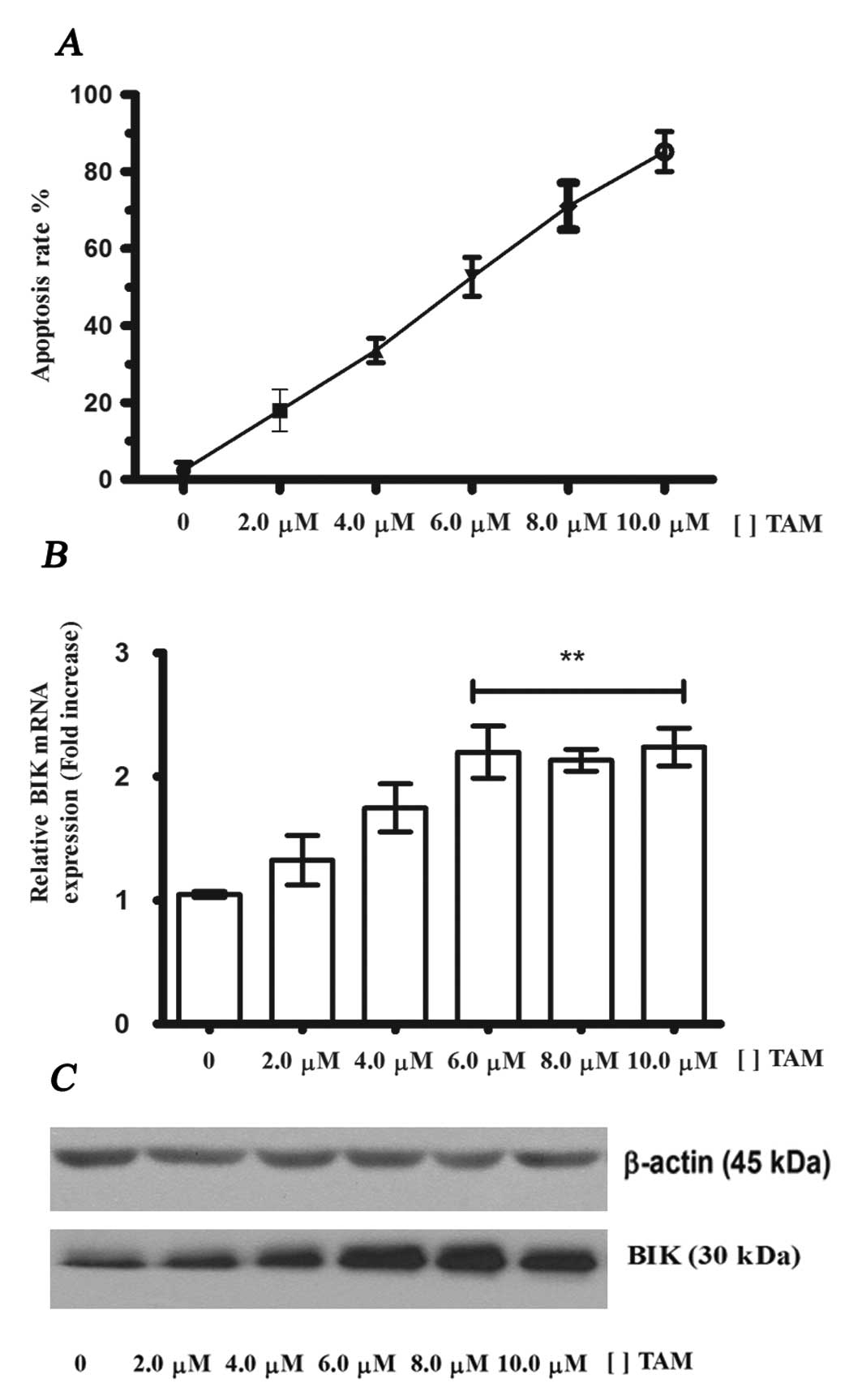
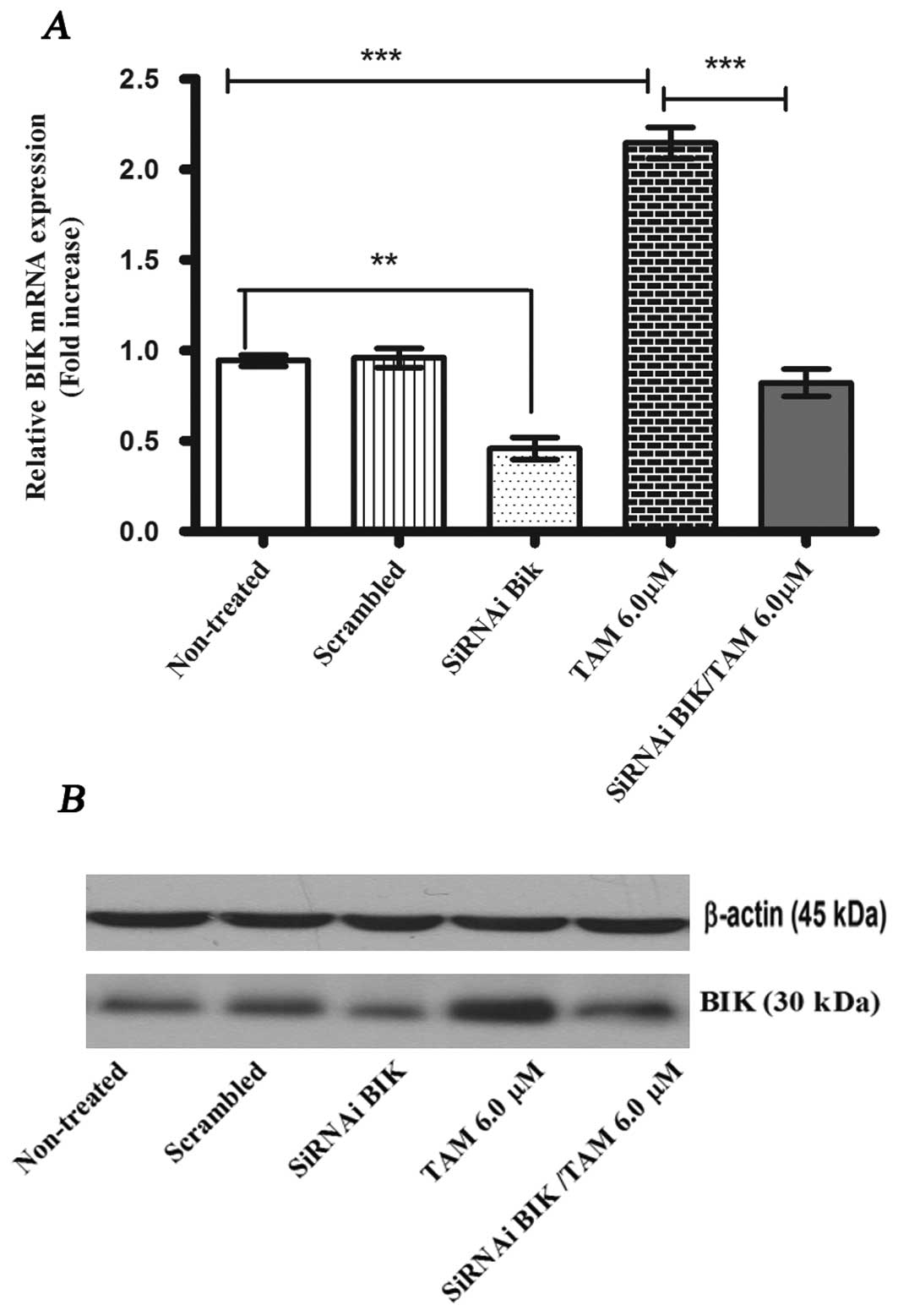
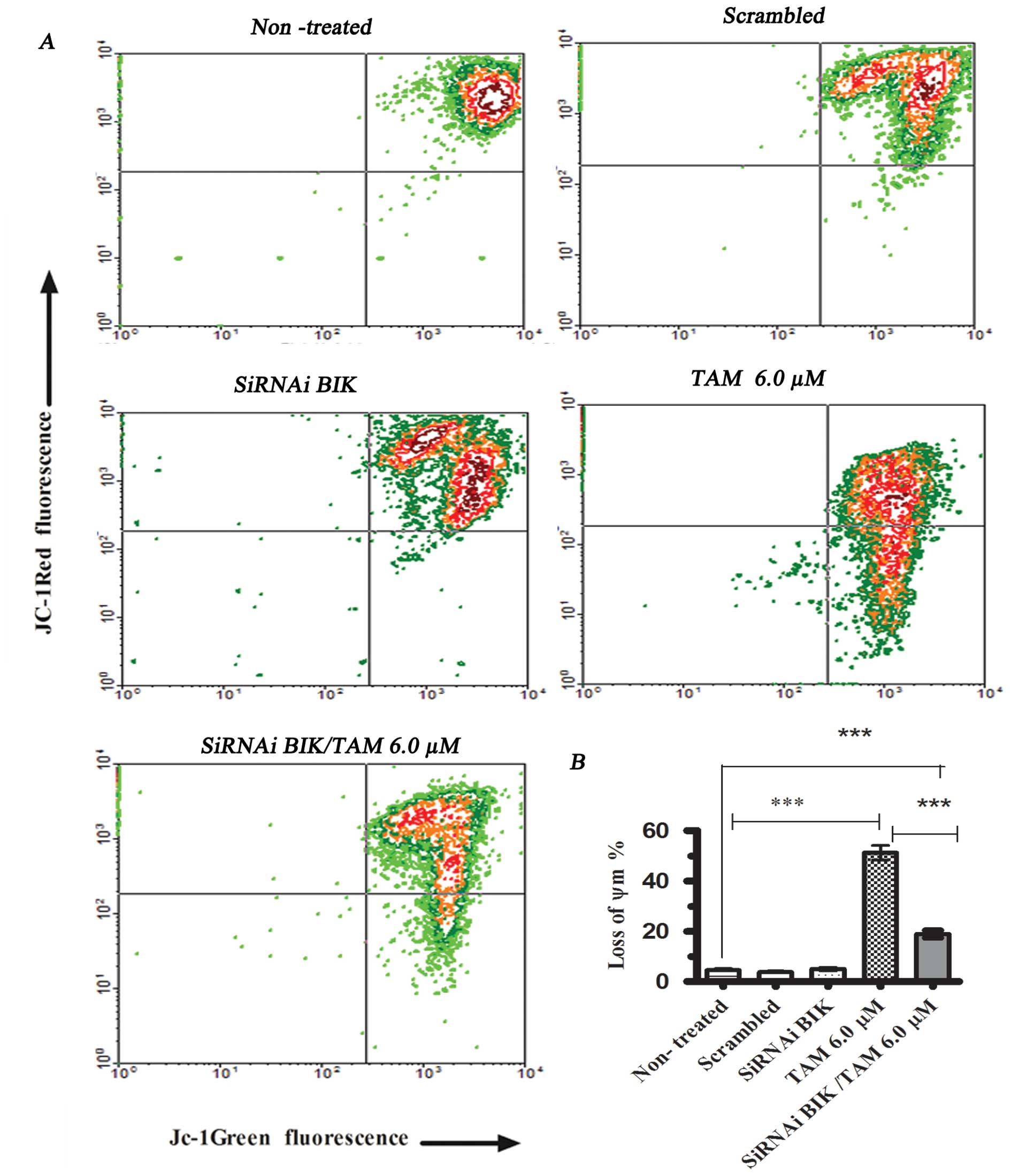
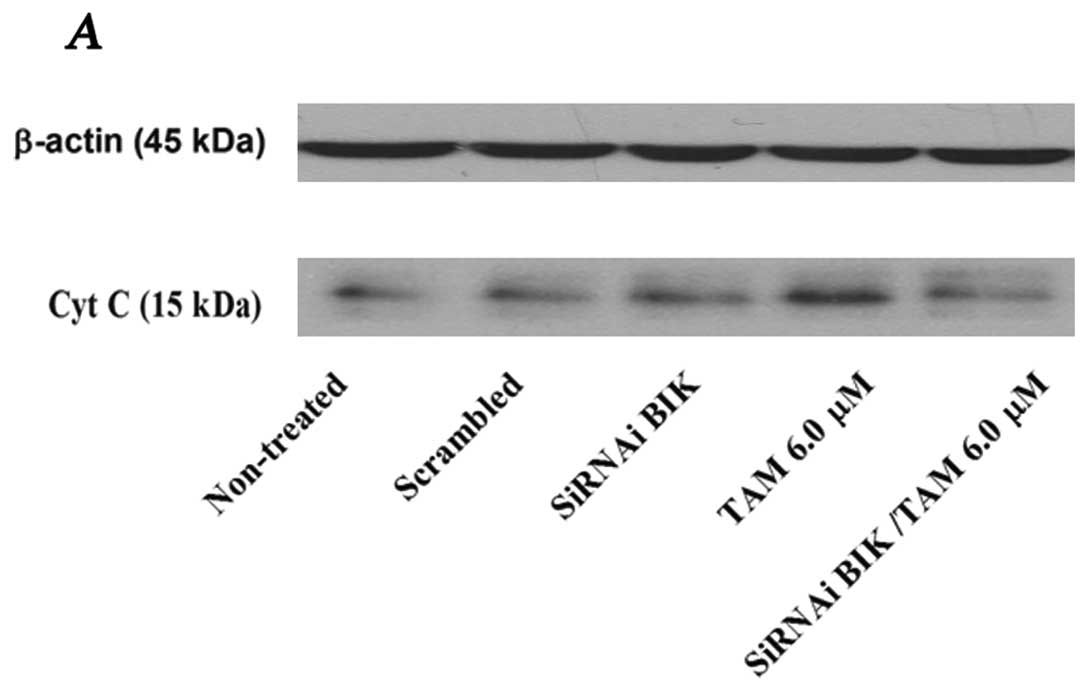
