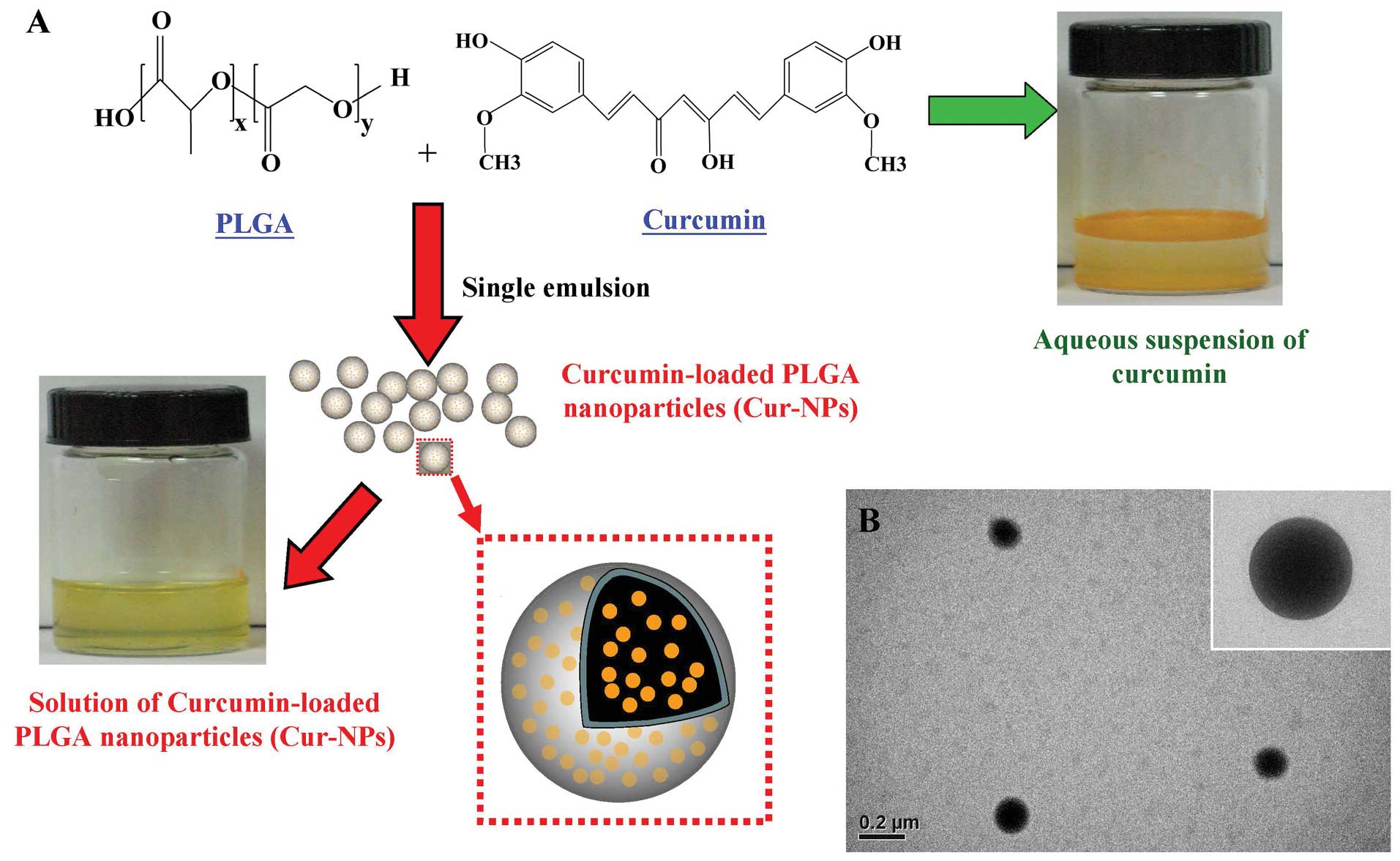
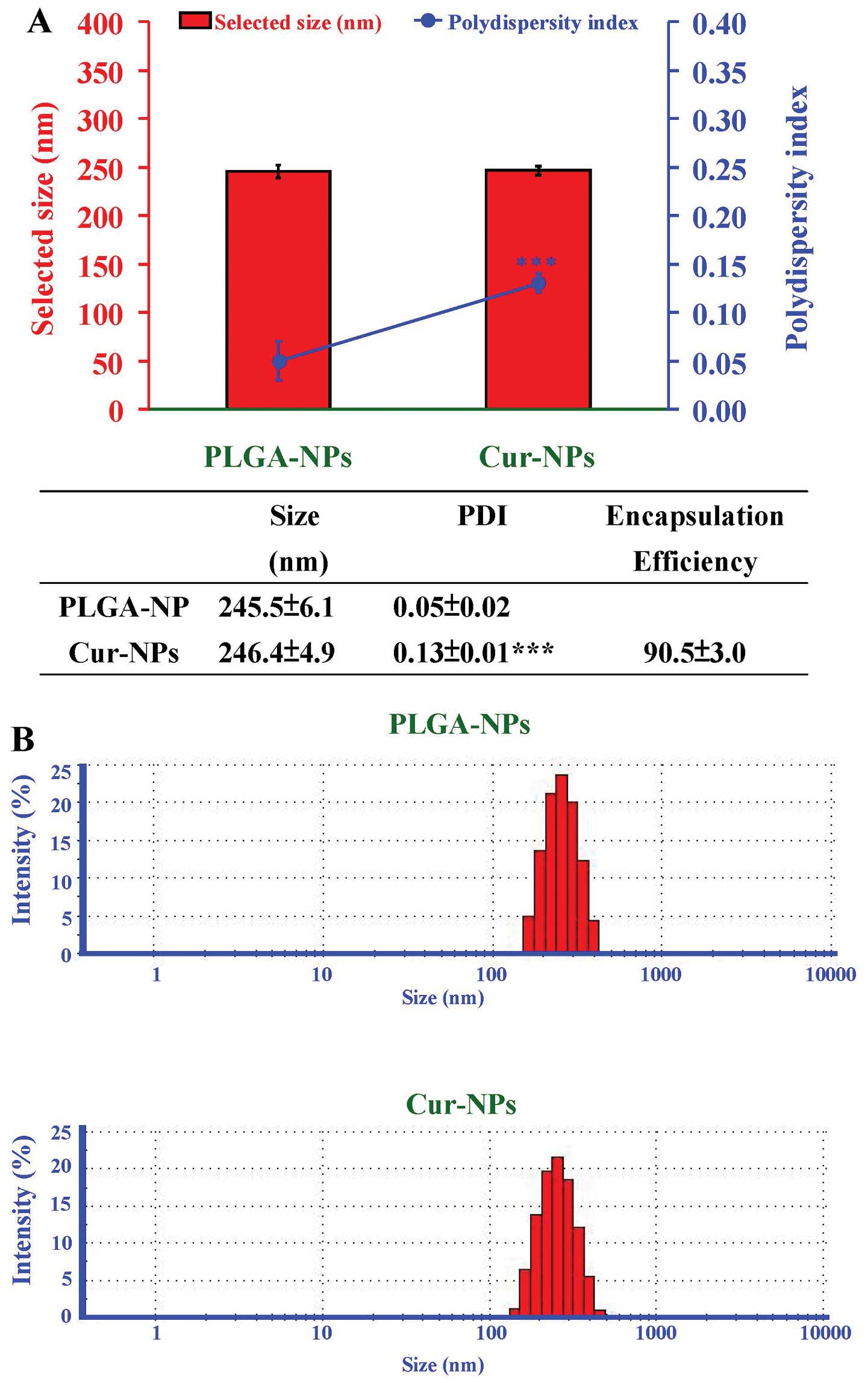
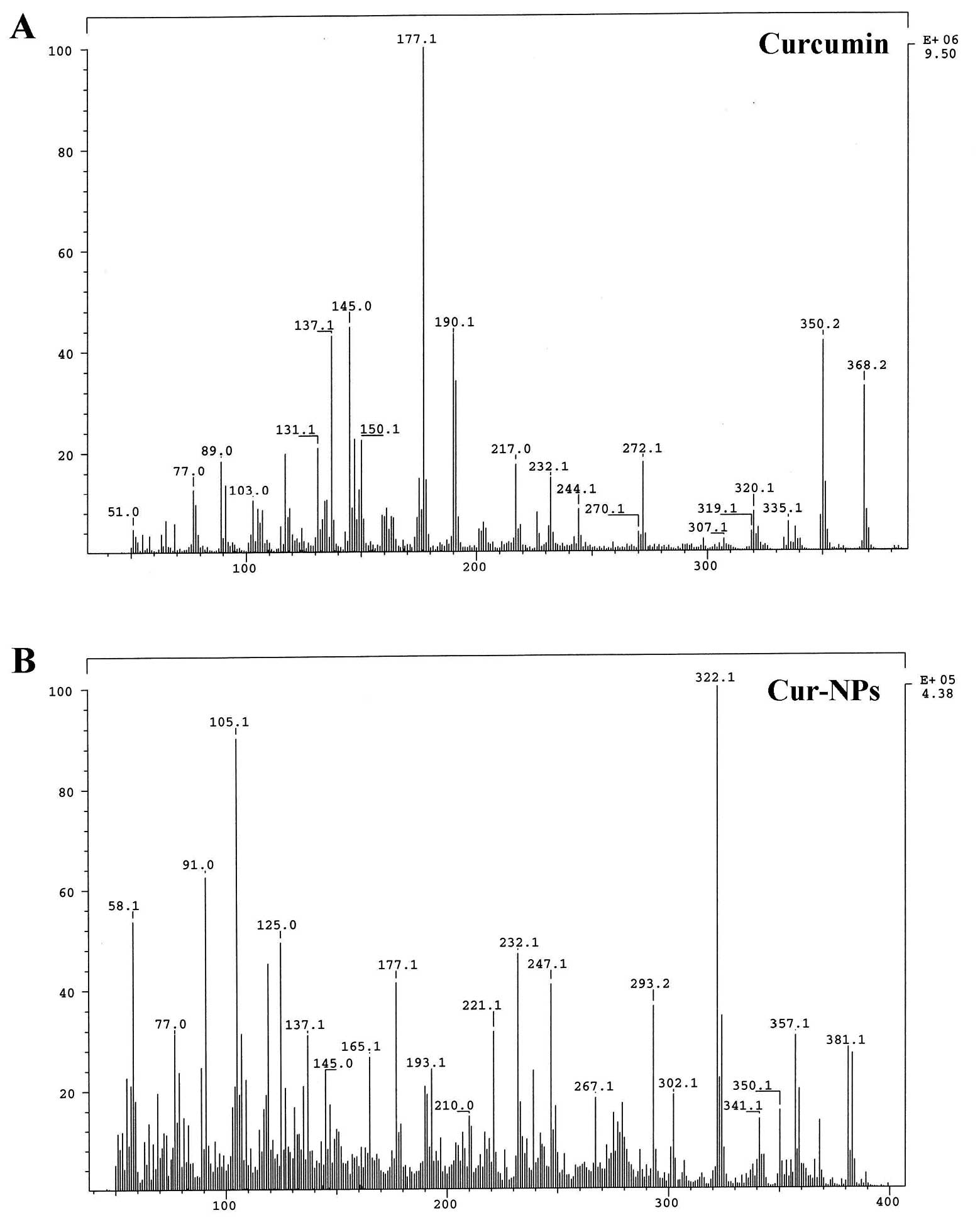
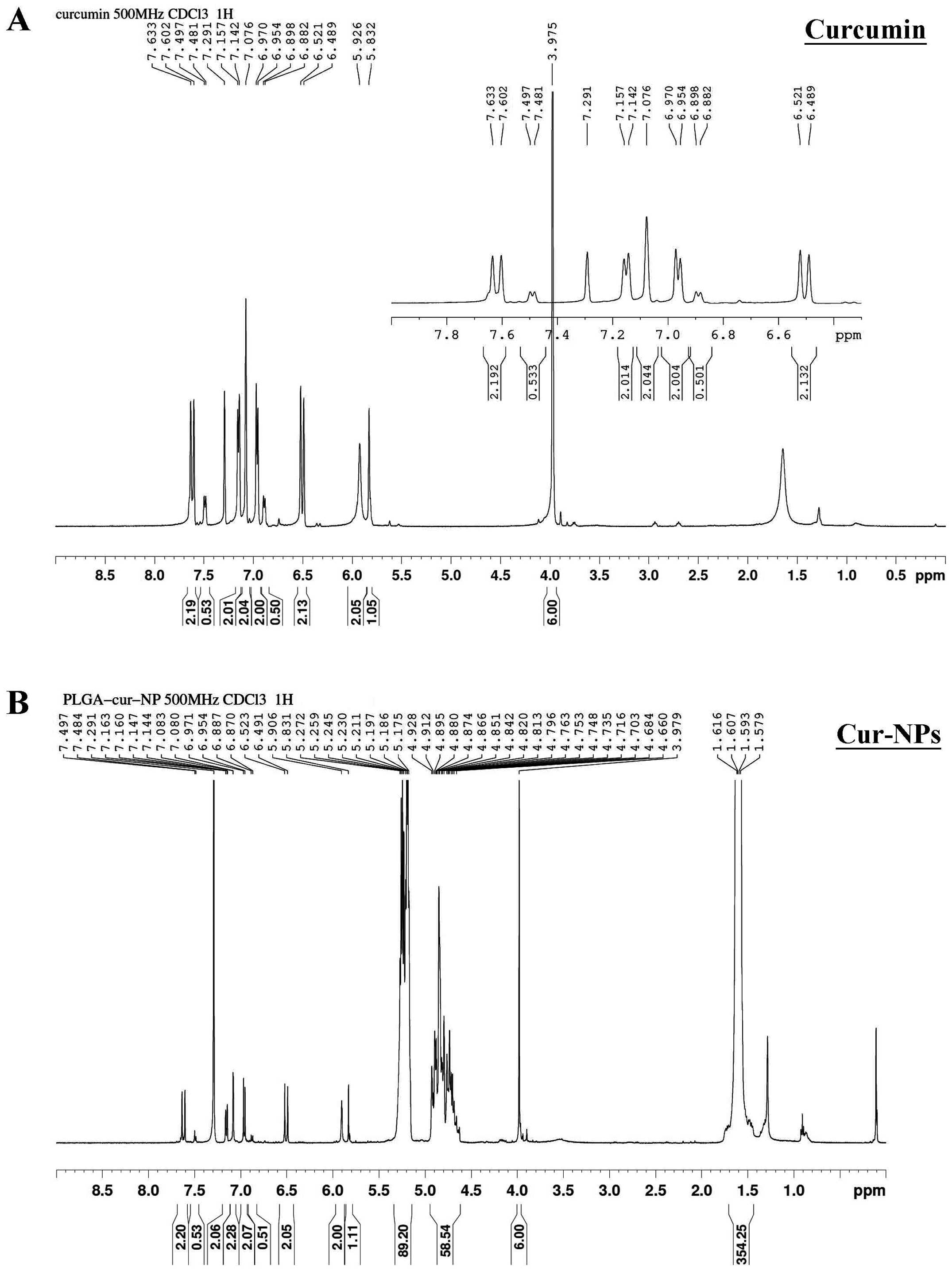
|
1.
|
Ferrari S, Palmerini E, Fabbri N, et al:
Osteosarcoma of the pelvis: a monoinstitutional experience in
patients younger than 41 years. Tumori. 98:702–708. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Anninga JK, Picci P, Fiocco M, et al:
Osteosarcoma of the hands and feet: a distinct clinico-pathological
subgroup. Virchows Arch. 462:109–120. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Colomina J, Peiro A, Trullols L and Garcia
I: Telangiectatic osteosarcoma. J Orthop Surg. 21:96–99. 2013.
|
|
4.
