Introduction
Cancer is subject to a unique microenvironment,
composed of cancer cells, cancer-associated stromal fibroblasts
(CAFs), endothelial cells, inflammatory cells and abundant
extracellular matrix (1). It has
been hypothesized that the components besides cancer cells in
cancer tissues are functionally organized to promote survival of
cancer cells against hypoxia in the host and generate a favorable
microenvironment for cancer cells in both primary and metastatic
sites (2). CAFs in the tumor
stroma are involved in all stages of tumor development. A previous
study has shown that fibroblasts from cancer mass produce
PGI2 but fibroblasts from adjacent normal tissues do not
(3). However, how CAFs are
activated to produce PGI2 and if the activated CAFs can
promote angiogenesis by generating VEGF itself are poorly
understood.
We investigated the modulation of the gene
expression in human fibroblasts under hypoxic condition using
GeneChip analysis, and found that the expression of prostacyclin
synthase (PGIS) was upregulated. PGIS, a membrane-bound heme
protein with spectral characteristics of cytochrome p450 (CYP), is
also an enzyme which catalyzes the conversion of prostaglandin
H2 (PGH2) to form prostacyclin
(PGI2). PGIS is localized to the microsomal fractions of
platelets, vascular endothelial cells, and vascular smooth muscle
cells (4–8). PGIS-deficient mice generated by gene
targeting are associated with thickening of arterial walls,
interstitial fibrosis with nephrosclerosis and kidney infarction
(9). Interestingly, some groups
reported that PGI2, the product of PGIS, promotes
colorectal cancer growth probably by activating peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor δ (PPARδ) (10). Inhibition of COX-2-derived
prostacyclin (PGI2) induces colon cancer cell apoptosis
(11). PGI2 also
regulates the transcription of VEGF by PPARδ (12,13).
In the present study, we focused our study on PGIS
and confirmed that the expression of PGIS was upregulated in human
fibroblasts under hypoxic condition and the induced PGIS was
involved in the induction of VEGF. We have suggested that PPARδ
enhances the hypoxic induction of VEGF.
Materials and methods
Antibodies
The polyclonal antibody against PGIS was purchased
from Cayman. The polyclonal antibody against Erk-1 was purchased
from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA). The monoclonal
antibody against GAPDH was purchased from Ambion Inc. (Austin,
TX).
Patients
The paraffin specimens of 3 cases of colon cancer
were supplied from Department of Surgical Oncology Kagoshima
University Faculty of Medicine. This study was performed with the
approval of the Ethics Committee for Epidemiological Studies in
Kagoshima University Graduate School of Medical and Dental
Sciences.
Cell lines and cell cultures
WI-38 and TIG-3-20 human fibroblasts were purchased
from Health Science Research Resources Bank (HSRRB), human
embryonic lung fibroblasts (HEL) and human neuroblastoma cells
(NB-1) cell lines were provided from Professor Y. Eizuru (Kagoshima
University, Kagoshima, Japan) and Professor A. Tomoda (Tokyo
Medical University, Tokyo, China), respectively. Other cell lines
were stocked in our laboratory. All of the cells were cultured in
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) containing 10% FCS, 2 mM
glutamine and 100 U/ml penicillin at 37°C in a 5% CO2
humidified atmosphere. Hypoxic condition was induced by incubating
the cells in a Personal Multigas Incubator (Astec) at 37°C with
humidified 1% O2.
GeneChip analysis
cDNA and biotinylated cRNA were synthesized
according to the standard protocols provided by Affymetrix (Santa
Clara, CA). Biotinylated cRNA were purified using the Sample
Cleanup Module (Affymetrix), and subsequently hybridized, according
to the manufacturer’s standard protocols, to Affymetrix HGU133A
GeneChips (which contain 22283 probe sets). Arrays were scanned
using an Affymetrix confocal laser scanner. A gene expression
analysis software program, GeneSpring, version 7.1 (Agilent), was
used to perform statistical analysis.
Reverse transcription-PCR
1 μg first-strand cDNA was used for each polymerase
chain reaction (PCR). The human PGIS primers were as
follows: forward, 5′-ctggctcctgc tcttccttctcaag-3′; reverse,
5′-caccacgtcgcaggttgaattcttg-3′. The human VEGF primers
were: forward, 5′-tgtcttgggtgcattggag ccttgc-3′; reverse,
5′-gttgtgctgtaggaagctcatctctc-3′. The human GAPDH primers
for internal control were: forward, 5′-tgcacc accaactgcttag-3′;
reverse, 5′-gaggcagggatgatgttc-3′. The human PPARδ primers
were: forward, 5′-actgagttcgccaagagcatc-3′; reverse,
5′-aacgttcatgaggcctggccg-3′.
The PCR amplification mixture was adjusted to a
final volume of 20 μl. Twenty-eight cycles were performed at 94°C
for 30 sec for denaturation, 58°C for 30 sec for annealing, and
72°C for 30 sec for extension. The PCR products were separated on
1.5% agarose gel and then stained with ethidium bromide.
Real-time reverse transcription-PCR
quantification
Total cellular RNA was extracted using TRIzol
reagent according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Invitrogen,
Carlsbad, CA). One microgram of RNA was reverse transcribed using a
first-strand cDNA synthesis kit (ReverTra Ace-α-, Toyobo, Osaka,
Japan). The set of SYBR Premix Ex Taq kit was purchased from Takara
Bio (Shiga, Japan). Human PGIS, VEGF, GAPDH
gene expression levels were assayed by real-time reverse PCR (PRISM
7900HT, Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) according to the
technical brochure of the company. Human GAPDH was used for
normalization. Quantification of target gene expression was
obtained with the comparative cycle threshold method according to
the instructions of the manufacturer (Applied Biosystems). All
experiments were performed in triplicate for each data point. Each
quantitation was performed with the standard curve method.
Protein extraction and immunoblot
analysis
Cells were harvested and lysed with RIPA buffer [50
mM Tris-HCI (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EGTA, 1 mM EDTA, 20 mM NaF,
100 mM Na3VO4, 0.5% Nonidet P-40 (NP-40), 1%
Triton X-100, 1 mM PMSF, DTT, aprotinin, APMSF and protease
inhibitor cocktail (Sigma)]. The lysates were passed through a
21-gauge needle to break up the cell aggregates and were cleared by
centrifugation at 14,000 × g for 15 min at 4°C; the supernatant
(total cell lysate) was immediately used or stored at −80°C until
use.
