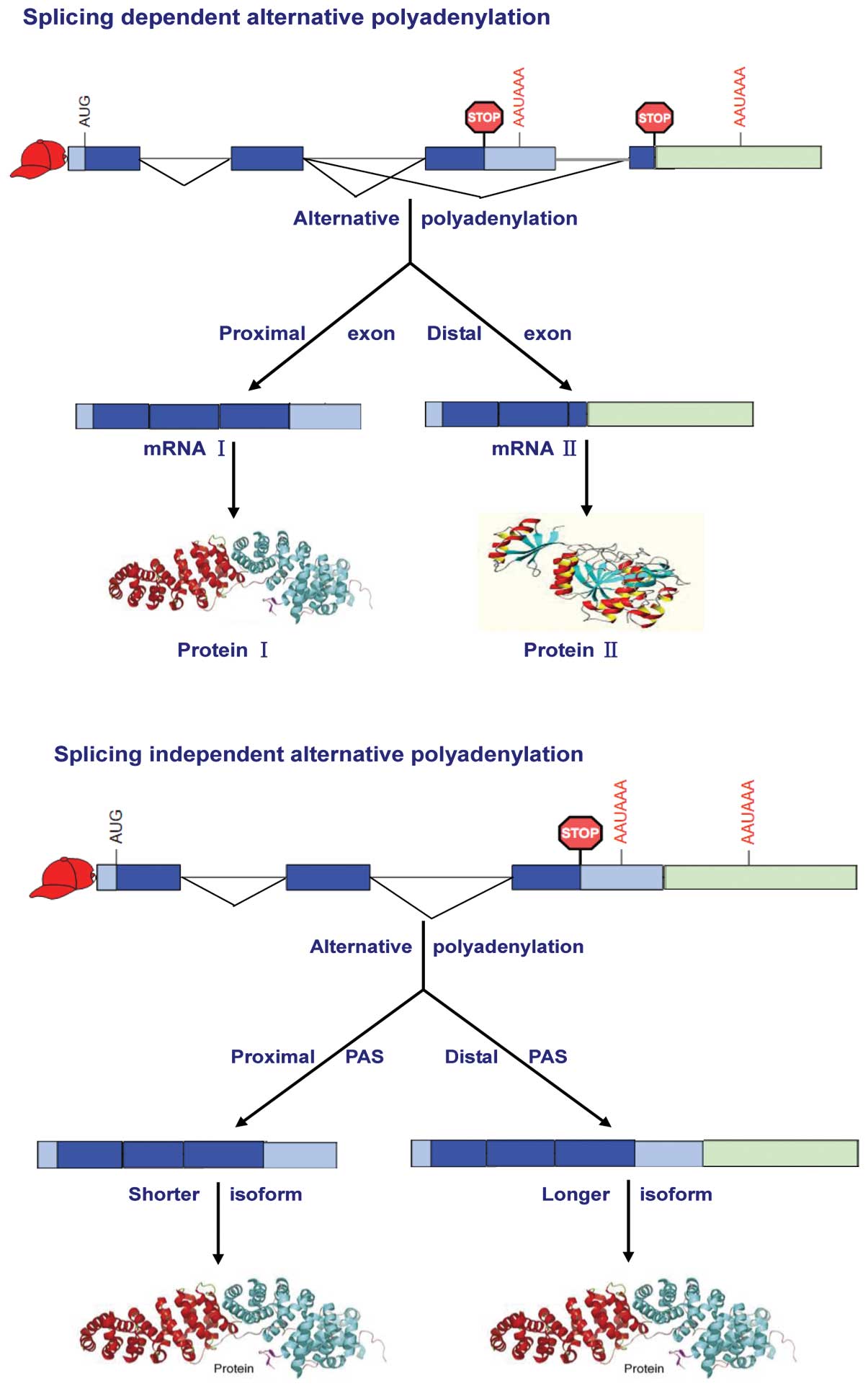
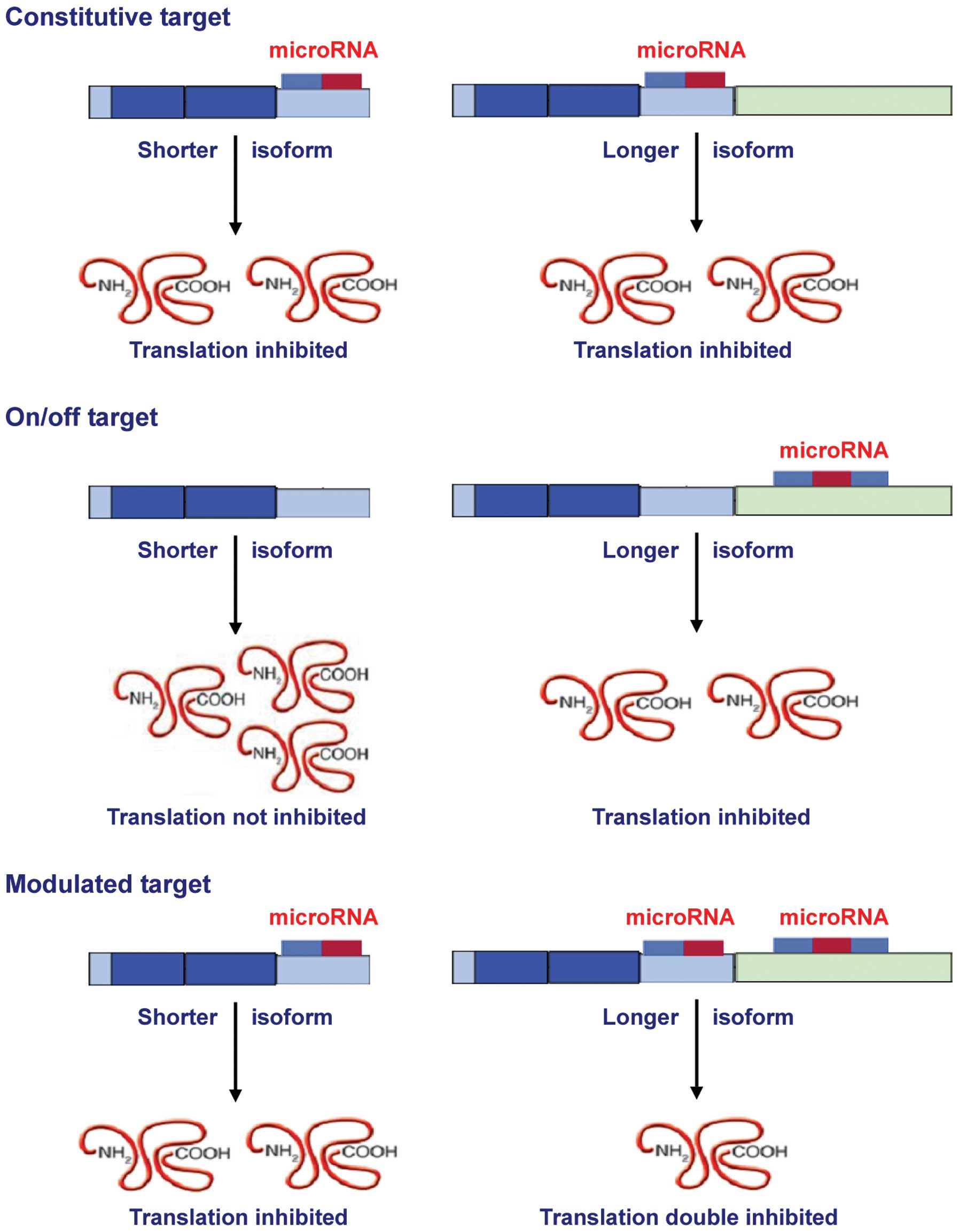
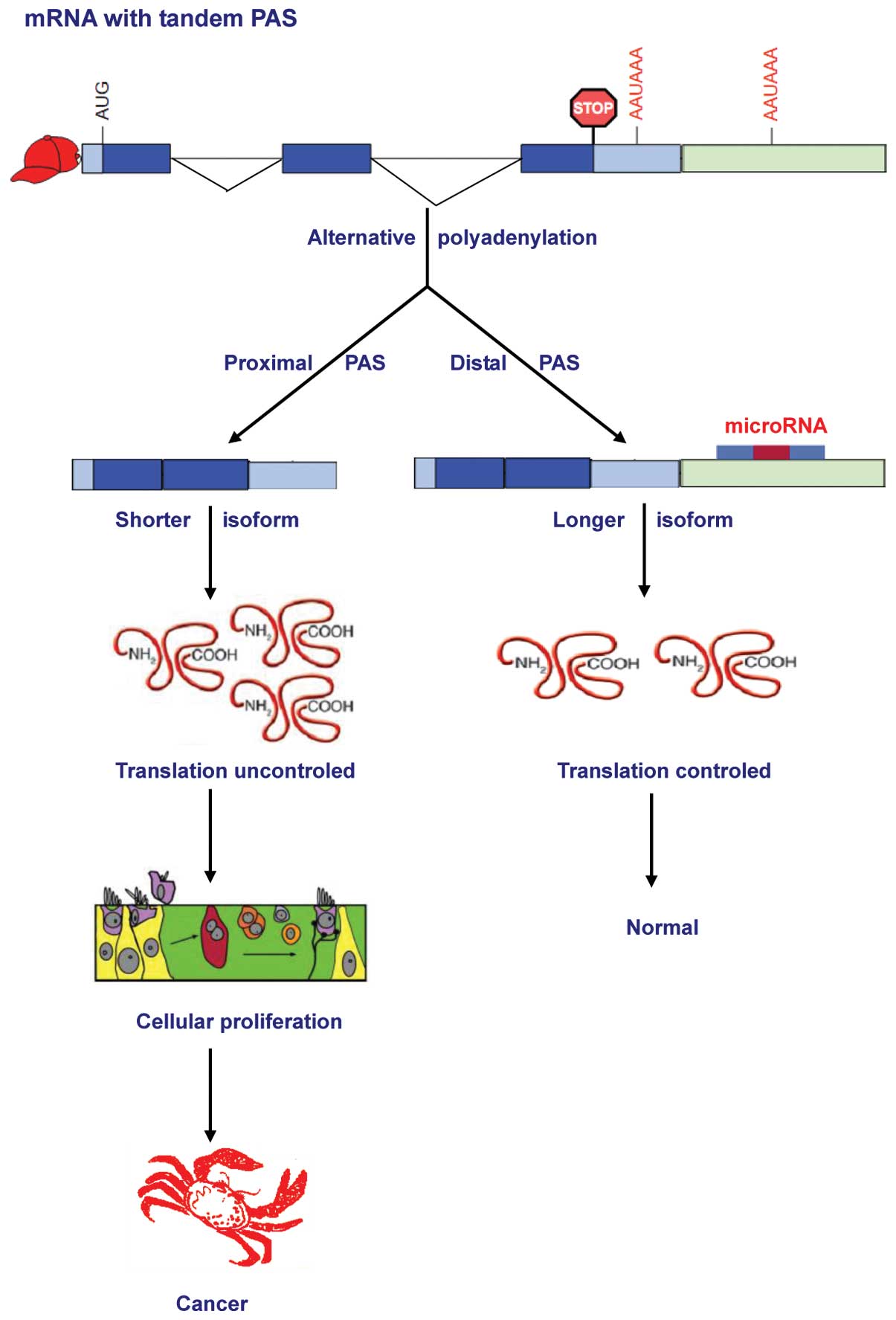
|
1.
|
Venter JC, Adams MD, Myers EW, et al: The
sequence of the human genome. Science. 291:1304–1351. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, et al:
Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature.
409:860–921. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Mignone F, Gissi C, Liuni S and Pesole G:
Untranslated regions of mRNAs. Genome Biol. 3:Reviews 0004. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Maniatis T and Reed R: An extensive
network of coupling among gene expression machines. Nature.
416:499–506. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Lackner DH, Beilharz TH, Marguerat S, et
al: A network of multiple regulatory layers shapes gene expression
in fission yeast. Mol Cell. 26:145–155. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
de la Grange P, Dutertre M, Correa M and
Auboeuf D: A new advance in alternative splicing databases: from
catalogue to detailed analysis of regulation of expression and
function of human alternative splicing variants. BMC
Bioinformatics. 8:1802007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Wang ET, Sandberg R, Luo S, et al:
Alternative isoform regulation in human tissue transcriptomes.
Nature. 456:470–476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Tian B, Pan Z and Lee JY: Widespread mRNA
polyadenylation events in introns indicate dynamic interplay
between polyadenylation and splicing. Genome Res. 17:156–165. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Hon LS and Zhang Z: The roles of binding
site arrangement and combinatorial targeting in microRNA repression
of gene expression. Genome Biol. 8:R1662007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Farh KK, Grimson A, Jan C, et al: The
widespread impact of mammalian MicroRNAs on mRNA repression and
evolution. Science. 310:1817–1821. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Ro S, Park C, Young D, Sanders KM and Yan
W: Tissue-dependent paired expression of miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res.