|
Ebb D, Meyers P, Grier H, et al: Phase II
trial of trastuzumab in combination with cytotoxic chemotherapy for
treatment of metastatic osteosarcoma with human epidermal growth
factor receptor 2 overexpression: a report from the Children’s
Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol. 30:2545–2551. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Ritter J and Bielack SS: Osteosarcoma. Ann
Oncol. 21(Suppl 7): vii320–vii325. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Seki K, Yoshikawa H, Shiiki K, Hamada Y,
Akamatsu N and Tasaka K: Cisplatin (CDDP) specifically induces
apoptosis via sequential activation of caspase-8, -3 and -6 in
osteosarcoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 45:199–206. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Warzecha J, Gottig S, Chow KU, et al:
Inhibition of osteosarcoma cell proliferation by the
Hedgehog-inhibitor cyclopamine. J Chemother. 19:554–561. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Valteau-Couanet D and Minard V: Poor
prognosis childhood cancers. Rev Prat. 57:1087–1091. 2007.(In
French).
|
|
9.
|
Rouesse J and Le Chevalier J: Combination
of chemotherapy and surgery in pulmonary metastases of tumors
considered not very chemosensitive. Chirurgie. 111:538–541.
1985.(In French).
|
|
10.
|
Wang Y, Fu Q and Zhao W:
Tetramethylpyrazine inhibits osteosarcoma cell proliferation via
downregulation of NF-κB in vitro and in vivo. Mol Med
Rep. 8:984–988. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Shi QW, Li SG, Li J and Ling CQ:
Anti-tumor effects of triptolide on osteosarcoma cells in vitro and
in vivo: an experimental research. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za
Zhi. 33:659–663. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
12.
|
Yang JY, Cheng FW, Wong KC, et al: Initial
presentation and management of osteosarcoma, and its impact on
disease outcome. Hong Kong Med J. 15:434–439. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Zhang YK, Zhang XH, Li JM, Sun de S, Yang
Q and Diao DM: A proteomic study on a human osteosarcoma cell line
Saos-2 treated with diallyl trisulfide. Anticancer Drugs.
20:702–712. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Yin H, Guo R, Xu Y, et al: Synergistic
antitumor efficiency of docetaxel and curcumin against lung cancer.
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 44:147–153. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Tang N, Zhang J and Du Y: Curcumin
promoted the apoptosis of cisplain-resistant human lung carcinoma
cells A549/DDP through down-regulating miR-186*.
Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 13:301–306. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
16.
|
Chen ZQ and Mo ZN: Curcumin in the
treatment of prostatic diseases. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 14:67–70.
2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
17.
|
Sagar SM, Yance D and Wong RK: Natural
health products that inhibit angiogenesis: a potential source for
investigational new agents to treat cancer - Part 2. Curr Oncol.
13:99–107. 2006.
|
|
18.
|
Shishodia S, Sethi G and Aggarwal BB:
Curcumin: getting back to the roots. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1056:206–217.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Sareen R, Jain N and Pandit V: Curcumin: a
boon to colonic diseases. Curr Drug Targets. 14:1210–1218. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Patra D, Ahmadieh D and Aridi R: Study on
interaction of bile salts with curcumin and curcumin embedded in
dipalmitoylsn-glycero-3-phosphocholine liposome. Colloids Surf B
Biointerfaces. 110:296–304. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Mathew A, Fukuda T, Nagaoka Y, et al:
Curcumin loaded-PLGA nanoparticles conjugated with Tet-1 peptide
for potential use in Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One.