Lysates were subjected to 9.4% SDS-polyacrylamide
gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), and then were transferred to
polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (Immobilon-P transfer membrane;
Millipore, Bedford, MA). The membrane was treated with buffer A
[350 mM NaCl, 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), and 0.05% Tween-20]
containing 3% skimmed milk for 1 h and incubated with the indicated
antibody (1:1,000) in buffer A containing 3% skimmed milk for 1
hour. Following four washes with buffer A (10 min each), the
membrane was incubated with a peroxidase-conjugated horse
anti-mouse IgG diluted 1:1,000 in buffer A containing 3% skimmed
milk for 1 hour. The membrane was washed with buffer A and
developed using the enhanced chemiluminescence western blot
analysis detection system (Amersham Biosciences, Buckinghamshire,
UK).
Subcellular fractionation
Cells were washed with PBS and then resuspended in 3
volumes of buffer B [10 mM HEPES-KOH (pH 7.8), 10 mM KCl, 0.1 mM
EDTA (pH 8.0), 1 μg/ml aprotinin and 1 mM p-aminophenyl
methanesulfonyl fluoride]. The cells were disrupted by dounce
homogenizer. The nuclear fractions were centrifuged at 13,000 rpm
for 5 min at 4°C. The supernatant was used as cytosolic
fractions.
Inhibition of PGIS and PPARδ expression
by small interfering RNA
Specific small interfering RNA (siRNA) of PGIS was
purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. SiRNA duplexes of
PPARδ were synthesized using the Silencer™ siRNA
construction kit (Ambion Inc.). The siRNA used in this study
consisted of a 21-nucleotide sense strand and a 21-nucleotide
antisense strand with a two-nucleotide overhang at 3′-end. The
sequences were: PPARδ-siRNA(1)
sense 5′-CAUGGAGUGCCGGGUGUG CUU-3′ starting at nucleotide 211 from
AUG start codon of human PPARδ coding sequence. PPARδ-siRNA(1)
antisense, 5′-GCACACCCGGCACUCCAUGUU-3′. PPARδ-siRNA(2) sense
5′-GCUGGAGUACGAGAAGUGUUU-3′ starting at nucleotide 313 from AUG
start codon of human PPARδ coding sequence. PPARδ-siRNA(2) antisense, 5′-ACACUUCUCG
UACUCCAGCUU-3′.
Transfections were accomplished using Lipofectamine
2000 (Invitrogen), according to the manufacturer’s protocol. After
transfection, the cells were incubated under normoxic condition for
5 h, then changed with fresh DMEM and incubated under hypoxic
condition until harvested at different time points. The effect of
the siRNA on the expression of PGIS and VEGF was
assessed using RT-PCR and real-time PCR, as described above.
6-Keto-prostaglandin F1α enzyme
immunoassay
6-Keto-prostaglandin F1α (stable hydrolysis product
of PGI2) was analyzed by specific enzyme immunoassay kit
(EIA) (Assay Designs), following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Lysates were added to every well of the kit plate. The resulting
values of 6-keto-prostaglandin F1α concentrations in the
supernatant were normalized for lyses buffer.
Confocal fluorescence microscopy
WI-38 and HEL cells were cultured under normoxic or
hypoxic condition for different time, and fixed with 4%
paraformaldehyde (PFA) in PBS for 30 min at room temperature. After
blocking with 5% normal goat serum in PBS/0.02% Tween-20, the cells
were incubated with an antibody against PGIS (1:100) at 4°C
overnight. After washing thrice in PBS/0.02% Tween-20, the cells
were incubated with secondary antibodies (anti-rabbit-FITC 1×100).
Nuclei were stained by incubating cells with 6 μmol/l
4′6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). The cells were observed using
confocal fluorescence microscopy (FV500, Olympus Corporation).
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemical studies for PGIS and HIF-1α were
performed on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded surgical sections
obtained from patients with colorectal cancer. Slides were
deparaffinized in xylene and rehydrated in a graded alcohol series.
To retrieve antigen, sections were heated in the citrate buffer pH
6.0 (Target retrieval solution, S1699, Dako, Carpinteria, CA) for 5
min at 121°C by means of an autoclave. For detection and
visualization, the retrieved antigens were reacted with the
appropriate specific primary antibodies solution (diluted to 1:100)
for 1 h and were visualized by means of a polymer method (ChemMate
Envision, K5027, Dako) and colorimetric diaminobenzidine
(DAB)-peroxide (H2O2) reaction (DAB+ liquid
system, K3468, Dako). Nuclear counterstaining was hematoxylin
(ChemMate hematoxylin, S2020, Dako). These procedures were
performed by an autostainer (Autostainer, Dako) with rinsing buffer
warmed at 35°C (14).
Results
GeneChip analysis
GeneChip analysis was used for identifying the
modulation of the gene expression in fibroblasts under hypoxic
condition. A total of 234 genes were differentially expressed
between fibroblasts under normoxic or hypoxic condition in this
study. Relative to normoxic condition data profiling, 172 genes
were upregulated and 62 genes were downregulated (3-fold change).
Of 172 upregulated genes, genes related to tumor metastasis,
endothelial cell biology and TGF-β signaling pathway etc. were
included. Table I lists some
upregulated genes in fibroblasts under hypoxic condition. Among
these genes, we focused on PGIS, which showed 13.5-fold increased
expression levels.
 | Table IGeneChip analysis of the modulation
of the gene expression in fibroblasts under hypoxic condition. |
Table I
GeneChip analysis of the modulation
of the gene expression in fibroblasts under hypoxic condition.
