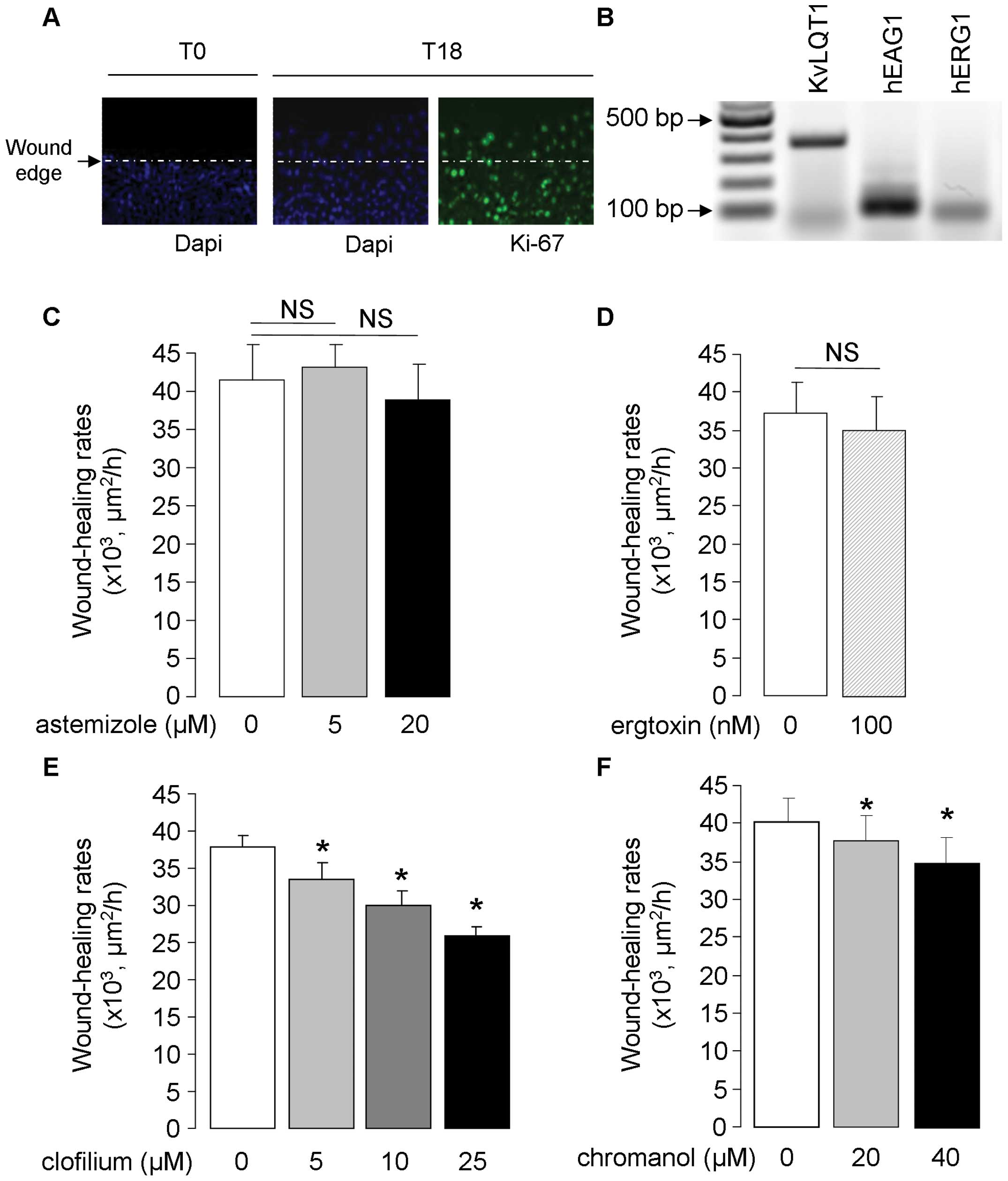