7:e326162012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Bolognesi ML, Bartolini M, Tarozzi A, et
al: Multitargeted drugs discovery: balancing anti-amyloid and
anticholinesterase capacity in a single chemical entity. Bioorg Med
Chem Lett. 21:2655–2658. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Khan S and Heikkila JJ: Curcumin-induced
inhibition of proteasomal activity, enhanced HSP accumulation and
the acquisition of thermotolerance in Xenopus laevis A6
cells. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 158:566–576.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Zhou H, Beevers CS and Huang S: The
targets of curcumin. Curr Drug Targets. 12:332–347. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25.
|
Khan MA, Gahlot S and Majumdar S:
Oxidative stress induced by curcumin promotes the death of
cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (HuT-78) by disrupting the function of
several molecular targets. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:1873–1883. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Han J, Pan XY, Xu Y, et al: Curcumin
induces autophagy to protect vascular endothelial cell survival
from oxidative stress damage. Autophagy. 8:812–825. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
O’Sullivan-Coyne G, O’Sullivan GC,
O’Donovan TR, Piwocka K and McKenna SL: Curcumin induces
apoptosis-independent death in oesophageal cancer cells. Br J
Cancer. 101:1585–1595. 2009.
|
|
28.
|
Chen HW, Lee JY, Huang JY, et al: Curcumin
inhibits lung cancer cell invasion and metastasis through the tumor
suppressor HLJ1. Cancer Res. 68:7428–7438. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Wang WX, Sun SZ, Guo XL and Song Y: Effect
of curcumin on invasion and migration of tongue squamous cell
carcinoma cell line Tca8113. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi.
43:101–104. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Lin CW, Hou WC, Shen SC, et al: Quercetin
inhibition of tumor invasion via suppressing PKC
delta/ERK/AP-1-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation in
breast carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis. 29:1807–1815. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Philip S, Bulbule A and Kundu GC: Matrix
metalloproteinase-2: mechanism and regulation of NF-kappaB-mediated
activation and its role in cell motility and ECM-invasion.
Glycoconj J. 21:429–441. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Cho YJ, Yi CO, Jeon BT, et al: Curcumin
attenuates radiation-induced inflammation and fibrosis in rat
lungs. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 17:267–274. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Bowden RG, J JM, Deike E, et al: The use
of an anti-inflammatory supplement in patients with chronic kidney
disease. J Complement Integr Med. 10:1–10. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Asher GN and Spelman K: Clinical utility
of curcumin extract. Altern Ther Health Med. 19:20–22.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Shehzad A, Wahid F and Lee YS: Curcumin in
cancer chemo-prevention: molecular targets, pharmacokinetics,
bioavailability, and clinical trials. Arch Pharm. 343:489–499.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Kossler S, Nofziger C, Jakab M, Dossena S
and Paulmichl M: Curcumin affects cell survival and cell volume
regulation in human renal and intestinal cells. Toxicology.
292:123–135. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Ji JL, Huang XF and Zhu HL: Curcumin and
its formulations: potential anti-cancer agents. Anticancer Agents
Med Chem. 12:210–218. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Gulcubuk A, Altunatmaz K, Sonmez K, et al:
Effects of curcumin on tumour necrosis factor-alpha and
interleukin-6 in the late phase of experimental acute pancreatitis.
J Vet Med A Physiol Pathol Clin Med. 53:49–54. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Greenwald P, Milner JA, Anderson DE and
McDonald SS: Micronutrients in cancer chemoprevention. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 21:217–230. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40.
|
Kelloff GJ, Boone CW, Crowell JA, et al:
New agents for cancer chemoprevention. J Cell Biochem (Suppl).
26:1–28. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41.
|
Kelloff GJ, Boone CW, Crowell JA, Steele
VE, Lubet R and Sigman CC: Chemopreventive drug development:
perspectives and progress. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
3:85–98. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Chang PY, Peng SF, Lee CY, et al:
Curcumin-loaded nanoparticles induce apoptotic cell death through
regulation of the function of MDR1 and reactive oxygen species in
cisplatin-resistant CAR human oral cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
43:1141–1150. 2013.
|
|
43.
|
Manju S and Sreenivasan K: Gold
nanoparticles generated and stabilized by water soluble
curcumin-polymer conjugate: blood compatibility evaluation and
targeted drug delivery onto cancer cells. J Colloid Interface Sci.
368:144–151. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44.
|
Bhawana, Basniwal RK, Buttar HS, Jain VK
and Jain N: Curcumin nanoparticles: preparation, characterization,
and antimicrobial study. J Agric Food Chem. 59:2056–2061. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Bansal SS, Vadhanam MV and Gupta RC:
Development and in vitro-in vivo evaluation of polymeric implants
for continuous systemic delivery of curcumin. Pharm Res.
