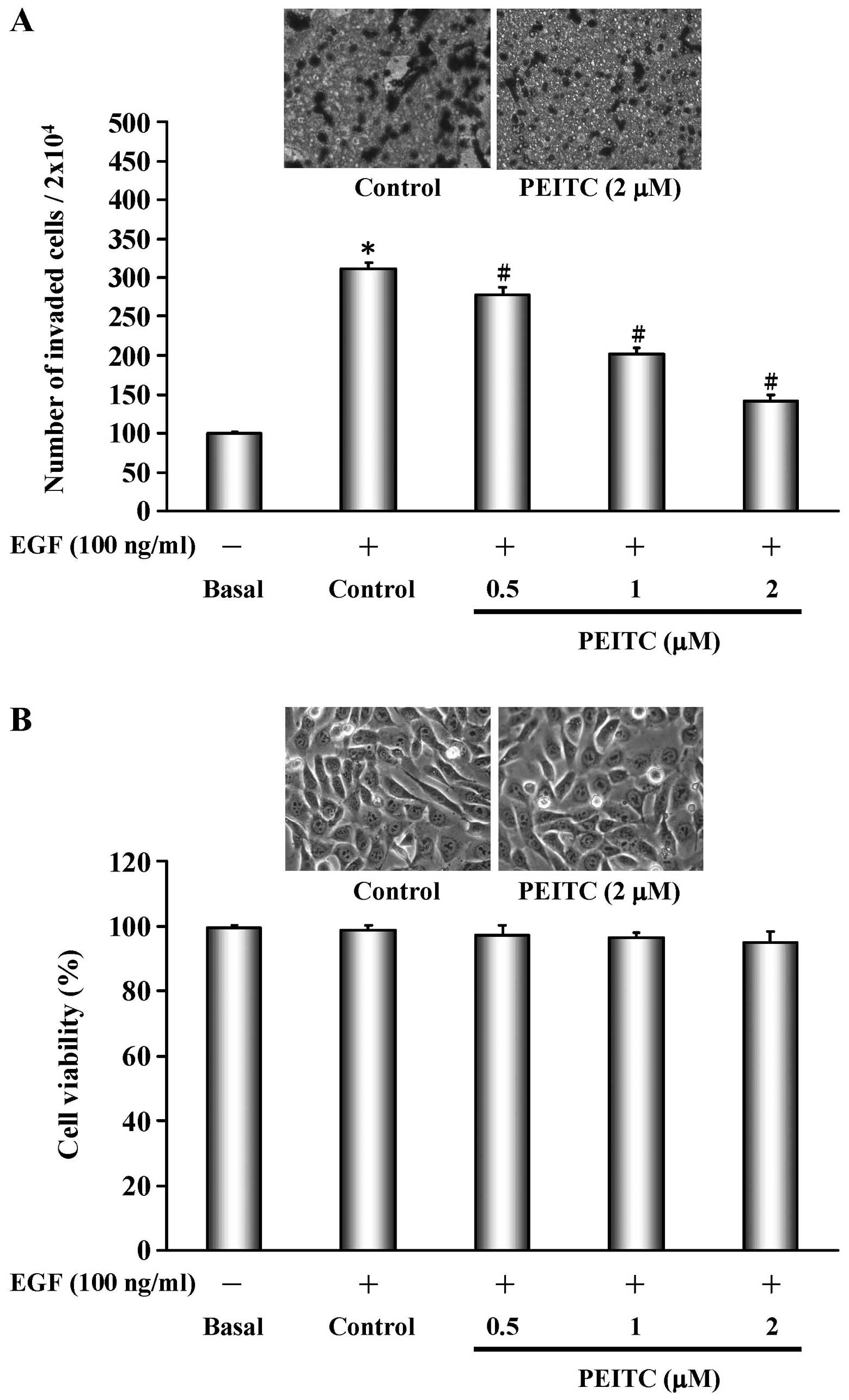
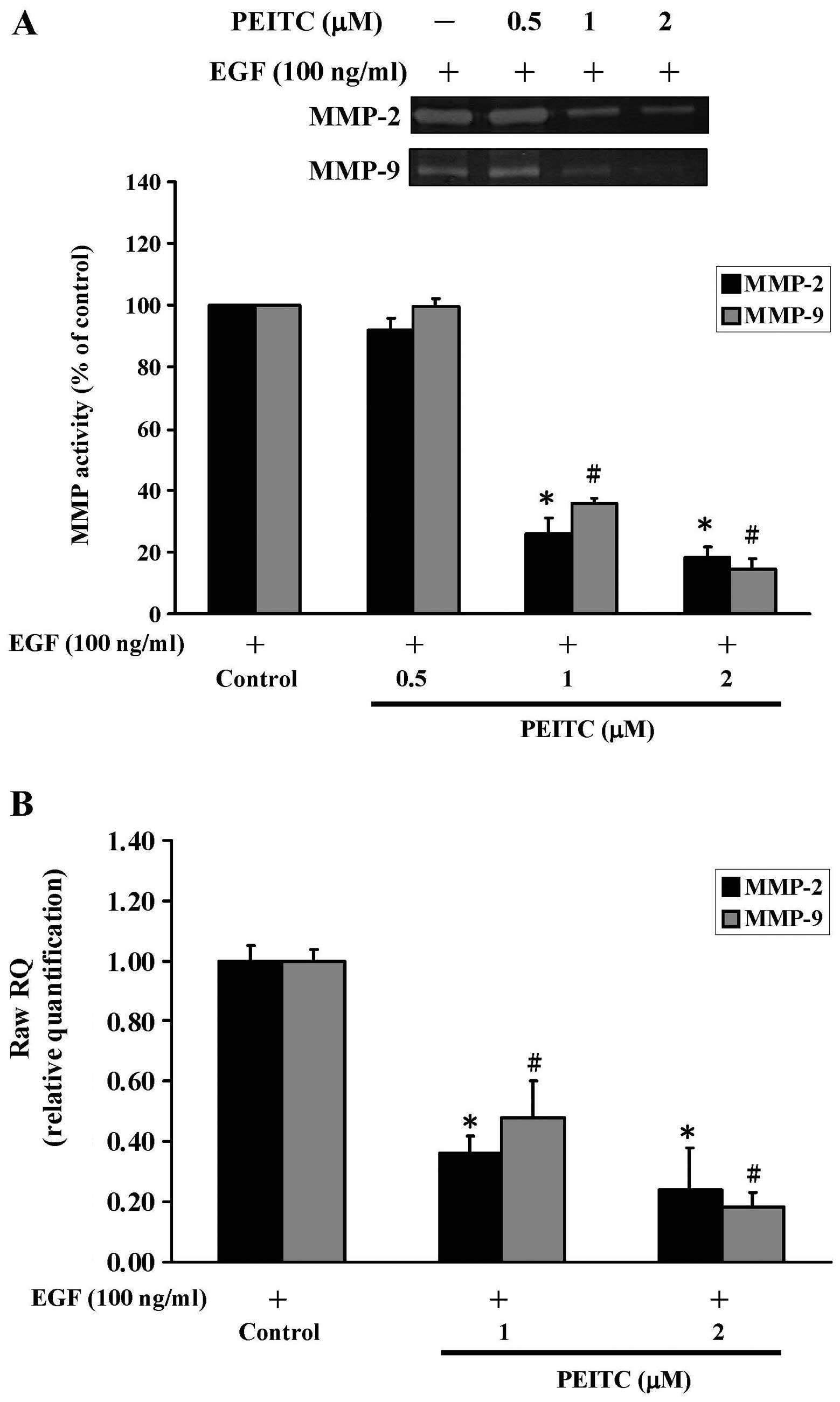
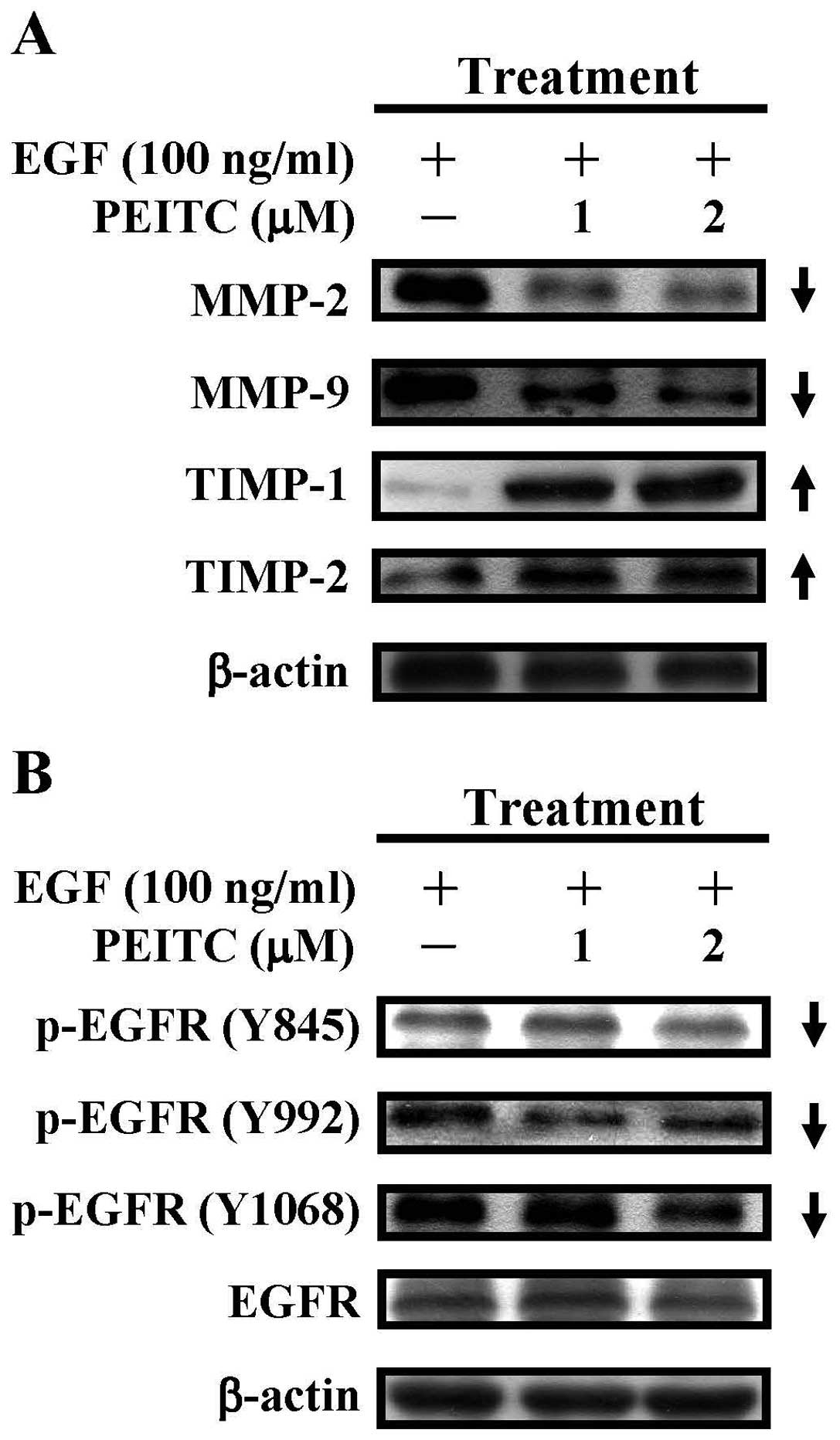
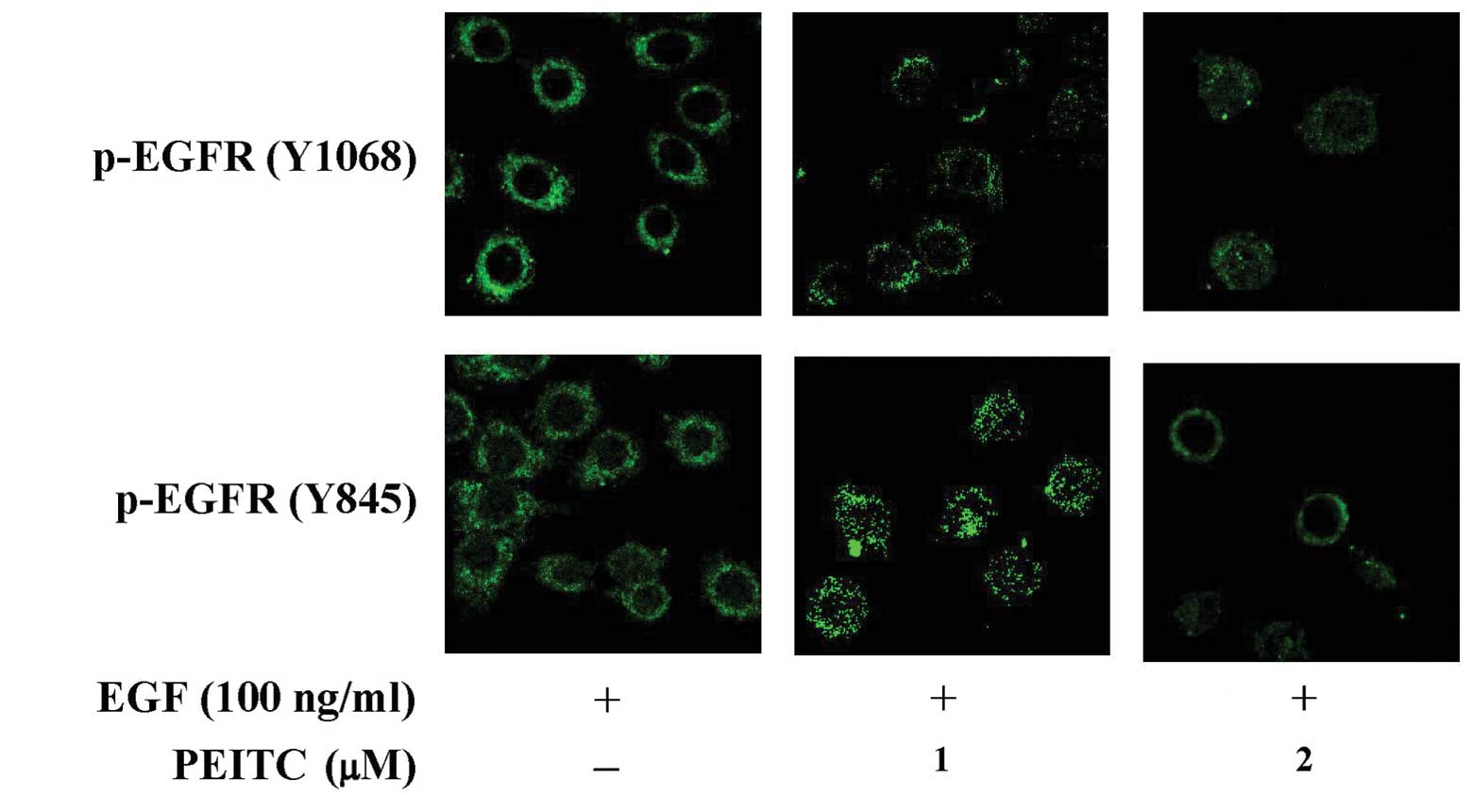
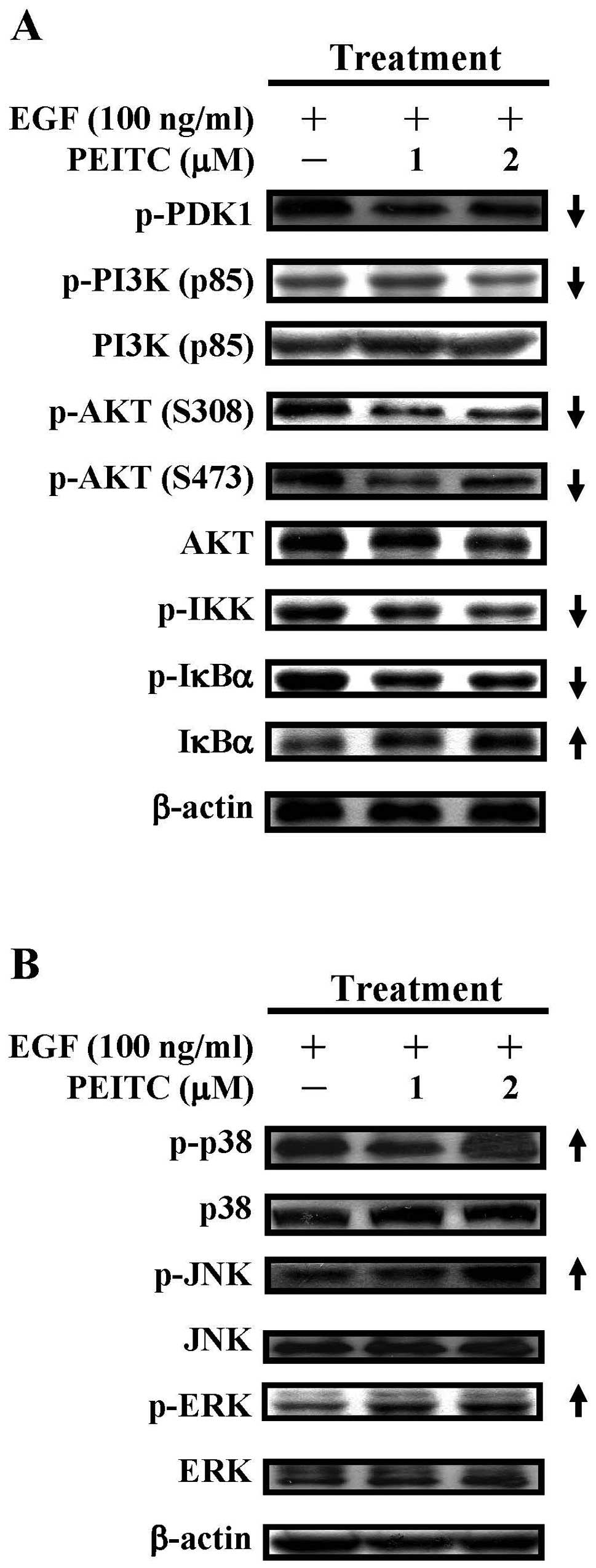
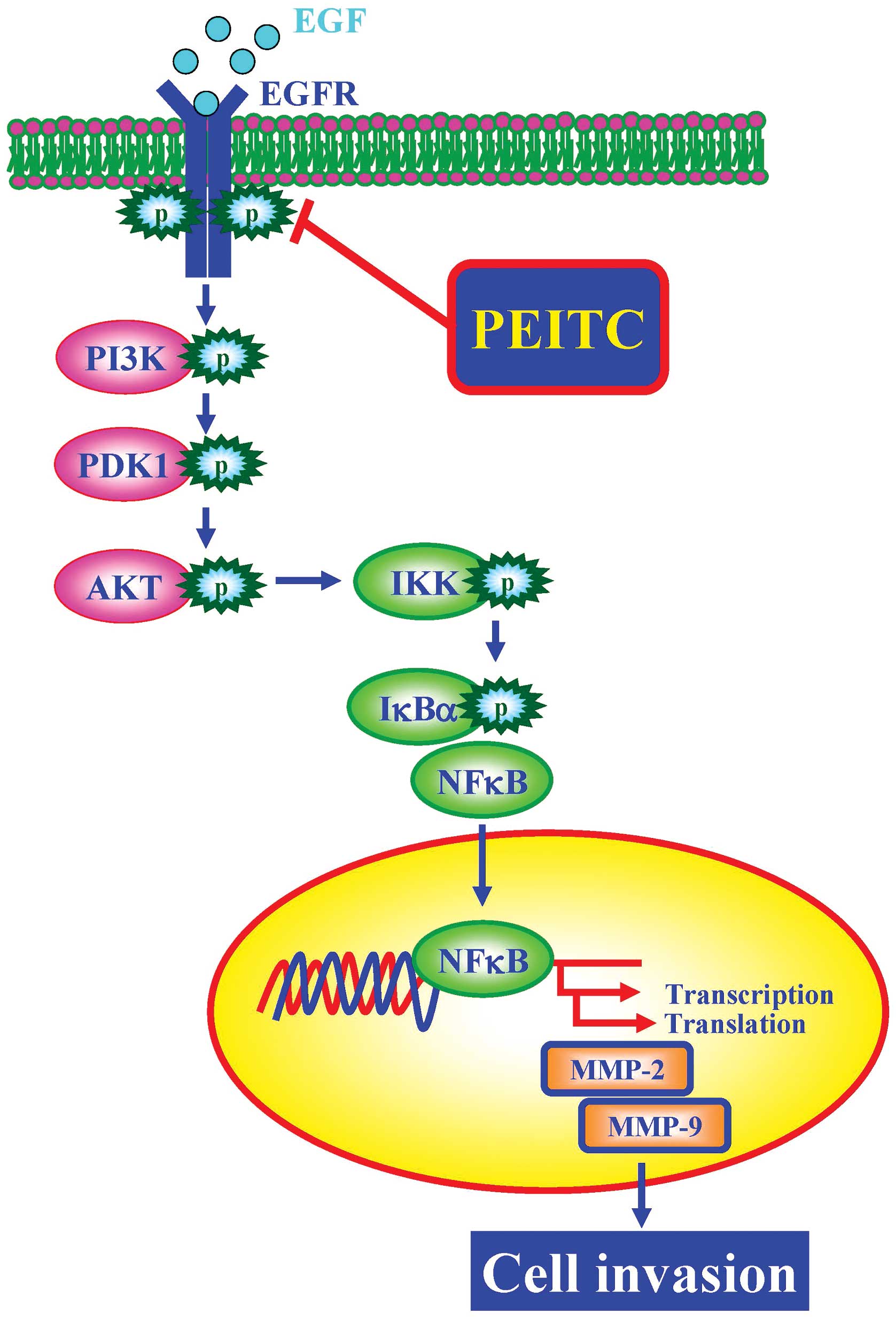
|
1.
|
Noguti J, De Moura CF, De Jesus GP, et al:
Metastasis from oral cancer: an overview. Cancer Genomics
Proteomics. 9:329–335. 2012.
|
|
2.
|
Sarode SC, Sarode GS, Karmarkar S and
Tupkari JV: A new classification for potentially malignant
disorders of the oral cavity. Oral Oncol. 47:920–921. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Seethala RR, Gooding WE, Handler PN, et
al: Immunohistochemical analysis of phosphotyrosine signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 and epidermal growth
factor receptor autocrine signaling pathways in head and neck
cancers and meta-static lymph nodes. Clin Cancer Res. 14:1303–1309.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Franceschi S, Bidoli E, Baron AE, et al:
Nutrition and cancer of the oral cavity and pharynx in north-east
Italy. Int J Cancer. 47:20–25. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Velly AM, Franco EL, Schlecht N, et al:
Relationship between dental factors and risk of upper aerodigestive
tract cancer. Oral Oncol. 34:284–291. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Ko YC, Huang YL, Lee CH, Chen MJ, Lin LM
and Tsai CC: Betel quid chewing, cigarette smoking and alcohol
consumption related to oral cancer in Taiwan. J Oral Pathol Med.
