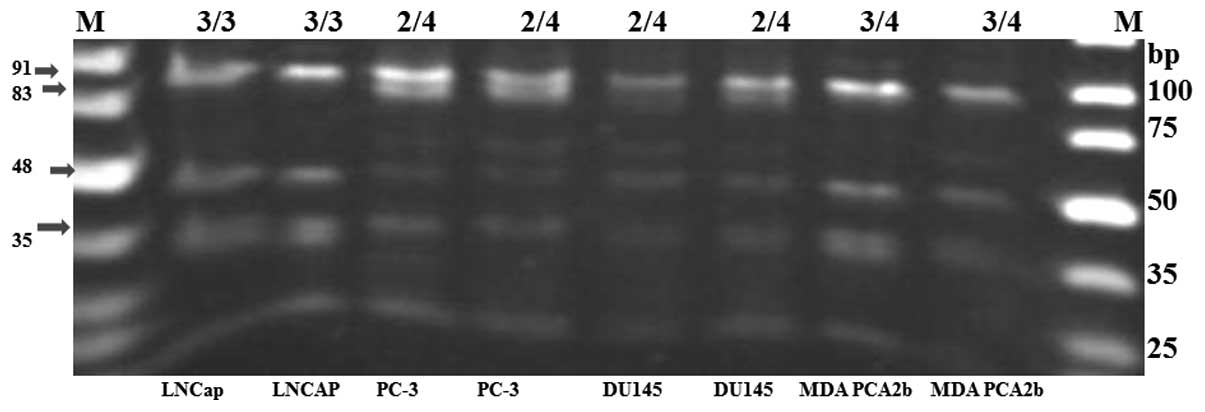
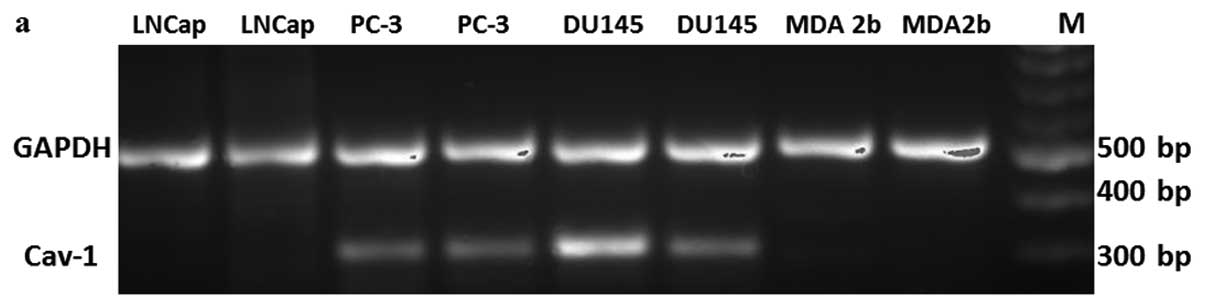