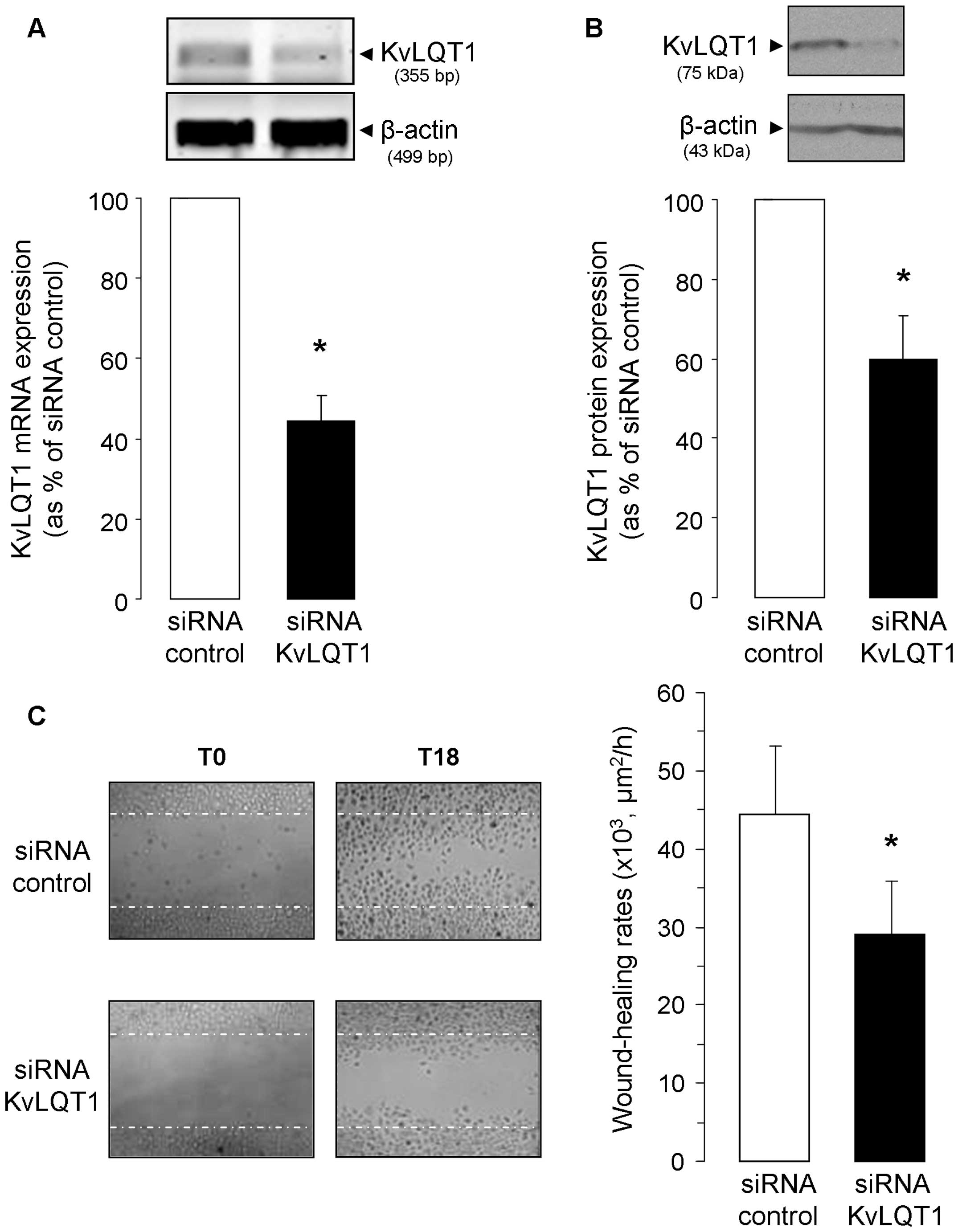