24:450–453. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Ichimiya Y, Fuwa N, Kamata M, et al:
Treatment results of stage I oral tongue cancer with definitive
radiotherapy. Oral Oncol. 41:520–525. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Xi S and Grandis JR: Gene therapy for the
treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Dent Res. 82:11–16.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Pereira MC, Oliveira DT, Landman G and
Kowalski LP: Histologic subtypes of oral squamous cell carcinoma:
prognostic relevance. J Can Dent Assoc. 73:339–344. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Okura M, Aikawa T, Sawai NY, Iida S and
Kogo M: Decision analysis and treatment threshold in a management
for the N0 neck of the oral cavity carcinoma. Oral Oncol.
45:908–911. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Greenberg JS, Fowler R, Gomez J, et al:
Extent of extracapsular spread: a critical prognosticator in oral
tongue cancer. Cancer. 97:1464–1470. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Stan SD, Kar S, Stoner GD and Singh SV:
Bioactive food components and cancer risk reduction. J Cell
Biochem. 104:339–356. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Stan SD, Singh SV and Brand RE:
Chemoprevention strategies for pancreatic cancer. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:347–356. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Keum YS, Jeong WS and Kong AN:
Chemopreventive functions of isothiocyanates. Drug News Perspect.
18:445–451. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Ambrosone CB, McCann SE, Freudenheim JL,
Marshall JR, Zhang Y and Shields PG: Breast cancer risk in
premenopausal women is inversely associated with consumption of
broccoli, a source of isothiocyanates, but is not modified by GST
genotype. J Nutr. 134:1134–1138. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Greenwald P, Clifford CK and Milner JA:
Diet and cancer prevention. Eur J Cancer. 37:948–965. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18.
|
Conaway CC, Yang YM and Chung FL:
Isothiocyanates as cancer chemopreventive agents: their biological
activities and metabolism in rodents and humans. Curr Drug Metab.
3:233–255. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Hecht SS: Inhibition of carcinogenesis by
isothiocyanates. Drug Metab Rev. 32:395–411. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Fahey JW, Zalcmann AT and Talalay P: The
chemical diversity and distribution of glucosinolates and
isothiocyanates among plants. Phytochemistry. 56:5–51. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Hayes JD, Kelleher MO and Eggleston IM:
The cancer chemopreventive actions of phytochemicals derived from
glucosinolates. Eur J Nutr. 47(Suppl 2): 73–88. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Kumar A and Sabbioni G: New biomarkers for
monitoring the levels of isothiocyanates in humans. Chem Res
Toxicol. 23:756–765. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Khor TO, Cheung WK, Prawan A, Reddy BS and
Kong AN: Chemoprevention of familial adenomatous polyposis in
Apc(Min/+) mice by phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC). Mol Carcinog.
47:321–325. 2008.
|
|
24.
|
Moy KA, Yuan JM, Chung FL, et al: Urinary
total isothiocyanates and colorectal cancer: a prospective study of
men in Shanghai, China. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
17:1354–1359. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Hecht SS: Chemoprevention by
isothiocyanates. J Cell Biochem. (Suppl 22): 195–209. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Zhang Y: Cancer-preventive
isothiocyanates: measurement of human exposure and mechanism of
action. Mutat Res. 555:173–190. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Xiao D, Johnson CS, Trump DL and Singh SV:
Proteasome-mediated degradation of cell division cycle 25C and
cyclin-dependent kinase 1 in phenethyl isothiocyanate-induced
G2-M-phase cell cycle arrest in PC-3 human prostate cancer cells.