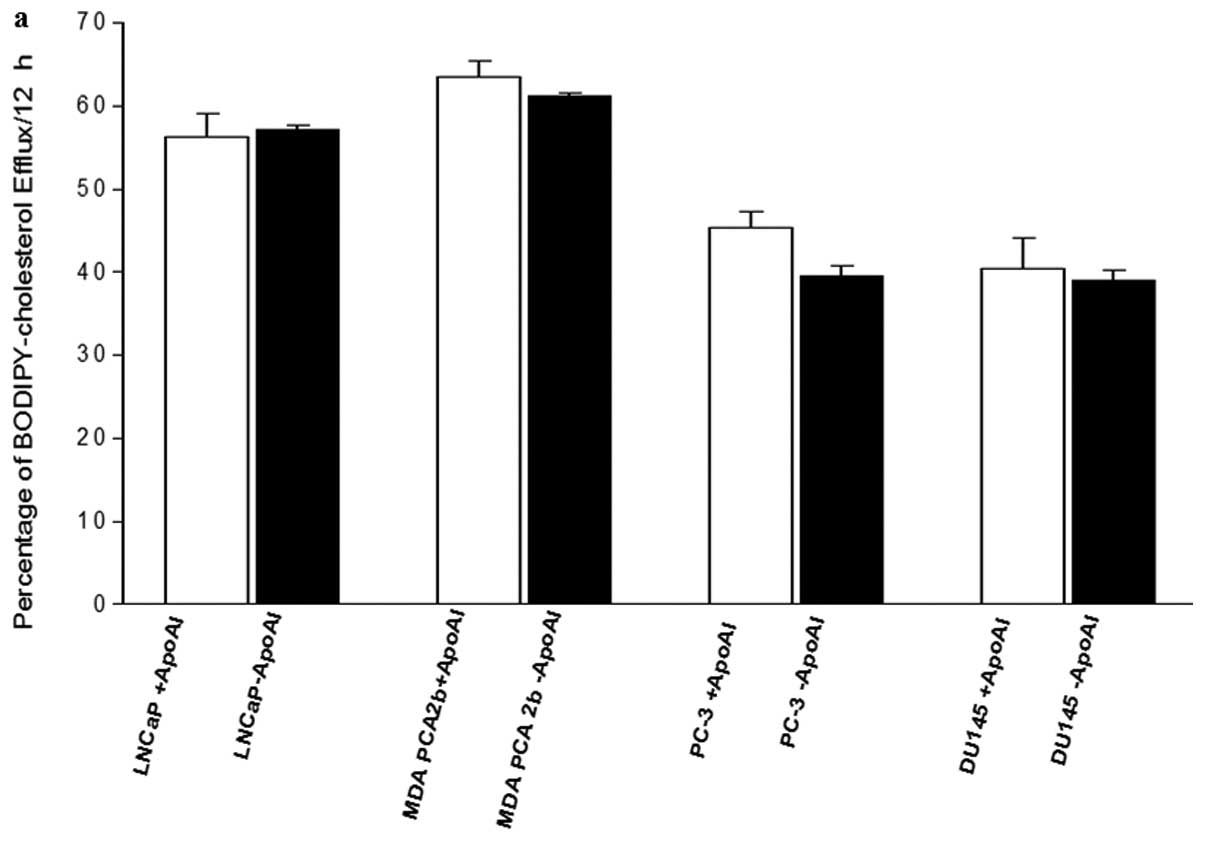
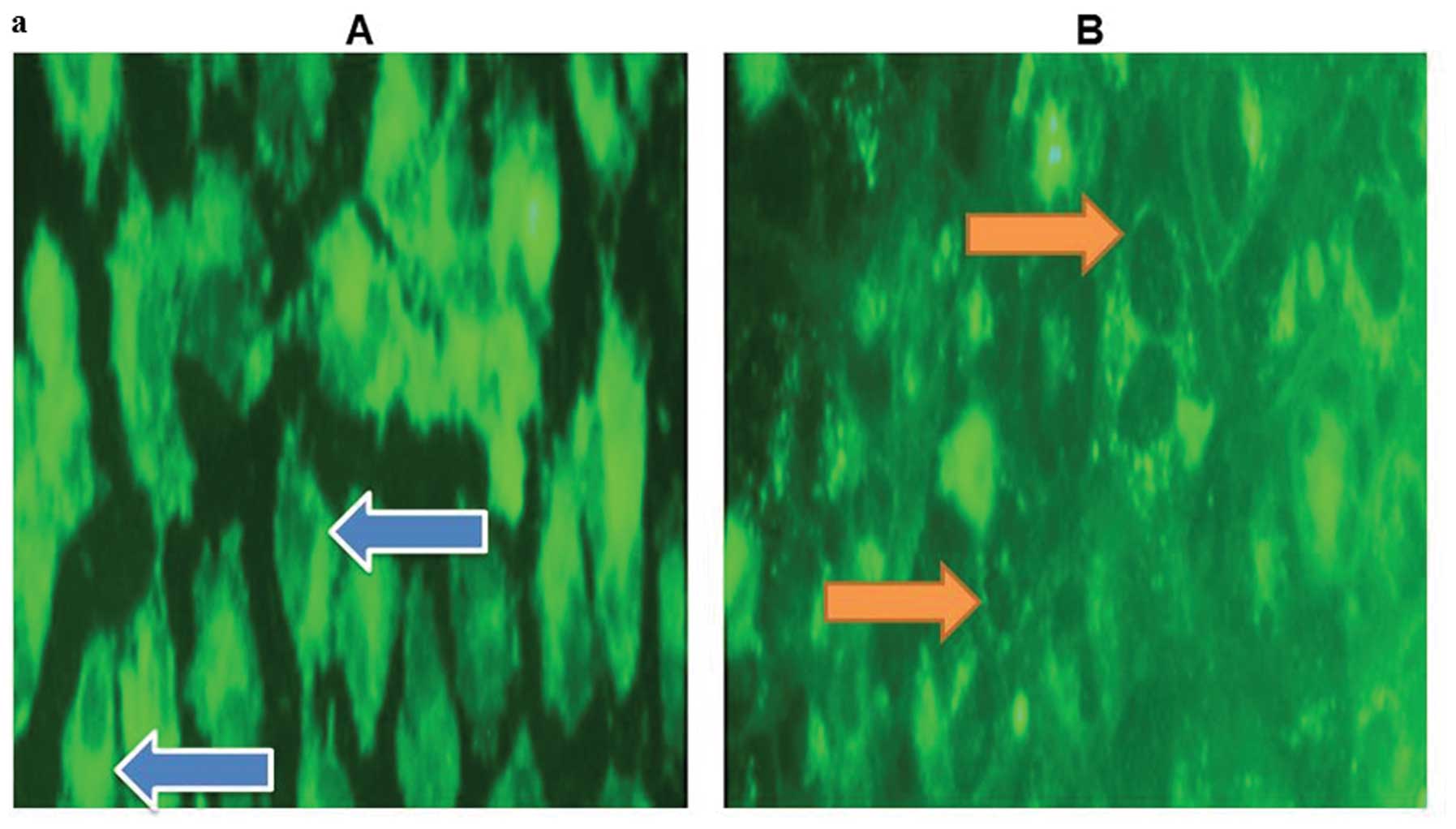
|
1.