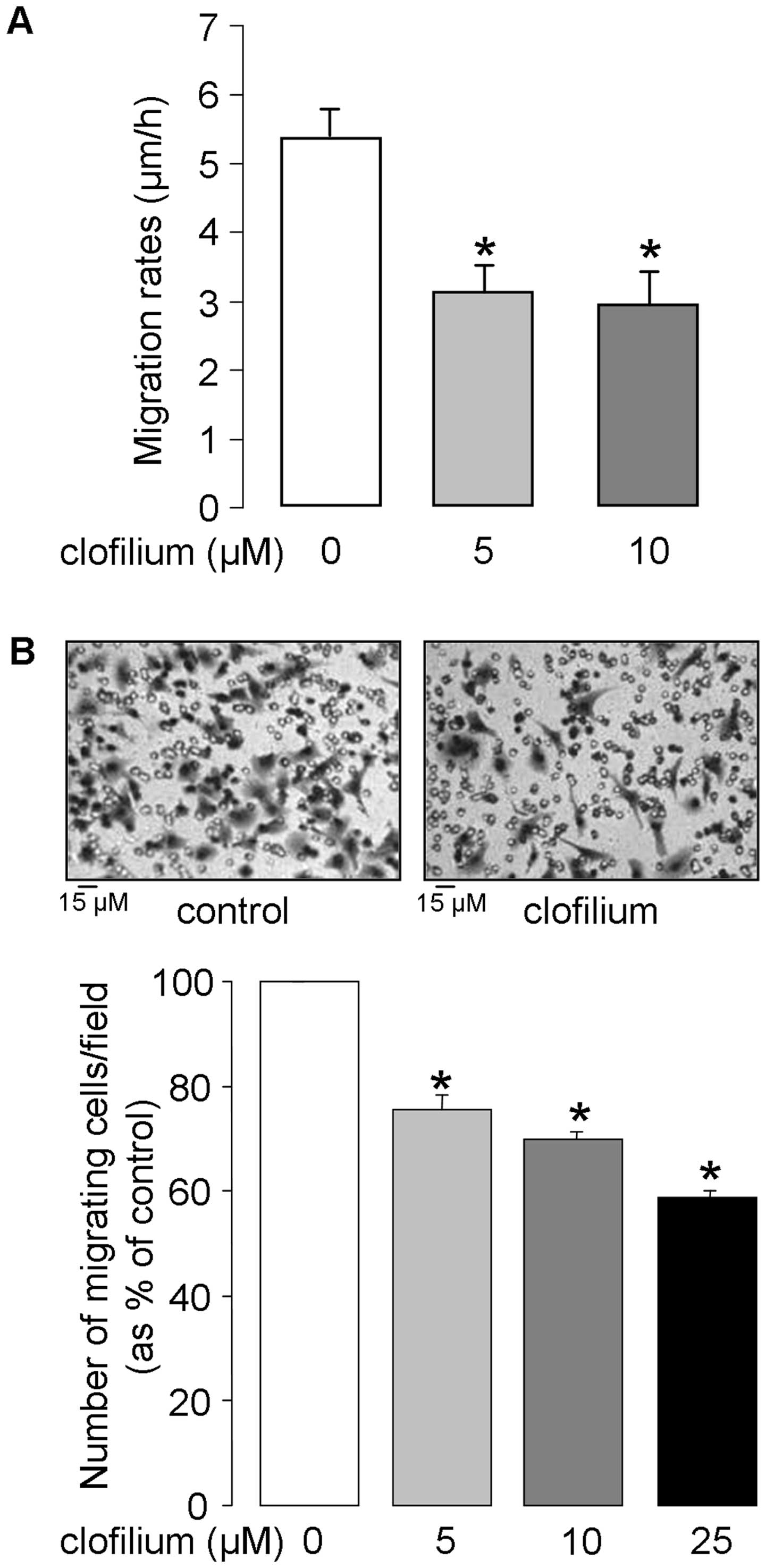
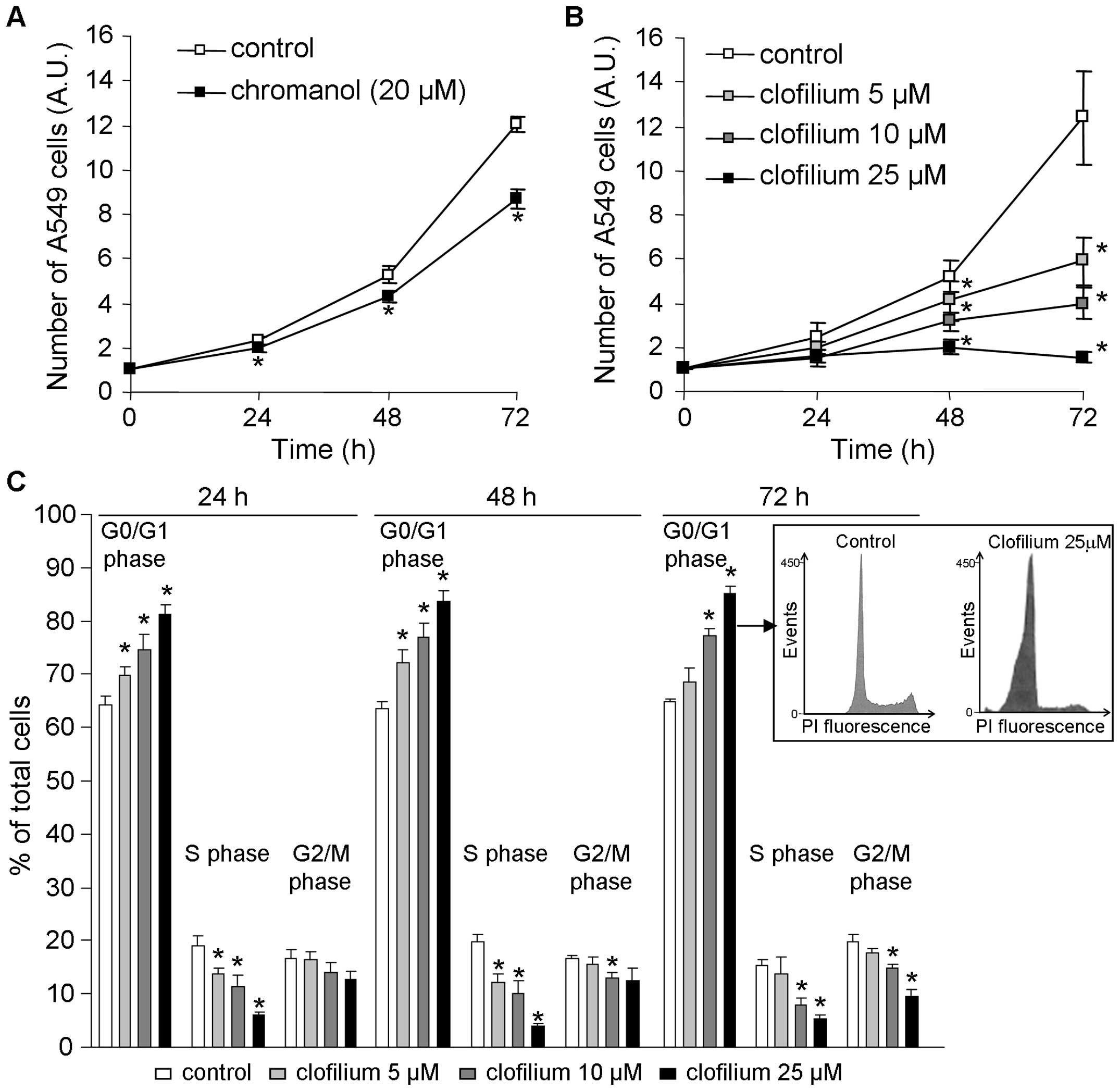
