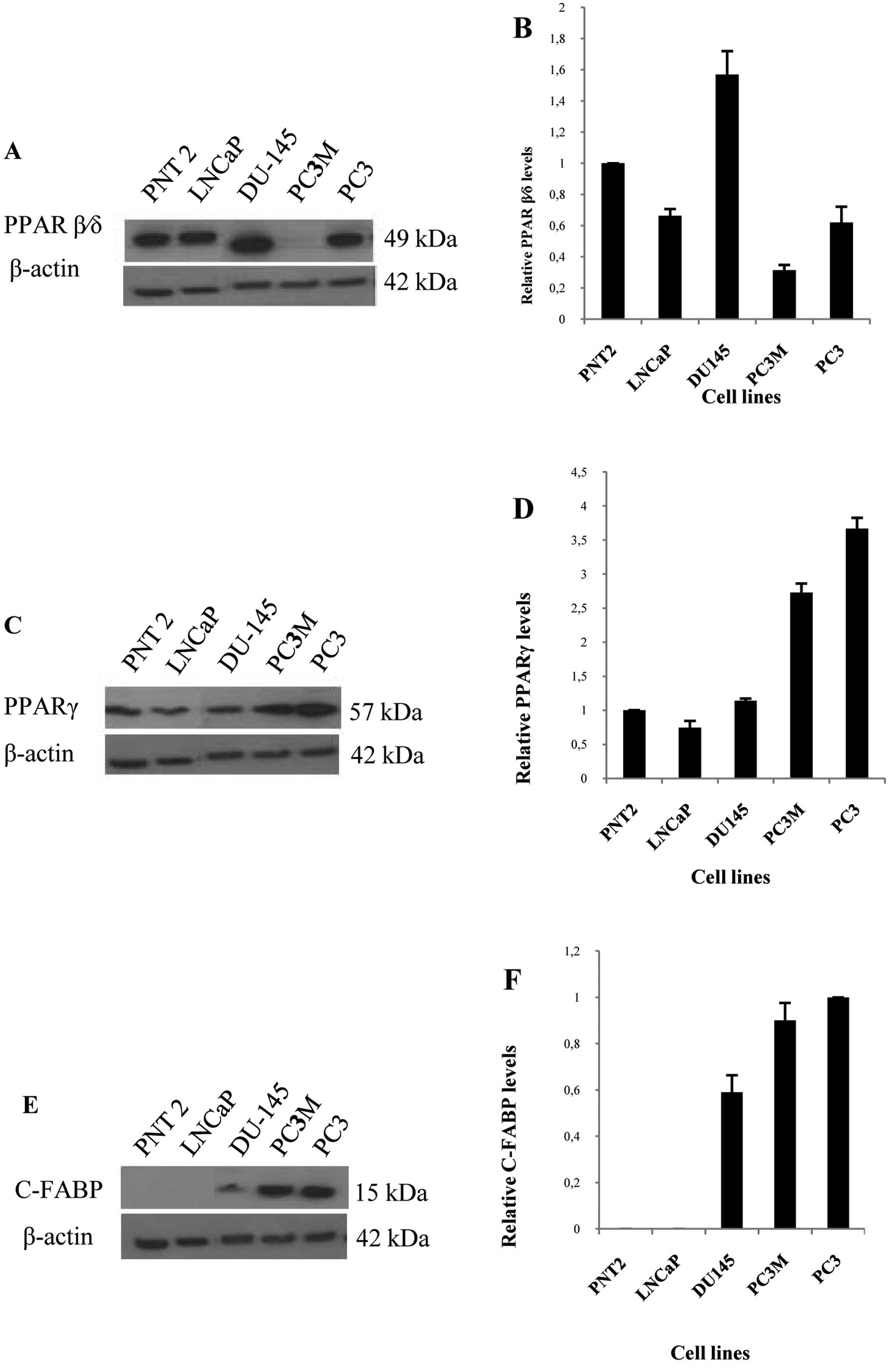
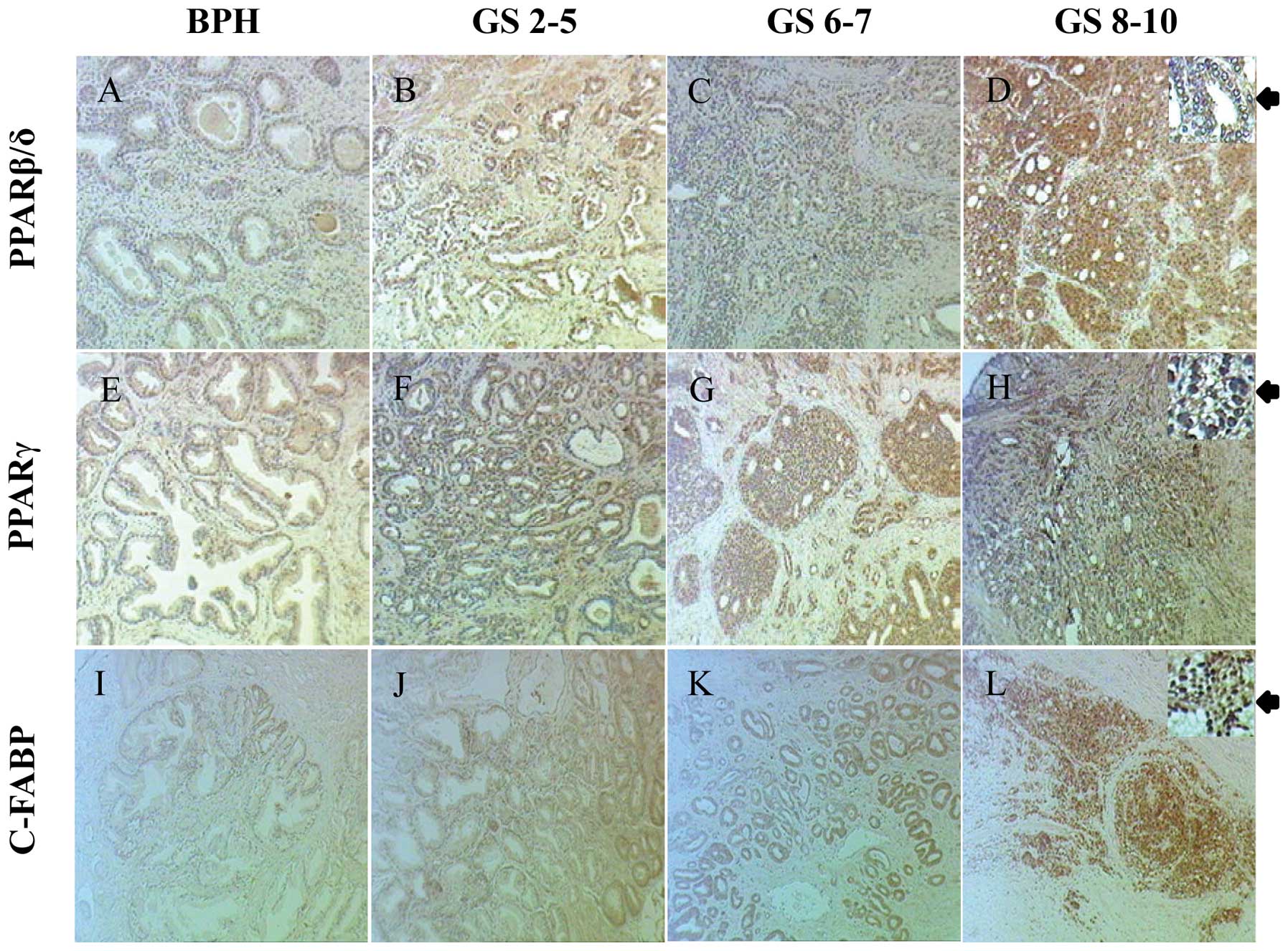
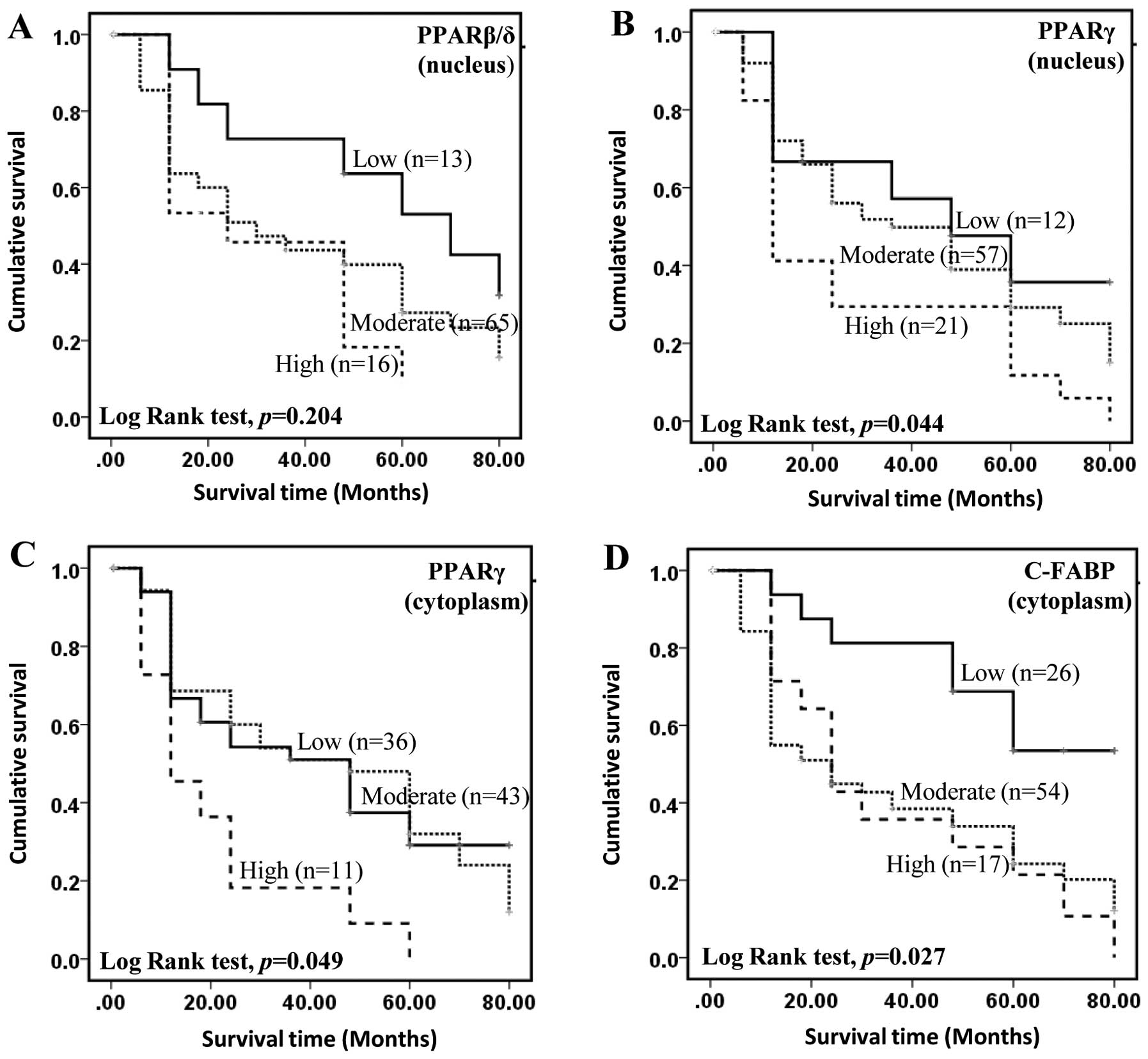
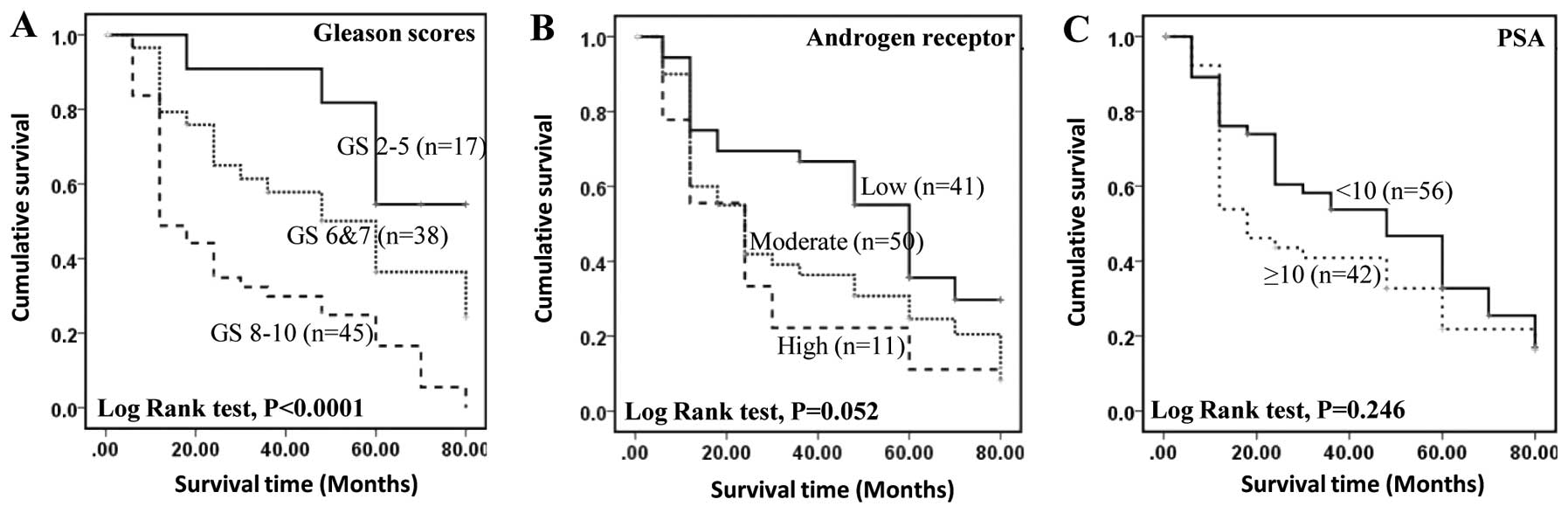
|
1.
|
Ferlay J, Parkin DM and Steliarova-Foucher
E: Estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2008.
Eur J Cancer. 46:765–781. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Lee JT, Lehmann BD, Terrian DM, et al:
Targeting prostate cancer based on signal transduction and cell
cycle pathways. Cell Cycle. 7:1745–1762. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Madsen P, Rasmussen HH, Leffers H, Honore
B and Celis JE: Molecular cloning and expression of a novel
keratinocyte protein (psoriasis-associated fatty acid-binding
protein [PA-FABP]) that is highly up-regulated in psoriatic skin
and that shares similarity to fatty acid-binding proteins. J Invest
Dermatol. 99:299–305. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Jing C, Beesley C, Foster CS, et al:
