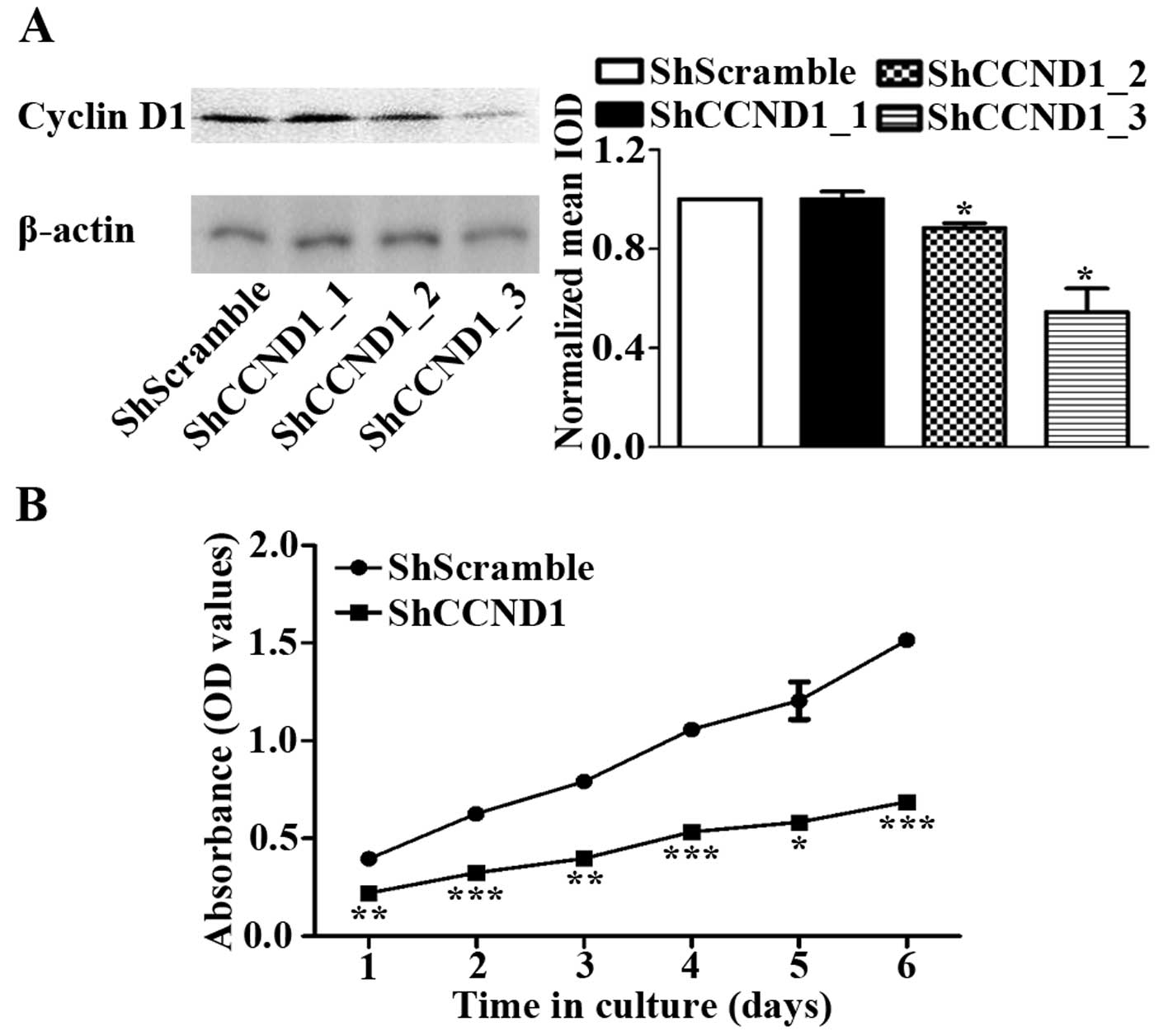
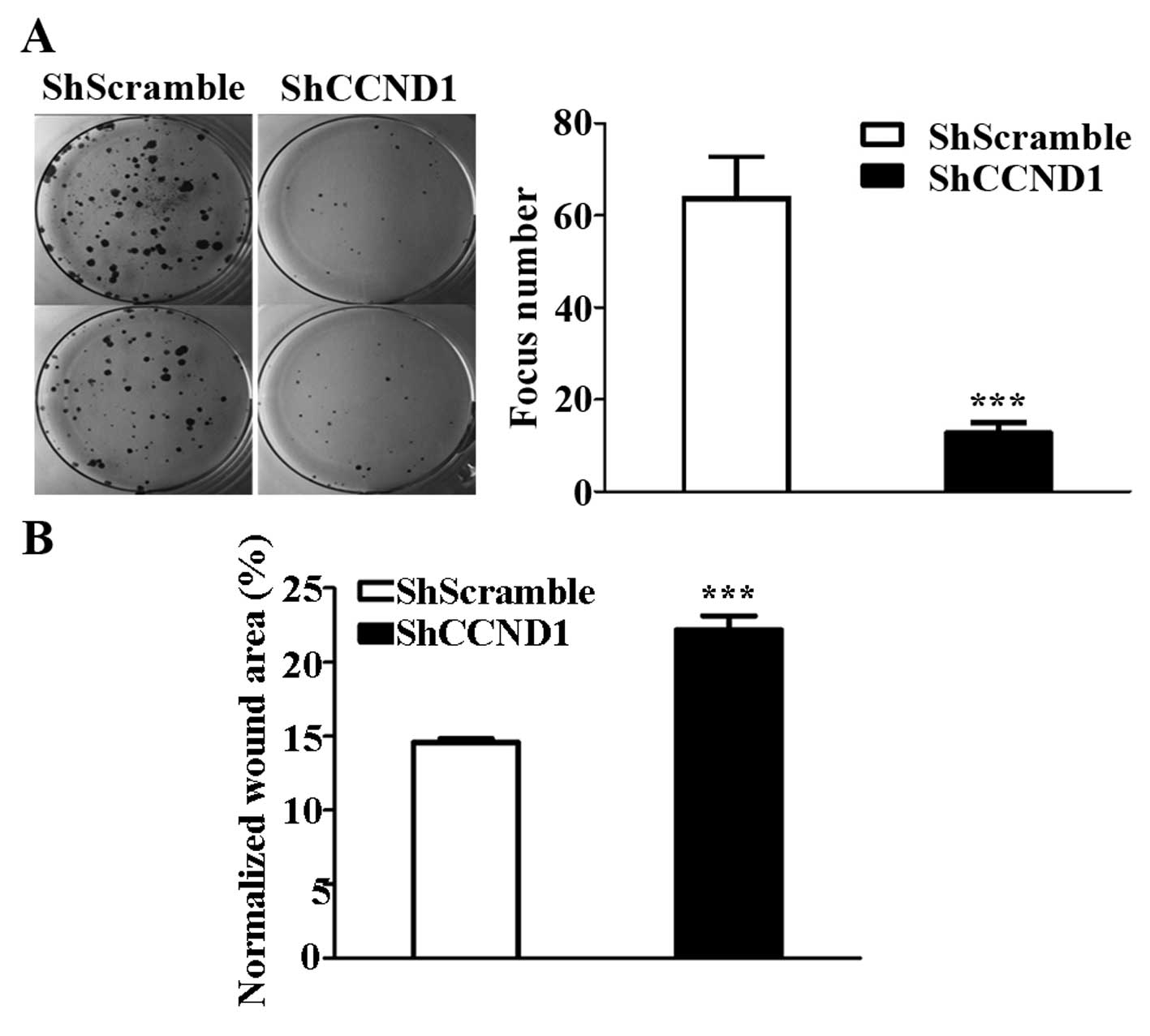
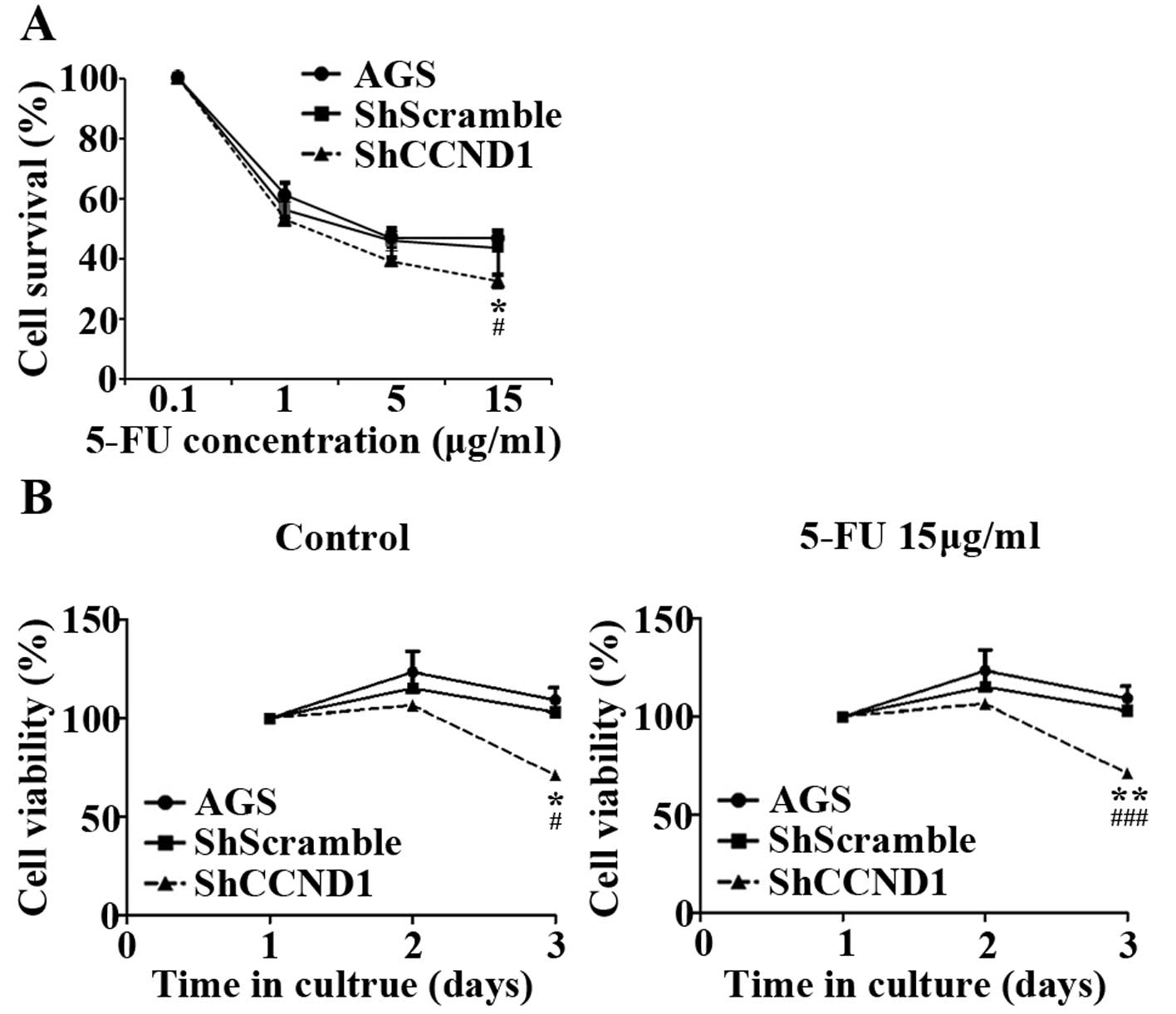
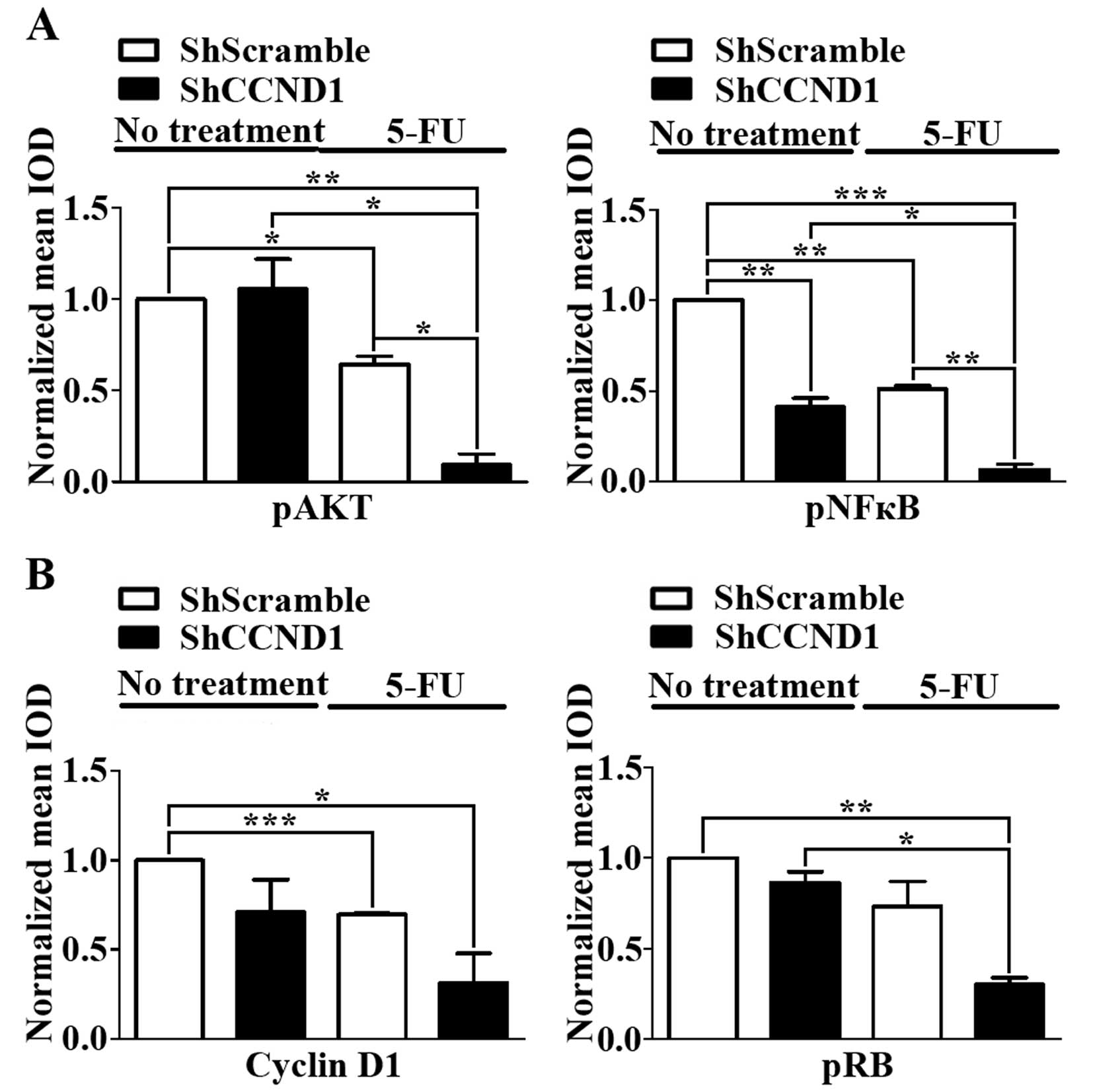
|
1.
|
Leung WK, Wu MS, Kakugawa Y, Kim JJ, Yeoh
KG, Goh KL, Wu KC, Wu DC, Sollano J, Kachintorn U, Gotoda T, Lin
JT, You WC, Ng EK and Sung JJ; Asia Pacific Working Group on
Gastric C: Screening for gastric cancer in Asia: current evidence
and practice. Lancet Oncol. 9:279–287. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Ohtsu A: Chemotherapy for metastatic
gastric cancer: past, present and future. J Gastroenterol.