Mol Cancer Ther. 3:567–575. 2004.
|
|
28.
|
Huong le D, Shim JH, Choi KH, et al:
Effect of beta-phenylethyl isothiocyanate from cruciferous
vegetables on growth inhibition and apoptosis of cervical cancer
cells through the induction of death receptors 4 and 5. J Agric
Food Chem. 59:8124–8131. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Yan H, Zhu Y, Liu B, et al:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates the apoptosis of highly
metastatic human non-small cell lung cancer cells induced by
isothiocyanates. Br J Nutr. 106:1779–1791. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Chen YR, Han J, Kori R, Kong AN and Tan
TH: Phenylethyl isothiocyanate induces apoptotic signaling via
suppressing phosphatase activity against c-Jun N-terminal kinase. J
Biol Chem. 277:39334–39342. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31.
|
Hwang ES and Lee HJ: Effects of
phenylethyl isothiocyanate and its metabolite on cell-cycle arrest
and apoptosis in LNCaP human prostate cancer cells. Int J Food Sci
Nutr. 61:324–336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Xu C, Shen G, Chen C, Gelinas C and Kong
AN: Suppression of NF-kappaB and NF-kappaB-regulated gene
expression by sulforaphane and PEITC through IkappaBalpha, IKK
pathway in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Oncogene.
24:4486–4495. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Bommareddy A, Hahm ER, Xiao D, et al: Atg5
regulates phenethyl isothiocyanate-induced autophagic and apoptotic
cell death in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res.
69:3704–3712. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Wu X, Kassie F and Mersch-Sundermann V:
Induction of apoptosis in tumor cells by naturally occurring
sulfur-containing compounds. Mutat Res. 589:81–102. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Morse MA, Amin SG, Hecht SS and Chung FL:
Effects of aromatic isothiocyanates on tumorigenicity,
O6-methylguanine formation and metabolism of the tobacco-specific
nitrosamine 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone in A/J
mouse lung. Cancer Res. 49:2894–2897. 1989.
|
|
36.
|
Zhang Y, Kensler TW, Cho CG, Posner GH and
Talalay P: Anticarcinogenic activities of sulforaphane and
structurally related synthetic norbornyl isothiocyanates. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 91:3147–3150. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Powolny AA, Bommareddy A, Hahm ER, et al:
Chemopreventative potential of the cruciferous vegetable
constituent phenethyl isothiocyanate in a mouse model of prostate
cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 103:571–584. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Kelloff GJ, Crowell JA, Hawk ET, et al:
Strategy and planning for chemopreventive drug development:
clinical development plans II. J Cell Biochem. (Suppl 26): 54–71.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Yang MD, Lai KC, Lai TY, et al: Phenethyl
isothiocyanate inhibits migration and invasion of human gastric
cancer AGS cells through suppressing MAPK and NF-kappaB signal
pathways. Anticancer Res. 30:2135–2143. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Lai KC, Huang AC, Hsu SC, et al: Benzyl
isothiocyanate (BITC) inhibits migration and invasion of human
colon cancer HT29 cells by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9
and urokinase plasminogen (uPA) through PKC and MAPK signaling
pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 58:2935–2942. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41.
|
Xiao D and Singh SV: Phenethyl
isothiocyanate inhibits angiogenesis in vitro and ex vivo. Cancer
Res. 67:2239–2246. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Lu KW, Chen JC, Lai TY, et al: Gypenosides
inhibits migration and invasion of human oral cancer SAS cells
through the inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-2 -9 and
urokinase-plasminogen by ERK1/2 and NF-kappa B signaling pathways.
Hum Exp Toxicol. 30:406–415. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Hour MJ, Tsai SC, Wu HC, et al: Antitumor
effects of the novel quinazolinone MJ-33: Inhibition of metastasis
through the MAPK, AKT, NF-kappaB and AP-1 signaling pathways in
DU145 human prostate cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 41:1513–1519.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Ohnishi Y, Lieger O, Attygalla M, Iizuka T
and Kakudo K: Effects of epidermal growth factor on the invasion
activity of the oral cancer cell lines HSC3 and SAS. Oral Oncol.
44:1155–1159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Yang JS, Liu CW, Ma YS, et al: Chlorogenic
acid induces apoptotic cell death in U937 leukemia cells through
caspase- and mitochondria-dependent pathways. In Vivo. 26:971–978.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Lan YH, Chiang JH, Huang WW, et al:
Activations of both extrinsic and intrinsic pathways in HCT 116
human colorectal cancer cells contribute to apoptosis through
p53-mediated ATM/Fas signaling by Emilia sonchifolia
extract, a folklore medicinal plant. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2012:1781782012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Tsai SC, Huang WW, Huang WC, et al:
ERK-modulated intrinsic signaling and G(2)/M phase arrest
contribute to the induction of apoptotic death by allyl
isothiocyanate in MDA-MB-468 human breast adenocarcinoma cells. Int
J Oncol. 41:2065–2072. 2012.
|
|
48.
|
Kao WT, Lin CY, Lee LT, et al:
Investigation of MMP-2 and -9 in a highly invasive A431 tumor cell
sub-line selected from a Boyden chamber assay. Anticancer Res.
