157:1319–1323. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Patnaik SK, Kannisto E, Knudsen S and
Yendamuri S: Evaluation of microRNA expression profiles that may
predict recurrence of localized stage I non-small cell lung cancer
after surgical resection. Cancer Res. 70:36–45. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Meng F, Henson R, Lang M, et al:
Involvement of human micro-RNA in growth and response to
chemotherapy in human cholangiocarcinoma cell lines.
Gastroenterology. 130:2113–2129. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Iorio MV, Visone R, Di LG, et al: MicroRNA
signatures in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 67:8699–8707. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Xi Y, Formentini A, Chien M, et al:
Prognostic values of microRNAs in colorectal cancer. Biomark
Insights. 2:113–121. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Gibbons DL, Lin W, Creighton CJ, et al:
Contextual extracellular cues promote tumor cell EMT and metastasis
by regulating miR-200 family expression. Genes Dev. 23:2140–2151.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Olson P, Lu J, Zhang H, et al: MicroRNA
dynamics in the stages of tumorigenesis correlate with hallmark
capabilities of cancer. Genes Dev. 23:2152–2165. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Roybal JD, Zang Y, Ahn YH, et al: miR-200
inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell invasion and metastasis by
targeting Flt1/VEGFR1. Mol Cancer Res. 9:25–35. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Dykxhoorn DM, Wu Y, Xie H, et al: miR-200
enhances mouse breast cancer cell colonization to form distant
metastases. PLoS One. 4:e71812009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Korpal M, Ell BJ, Buffa FM, et al: Direct
targeting of Sec23a by miR-200s influences cancer cell secretome
and promotes metastatic colonization. Nat Med. 17:1101–1108. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Chang CJ, Chao CH, Xia W, et al: p53
regulates epithelialmesenchymal transition and stem cell properties
through modulating miRNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 13:317–323. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Schubert J and Brabletz T: p53 spreads out
further: suppression of EMT and stemness by activating miR-200c
expression. Cell Res. 21:705–707. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Kim T, Veronese A, Pichiorri F, et al: p53
regulates epithelialmesenchymal transition through microRNAs
targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Exp Med. 208:875–883. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Hermeking H: p53 enters the microRNA
world. Cancer Cell. 12:414–418. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Wang G, Hu X, Lu C, et al:
Promoter-hypermethylation associated defective expression of
E-cadherin in primary non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
62:162–172. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Suzuki M, Sunaga N, Shames DS, et al: RNA
interference-mediated knockdown of DNA methyltransferase 1 leads to
promoter demethylation and gene re-expression in human lung and
breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 64:3137–3143. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Sansom SE, Nuovo GJ, Martin MM, et al:
miR-802 regulates human angiotensin II type 1 receptor expression
in intestinal epithelial C2BBe1 cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 299:G632–G642. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Yan M, Huang HY, Wang T, et al:
Dysregulated expression of dicer and drosha in breast cancer.
Pathol Oncol Res. 18:343–348. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55.
|
Martin PM, Gnana-Prakasam JP, Roon P, et
al: Expression and polarized localization of the hemochromatosis
gene product HFE in retinal pigment epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 47:4238–4244. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
Lee SY, Liu S, Mitchell RM, et al: HFE
polymorphisms influence the response to chemotherapeutic agents via
induction of p16INK4A. Int J Cancer. 129:2104–2114. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57.
|
Josson S, Nomura T, Lin JT, et al:
β2-microglobulin induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition and
confers cancer lethality and bone metastasis in human cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 71:2600–2610. 2011.
|
|
58.
|
Shankar J, Messenberg A, Chan J, et al:
Pseudopodial actin dynamics control epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in meta-static cancer cells. Cancer Res. 70:3780–3790.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59.
|
Boukakis G, Patrinou-Georgoula M,
Lekarakou M, Valavanis C and Guialis A: Deregulated expression of
hnRNP A/B proteins in human non-small cell lung cancer: parallel
assessment of protein and mRNA levels in paired tumour/non-tumour
tissues. BMC Cancer. 10:4342010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60.
|
Durkin ME, Yuan BZ, Zhou X, et al: DLC-1:
a Rho GTPase-activating protein and tumour suppressor. J Cell Mol
Med. 11:1185–1207. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61.
|
Yuan BZ, Miller MJ, Keck CL, et al:
Cloning, characterization, and chromosomal localization of a gene
frequently deleted in human liver cancer (DLC-1) homologous to rat
RhoGAP. Cancer Res. 58:2196–2199. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62.
|
Banaudha K, Kaliszewski M, Korolnek T, et
al: MicroRNA silencing of tumor suppressor DLC-1 promotes efficient
hepatitis C virus replication in primary human hepatocytes.
Hepatology. 53:53–61. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|