| Gene symbol | Description | Fold change
MAX |
|---|
| AK3 | Adenylate kinase
3-like 1 | 3.2 |
| BNIP3 | BCL2/adenovirus E1B
19 kD-interacting protein 3 | 4.9 |
| CYR61 | Cysteine-rich,
angiogenic inducer, 61 | 2.3 |
| FAM13A1 | Family with
sequence similarity 13, member A1 | 5.9 |
| FGF1 | Fibroblast growth
factor 1 (acidic) | 3.0 |
| FGFR1 | Fibroblast growth
factor receptor 1 | 3.7 |
| IGFBP3 | Insulin-like growth
factor-binding protein | 26.6 |
| MBNL1 | Muscleblind-like
(Drosophila) | 3.0 |
| MYH10 | Myosin, heavy
polypeptide 10, non-muscle | 3.4 |
| NDRG1 | Homo sapiens
N-myc downstream regulated gene 1 | 8.5 |
| PDGFC | Platelet derived
growth factor C | 7.2 |
| PGK1 | Phosphoglycerate
kinase 1 | 2.3 |
| PTGIS/PGIS | Homo sapiens
prostaglandin I2 (prostacyclin) synthase | 13.5 |
| STC1 | Stanniocalcin
1 | 3.9 |
| VEGF | Vascular
endothelial growth factor | 5.8 |
| WISP1 | WNT1 inducible
signaling pathway protein 1 | 9.9 |
| XDH | Xanthine
dehydrogenase | 60.1 |
Expression of mRNA for PGIS proteins
determined by RT-PCR or real-time qualitative PCR
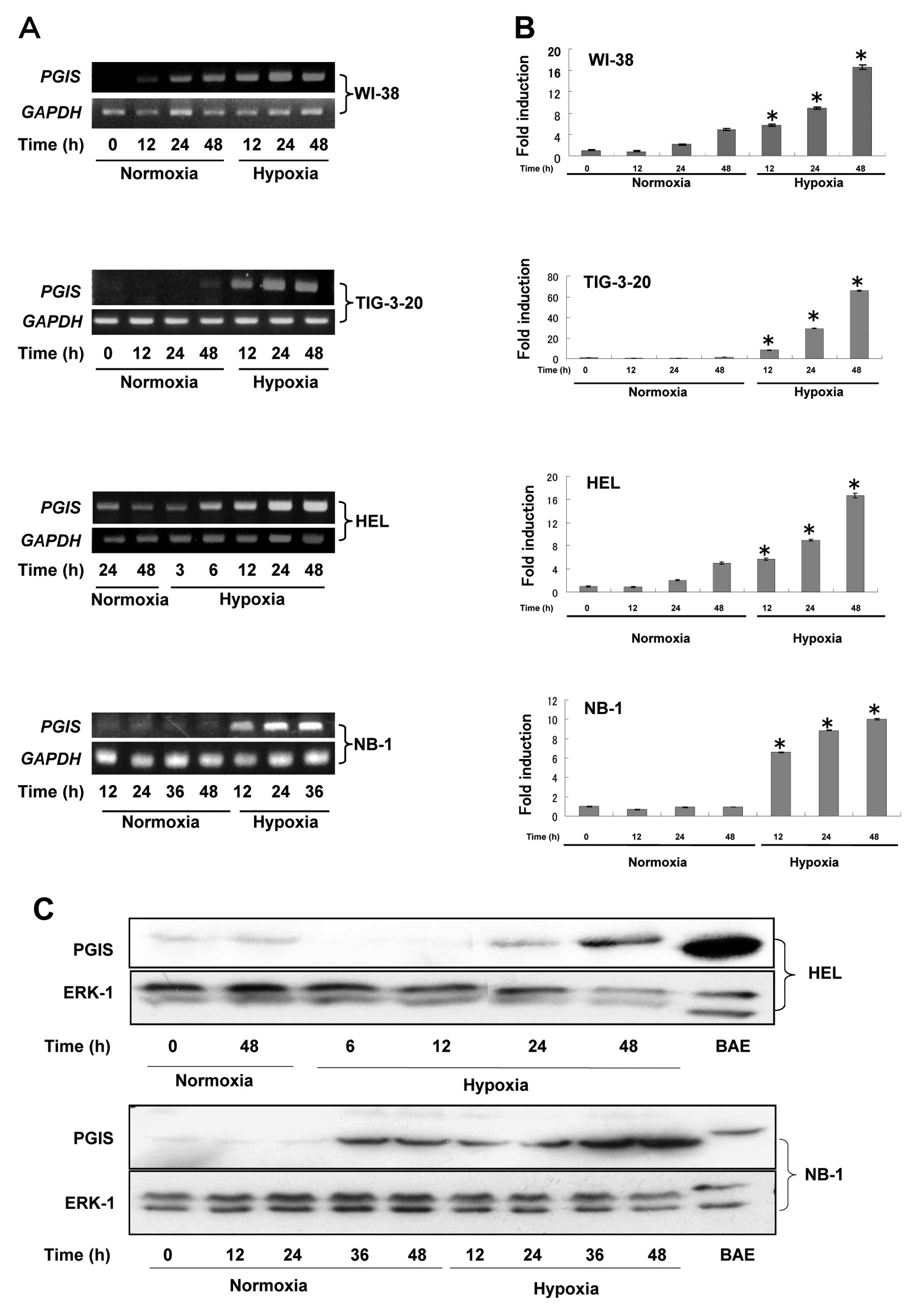
As shown in Fig.
1A, the expression levels of PGIS gene were
significantly enhanced in fibroblasts such as WI-38, TIG-3-20 and
HEL time-dependently under hypoxic condition. To quantitate the
mRNA expression levels of PGIS in fibroblasts, real-time
quantitative RT-PCR was performed (Fig. 1B). Moreover, the expression levels
of PGIS in some human cancer cells were also investigated in
this study. The time-dependently enhanced expression levels of
PGIS under hypoxic condition were detected in human
neuroblastomas (NB-1) (Fig. 1A and
B) and human melanomas (G361), but not in glioblastomas
(U251MG), pancreas cancer (MiapacaII), non-small cell lung cancer
(A549), KB/TP and EJ/TP cells (15) (data not shown). PGIS mRNA
was not detected in human macrophages (U937 and THP1) under
normoxic or hypoxic condition (data now shown). Since the enhanced
expression levels of PGIS were not detected in fibroblasts
cultured in the medium containing 1% FCS (data not shown), the
induction of PGIS could not be attributed to the low nutrient
condition. These results suggested that the enhanced expression of
PGIS mRNA in fibroblasts and some cancer cells was induced
by hypoxic condition.