|
Williams SD, Cook ED, Anderson KB and
Hamilton SJ: Bridging the gap between populations: the challenge of
reducing cancer disparities among African-American and other ethnic
minority populations. US Oncol. 4:72–75. 2008.
|
|
2.
|
Ifere GO, Abebe F and Ananaba GA: Emergent
trends in the reported incidence of prostate cancer in Nigeria.
Clin Epidemiol. 4:19–32. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Sakr WA: Prostatic intraepithelial
neoplasia: A marker for high-risk groups and a potential target for
chemoprevention. Eur Urol. 35:474–478. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Bock CH, Powell I, Kittles RA, Hsing AW
and Carpten J: Racial disparity in prostate cancer incidence,
biochemical recurrence, and mortality. Prostate Cancer. 716178:1–2.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Bigler SA, Pound CR and Zhou X: A
retrospective study on pathological features and racial disparities
in prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer. 2011:2394602011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Lee J, Demissie K, Lu SE and Rhoads GG:
Cancer incidence among Korean-American immigrants in the United
States and native Koreans of South Korea. Cancer Control. 14:78–85.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Ma RW and Chapman K: A systematic review
of the effect of diet in prostate cancer prevention and treatment.
J Hum Nutr Diet. 22:187–199. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Michaud DS, Augustsson K, Rimm EB,
Stampfer MJ, Willet WC and Giovanucci E: A prospective study on
intake of animal products and risk of prostate cancer. Cancer
Causes Control. 12:557–567. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Waddell WJ: Epidemiological studies and
effects of environmental estrogens. Int J Toxicol. 17:173–191.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Le Marchand L and Wilkens LR: Design
considerations for genomic association studies: importance of
gene-environment interactions. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
17:263–267. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Nothlings U, Yamamoto JF, Wilkens LR,
Murphy SP, Park SY, Henderson BE, Kolonel LN and Le Marchand L:
Meat and heterocyclic amine intake, smoking, NAT1 and NAT2
polymorphisms, and colorectal cancer risk in the multiethnic cohort
study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 18:2097–2106. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Wünsch Filho V and Zago MA: Modern cancer
epidemiology research: genetic polymorphism and environment. Rev
Saude Publica. 39:490–497. 2005.
|
|
13.
|
Finch CE and Stanford CB: Meat-adaptive
genes and the evolution of slower aging in humans. Q Rev Biol.
79:3–50. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Mahley RW: Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol
transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science.
240:622–630. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Tziakas DN, Chalikias GK, Antonoglou CO,
Veletza S, Tentes IK, Kortsaris AX, Hatseras DI and Kaski JC:
Apolipoprotein E genotype and circulating interleukin-10 levels in
patients with stable and unstable coronary artery disease. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 48:2471–2481. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Leduc V, Domenger D, De Beaumont L,
Lalonde D, Bélanger-Jasmin S and Poirier J: Function and
comorbidities of apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J
Alzheimers Dis. 2011:1–22. 2011.
|
|
17.