28:2109–2120. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Chen KT, Hour MJ, Tsai SC, et al: The
novel synthesized
6-fluoro-(3-fluorophenyl)-4-(3-methoxyanilino)quinazoline (LJJ-10)
compound exhibits anti-metastatic effects in human osteosarcoma U-2
OS cells through targeting insulin-like growth factor-I receptor.
Int J Oncol. 39:611–619. 2011.
|
|
50.
|
Yang JS, Wu CC, Kuo CL, et al: Solanum
lyratum extracts induce extrinsic and intrinsic pathways of
apoptosis in WEHI-3 murine leukemia cells and inhibit allograft
tumor. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2012:2549602012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Chiu YJ, Hour MJ, Lu CC, et al: Novel
quinazoline HMJ-30 induces U-2 OS human osteogenic sarcoma cell
apoptosis through induction of oxidative stress and up-regulation
of ATM/p53 signaling pathway. J Orthop Res. 29:1448–1456. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Bjorklund M and Koivunen E:
Gelatinase-mediated migration and invasion of cancer cells. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1755:37–69. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Bode W, Fernandez-Catalan C, Grams F, et
al: Insights into MMP-TIMP interactions. Ann NY Acad Sci.
878:73–91. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Kalyankrishna S and Grandis JR: Epidermal
growth factor receptor biology in head and neck cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 24:2666–2672. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55.
|
Zimmermann M, Zouhair A, Azria D and
Ozsahin M: The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in head and
neck cancer: its role and treatment implications. Radiat Oncol.
1:112006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
Rogers SJ, Harrington KJ, Rhys-Evans P,
O-Charoenrat P and Eccles SA: Biological significance of c-erbB
family oncogenes in head and neck cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
24:47–69. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57.
|
Jemal A, Murray T, Samuels A, Ghafoor A,
Ward E and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2003. CA Cancer J Clin.
53:5–26. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58.
|
Lo HW and Hung MC: Nuclear EGFR signalling
network in cancers: linking EGFR pathway to cell cycle progression,
nitric oxide pathway and patient survival. Br J Cancer. 94:184–188.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59.
|
Yarden Y: The EGFR family and its ligands
in human cancer. signalling mechanisms and therapeutic
opportunities. Eur J Cancer. 37(Suppl 4): S3–S8. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60.
|
Temam S, Kawaguchi H, El-Naggar AK, et al:
Epidermal growth factor receptor copy number alterations correlate
with poor clinical outcome in patients with head and neck squamous
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 25:2164–2170. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61.
|
Chung CH, Ely K, McGavran L, et al:
Increased epidermal growth factor receptor gene copy number is
associated with poor prognosis in head and neck squamous cell
carcinomas. J Clin Oncol. 24:4170–4176. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62.
|
Kim JH, Xu C, Keum YS, Reddy B, Conney A
and Kong AN: Inhibition of EGFR signaling in human prostate cancer
PC-3 cells by combination treatment with beta-phenylethyl
isothiocyanate and curcumin. Carcinogenesis. 27:475–482. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63.
|
Thomas GT, Lewis MP and Speight PM: Matrix
metalloproteinases and oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 35:227–233. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64.
|
Xiao D, Choi S, Lee YJ and Singh SV: Role
of mitogen-activated protein kinases in phenethyl
isothiocyanate-induced apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells.
Mol Carcinog. 43:130–140. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65.
|
Huong LD, Shin JA, Choi ES, et al:
beta-Phenethyl isothiocyanate induces death receptor 5 to induce
apoptosis in human oral cancer cells via p38. Oral Dis. 18:513–519.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66.
|
Yang YM, Conaway CC, Chiao JW, et al:
Inhibition of benzo(a) pyrene-induced lung tumorigenesis in A/J
mice by dietary N-acetylcysteine conjugates of benzyl and phenethyl
isothiocyanates during the postinitiation phase is associated with
activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and p53 activity
and induction of apoptosis. Cancer Res. 62:2–7. 2002.
|
|
67.
|
Xiao D and Singh SV: Phenethyl
isothiocyanate-induced apoptosis in p53-deficient PC-3 human
prostate cancer cell line is mediated by extracellular
signal-regulated kinases. Cancer Res. 62:3615–3619. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68.
|
Hu R, Kim BR, Chen C, Hebbar V and Kong
AN: The roles of JNK and apoptotic signaling pathways in
PEITC-mediated responses in human HT-29 colon adenocarcinoma cells.
Carcinogenesis. 24:1361–1367. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|