Expression and intracellular localization
of PGIS in fibroblasts and neuroblastomas
We next examined expression levels of PGIS in
fibroblasts (HEL) and neuroblastomas (NB-1) by western blot
analysis (Fig. 1C). Expression
levels of PGIS protein in both cell lines were also enhanced
time-dependently under hypoxic condition consistent with mRNA
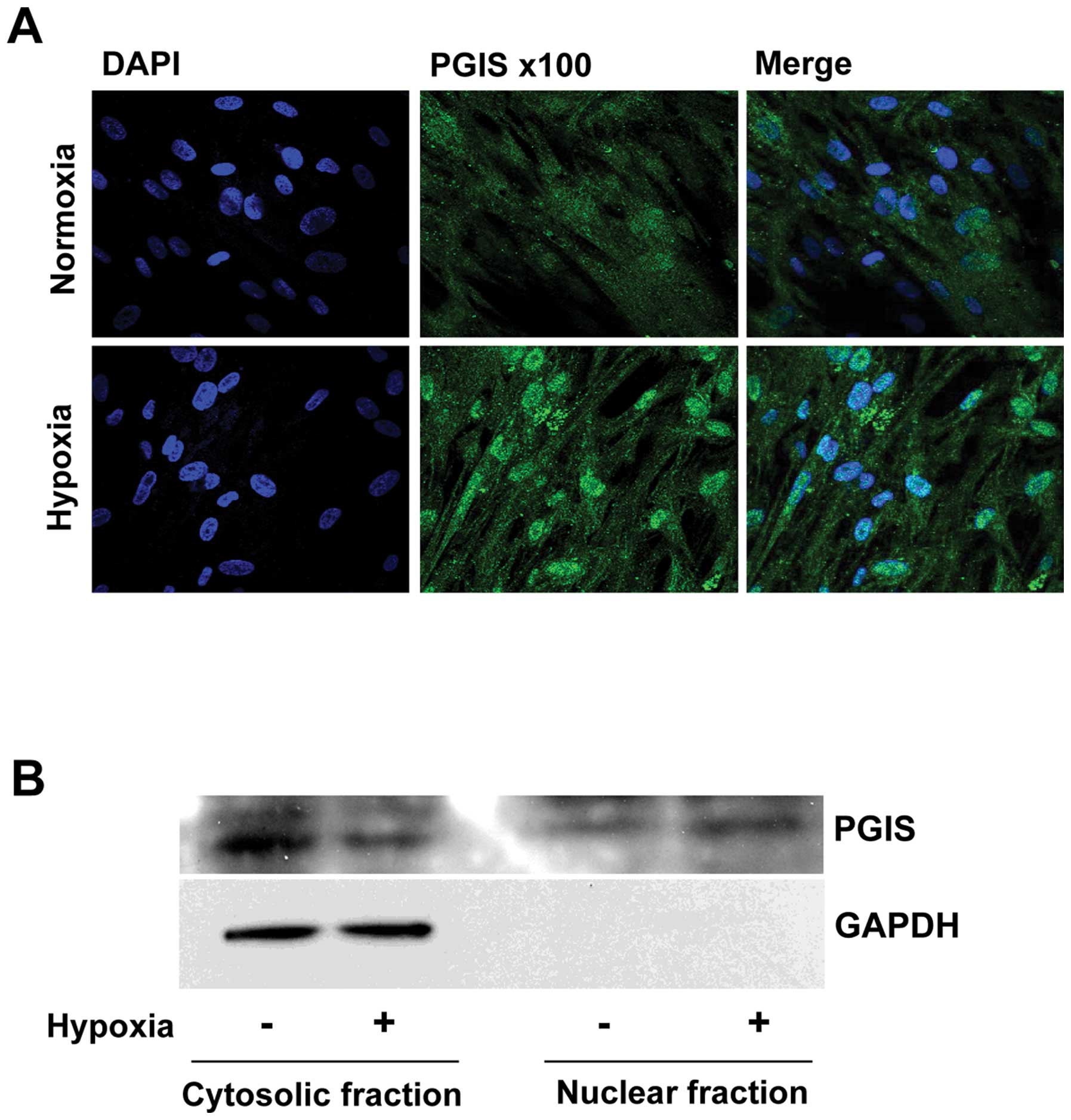
level. To identify the subcellular localization of PGIS induced by
hypoxia, PGIS was observed using confocal fuorescence microscopy.
As shown in Fig. 2A, the
expressions of PGIS were mainly localized in the cytoplasm of WI-38
cells, and translocated to nuclei under hypoxic condition.
Immunoblot analysis also showed that PGIS was translocated from
cytoplasm to nuclei when the cells were cultured under hypoxic
condition (Fig. 2B).
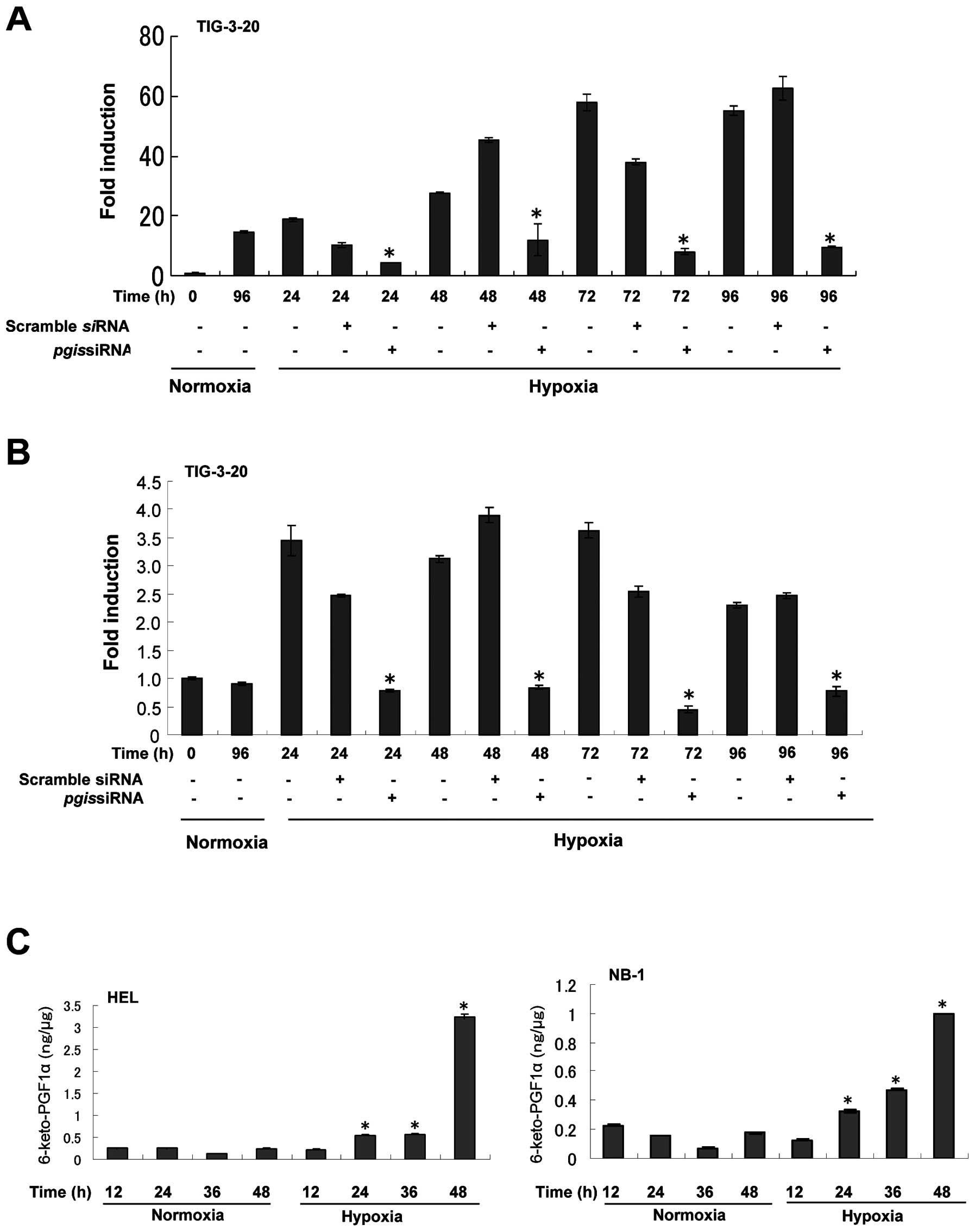
The effect of PGIS knockdown on the
induction of VEGF under hypoxic condition in fibroblasts
PGI2 is known to increase the expression
levels of the pro-angiogenic factor VEGF (16,17).