35:5944–5953. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Rodriguez A, Griffiths-Jones S, Ashurst JL
and Bradley A: Identification of mammalian microRNA host genes and
transcription units. Genome Res. 14:1902–1910. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Linsley PS, Schelter J, Burchard J, et al:
Transcripts targeted by the microRNA-16 family cooperatively
regulate cell cycle progression. Mol Cell Biol. 27:2240–2252. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Kertesz S, Kerenyi Z, Merai Z, et al: Both
introns and long 3′-UTRs operate as cis-acting elements to trigger
nonsense-mediated decay in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:6147–6157.
2006.
|
|
15.
|
Gilat R and Shweiki D: A novel function
for alternative polyadenylation as a rescue pathway from NMD
surveillance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 353:487–492. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Lewis BP, Green RE and Brenner SE:
Evidence for the widespread coupling of alternative splicing and
nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:189–192. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Makeyev EV, Zhang J, Carrasco MA and
Maniatis T: The MicroRNA miR-124 promotes neuronal differentiation
by triggering brain-specific alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Mol
Cell. 27:435–448. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Durand C, Roeth R, Dweep H, et al:
Alternative splicing and nonsense-mediated RNA decay contribute to
the regulation of SHOX expression. PloS One. 6:e181152011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Li XL, Andersen JB, Ezelle HJ, Wilson GM
and Hassel BA: Post-transcriptional regulation of RNase-L
expression is mediated by the 3′-untranslated region of its mRNA. J
Biol Chem. 282:7950–7960. 2007.
|
|
20.
|
Rimokh R, Berger F, Bastard C, et al:
Rearrangement of CCND1 (BCL1/PRAD1) 3′ untranslated region in
mantle-cell lymphomas and t(11q13)-associated leukemias. Blood.
83:3689–3696. 1994.
|
|
21.
|
von Roretz C and Gallouzi IE: Decoding
ARE-mediated decay: is microRNA part of the equation? J Cell Biol.
181:189–194. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Muhlrad D and Parker R: Aberrant mRNAs
with extended 3′ UTRs are substrates for rapid degradation by mRNA
surveillance. RNA. 5:1299–1307. 1999.
|
|
23.
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN and
Sonenberg N: Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by
microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 9:102–114.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
D: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Yekta S, Shih IH and Bartel DP:
MicroRNA-directed cleavage of HOXB8 mRNA. Science. 304:594–596.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Pillai RS, Bhattacharyya SN, Artus CG, et
al: Inhibition of translational initiation by Let-7 MicroRNA in
human cells. Science. 309:1573–1576. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Wu L, Fan J and Belasco JG: MicroRNAs
direct rapid dead-enylation of mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:4034–4039. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Didiano D and Hobert O: Molecular
architecture of a miRNA-regulated 3′ UTR. RNA. 14:1297–1317.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Stark A, Brennecke J, Bushati N, Russell
RB and Cohen SM: Animal MicroRNAs confer robustness to gene
expression and have a significant impact on 3′UTR evolution. Cell.
123:1133–1146. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Kertesz M, Iovino N, Unnerstall U, Gaul U
and Segal E: The role of site accessibility in microRNA target
recognition. Nat Genet. 39:1278–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Lopez F, Granjeaud S, Ara T, Ghattas B and
Gautheret D: The disparate nature of ‘intergenic’ polyadenylation
sites. RNA. 12:1794–1801. 2006.
|
|
33.
|
Legendre M and Gautheret D: Sequence
determinants in human polyadenylation site selection. BMC Genomics.
4:72003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Kubo T, Wada T, Yamaguchi Y, Shimizu A and
Handa H: Knockdown of 25 kDa subunit of cleavage factor Im in Hela
cells alters alternative polyadenylation within 3′-UTRs. Nucleic
Acids Res. 34:6264–6271. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Edwalds-Gilbert G, Veraldi KL and Milcarek
C: Alternative poly(A) site selection in complex transcription
units: means to an end? Nucleic Acids Res. 25:2547–2561. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Ara T, Lopez F, Ritchie W, Benech P and
Gautheret D: Conservation of alternative polyadenylation patterns
in mammalian genes. BMC Genomics. 7:1892006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Zhang H, Lee JY and Tian B: Biased
alternative polyadenylation in human tissues. Genome Biol.