28:1121–1130. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Mukerjee A and Vishwanatha JK:
Formulation, characterization and evaluation of curcumin-loaded
PLGA nanospheres for cancer therapy. Anticancer Res. 29:3867–3875.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Chen HJ, Lin CM, Lee CY, et al: Kaempferol
suppresses cell metastasis via inhibition of the ERK-p38-JNK and
AP-1 signaling pathways in U-2 OS human osteosarcoma cells. Oncol
Rep. 30:925–932. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Chen KT, Hour MJ, Tsai SC, et al: The
novel synthesized
6-fluoro-(3-fluorophenyl)-4-(3-methoxyanilino)quinazoline (LJJ-10)
compound exhibits anti-metastatic effects in human osteosarcoma U-2
OS cells through targeting insulin-like growth factor-I receptor.
Int J Oncol. 39:611–619. 2011.
|
|
49.
|
Hour MJ, Yang JS, Chen TL, et al: The
synthesized novel fluorinated compound (LJJ-10) induces death
receptor- and mitochondria-dependent apoptotic cell death in the
human osteogenic sarcoma U-2 OS cells. Eur J Med Chem.
46:2709–2721. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Chiu YJ, Hour MJ, Lu CC, et al: Novel
quinazoline HMJ-30 induces U-2 OS human osteogenic sarcoma cell
apoptosis through induction of oxidative stress and up-regulation
of ATM/p53 signaling pathway. J Orthop Res. 29:1448–1456. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Anton N, Gayet P, Benoit JP and Saulnier
P: Nano-emulsions and nanocapsules by the PIT method: an
investigation on the role of the temperature cycling on the
emulsion phase inversion. Int J Pharm. 344:44–52. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Witt E, Witt F, Trautwein N, et al:
Synthesis of lead chalcogenide nanocrystals and study of charge
transfer in blends of PbSe nano-crystals and
poly(3-hexylthiophene). Phys Chem Chem Phys. 14:11706–11714. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Dass A, Guo R, Tracy JB, Balasubramanian
R, Douglas AD and Murray RW: Gold nanoparticles with
perfluorothiolate ligands. Langmuir. 24:310–315. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Lin C, Tsai SC, Tseng MT, et al: AKT
serine/threonine protein kinase modulates baicalin-triggered
autophagy in human bladder cancer T24 cells. Int J Oncol.
42:993–1000. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55.
|
Tsai SC, Yang JS, Peng SF, et al: Bufalin
increases sensitivity to AKT/mTOR-induced autophagic cell death in
SK-HEP-1 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol.
41:1431–1442. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
Chen HJ, Lin CM, Lee CY, et al: Phenethyl
isothiocyanate suppresses EGF-stimulated SAS human oral squamous
carcinoma cell invasion by targeting EGF receptor signaling. Int J
Oncol. 43:629–637. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57.
|
Tsai SC, Huang WW, Huang WC, et al:
ERK-modulated intrinsic signaling and G(2)/M phase arrest
contribute to the induction of apoptotic death by allyl
isothiocyanate in MDA-MB-468 human breast adenocarcinoma cells. Int
J Oncol. 41:2065–2072. 2012.
|
|
58.
|
Liao YR, Lu CC, Lai KC, et al: The novel
carboxamide analog ITR-284 induces caspase-dependent apoptotic cell
death in human hepatocellular and colorectal cancer cells. Mol Med
Rep. 7:1539–1544. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59.
|
Liu CY, Yang JS, Huang SM, et al: Smh-3
induces G(2)/M arrest and apoptosis through calcium mediated
endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial signaling in human
hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells. Oncol Rep. 29:751–762.