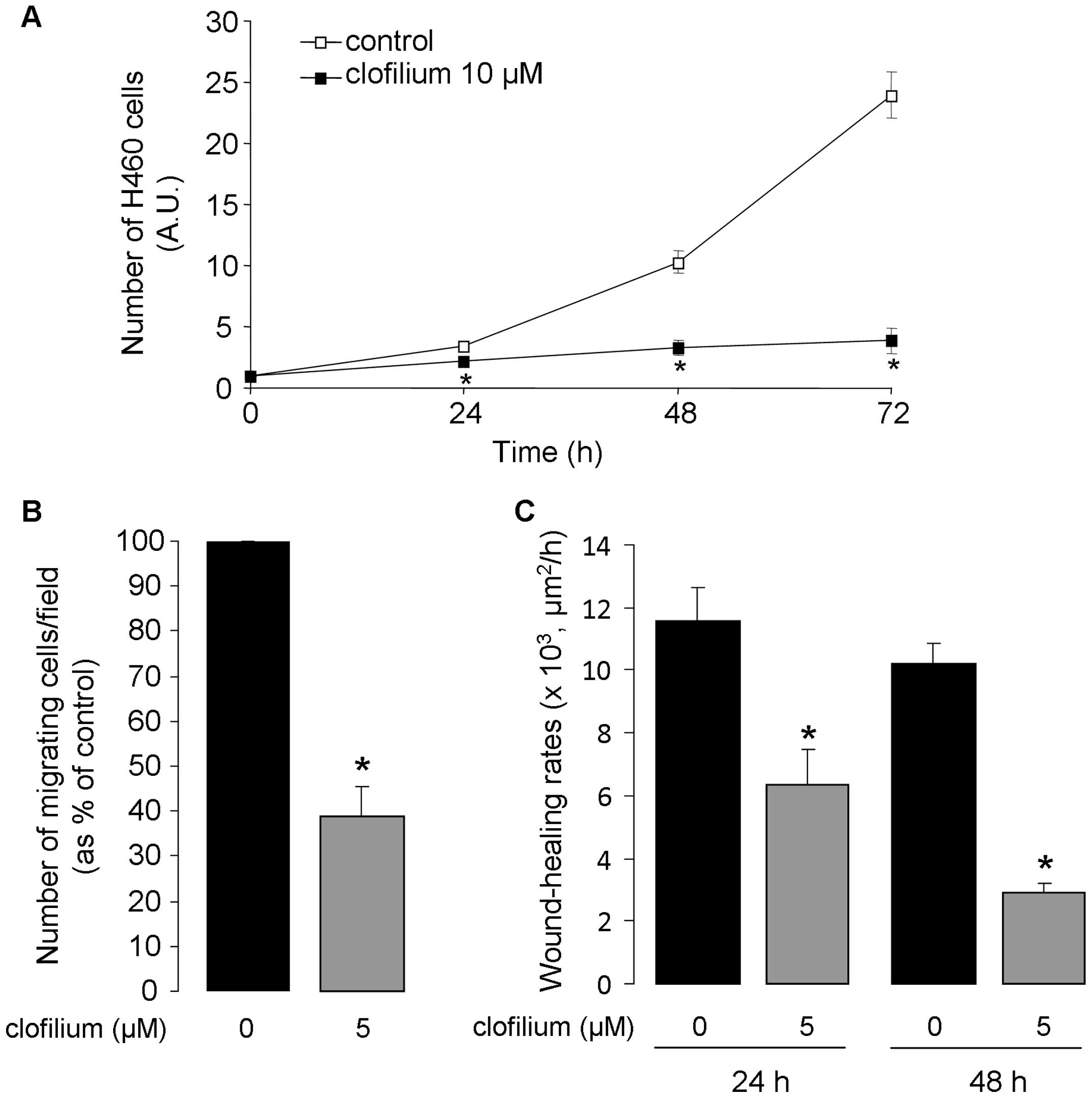