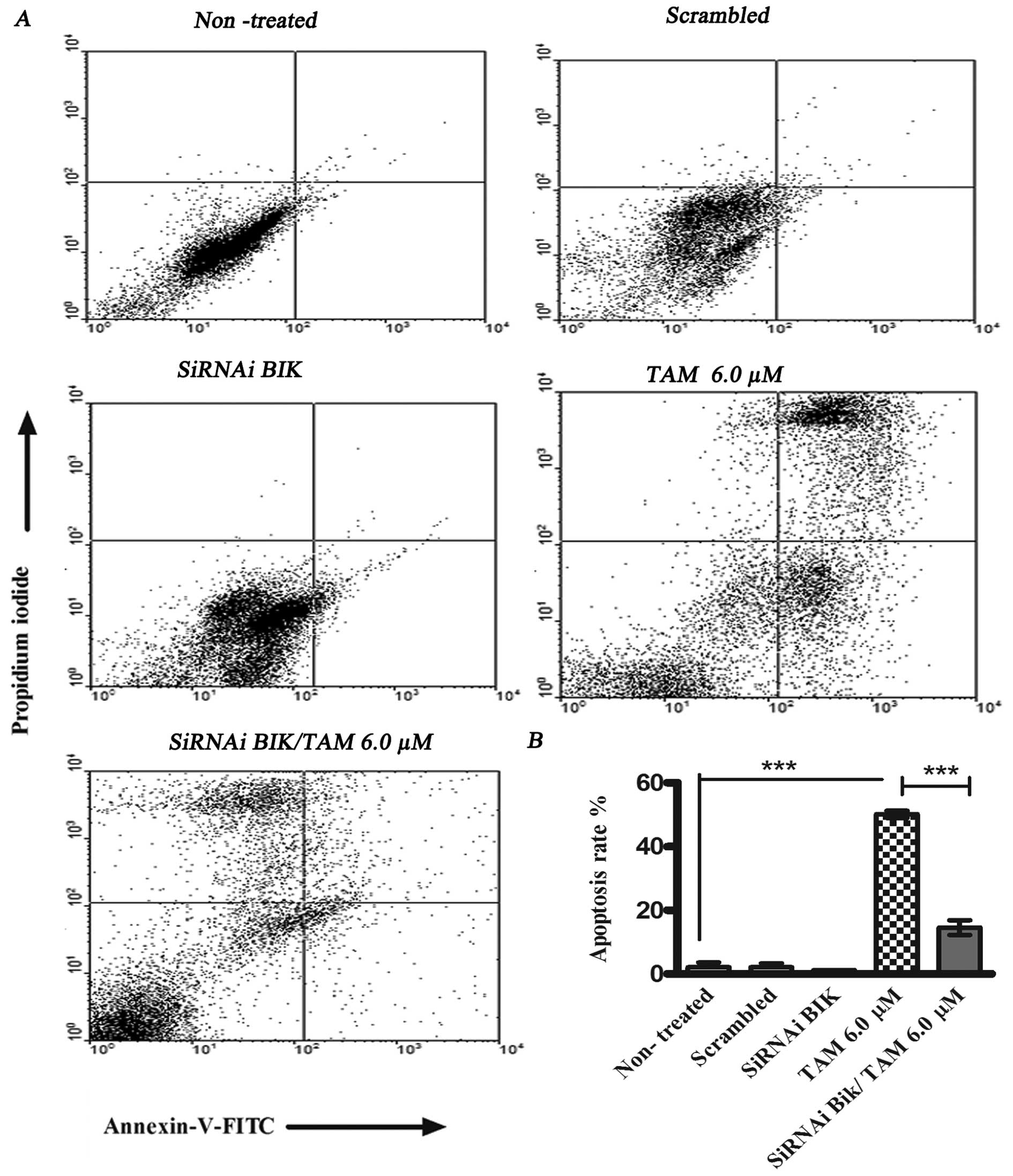
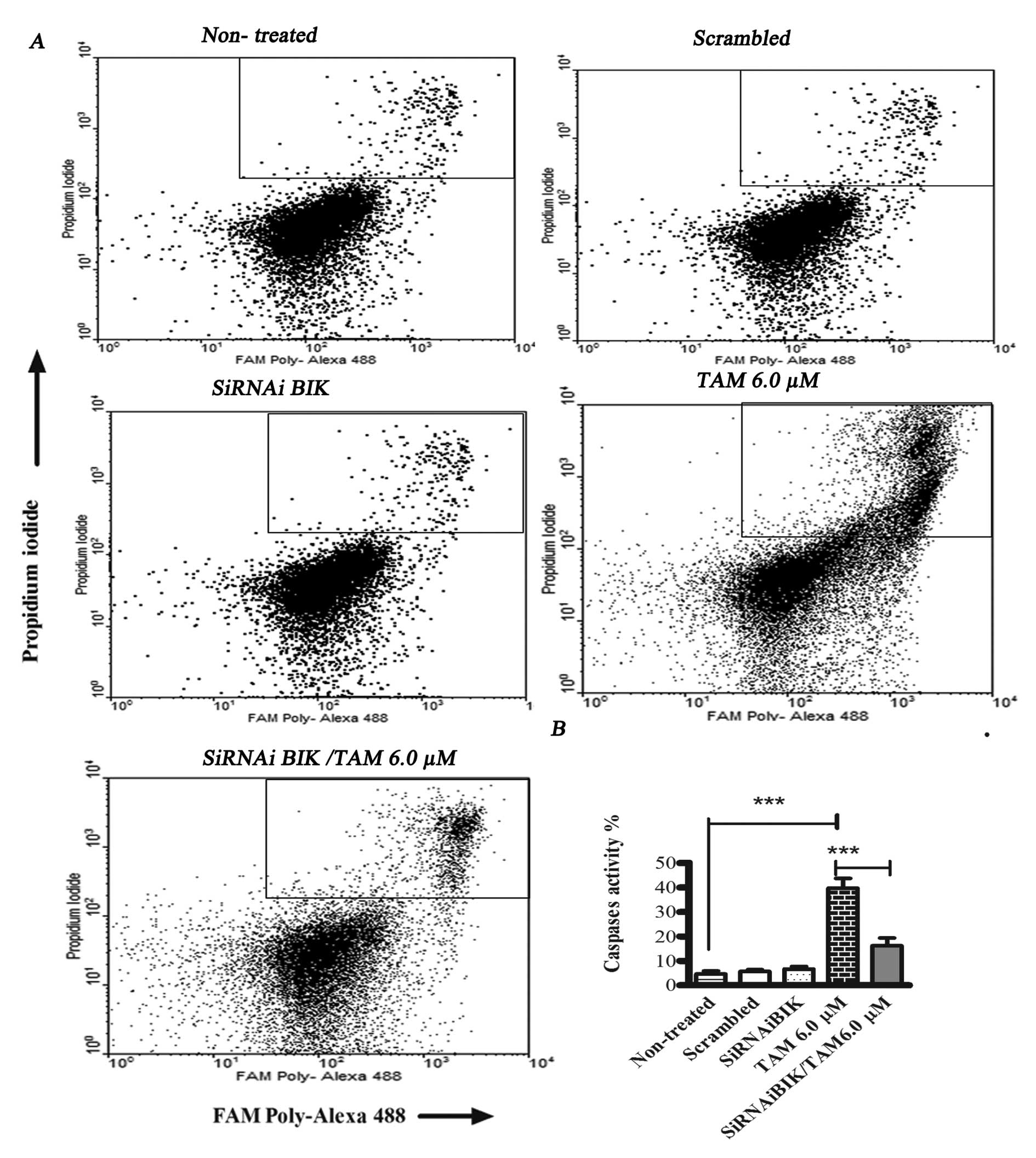
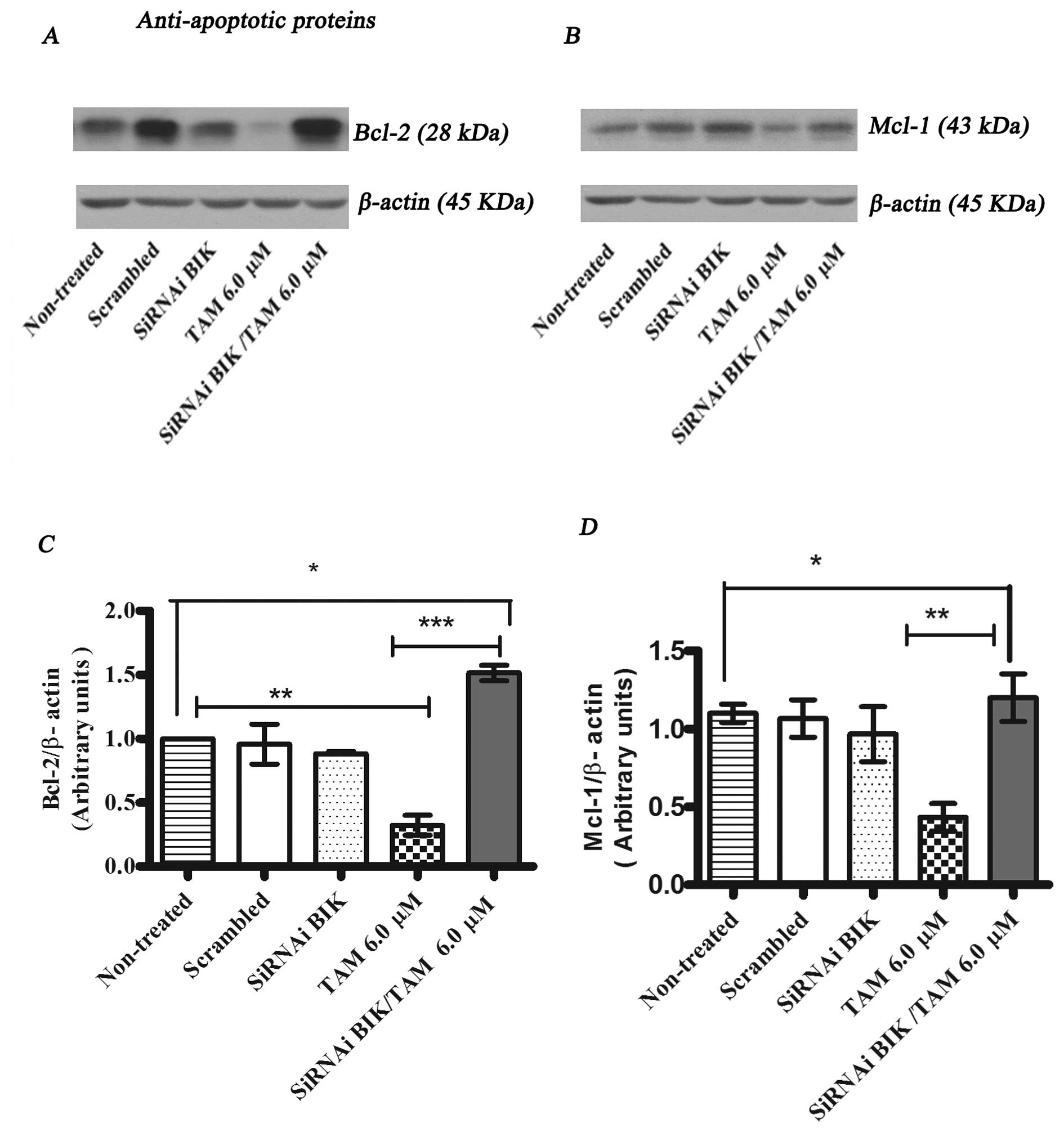
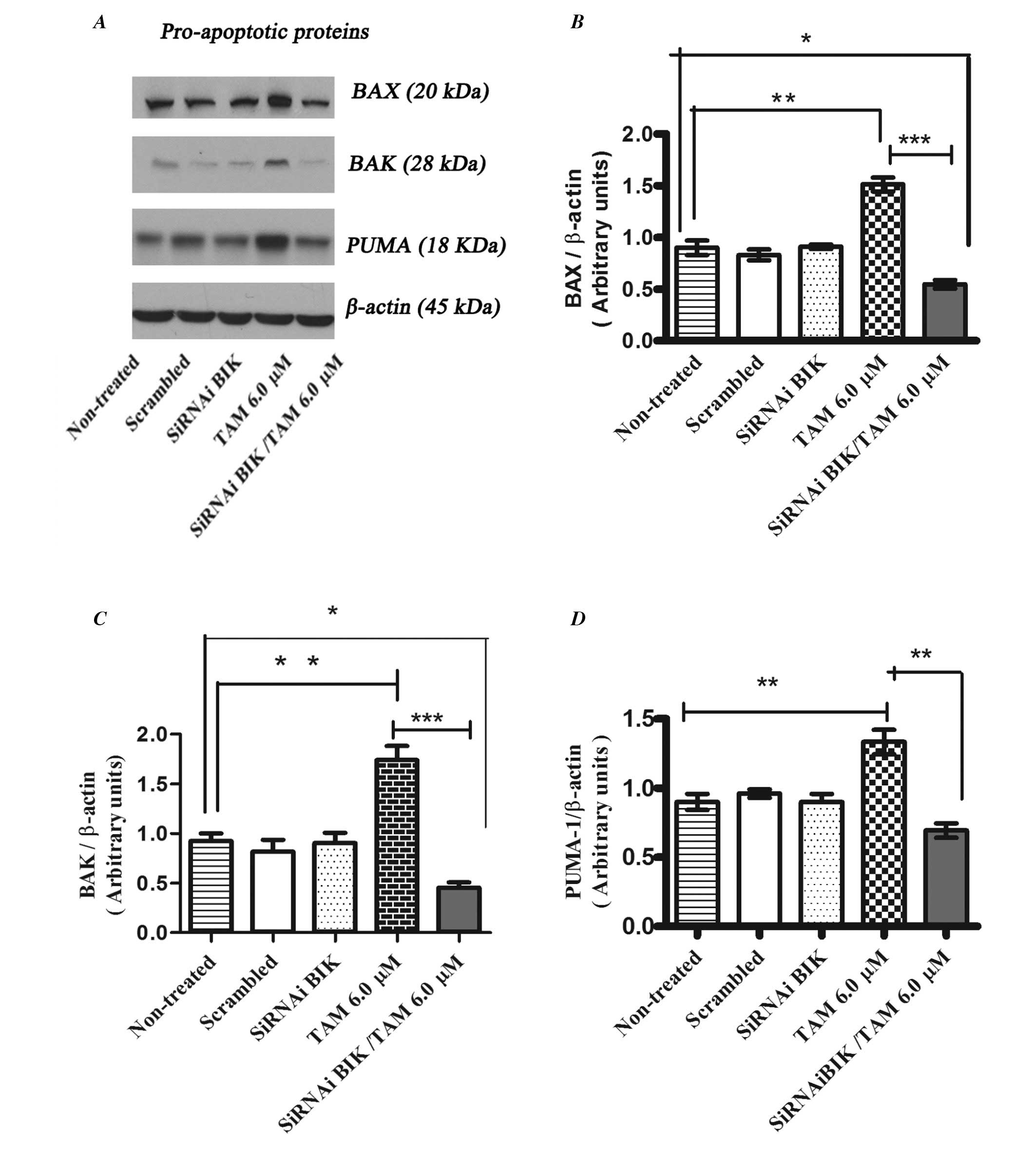
|
1.
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: a review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Zhao X, Wang L, Sun Y, et al: The
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-target protein Bik induces Hep3B cell
apoptosis by the depletion of the ER Ca2+stores. Mol
Cell Biochem. 312:33–38. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Lan KL, Yen SH, Liu RS, Shih HL, Tseng FW
and Lan KH: Mutant Bik gene transferred by cationic liposome
inhibits peritoneal disseminated murine colon cancer. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 24:461–470. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Sturm I, Stephan C, Gillissen B, et al:
Loss of the tissue-specific proapoptotic BH3-only protein Nbk/Bik
is a unifying feature of renal cell carcinoma. Cell Death Differ.