6:R1002005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Feng Z, Wu CF, Zhou X and Kuang J:
Alternative polyadenylation produces two major transcripts of Alix.
Arch Biochem Biophys. 465:328–335. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Moucadel V, Lopez F, Ara T, Benech P and
Gautheret D: Beyond the 3′ end: experimental validation of extended
transcript isoforms. Nucleic Acids Res. 35:1947–1957. 2007.
|
|
40.
|
Lutz CS: Alternative polyadenylation: a
twist on mRNA 3′ end formation. ACS Chem Biol. 3:609–617.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Heuze-Vourc’h N, Leblond V and Courty Y:
Complex alternative splicing of the hKLK3 gene coding for the tumor
marker PSA (prostate-specific-antigen). Eur J Biochem. 270:706–714.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Liu H and Johnson EM: Distinct proteins
encoded by alternative transcripts of the PURG gene, located
contrapodal to WRN on chromosome 8, determined by differential
termination/polyadenylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:2417–2426. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43.
|
Yu M, Sha H, Gao Y, Zeng H, Zhu M and Gao
X: Alternative 3′ UTR polyadenylation of Bzw1 transcripts display
differential translation efficiency and tissue-specific expression.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 345:479–485. 2006.
|
|
44.
|
Hughes TA: Regulation of gene expression
by alternative untranslated regions. Trends Genet. 22:119–122.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Stojic J, Stohr H and Weber BH: Three
novel ABCC5 splice variants in human retina and their role as
regulators of ABCC5 gene expression. BMC Mol Biol. 8:422007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Hager S, Frame FM, Collins AT, Burns JE
and Maitland NJ: An internal polyadenylation signal substantially
increases expression levels of lentivirus-delivered transgenes but
has the potential to reduce viral titer in a promoter-dependent
manner. Hum Gene Ther. 19:840–850. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47.
|
Legendre M, Ritchie W, Lopez F and
Gautheret D: Differential repression of alternative transcripts: a
screen for miRNA targets. PLoS Comput Biol. 2:e432006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Tan S, Guo J, Huang Q, et al: Retained
introns increase putative microRNA targets within 3′ UTRs of human
mRNA. FEBS Lett. 581:1081–1086. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Sivakumaran TA, Resendes BL, Robertson NG,
Giersch AB and Morton CC: Characterization of an abundant COL9A1
transcript in the cochlea with a novel 3′ UTR: expression studies
and detection of miRNA target sequence. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol.
7:160–172. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Majoros WH and Ohler U: Spatial
preferences of microRNA targets in 3′ untranslated regions. BMC
Genomics. 8:1522007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Hla T, Bishop-Bailey D, Liu CH, Schaefers
HJ and Trifan OC: Cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 isoenzymes. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 31:551–557. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52.
|
Harper KA and Tyson-Capper AJ: Complexity
of COX-2 gene regulation. Biochem Soc Trans. 36:543–545. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Hall-Pogar T, Zhang H, Tian B and Lutz CS:
Alternative polyadenylation of cyclooxygenase-2. Nucleic Acids Res.
33:2565–2579. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Sawaoka H, Dixon DA, Oates JA and Boutaud
O: Tristetraprolin binds to the 3′-untranslated region of
cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA. A polyadenylation variant in a cancer cell
line lacks the binding site. J Biol Chem. 278:13928–13935.
2003.
|
|
55.
|
Chakrabarty A, Tranguch S, Daikoku T,
Jensen K, Furneaux H and Dey SK: MicroRNA regulation of
cyclooxygenase-2 during embryo implantation. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 104:15144–15149. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
Sandberg R, Neilson JR, Sarma A, Sharp PA
and Burge CB: Proliferating cells express mRNAs with shortened 3′
untranslated regions and fewer microRNA target sites. Science.
320:1643–1647. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57.
|
Zlotorynski E and Agami R: A PASport to
cellular proliferation. Cell. 134:208–210. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58.
|
Ghosh T, Soni K, Scaria V, Halimani M,
Bhattacharjee C and Pillai B: MicroRNA-mediated up-regulation of an
alternatively polyadenylated variant of the mouse cytoplasmic
{beta}-actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 36:6318–6332. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59.
|
Gammell P: MicroRNAs: recently discovered
key regulators of proliferation and apoptosis in animal cells:
identification of miRNAs regulating growth and survival.