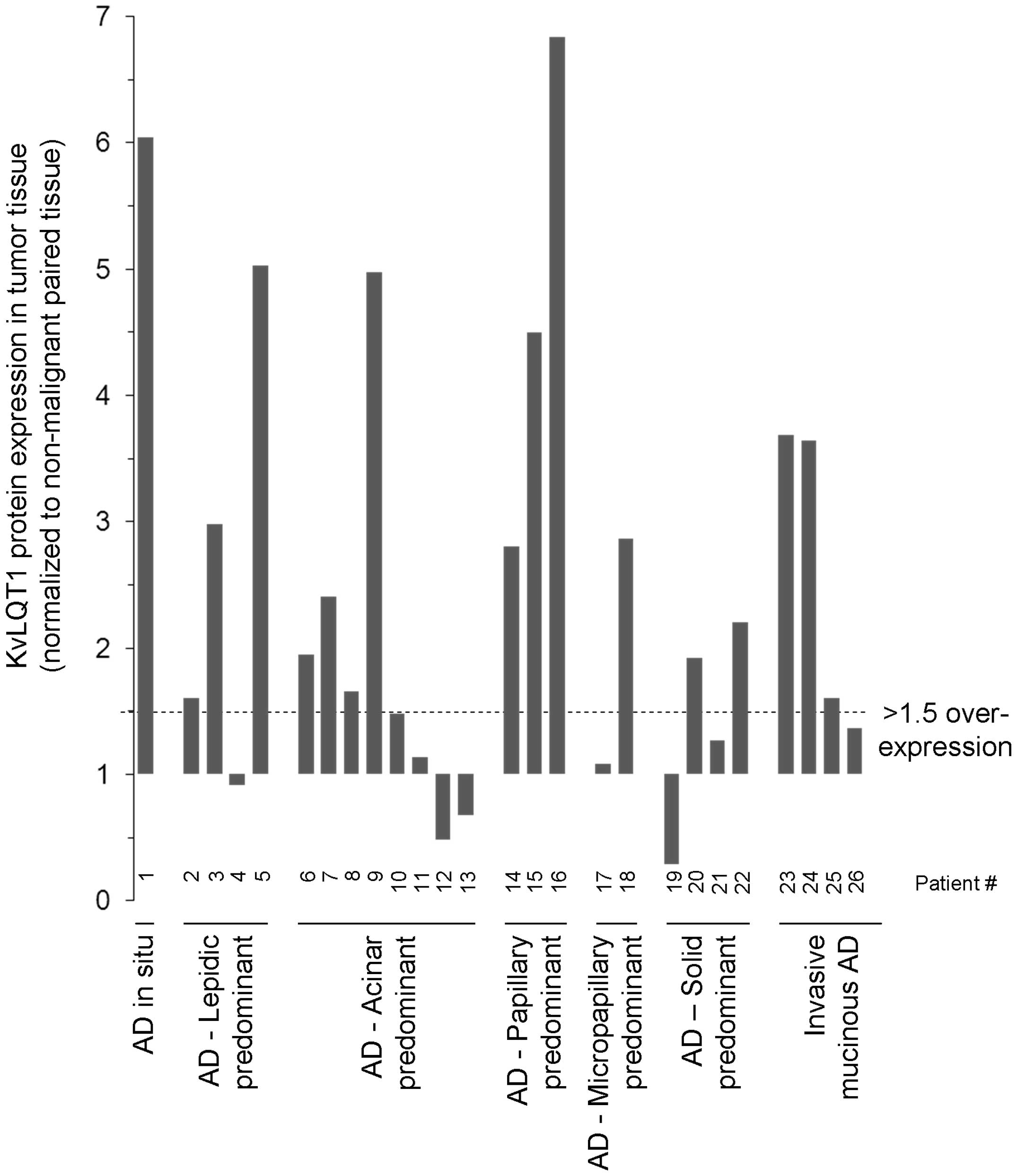
|
1.