13:619–627. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Gillissen B, Essmann F, Graupner V, et al:
Induction of cell death by the BH3-only Bcl-2 homolog Nbk/Bik is
mediated by an entirely Bax-dependent mitochondrial pathway. EMBO
J. 22:3580–3590. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Chinnadurai G, Vijayalingam S and Rashmi
R: BIK, the founding member of the BH3-only family proteins:
mechanisms of cell death and role in cancer and pathogenic
processes. Oncogene. 27(Suppl 1): S20–S29. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Chinnadurai G, Vijayalingam S and Gibson
SB: BNIP3 subfamily BH3-only proteins: mitochondrial stress sensors
in normal and pathological functions. Oncogene. 27(Suppl 1):
S114–S127. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Zou Y, Peng H, Zhou B, et al: Systemic
tumor suppression by the proapoptotic gene bik. Cancer Res.
62:8–12. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Garcia N, Salamanca F, Astudillo-de la
Vega H, et al: A molecular analysis by gene expression profiling
reveals Bik/NBK overexpression in sporadic breast tumor samples of
Mexican females. BMC Cancer. 5:932005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Real PJ, Sanz C, Gutierrez O, Pipaon C,
Zubiaga AM and Fernandez-Luna JL: Transcriptional activation of the
proapoptotic bik gene by E2F proteins in cancer cells. FEBS Lett.
580:5905–5909. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Mathai JP, Germain M, Marcellus RC and
Shore GC: Induction and endoplasmic reticulum location of BIK/NBK
in response to apoptotic signaling by E1A and p53. Oncogene.
21:2534–2544. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Boyd JM, Gallo GJ, Elangovan B, et al:
Bik, a novel death-inducing protein shares a distinct sequence
motif with Bcl-2 family proteins and interacts with viral and
cellular survival-promoting proteins. Oncogene. 11:1921–1928.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Hur J, Bell DW, Dean KL, et al: Regulation
of expression of BIK proapoptotic protein in human breast cancer
cells: p53-dependent induction of BIK mRNA by fulvestrant and
proteasomal degradation of BIK protein. Cancer Res. 66:10153–10161.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Nikrad M, Johnson T, Puthalalath H,
Coultas L, Adams J and Kraft AS: The proteasome inhibitor
bortezomib sensitizes cells to killing by death receptor ligand
TRAIL via BH3-only proteins Bik and Bim. Mol Cancer Ther.
4:443–449. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Monick MM, Powers LS, Butler NS and
Hunninghake GW: Inhibition of Rho family GTPases results in
increased TNF-alpha production after lipopolysaccharide exposure. J
Immunol. 171:2625–2630. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Gottlieb E, Armour SM, Harris MH and
Thompson CB: Mitochondrial membrane potential regulates matrix
configuration and cytochrome c release during apoptosis. Cell Death
Differ. 10:709–717. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Hur J, Chesnes J, Coser KR, et al: The Bik
BH3-only protein is induced in estrogen-starved and
antiestrogen-exposed breast cancer cells and provokes apoptosis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:2351–2356. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Prieto-Remon I, Sanchez-Carrera D,
Lopez-Duarte M, Richard C and Pipaon C: BIK (NBK) is a mediator of
the sensitivity of Fanconi anemia group C lymphoblastoid cell lines
to interstrand DNA cross-linking agents. Biochem J. 448:153–163.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Mebratu YA, Schwalm K, Smith KR, Schuyler
M and Tesfaigzi Y: Cigarette smoke suppresses Bik to cause
epithelial cell hyperplasia and mucous cell metaplasia. Am J Respir
Crit Care Med. 183:1531–1538. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Fu Y, Li J and Lee AS: GRP78/BiP inhibits
endoplasmic reticulum BIK and protects human breast cancer cells
against estrogen starvation-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res.
67:3734–3740. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Weng SC, Kashida Y, Kulp SK, et al:
Sensitizing estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cells to
tamoxifen with OSU-03012, a novel celecoxib-derived
phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1/Akt signaling
inhibitor. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:800–808. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23.
|
Fisher B, Costantino JP, Wickerham DL, et
al: Tamoxifen for prevention of breast cancer: report of the
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project P-1 Study. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 90:1371–1388. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Musgrove EA and Sutherland RL: Biological
determinants of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:631–643. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Mandlekar S and Kong AN: Mechanisms of
tamoxifen-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis. 6:469–477. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Simonian PL, Grillot DA and Nunez G: Bak
can accelerate chemotherapy-induced cell death independently of its
heterodimerization with Bcl-XL and Bcl-2. Oncogene. 15:1871–1875.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Zhang H, Nimmer PM, Tahir SK, et al: Bcl-2
family proteins are essential for platelet survival. Cell Death
Differ. 14:943–951. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|