2013.
|
|
60.
|
Lee CY, Chien YS, Chiu TH, et al:
Apoptosis triggered by vitexin in U937 human leukemia cells via a
mitochondrial signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 28:1883–1888.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61.
|
Yang JS, Wu CC, Kuo CL, et al: Solanum
lyratum extracts induce extrinsic and intrinsic pathways of
apoptosis in WEHI-3 murine leukemia cells and inhibit allograft
tumor. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012:2549602012.
|
|
62.
|
Yin HT, Zhang DG, Wu XL, Huang XE and Chen
G: In vivo evaluation of curcumin-loaded nanoparticles in a A549
xenograft mice model. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:409–412. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63.
|
Jiang L, Luo M, Liu D, et al: BAD
overexpression inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis via
mitochondrial-dependent pathway in non-small cell lung cancer.
Cancer Cell Int. 13:532013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64.
|
Balogova L, Maslanakova M, Dzurova L,
Miskovsky P and Stroffekova K: Bcl-2 proapoptotic proteins
distribution in U-87 MG glioma cells before and after hypericin
photodynamic action. Gen Physiol Biophys. 32:179–187. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65.
|
Plourde MB, Morchid A, Iranezereza L and
Berthoux L: The Bcl-2/Bcl-xL inhibitor BH3I-2′ affects the dynamics
and subcellular localization of sumoylated proteins. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 45:826–835. 2013.
|
|
66.
|
Kastelan M, Massari LP and Brajac I: The
role of bcl-2 family proteins in psoriasis. Lijec Vjesn. 132:31–33.
2010.(In Croatian).
|
|
67.
|
Danial NN: BAD: undertaker by night,
candyman by day. Oncogene. 27 (Suppl 1): S53–S70. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68.
|
Levine B, Sinha S and Kroemer G: Bcl-2
family members: dual regulators of apoptosis and autophagy.
Autophagy. 4:600–606. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69.
|
Stauffer SR: Small molecule inhibition of
the Bcl-X(L)-BH3 protein-protein interaction: proof-of-concept of
an in vivo chemopotentiator ABT-737. Curr Top Med Chem. 7:961–965.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70.
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 apoptotic
switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene. 26:1324–1337.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71.
|
Kuroda J and Taniwaki M: Involvement of
BH3-only proteins in hematologic malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 71:89–101. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72.
|
Li Y, Gu J, Liu Y, et al: iNOS
participates in apoptosis of spinal cord neurons via p-BAD
dephosphorylation following ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury in
rat spinal cord. Neurosci Lett. 545:117–122. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73.
|
Hojabrpour P, Waissbluth I, Ghaffari M,
Cox ME and Duronio V: CaMKII-gamma mediates phosphorylation of BAD
at Ser170 to regulate cytokine-dependent survival and
proliferation. Biochem J. 442:139–149. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74.
|
Kim W, Yang HJ, Youn H, Yun YJ, Seong KM
and Youn B: Myricetin inhibits Akt survival signaling and induces
Bad-mediated apoptosis in a low dose ultraviolet (UV)-B-irradiated
HaCaT human immortalized keratinocytes. J Radiat Res. 51:285–296.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75.
|
Yang J: Molecular modeling of human BAD, a
pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family member, integrating glycolysis and
apoptosis. Protein Pept Lett. 17:206–220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76.
|
Bhat V, Olenick MB, Schuchardt BJ, et al:
Heat-induced fibrillation of BclXL apoptotic repressor. Biophys
Chem. 179:12–25. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77.
|
Dorjgochoo T, Xiang YB, Long J, et al:
Association of genetic markers in the BCL-2 family of
apoptosis-related genes with endometrial cancer risk in a Chinese
population. PLoS One. 8:e609152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78.
|
Zhang XH, Chen SY, Tang L, et al:
Myricetin induces apoptosis in Hepg2 cells through Akt/P70s6k/Bad
signaling and mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Anticancer Agents
Med Chem. Feb 7–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
79.
|
Lim GE, Piske M and Johnson JD: 14-3-3
proteins are essential signalling hubs for beta cell survival.
Diabetologia. 56:825–837. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80.
|
Riaz A, Zeller KS and Johansson S:
Receptor-specific mechanisms regulate phosphorylation of AKT at
Ser473: role of RICTOR in beta1 integrin-mediated cell survival.
PLoS One. 7:e320812012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|