To confirm that PGIS is involved in the enhanced expression of VEGF
under hypoxic condition in fibroblasts, PGIS siRNA was used
to knockdown the expression of PGIS. The induction of
PGIS mRNA expression by hypoxia was considerably suppressed
by PGIS siRNA (Fig. 3A).
PGIS knockdown resulted in the decreased expression of
VEGF mRNA (Fig. 3B). These
results show that PGIS is required for the hypoxic induction of
VEGF.
Expression of 6-keto-prostaglandin F1α in
HEL and NB-1 cells under hypoxic condition
Since PGI2 is unstable, the level of the
stable hydrolysis metabolite of PGI2,
6-keto-prostaglandin F1α was analyzed in HEL and NB-1 cells under
hypoxic condition. The level of 6-keto-prostaglandin F1α was also
significantly increased in a time-dependent manner under hypoxic
condition compared with that under normoxic condition (p<0.05,
triplicate determinations; Fig.
3C).
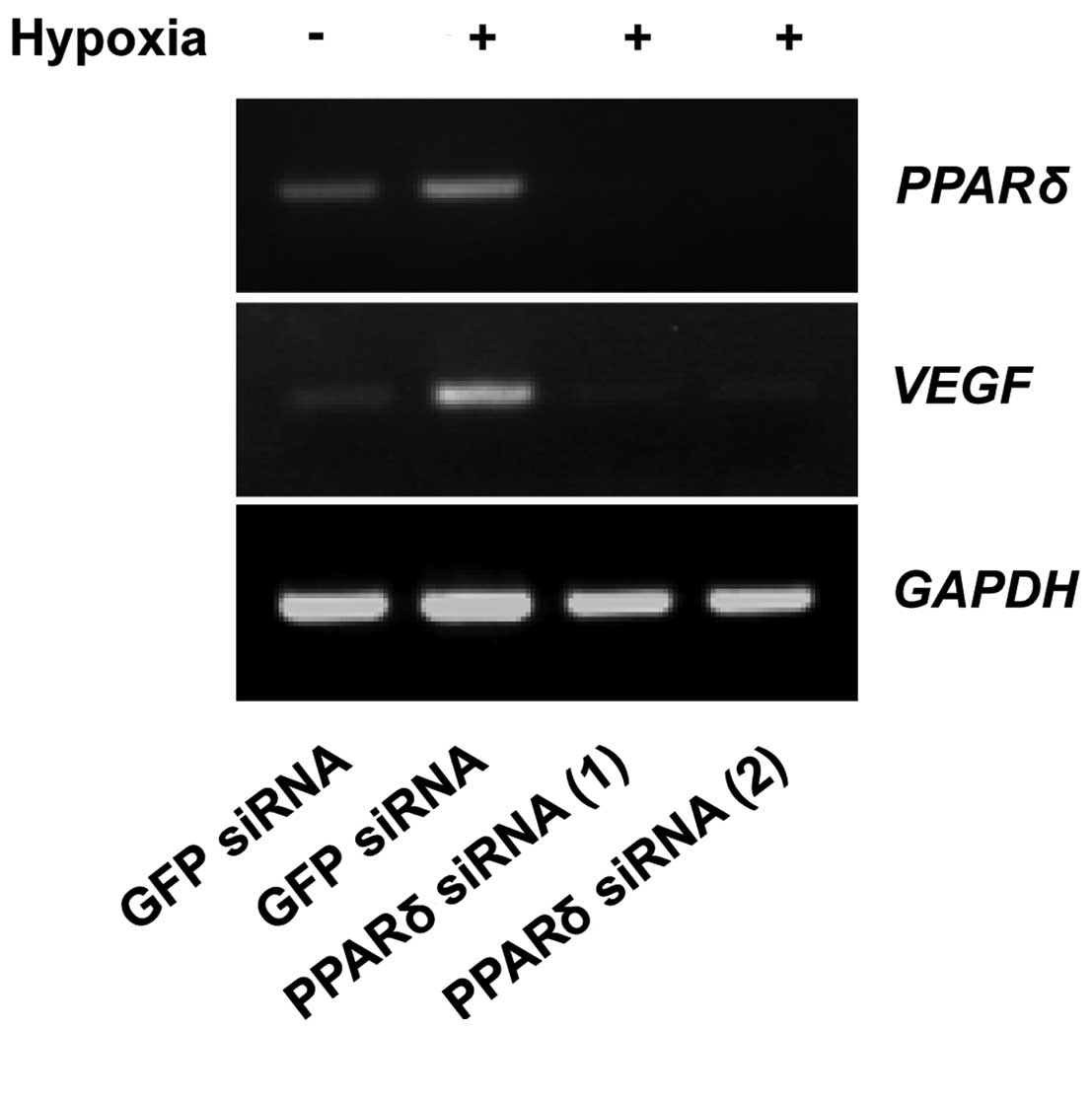
The effect of PPARδ-targeting siRNAs on
the expression of VEGF under hypoxic condition
It was previously reported that endogenous
PGI2 generation by co-expression of COX-2 and PGIS
activated PPARδ (18). Because the
expression of COX-2 was not induced under hypoxic condition in
fibroblasts and tumor cells (data not shown), we considered that
PGI2 produced by the hypoxia-induced PGIS entered the
nuclei and interacted with PPARδ.