|
Berthiaume Y, Lesur O and Dagenais A:
Treatment of adult respiratory distress syndrome: plea for rescue
therapy of the alveolar epithelium. Thorax. 54:150–160. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Sacco O, Silvestri M, Sabatini F, Sale R,
Defilippi AC and Rossi GA: Epithelial cells and fibroblasts:
structural repair and remodelling in the airways. Paediatr Respir
Rev. 5(Suppl A): S35–S40. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Zahm JM, Kaplan H, Herard AL, Doriot F,
Pierrot D, Somelette P and Puchelle E: Cell migration and
proliferation during the in vitro wound repair of the respiratory
epithelium. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 37:33–43. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Crosby LM and Waters CM: Epithelial repair
mechanisms in the lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
298:L715–L731. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Mareel M and Leroy A: Clinical, cellular,
and molecular aspects of cancer invasion. Physiol Rev. 83:337–376.
2003.
|
|
7.
|
Prevarskaya N, Skryma R and Shuba Y: Ion
channels and the hallmarks of cancer. Trends Mol Med. 16:107–121.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
O’Grady SM and Lee SY: Molecular diversity
and function of voltage-gated (Kv) potassium channels in epithelial
cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 37:1578–1594. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Wonderlin WF and Strobl JS: Potassium
channels, proliferation and G1 progression. J Membr Biol.
154:91–107. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Villalonga N, Ferreres JC, Argiles JM,
Condom E and Felipe A: Potassium channels are a new target field in
anticancer drug design. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov.
2:212–223. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Schwab A, Hanley P, Fabian A and Stock C:
Potassium channels keep mobile cells on the go. Physiology.
23:212–220. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Arcangeli A, Crociani O, Lastraioli E,
Masi A, Pillozzi S and Becchetti A: Targeting ion channels in
cancer: a novel frontier in antineoplastic therapy. Curr Med Chem.
16:66–93. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Girault A, Haelters JP, Potier-Cartereau
M, Chantome A, Jaffres PA, Bougnoux P, Joulin V and Vandier C:
Targeting SKCa channels in cancer: potential new therapeutic
approaches. Curr Med Chem. 19:697–713. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Afrasiabi E, Hietamaki M, Viitanen T,
Sukumaran P, Bergelin N and Tornquist K: Expression and
significance of HERG (KCNH2) potassium channels in the regulation
of MDA-MB-435S melanoma cell proliferation and migration. Cell
Signal. 22:57–64. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Huang L, Li B, Li W, Guo H and Zou F:
ATP-sensitive potassium channels control glioma cells proliferation
by regulating ERK activity. Carcinogenesis. 30:737–744. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Lallet-Daher H, Roudbaraki M, Bavencoffe
A, Mariot P, Gackiere F, Bidaux G, Urbain R, Gosset P, Delcourt P,
Fleurisse L, Slomianny C, Dewailly E, Mauroy B, Bonnal JL, Skryma R
and Prevarskaya N: Intermediate-conductance
Ca2+-activated K+ channels (IKCa1) regulate
human prostate cancer cell proliferation through a close control of
calcium entry. Oncogene. 28:1792–1806. 2009.
|
|
17.
|
Alvarez-Baron CP, Jonsson P, Thomas C,
Dryer SE and Williams C: The two-pore domain potassium channel
KCNK5: induction by estrogen receptor alpha and role in
proliferation of breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol. 25:1326–1336.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Trinh NT, Prive A, Kheir L, Bourret JC,
Hijazi T, Amraei MG, Noel J and Brochiero E: Involvement of KATP
and KvLQT1 K+ channels in EGF-stimulated alveolar
epithelial cell repair processes. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 293:L870–L882. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Trinh NT, Prive A, Maille E, Noel J and
Brochiero E: EGF and K+ channel activity control normal
and cystic fibrosis bronchial epithelia repair. Am J Physiol Lung
Cell Mol Physiol. 295:L866–L880. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Jang SH, Choi SY, Ryu PD and Lee SY:
Anti-proliferative effect of Kv1.3 blockers in A549 human lung
adenocarcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 651:26–32.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Plummer HK III, Dhar MS, Cekanova M and
Schuller HM: Expression of G-protein inwardly rectifying potassium
channels (GIRKs) in lung cancer cell lines. BMC Cancer. 5:1042005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Pancrazio JJ, Tabbara IA and Kim YI:
Voltage-activated K+ conductance and cell proliferation
in small-cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 13:1231–1234. 1993.