Identification of the messenger RNA for human cutaneous fatty
acid-binding protein as a metastasis inducer. Cancer Res.
60:2390–2398. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Jing C, Beesley C, Foster CS, et al: Human
cutaneous fatty acid-binding protein induces metastasis by
up-regulating the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor
gene in rat Rama 37 model cells. Cancer Res. 61:4357–4364.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Bao ZZ, Malki MI, Forootan SS, et al: A
novel cutaneous fatty acid-binding protein-related signaling
pathway leading to malignant progression in prostate cancer cells.
Genes Cancer. Sep 18–2013.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7.
|
Adamson J, Morgan EA, Beesley C, et al:
High-level expression of cutaneous fatty acid-binding protein in
prostatic carcinomas and its effect on tumorigenicity. Oncogene.
22:2739–2749. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Forootan SS, Bao ZZ, Forootan FS, et al:
Atelocollagen-delivered siRNA targeting the FABP5 gene as an
experimental therapy for prostate cancer in mouse xenografts. Int J
Oncol. 36:69–76. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Morgan EA, Forootan SS, Adamson J, et al:
Expression of cutaneous fatty acid-binding protein (C-FABP) in
prostate cancer: potential prognostic marker and target for
tumourigenicity-suppression. Int J Oncol. 32:767–775. 2008.
|
|
10.
|
Gebert N, Gebert M, Oeljeklaus S, et al:
Dual function of Sdh3 in the respiratory chain and TIM22 protein
translocase of the mitochondrial inner membrane. Mol Cell.
44:811–818. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Xu HE, Lambert MH, Montana VG, et al:
Molecular recognition of fatty acids by peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors. Mol Cell. 3:397–403. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Santos CR and Schulze A: Lipid metabolism
in cancer. FEBS J. 279:2610–2623. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Matsuyama M and Yoshimura R: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma is a potent target for
prevention and treatment in human prostate and testicular cancer.
PPAR Res. 2008:2498492008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Kliewer SA, Xu HE, Lambert MH and Willson
TM: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: from genes to
physiology. Rec Prog Horm Res. 56:239–263. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Qi C, Zhu Y and Reddy JK: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors, coactivators, and downstream
targets. Cell Biochem Biophys. 32:187–204. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Sterchele PF, Sun H, Peterson RE and
Vanden Heuvel JP: Regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor-alpha mRNA in rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys.