To examine whether PPARδ regulates the expression of
VEGF, WI-38 cells transfected with PPARδ siRNA or green
fluorescent protein (GFP) siRNA as a control were cultured under
hypoxic condition. As shown in Fig.
4, downregulation of PPARδ suppressed the expression of
VEGF mRNA. These results indicate that PPARδ
regulates transcription of VEGF in WI-38 cells.
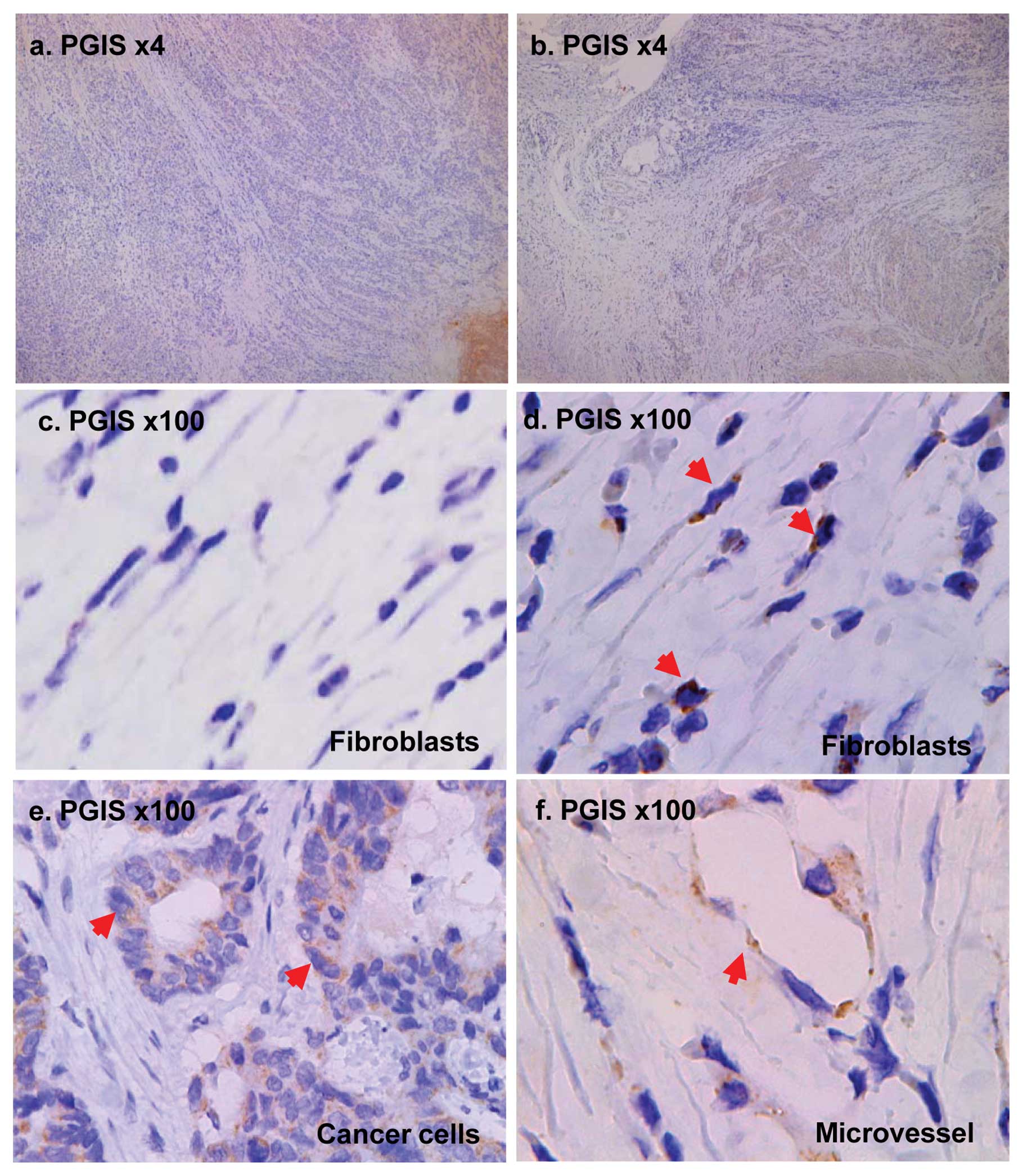
Expression of PGIS in clinical patients
by immunohistochemistry
To determine whether PGIS is expressed in
fibroblasts and cancer cells in clinical human tumor tissues, we
examined 3 cases of human colon cancer tissues. As shown in
Fig. 5, PGIS was expressed in
cancer cells and fibroblasts which are located in the deep layers
of the intestinal wall but not in the surface layers (Fig. 5a–b). Immunohistochemical staining
of PGIS validated the induced expression of PGIS in fibroblasts
under hypoxic condition in tumors (Fig. 5d).
Discussion
In this study, we observed the induction of PGIS
expression under hypoxic condition, and confirmed that the induced
PGIS was, at least in part, responsible for the increased
expression of VEGF in human fibroblasts. We showed that PGIS was
induced in fibroblasts and cancer cells by hypoxia, but not in
cells under low nutrient condition (Fig. 1).
PGIS was accumulated in the nuclei of fibroblasts
under hypoxia, and the amount of 6-keto-PGF1α was
increased with increasing expression of PGIS, suggesting that
PGI2 was produced by the induced PGIS.
We considered that the increased PGI2 was
caused by the hypoxia-induced PGIS, since the expression of COX-2
was not induced under hypoxic condition in both fibroblasts and
tumor cells (data not shown). PGI2 has been shown to be
a ligand for peroxisomal-proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR).