|
|
23.
|
Wang ZH, Shen B, Yao HL, Jia YC, Ren J,
Feng YJ and Wang YZ: Blockage of intermediate-conductance-Ca(2+)
-activated K(+) channels inhibits progression of human endometrial
cancer. Oncogene. 26:5107–5114. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Gomez-Varela D, Zwick-Wallasch E, Knotgen
H, Sanchez A, Hettmann T, Ossipov D, Weseloh R, Contreras-Jurado C,
Rothe M, Stuhmer W and Pardo LA: Monoclonal antibody blockade of
the human Eag1 potassium channel function exerts antitumor
activity. Cancer Res. 67:7343–7349. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Felipe A, Vicente R, Villalonga N,
Roura-Ferrer M, Martinez-Marmol R, Sole L, Ferreres JC and Condom
E: Potassium channels: new targets in cancer therapy. Cancer Detect
Prev. 30:375–385. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Woodfork KA, Wonderlin WF, Peterson VA and
Strobl JS: Inhibition of ATP-sensitive potassium channels causes
reversible cell-cycle arrest of human breast cancer cells in tissue
culture. J Cell Physiol. 162:163–171. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27.
|
Zhanping W, Xiaoyu P, Na C, Shenglan W and
Bo W: Voltage-gated K+ channels are associated with cell
proliferation and cell cycle of ovarian cancer cell. Gynecol Oncol.
104:455–460. 2007.
|
|
28.
|
Restrepo-Angulo I, Sanchez-Torres C and
Camacho J: Human EAG1 potassium channels in the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells.
Anticancer Res. 31:1265–1270. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Hammadi M, Chopin V, Matifat F,
Dhennin-Duthille I, Chasseraud M, Sevestre H and Ouadid-Ahidouch H:
Human ether a-gogo K(+) channel 1 (hEag1) regulates MDA-MB-231
breast cancer cell migration through Orai1-dependent calcium entry.
J Cell Physiol. 227:3837–3846. 2012.
|
|
30.
|
Yasukagawa T, Niwa Y, Simizu S and Umezawa
K: Suppression of cellular invasion by glybenclamide through
inhibited secretion of platelet-derived growth factor in ovarian
clear cell carcinoma ES-2 cells. FEBS Lett. 586:1504–1509. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Potier M, Joulin V, Roger S, Besson P,
Jourdan ML, Leguennec JY, Bougnoux P and Vandier C: Identification
of SK3 channel as a new mediator of breast cancer cell migration.
Mol Cancer Ther. 5:2946–2953. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Mu D, Chen L, Zhang X, See LH, Koch CM,
Yen C, Tong JJ, Spiegel L, Nguyen KC, Servoss A, Peng Y, Pei L,
Marks JR, Lowe S, Hoey T, Jan LY, McCombie WR, Wigler MH and Powers
S: Genomic amplification and oncogenic properties of the KCNK9
potassium channel gene. Cancer Cell. 3:297–302. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Ohya S, Kimura K, Niwa S, Ohno A, Kojima
Y, Sasaki S, Kohri K and Imaizumi Y: Malignancy grade-dependent
expression of k(+)-channel subtypes in human prostate cancer. J
Pharmacol Sci. 109:148–151. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Voloshyna I, Besana A, Castillo M, Matos
T, Weinstein IB, Mansukhani M, Robinson RB, Cordon-Cardo C and
Feinmark SJ: TREK-1 is a novel molecular target in prostate cancer.
Cancer Res. 68:1197–1203. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Tsevi I, Vicente R, Grande M,
Lopez-Iglesias C, Figueras A, Capella G, Condom E and Felipe A:
KCNQ1/KCNE1 channels during germ-cell differentiation in the rat:
expression associated with testis pathologies. J Cell Physiol.
202:400–410. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Than BL, Goos JA, Sarver AL, O’Sullivan
MG, Rod A, Starr TK, Fijneman RJ, Meijer GA, Zhao L, Zhang Y,
Largaespada DA, Scott PM and Cormier RT: The role of KCNQ1 in mouse
and human gastrointestinal cancers. Oncogene. Aug 26–2013.(Epub
ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37.