|
Eichner JE, Dunn ST, Perveen G, Thompson
DM, Stewart KE and Stroehla BC: Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and
cardiovascular disease: a HuGE review. Am J Epidemiol. 155:487–495.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Mahley RW and Rall SC Jr: Apolipoprotein
E: far more than a lipid transport protein. Annu Rev Genomics Hum
Genet. 1:507–537. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Moore RJ, Chamberlain RM and Khuri FR:
Apolipoprotein E and the risk of breast cancer in African-American
and non-Hispanic white women. A review. Oncology. 66:79–93. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Kallio MJ, Salmenperä L, Siimes MA,
Perheentupa J, Gylling H and Miettinen TA: Apolipoprotein E
phenotype determines serum cholesterol in infants during both
high-cholesterol breast feeding and low-cholesterol formula
feeding. J Lipid Res. 38:759–764. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Berglund L: The APOE gene and diets - food
(and drink) for thought. Am J Clin Nutr. 73:669–670.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Papaioannou I, Simmons JP and Owen JS:
Targeted in situ gene correction of dysfunctional APOE alleles to
produce atheroprotective plasma ApoE3 protein. Cardiol Res Pract.
2012:1487962012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Kockx M, Jessup W and Kritharides L:
Regulation of endogenous apolipoprotein E secretion by macrophages.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:1060–1067. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Huang ZH, Fitzgerald ML and Mazzone T:
Distinct cellular loci for the ABCA1-dependent and
ABCA1-independent lipid efflux mediated by endogenous
apolipoprotein E expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
26:157–162. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Huang Y, von Eckardstein A, Wu S and
Assmann G: Effects of the apolipoprotein E polymorphism on uptake
and transfer of cell derived cholesterol in plasma. J Clin Invest.
96:2693–2701. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Lane RM and Farlow MR: Lipid homeostasis
and apolipoprotein E in the development and progression of
Alzheimer’s disease. J Lipid Res. 46:949–968. 2005.
|
|
27.
|
Uittenbogaard A, Ying Y and Smart EJ:
Characterization of a cytosolic heat-shock protein-caveolin
chaperone complex. Involvement in cholesterol trafficking. J Biol
Chem. 273:6525–6532. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Liscum L and Munn NJ: Intracellular
cholesterol transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1438:19–37. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Li YC, Park MJ, Ye SK, Kim CW and Kim YN:
Elevated levels of cholesterol-rich lipid rafts in cancer cells are
correlated with apoptosis sensitivity induced by
cholesterol-depleting agents. Am J Pathol. 168:1107–1118. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Hixson JE and Vernier DT: Restriction
isotyping of human apolipoprotein E by gene amplification and
cleavage with Hha I. J Lipid Res. 31:545–548.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Sankaranarayanan S, Kellner-Weibel G, de
la Llera-Moya M, Phillips MC, Asztalos BF, Bittmam R and Rothblat
GH: A sensitive assay for ABCA1-mediated cholesterol efflux using
BODIPY-cholesterol. J Lipid Res. 52:2332–2340. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Yue L and Mazzone T: Endogenous adipocyte
apolipoprotein E is colocalized with caveolin at the adipocyte
plasma membrane. J Lipid Res. 52:489–498. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Nair HK, Rao KV, Aalinkeel R, Mahajan S,
Chawda R and Schwartz SA: Inhibition of prostate cancer cell colony
formation by the flavonoid quercetin correlates with modulation of
specific regulatory genes. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 11:63–69.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Saraon P, Musrap N, Cretu D, Karagiannis
GS, Batruch I, Smith C, Drabovich AP, Trudel D, van der Kwast T,
Morrissey C, Jarvi KA and Diamandis EP: Proteomic profiling of
androgen-independent prostate cancer cell lines reveals a role for
protein S during the development of high grade and
castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Biol Chem. 287:34019–34031.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35.
|
Wang B, Yang Q, Ceniccola K, Bianco F,
Andrawis R, Jarret T, Frazier H, Patierno SR and Lee NH: Androgen
receptor-target gene in African American prostate cancer
disparities. Prostate Cancer. 2013:7635692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Kim DH and Wirtz D: Recapitulating cancer
cell invasion in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:6693–6694.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Hoosein NM: Neuroendocrine and immune
mediators in prostate cancer progression. Front Biosci.
3:D1274–D1279. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Hara T, Miyazaki H, Lee A, Tran CP and
Reiter RE: Androgen receptor and invasion in prostate cancer.
Cancer Res. 68:1128–1135. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Nomura DK, Lombardi DP, Chang JW, Niessen
S, Ward AM, Long JZ, Hoover HH and Cravatt BF: Monoacylglycerol
lipase exerts dual control over endocannabinoid and fatty acid
pathways to support prostate cancer. Chem Biol. 18:846–856. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Venanzoni MC, Giunta S, Murara GB, Storari
L, Crescini C, Mazzucchelli R, Montironi R and Seth A:
Apolipoprotein E expression in localized prostate cancers. Int J
Oncol. 22:779–786. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Saadat M: Apolipoprotein E (ApoE)
polymorphism and susceptibility to breast cancer: a meta-analysis.