Cytotechnology. 53:55–63. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60.
|
Jovanovic M and Hengartner MO: miRNAs and
apoptosis: RNAs to die for. Oncogene. 25:6176–6187. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61.
|
O’Rourke JR, Swanson MS and Harfe BD:
MicroRNAs in mammalian development and tumorigenesis. Birth Defects
Res C Embryo Today. 78:172–179. 2006.
|
|
62.
|
Bandres E, Agirre X, Ramirez N, Zarate R
and Garcia-Foncillas J: MicroRNAs as cancer players: potential
clinical and biological effects. DNA Cell Biol. 26:273–282. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63.
|
Dixon DA: Dysregulated
post-transcriptional control of COX-2 gene expression in cancer.
Curr Pharm Des. 10:635–646. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64.
|
Eberhart CE, Coffey RJ, Radhika A,
Giardiello FM, Ferrenbach S and DuBois RN: Up-regulation of
cyclooxygenase 2 gene expression in human colorectal adenomas and
adenocarcinomas. Gastroenterology. 107:1183–1188. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65.
|
Kutchera W, Jones DA, Matsunami N, et al:
Prostaglandin H synthase 2 is expressed abnormally in human colon
cancer: evidence for a transcriptional effect. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 93:4816–4820. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66.
|
Ristimaki A, Sivula A, Lundin J, et al:
Prognostic significance of elevated cyclooxygenase-2 expression in
breast cancer. Cancer Res. 62:632–635. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67.
|
Wolff H, Saukkonen K, Anttila S,
Karjalainen A, Vainio H and Ristimaki A: Expression of
cyclooxygenase-2 in human lung carcinoma. Cancer Res. 58:4997–5001.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68.
|
Yoshimura R, Sano H, Masuda C, et al:
Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in prostate carcinoma. Cancer.
89:589–596. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69.
|
Tucker ON, Dannenberg AJ, Yang EK, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is up-regulated in human pancreatic
cancer. Cancer Res. 59:987–990. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70.
|
Ristimaki A, Nieminen O, Saukkonen K,
Hotakainen K, Nordling S and Haglund C: Expression of
cyclooxygenase-2 in human transitional cell carcinoma of the
urinary bladder. Am J Pathol. 158:849–853. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71.
|
Ristimaki A, Honkanen N, Jankala H,
Sipponen P and Harkonen M: Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human
gastric carcinoma. Cancer Res. 57:1276–1280. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72.
|
Ratnasinghe D, Tangrea J, Roth MJ, et al:
Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human squamous cell carcinoma of
the esophagus; an immunohistochemical survey. Anticancer Res.
19:171–174. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73.
|
Chan G, Boyle JO, Yang EK, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is up-regulated in squamous cell
carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer Res. 59:991–994.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74.
|
Sherr CJ: Mammalian G1 cyclins. Cell.
73:1059–1065. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75.
|
Wiestner A, Tehrani M, Chiorazzi M, et al:
Point mutations and genomic deletions in CCND1 create stable
truncated cyclin D1 mRNAs that are associated with increased
proliferation rate and shorter survival. Blood. 109:4599–4606.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76.
|
Yu Z, Wang C, Wang M, et al: A cyclin
D1/microRNA 17/20 regulatory feedback loop in control of breast
cancer cell proliferation. J Cell Biol. 182:509–517. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77.
|
Nosho K, Kawasaki T, Chan AT, et al:
Cyclin D1 is frequently overexpressed in microsatellite unstable
colorectal cancer, independent of CpG island methylator phenotype.
Histopathology. 53:588–598. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78.
|
Elsheikh S, Green AR, Aleskandarany MA, et
al: CCND1 amplification and cyclin D1 expression in breast cancer
and their relation with proteomic subgroups and patient outcome.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 109:325–335. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79.
|
Radovic S, Babic M, Doric M, et al:
Non-small cell lung carcinoma: cyclin D1, bcl-2, p53, Ki-67 and
HER-2 proteins expression in resected tumors. Bosn J Basic Med Sci.
7:205–211. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80.
|
Shakir R, Ngo N and Naresh KN: Correlation
of cyclin D1 transcript levels, transcript type and protein
expression with proliferation and histology among mantle cell
lymphoma. J Clin Pathol. 61:920–927. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81.
|
Chen RW, Bemis LT, Amato CM, et al:
Truncation in CCND1 mRNA alters miR-16-1 regulation in mantle cell
lymphoma. Blood. 112:822–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|