326:281–289. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Lemberger T, Saladin R, Vazquez M, et al:
Expression of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha
gene is stimulated by stress and follows a diurnal rhythm. J Biol
Chem. 271:1764–1769. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Braissant O, Foufelle F, Scotto C, Dauca M
and Wahli W: Differential expression of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs): tissue distribution of
PPAR-alpha, -beta, and -gamma in the adult rat. Endocrinology.
137:354–366. 1996.
|
|
19.
|
Mansure JJ, Nassim R and Kassouf W:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in bladder cancer:
a promising therapeutic target. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:6–15. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Chawla A, Barak Y, Nagy L, Liao D,
Tontonoz P and Evans RM: PPAR-gamma dependent and independent
effects on macrophage-gene expression in lipid metabolism and
inflammation. Nat Med. 7:48–52. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Segawa Y, Yoshimura R, Hase T, et al:
Expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) in
human prostate cancer. Prostate. 51:108–116. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Berthon P, Cussenot O, Hopwood L, Leduc A
and Maitland N: Functional expression of sv40 in normal human
prostatic epithelial and fibroblastic cells - differentiation
pattern of nontumorigenic cell lines. Int J Oncol. 6:333–343.
1995.
|
|
23.
|
Cussenot O, Berthon P, Berger R, et al:
Immortalization of human adult normal prostatic epithelial cells by
liposomes containing large T-SV40 gene. J Urol. 146:881–886.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Horoszewicz JS, Leong SS, Kawinski E, et
al: LNCaP model of human prostatic carcinoma. Cancer Res.
43:1809–1818. 1983.
|
|
25.
|
Stone KR, Mickey DD, Wunderli H, Mickey GH
and Paulson DF: Isolation of a human prostate carcinoma cell line
(DU 145). Int J Cancer. 21:274–281. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Kaighn ME, Lechner JF, Narayan KS and
Jones LW: Prostate carcinoma: tissue culture cell lines. Natl
Cancer Inst Monogr. 17–21. 1978.
|
|
27.
|
Kozlowski JM, Fidler IJ, Campbell D, Xu
ZL, Kaighn ME and Hart IR: Metastatic behavior of human tumor cell
lines grown in the nude mouse. Cancer Res. 44:3522–3529.
1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Forootan SS, Foster CS, Aachi VR, et al:
Prognostic significance of osteopontin expression in human prostate
cancer. Int J Cancer. 118:2255–2261. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Forootan SS, Wong YC, Dodson A, et al:
Increased Id-1 expression is significantly associated with poor
survival of patients with prostate cancer. Hum Pathol.
38:1321–1329. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Jing C, El-Ghany MA, Beesley C, et al:
Tazarotene-induced gene 1 (TIG1) expression in prostate carcinomas
and its relationship to tumorigenicity. J Natl Cancer Inst.
94:482–490. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Zhang Y, Forootan SS, Liu D, et al:
Increased expression of anterior gradient-2 is significantly
associated with poor survival of prostate cancer patients. Prostate
Cancer Prostatic Dis. 10:293–300. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Gleason DF and Mellinger GT: Prediction of
prognosis for prostatic adenocarcinoma by combined histological
grading and clinical staging. J Urol. 111:58–64. 1974.
|
|
33.
|
Keller H, Dreyer C, Medin J, Mahfoudi A,
Ozato K and Wahli W: Fatty acids and retinoids control lipid
metabolism through activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor-retinoid X receptor heterodimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
90:2160–2164. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34.
|
Foster CS, Gosden CM and Ke YQ: Primer:
tissue fixation and preservation for optimal molecular analysis of
urologic tissues. Nat Clin Pract Urol. 3:268–278. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Remmele W and Stegner HE: Recommendation
for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for
immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast
cancer tissue. Pathologe. 8:138–140. 1987.(In German).
|
|
36.
|
Masouye I, Saurat JH and Siegenthaler G:
Epidermal fatty-acid-binding protein in psoriasis, basal and
squamous cell carcinomas: an immunohistological study. Dermatology.
192:208–213. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Celis A, Rasmussen HH, Celis P, et al:
Short-term culturing of low-grade superficial bladder transitional
cell carcinomas leads to changes in the expression levels of
several proteins involved in key cellular activities.