It was previously reported that endogenous PGI2
generation by co-expression of COX-2 and PGIS led to
transcriptional activation of PPARδ (18). Increased PPARδ augmented the
transcription of its target genes such as VEGF (19), PGI2 is also known to
increase the expression of VEGF in cultured lung fibroblasts
(17). PGI2 seems to
play an important role in generating VEGF and consequently
angiogenesis and tumor growth. Therefore, we investigated VEGF
expression in fibroblasts under hypoxic condition. VEGF was
time-dependently induced under hypoxic condition in a manner
similar to PGIS. Downregulation of PGIS suppressed the
increased expression of VEGF under hypoxic condition, indicating
that PGIS is involved in the regulation of VEGF expression under
hypoxic condition (Figs. 3A, B and
4). These results suggest that
PGIS locates upstream of the VEGF gene in agreement with previous
results (12,13).
The pro-angiogenic factor VEGF overexpressed in most
cancer cells is part of the system that restores oxygen supply to
tumor tissues when blood circulation is inadequate (20). It is generally accepted that VEGF
recruited by cancer cells acts on cancer mesenchyme-like
endothelial and inflammatory cells to cause angiogenesis. VEGF
induced by PGIS in fibroblasts under hypoxic condition may play an
important role in the progression of carcinomas.
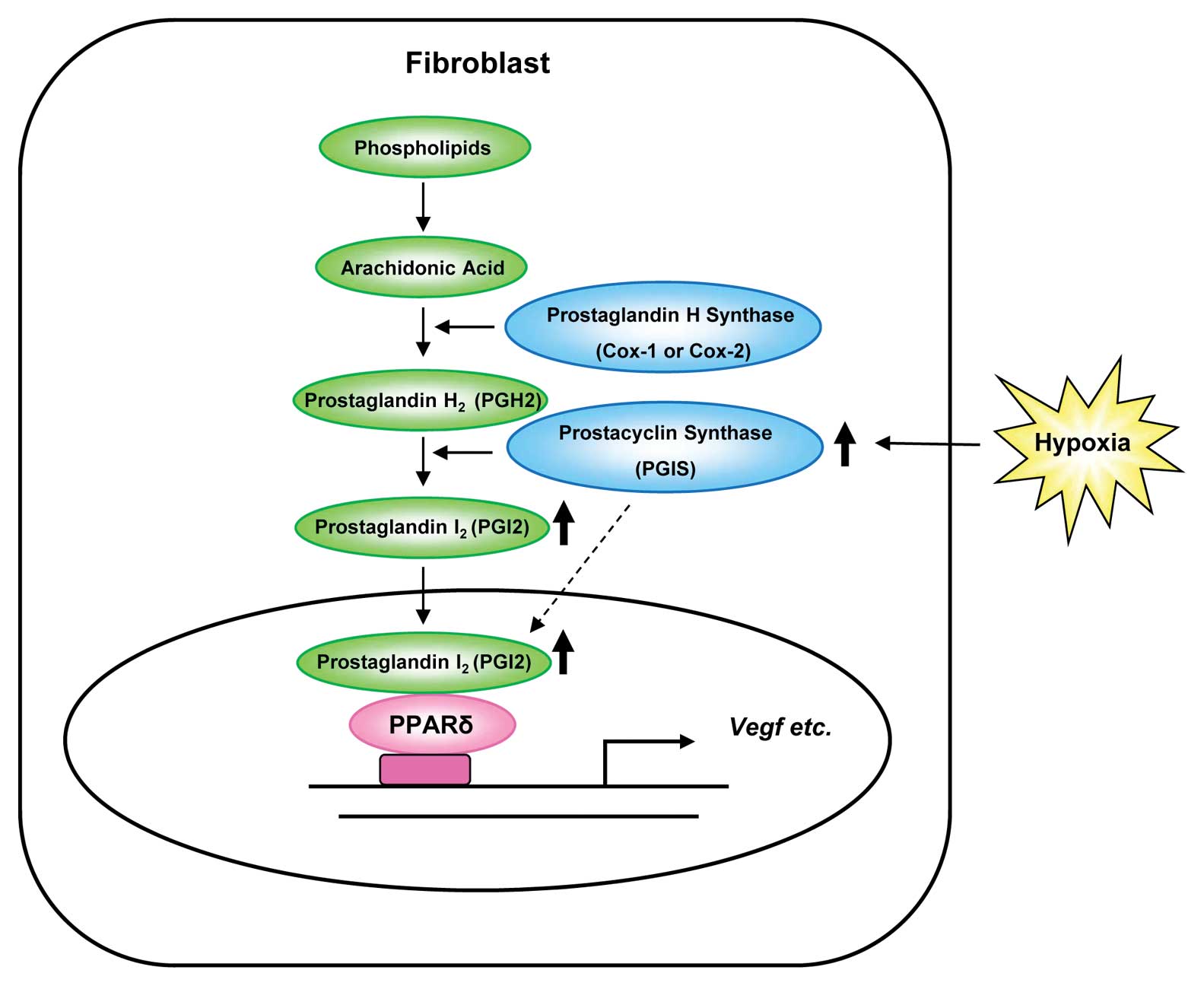
Moreover, the main localization of PGIS changed from
cytoplasm to nuclei by hypoxia in human fibroblast cells (Fig. 2). This finding suggested that PGIS
itself may enter the nuclei, where it synthesizes PGI2
to regulate the expression of VEGF (Fig. 6). The mechanism of this nuclear
translocation of PGIS remains to be uncovered.
Finally, the immunostaining patterns of tumors from
clinical cancer patients were in accord with the data obtained from
in vitro experiments (Fig.
5). The PGIS-positive cancer cells and fibroblasts were only
detected in the deep layers of the intestinal wall where is thought
to be deficient in oxygen but not in the surface layers. These
findings might support the view that PGIS is involved in tumor
progression and angiogenesis under hypoxic condition.
PGI2 was previously shown to activate PPARδ leading to
subsequent acceleration in intestinal tumor growth in
ApcMin/+ mice (21).
Meanwhile, PGI2-mediated activation of PPARδ was
implicated in negative growth of lung cancer cell lines (22). The role of PGIS in tumor growth
might be different in respective cells.
Transcriptional regulation of the PGIS gene has
rarely been reported in the literature. Recently, Camacho et
al defined the minimal PGIS promoter region responsive to
hypoxia. However, it did not contain a putative hypoxia responsive
element (HRE). Furthermore, they observed that knockdown of
HIF-1α abrogated hypoxia-induced PGIS upregulation in human
vascular cells, and suggested that PGIS transcriptional
activity enhanced by hypoxia could be the results of the
cooperative binding of several transcription factors to PGIS
promoter (23). Further study is
needed to elucidate the molecular basis for the induction of PGIS
by hypoxia.