43:256–264. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Sakuramoto S, Sasako M, Yamaguchi T,
Kinoshita T, Fujii M, Nashimoto A, Furukawa H, Nakajima T, Ohashi
Y, Imamura H, Higashino M, Yamamura Y, Kurita A and Arai K:
Adjuvant chemotherapy for gastric cancer with S-1, an oral
fluoropyrimidine. N Engl J Med. 357:1810–1820. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
GASTRIC (Global Advanced/Adjuvant Stomach
Tumor Research International Collaboration) Group; Paoletti X, Oba
K, Burzykowski T, Michiels S, Ohashi Y, Pignon JP, Rougier P,
Sakamoto J, Sargent D, Sasako M, Van Cutsem E and Buyse M: Benefit
of adjuvant chemotherapy for resectable gastric cancer: a
meta-analysis. JAMA. 303:1729–1737. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Sherr CJ: G1 phase progression: cycling on
cue. Cell. 79:551–555. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Weinberg RA: The retinoblastoma protein
and cell cycle control. Cell. 81:323–330. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Gao P, Zhou GY, Liu Y, Li JS, Zhen JH and
Yuan YP: Alteration of cyclin D1 in gastric carcinoma and its
clinicopathologic significance. World J Gastroenterol.
10:2936–2939. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Motokura T and Arnold A: Cyclin D and
oncogenesis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 3:5–10. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Coco Martin JM, Balkenende A, Verschoor T,
Lallemand F and Michalides R: Cyclin D1 overexpression enhances
radiation-induced apoptosis and radiosensitivity in a breast tumor
cell line. Cancer Res. 59:1134–1140. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Han EK, Begemann M, Sgambato A, Soh JW,
Doki Y, Xing WQ, Liu W and Weinstein IB: Increased expression of
cyclin D1 in a murine mammary epithelial cell line induces p27kip1,
inhibits growth and enhances apoptosis. Cell Growth Differ.
7:699–710. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Kuroda Y, Sakai A, Tsuyama N, Katayama Y,
Munemasa S, Asaoku H, Okikawa Y, Nakaju N, Mizuno M, Ogawa K,
Nishisaka T, Matsui H, Tanaka H and Kimura A: Ectopic cyclin D1
overexpression increases chemosensitivity but not cell
proliferation in multiple myeloma. Int J Oncol. 33:1201–1213.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Kornmann M, Arber N and Korc M: Inhibition
of basal and mitogen-stimulated pancreatic cancer cell growth by
cyclin D1 antisense is associated with loss of tumorigenicity and
potentiation of cytotoxicity to cisplatinum. J Clin Invest.
101:344–352. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Warenius HM, Seabra LA and Maw P:
Sensitivity to cis-diamminedichloroplatinum in human cancer cells
is related to expression of cyclin D1 but not C-RAF-1 protein. Int
J Cancer. 67:224–231. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Simizu S, Shibasaki F and Osada H: Bcl-2
inhibits calcineurin-mediated Fas ligand expression in antitumor
drug-treated baby hamster kidney cells. Jpn J Cancer Res.
91:706–714. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Zhou X, Zhang Z, Yang X, Chen W and Zhang
P: Inhibition of cyclin D1 expression by cyclin D1 shRNAs in human
oral squamous cell carcinoma cells is associated with increased
cisplatin chemosensitivity. Int J Cancer. 124:483–489. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Sun Y, Luo D and Liao DJ: Cyclin D1
protein plays different roles in modulating chemoresponses in MCF7
and MDA-MB231 cells. J Carcinog. 11:122012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Salvesen
GS, Franke TF, Stanbridge E, Frisch S and Reed JC: Regulation of
cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science.
282:1318–1321. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo
P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J and Greenberg ME: Akt
promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead
transcription factor. Cell. 96:857–868. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Curnock AP, Logan MK and Ward SG:
Chemokine signalling: pivoting around multiple phosphoinositide
3-kinases. Immunology. 105:125–136. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Baldwin AS: Control of oncogenesis and
cancer therapy resistance by the transcription factor NF-kappaB. J
Clin Invest. 107:241–246. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Ozes ON, Mayo LD, Gustin JA, Pfeffer SR,
Pfeffer LM and Donner DB: NF-kappaB activation by tumour necrosis
factor requires the Akt serine-threonine kinase. Nature. 401:82–85.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Wang C-Y, Mayo MW and Baldwin AS: TNF- and
cancer therapy-induced apoptosis: potentiation by inhibition of
NF-kappaB. Science. 274:784–787. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Camp ER, Li J, Minnich DJ, Brank A,
Moldawer LL, MacKay SL and Hochwald SN: Inducible nuclear
factor-kappaB activation contributes to chemotherapy resistance in
gastric cancer. J Am Coll Surg. 199:249–258. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Lu YS, Yeh PY, Chuang SE, Gao M, Kuo ML
and Cheng AL: Glucocorticoids enhance cytotoxicity of cisplatin via
suppression of NF-κB activation in the glucocorticoid receptor-rich
human cervical carcinoma cell line SiHa. J Endocrinol. 188:311–319.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Sauter ER, Nesbit M, Litwin S,
Klein-Szanto AJ, Cheffetz S and Herlyn M: Antisense cyclin D1
induces apoptosis and tumor shrinkage in human squamous carcinomas.