Electrophoresis. 20:355–361. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38.
|
Ostergaard M, Rasmussen HH, Nielsen HV, et
al: Proteome profiling of bladder squamous cell carcinomas:
identification of markers that define their degree of
differentiation. Cancer Res. 57:4111–4117. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Sinha P, Hutter G, Kottgen E, Dietel M,
Schadendorf D and Lage H: Increased expression of epidermal fatty
acid binding protein, cofilin, and 14-3-3-sigma (stratifin)
detected by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, mass spectrometry
and microsequencing of drug-resistant human adenocarcinoma of the
pancreas. Electrophoresis. 20:2952–2960. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40.
|
Liu RZ, Graham K, Glubrecht DD, Germain
DR, Mackey JR and Godbout R: Association of FABP5 expression with
poor survival in triple-negative breast cancer: implication for
retinoic acid therapy. Am JPathol. 178:997–1008. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Barbus S, Tews B, Karra D, et al:
Differential retinoic acid signaling in tumors of long- and
short-term glioblastoma survivors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 103:598–606.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Lemberger T, Desvergne B and Wahli W:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: a nuclear receptor
signaling pathway in lipid physiology. An Rev Cell Dev Biol.
12:335–363. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Roberts-Thomson SJ: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors in tumorigenesis: targets of
tumour promotion and treatment. Immunol Cell Biol. 78:436–441.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Jiang Y, Zou L, Zhang C, et al: PPARgamma
and Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in human breast cancer: expression
pattern, molecular interaction and clinical/prognostic
correlations. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 135:1551–1559. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45.
|
Papadaki I, Mylona E, Giannopoulou I,
Markaki S, Keramopoulos A and Nakopoulou L: PPARgamma expression in
breast cancer: clinical value and correlation with ERbeta.
Histopathology. 46:37–42. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Rohrl C, Kaindl U, Koneczny I, et al:
Peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptors gamma and beta/delta
mediate vascular endothelial growth factor production in colorectal
tumor cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 137:29–39. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47.
|
Bishop-Bailey D: PPARs and angiogenesis.
Biochem Soc Trans. 39:1601–1605. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48.
|
Roobol MJ, Haese A and Bjartell A: Tumour
markers in prostate cancer III: biomarkers in urine. Acta Oncol.
50(Suppl 1): 85–89. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Theocharis S, Giaginis C, Parasi A, et al:
Expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma in
colon cancer: correlation with histopathological parameters, cell
cycle-related molecules, and patients’ survival. Dig Dis Sci.
52:2305–2311. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Han SW, Greene ME, Pitts J, Wada RK and
Sidell N: Novel expression and function of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) in human
neuroblastoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 7:98–104. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Zhang GY, Ahmed N, Riley C, et al:
Enhanced expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
gamma in epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 92:113–119.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Lee TW, Chen GG, Xu H, et al: Differential
expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma in non-small cell lung
carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 39:1296–1301. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Jiang WG, Redfern A, Bryce RP and Mansel
RE: Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-gamma)
mediates the action of gamma linolenic acid in breast cancer cells.
Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 62:119–127. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Katagiri Y, Takeda K, Yu ZX, Ferrans VJ,
Ozato K and Guroff G: Modulation of retinoid signalling through
NGF-induced nuclear export of NGFI-B. Nat Cell Biol. 2:435–440.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55.
|
Jiang M, Shappell SB and Hayward SW:
Approaches to understanding the importance and clinical
implications of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
(PPARgamma) signaling in prostate cancer. J Cell Biochem.
91:513–527. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56.
|
Morgan E, Kannan-Thulasiraman P and Noy N:
Involvement of Fatty acid binding protein 5 and PPARbeta/delta in
prostate cancer cell growth. PPAR Res. 2010.Article No. 234629.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57.
|
Foster CS, Dodson AR, Ambroisine L, et al:
Hsp-27 expression at diagnosis predicts poor clinical outcome in
prostate cancer independent of ETS-gene rearrangement. Br J Cancer.
101:1137–1144. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58.
|
Yao S, Bee A, Brewer D, et al: PRKC-ζ
expression promotes the aggressive phenotype of human prostate
cancer cells and is a novel target for therapeutic intervention.
Genes Cancer. 1:444–464. 2010.
|