In conclusion, this study provides new and important
information about PGIS induced in fibroblasts under hypoxic
condition. Since PGIS is involved in the enhanced expression of
VEGF under hypoxic condition in human fibroblasts, PGIS may be a
novel target for antitumor angiogenesis therapy.
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Akio Tomoda of Tokyo Medical
University for providing NB-1 cells; Professor Shoji Natsugoe of
Kagoshima University for human coloncancer paraffin block; Dr
Hiroshi Shirahama, Dr Yukie Tashiro, Mr. Keishi Tokunagana, Ms.
Yasuko Shinmura of Imakiire General Hospital for preparing good
paraffin sections from the archival paraffin block specimens; and
Ms. Hiromi Mitsuo and Ms. Naomi Nakanishi for valuable secretarial
assistance.
References
|
1
|
Nakagawa H, Liyanarachchi S, Davuluri RV,
Auer H, Martin EW Jr, de la Chapelle A and Frankel WL: Role of
cancer-associated stromal fibroblasts in metastatic colon cancer to
the liver and their expression profiles. Oncogene. 23:7366–7377.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fidler IJ: The pathogenesis of cancer
metastasis: the ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:453–458. 2003.
|
|
3
|
Cutler NS, Graves-Deal R, LaFleur BJ, Gao
Z, Boman BM, Whitehead RH, Terry E, Morrow JD and Coffey RJ:
Stromal production of prostacyclin confers an antiapoptotic effect
to colonic epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 63:1748–1751.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ingerman-Wojenski C, Silver MJ, Smith JB
and Macarak E: Bovine endothelial cells in culture produce
thromboxane as well as prostacyclin. J Clin Invest. 67:1292–1296.
1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Moncada S, Gryglewski R, Bunting S and
Vane JR: An enzyme isolated from arteries transforms prostaglandin
endoperoxides to an unstable substance that inhibits platelet
aggregation. Nature. 263:663–665. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Moncada S, Herman AG, Higgs EA and Vane
JR: Differential formation of prostacyclin (PGX or PGI2) by layers
of the arterial wall. An explanation for the anti-thrombotic
properties of vascular endothelium. Thromb Res. 11:323–344. 1977.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ullrich V, Castle L and Weber P: Spectral
evidence for the cytochrome P450 nature of prostacyclin synthetase.
Biochem Pharmacol. 30:2033–2036. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Weksler BB, Ley CW and Jaffe EA:
Stimulation of endothelial cell prostacyclin production by
thrombin, trypsin, and the ionophore A 23187. J Clin Invest.
62:923–930. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yokoyama C, Yabuki T, Shimonishi M, Wada
M, Hatae T, Ohkawara S, Takeda J, Kinoshita T, Okabe M and Tanabe
T: Prostacyclin-deficient mice develop ischemic renal disorders,
including nephrosclerosis and renal infarction. Circulation.
106:2397–2403. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Gupta RA, Tan J, Krause WF, Geraci MW,
Willson TM, Dey SK and DuBois RN: Prostacyclin-mediated activation
of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta in colorectal
cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:13275–13280. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu KK and Liou JY: Cyclooxygenase
inhibitors induce colon cancer cell apoptosis via PPARdelta →
14-3-3epsilon pathway. Methods Mol Biol. 512:295–307.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Arany Z, Foo SY, Ma Y, Ruas JL,
Bommi-Reddy A, Girnun G, Cooper M, Laznik D, Chinsomboon J,
Rangwala SM, Baek KH, Rosenzweig A and Spiegelman BM:
HIF-independent regulation of VEGF and angiogenesis by the
transcriptional coactivator PGC-1alpha. Nature. 451:1008–1012.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mizukami Y, Li J, Zhang X, Zimmer MA,
Iliopoulos O and Chung DC: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1-independent
regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor by hypoxia in
colon cancer. Cancer Res. 64:1765–1772. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang J, Hasui K, Jia X, Matsuyama T and
Eizuru Y: Possible role for external environmental stimuli in
nasopharyngeal NK/T-cell lymphomas in the northeast of China with
EBV infection-related autophagic cell death: a pathoepidemiological
analysis. J Clin Exp Hematop. 49:97–108. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Nakajima Y, Gotanda T, Uchimiya H,
Furukawa T, Haraguchi M, Ikeda R, Sumizawa T, Yoshida H and Akiyama
S: Inhibition of metastasis of tumor cells overexpressing thymidine
phosphorylase by 2-deoxy-L-ribose. Cancer Res. 64:1794–1801. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Buchanan FG, Chang W, Sheng H, Shao J,
Morrow JD and DuBois RN: Up-regulation of the enzymes involved in
prostacyclin synthesis via Ras induces vascular endothelial growth
factor. Gastroenterology. 127:1391–1400. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kamio K, Sato T, Liu X, Sugiura H, Togo S,
Kobayashi T, Kawasaki S, Wang X, Mao L, Ahn Y, Holz O, Magnussen H
and Rennard SI: Prostacyclin analogs stimulate VEGF production from
human lung fibroblasts in culture. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 294:L1226–L1232. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tong BJ, Tan J, Tajeda L, Das SK, Chapman
JA, DuBois RN and Dey SK: Heightened expression of cyclooxygenase-2
and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-delta in human
endometrial adenocarcinoma. Neoplasia. 2:483–490. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Piqueras L, Reynolds AR, Hodivala-Dilke
KM, Alfranca A, Redondo JM, Hatae T, Tanabe T, Warner TD and
Bishop-Bailey D: Activation of PPARbeta/delta induces endothelial
cell proliferation and angiogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
27:63–69. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Moreira IS, Fernandes PA and Ramos MJ:
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibition - a critical
review. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 7:223–245. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang D, Wang H, Guo Y, Ning W, Katkuri S,
Wahli W, Desvergne B, Dey SK and DuBois RN: Crosstalk between
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta and VEGF
stimulates cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:19069–19074. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fukumoto K, Yano Y, Virgona N, Hagiwara H,
Sato H, Senba H, Suzuki K, Asano R, Yamada K and Yano T: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor delta as a molecular target to
regulate lung cancer cell growth. FEBS Lett. 579:3829–3836. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Camacho M, Rodríguez C, Guadall A, Alcolea
S, Orriols M, Escudero JR, Martínez-González J and Vila L: Hypoxia
upregulates PGI-synthase and increases PGI release in human
vascular cells exposed to inflammatory stimuli. J Lipid Res.
52:720–731. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|