Cancer Res. 59:4876–4881. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Huang WS, Wang JP, Wang T, Fang JY, Lan P
and Ma JP: ShRNA-mediated gene silencing of beta-catenin inhibits
growth of human colon cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol.
13:6581–6587. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Liang CC, Park AY and Guan JL: In vitro
scratch assay: a convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of
cell migration in vitro. Nat Protoc. 2:329–333. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Tiang JM, Butcher NJ and Minchin RF: Small
molecule inhibition of arylamine N-acetyltransferase Type I
inhibits proliferation and invasiveness of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 393:95–100. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Pearson G, English JM, White MA and Cobb
MH: ERK5 and ERK2 cooperate to regulate NF-kappaB and cell
transformation. J Biol Chem. 276:7927–7931. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Martin V, Herrera F, Carrera-Gonzalez P,
Garcia-Santos G, Antolin I, Rodriguez-Blanco J and Rodriguez C:
Intracellular signaling pathways involved in the cell growth
inhibition of glioma cells by melatonin. Cancer Res. 66:1081–1088.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Cheng JC, Chou CH, Kuo ML and Hsieh CY:
Radiation-enhanced hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion with
MMP-9 expression through PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB signal transduction
pathway. Oncogene. 25:7009–7018. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Shin JY, Kim JO, Lee SK, Chae HS and Kang
JH: LY294002 may overcome 5-FU resistance via down-regulation of
activated p-AKT in Epstein-Barr virus-positive gastric cancer
cells. BMC Cancer. 10:4252010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Kim TW, Kang YK, Ahn JH, Chang HM, Yook
JH, Oh ST, Kim BS and Lee JS: Phase II study of capecitabine plus
cisplatin as first-line chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer.
Ann Oncol. 13:1893–1898. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Song M, Zhang R, Dai Y, Gao F, Chi H, Lv
G, Chen B and Wang X: The in vitro inhibition of multidrug
resistance by combined nanoparticulate titanium dioxide and UV
irradition. Biomaterials. 27:4230–4238. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Yoshida K and Toge T: Combination
chemotherapy of TS-1 and docetaxel on advanced and recurrent
gastric cancer. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 31:1982–1986. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Arlt A, Gehrz A, Muerkoster S, Vorndamm J,
Kruse ML, Folsch UR and Schafer H: Role of NF-kappaB and Akt/PI3K
in the resistance of pancreatic carcinoma cell lines against
gemcitabine-induced cell death. Oncogene. 22:3243–3251. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Fu M, Wang C, Li Z, Sakamaki T and Pestell
RG: Minireview: Cyclin D1: normal and abnormal functions.
Endocrinology. 145:5439–5447. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Kornmann M, Danenberg KD, Arber N, Beger
HG, Danenberg PV and Korc M: Inhibition of cyclin D1 expression in
human pancreatic cancer cells is associated with increased
chemosensitivity and decreased expression of multiple
chemoresistance genes. Cancer Res. 59:3505–3511. 1999.
|
|
39.
|
Zhou H, Fujigaki Y, Kato A, Miyaji T,
Yasuda H, Tsuji T, Yamamoto T, Yonemura K and Hishida A: Inhibition
of p21 modifies the response of cortical proximal tubules to
cisplatin in rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 291:F225–F235. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Liu N, Zhang J, Zhang J, Liu S, Liu Y and
Zheng D: Erbin-regulated sensitivity of MCF-7 breast cancer cells
to TRAIL via ErbB2/AKT/NF-kappaB pathway. J Biochem. 143:793–801.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|