Cancer Res Treat. 44:121–126. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Niemi M, Kervinen K, Kiviniemi H,
Lukkarinen O, Kyllönen AP, Apaja-Sarkkinen M, Savolainen MJ,
Kairaluoma MI and Kesäniemi YA: Apolipoprotein E phenotype,
cholesterol and breast and prostate cancer. J Epidemiol Community
Health. 54:938–939. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Haapla K, Lehtimäki T, Ilveskoski E and
Koivisto PA: Apolipoprotein E is not linked to locally recurrent
hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis.
3:107–109. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Koivisto P, Visakorpi T, Rantala I and
Isola J: Increased cell proliferation activity and decreased cell
death are associated with the emergence of hormone-refractory
recurrent prostate cancer. J Pathol. 183:51–56. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Mostaghel EA, Solomon KR, Pelton K,
Freeman MR and Montgomery RB: Impact of circulating cholesterol
levels on growth and intratumoral androgen concentration of
prostate tumors. PLoS One. 7:e300622012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Krimbou L, Denis M, Haidar B, Carrier M,
Marci M and Genest J Jr: Molecular interactions between apoE and
ABCA1: impact on apoE lipidation. J Lipid Res. 45:839–848. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Cullen P, Cignarella A, Brennhausen B,
Mohr S, Assmann G and Von Eckardstein A: Phenotype-dependent
differences in apolipoprotein E metabolism and in cholesterol
homeostasis in human monocyte-derived macrophages. J Clin Invest.
101:1670–1677. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Murtola TJ, Syvälä H, Pennanen P, Bläuer
M, Solakivi T, Ylikomi T and Tammela TL: The importance of LDL and
cholesterol metabolism for prostate epithelial cell growth. PLoS
One. 7:e394452012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Smith JD, Miyata M, Ginsberg M, Grigaux C,
Shmookler E and Plump AS: Cyclic AMP induces apolipoprotein E
binding activity and promotes cholesterol efflux from a macrophage
cell line to apolipoprotein acceptors. J Biol Chem.
271:30647–30655. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Hara M, Matsushima T, Satoh H, Iso-o N,
Noto H, Togo M, Kimura S, Hashimoto Y and Tsukamoto K:
Isoform-dependent cholesterol efflux from macrophages by
apolipoprotein E is modulated by cell surface proteoglycan.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:269–274. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Karasinska JM and Hayden MR: Cholesterol
metabolism in Huntington disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 7:561–572. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Fernández-Hernando C, Yu J, Dávalos A,
Prendergast J and Sessa WC: Endothelial-specific overexpression of
caveolin-1 accelerates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein
E-deficient mice. Am J Pathol. 177:998–1003. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Cohen AW, Hnaska R, Schubert W and Lisanti
MP: Role of caveolae and caveolins in health and disease. Physiol
Rev. 84:1341–1379. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Frank PG, Cheung MW, Pavlides S, Llaverias
G, Park DS and Lisanti MP: Caveolin-1 and regulation of cellular
cholesterol homeostasis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
291:H677–H686. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55.
|
Daniel EE, El-Yazbi A and Cho WJ: Caveolae
and calcium handling, a review and a hypothesis. J Cell Mol Med.
10:529–544. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
Yang G, Truong LD, Wheeler TM and Thompson
TC: Caveolin-1 expression in clinically confined human prostate
cancer: a novel prognostic marker. Cancer Res. 59:5719–5723.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57.
|
Thompson TC: Metastasis-related genes in
prostate cancer: the role of caveolin-1. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
17:439–442. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58.
|
Williams TM, Hassan GS, Li J, Cohen AW,
Medina F, Frank PG, Pestell RG, Di Vizio D, Loda M and Lisanti MP:
Caveolin-1 promotes tumor progression in an autochthonous mouse
model of prostate cancer. J Biol Chem. 280:25134–25145. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59.
|
Lin YC, Ma C, Hsu WC, Lo HF and Yang VC:
Molecular interaction between caveolin-1 and ABCA1 on high-density
lipoprotein-mediated cholesterol efflux in aortic endothelial
cells. Cardiovasc Res. 75:575–583. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60.
|
Le Lay S, Rodriguez M, Jessup W, Rentero
C, Li Q, Cartland S, Grewal T and Gaus K: Caveolin-1-mediated
apolipoprotein A-I membrane binding sites are not required for
cholesterol efflux. PLoS One. 6:e233532011.PubMed/NCBI
|