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M,
Nicholson AG, Geisinger KR, Yatabe Y, Beer DG, Powell CA, Riely GJ,
Van Schil PE, Garg K, Austin JH, Asamura H, Rusch VW, Hirsch FR,
Scagliotti G, Mitsudomi T, Huber RM, Ishikawa Y, Jett J,
Sanchez-Cespedes M, Sculier JP, Takahashi T, Tsuboi M,
Vansteenkiste J, Wistuba I, Yang PC, Aberle D, Brambilla C, Flieder
D, Franklin W, Gazdar A, Gould M, Hasleton P, Henderson D, Johnson
B, Johnson D, Kerr K, Kuriyama K, Lee JS, Miller VA, Petersen I,
Roggli V, Rosell R, Saijo N, Thunnissen E, Tsao M and Yankelewitz
D: International association for the study of lung cancer/american
thoracic society/european respiratory society international
multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac
Oncol. 6:244–285. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38.
|
Maille E, Trinh NT, Prive A, Bilodeau C,
Bissonnette E, Grandvaux N and Brochiero E: Regulation of normal
and cystic fibrosis airway epithelial repair processes by TNF-alpha
after injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 301:L945–L955.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Trinh NT, Bardou O, Prive A, Maille E,
Adam D, Lingée S, Ferraro P, Desrosiers M, Coraux C and Brochiero
E: Improvement of defective cystic fibrosis airway epithelial wound
repair after CFTR rescue. Eur Respir J. 40:1390–1400. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Bardou O, Prive A, Migneault F,
Roy-Camille K, Dagenais A, Berthiaume Y and Brochiero E: K(+)
channels regulate ENaC expression via changes in promoter activity
and control fluid clearance in alveolar epithelial cells. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1818:1682–1690. 2012.
|
|
41.
|
Wang Q, Curran ME, Splawski I, Burn TC,
Millholland JM, VanRaay TJ, Shen J, Timothy KW, Vincent GM, de
Jager T, Schwartz PJ, Toubin JA, Moss AJ, Atkinson DL, Landes GM,
Connors TD and Keating MT: Positional cloning of a novel potassium
channel gene: KVLQT1 mutations cause cardiac arrhythmias. Nat
Genet. 12:17–23. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Cowley EA and Linsdell P: Characterization
of basolateral K+ channels underlying anion secretion in
the human airway cell line Calu-3. J Physiol. 538:747–757.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Devor DC, Bridges RJ and Pilewski JM:
Pharmacological modulation of ion transport across wild-type and
DeltaF508 CFTR-expressing human bronchial epithelia. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 279:C461–C479. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
MacVinish LJ, Hickman ME, Mufti DA,
Durrington HJ and Cuthbert AW: Importance of basolateral
K+ conductance in maintaining Cl- secretion in murine
nasal and colonic epithelia. J Physiol. 510:237–247. 1998.
|
|
45.
|
Ouadid-Ahidouch H and Ahidouch A: K(+)
channels and cell cycle progression in tumor cells. Front Physiol.
4:2202013.
|
|
46.
|
Inglis SK, Brown SG, Constable MJ,
McTavish N, Olver RE and Wilson SM: A Ba2+-resistant,
acid-sensitive K+ conductance in
Na+-absorbing H441 human airway epithelial cells. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 292:L1304–L1312. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Asher V, Warren A, Shaw R, Sowter H, Bali
A and Khan R: The role of Eag and HERG channels in cell
proliferation and apoptotic cell death in SK-OV-3 ovarian cancer
cell line. Cancer Cell Int. 11:62011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Perry M, Stansfeld PJ, Leaney J, Wood C,
de Groot MJ, Leishman D, Sutcliffe MJ and Mitcheson JS: Drug
binding interactions in the inner cavity of HERG channels:
molecular insights from structure-activity relationships of
clofilium and ibutilide analogs. Mol Pharmacol. 69:509–519. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Niemeyer MI, Cid LP, Barros LF and
Sepulveda FV: Modulation of the two-pore domain acid-sensitive
K+ channel TASK-2 (KCNK5) by changes in cell volume. J
Biol Chem. 276:43166–43174. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Pardo LA: Voltage-gated potassium channels
in cell proliferation. Physiology. 19:285–292. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Klimatcheva E and Wonderlin WF: An
ATP-sensitive K(+) current that regulates progression through early
G1 phase of the cell cycle in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J
Membr Biol. 171:35–46. 1999.
|
|
52.
|
Arcangeli A and Becchetti A: Complex
functional interaction between integrin receptors and ion channels.
Trends Cell Biol. 16:631–639. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Pei L, Wiser O, Slavin A, Mu D, Powers S,
Jan LY and Hoey T: Oncogenic potential of TASK3 (Kcnk9) depends on
K+ channel function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:7803–7807. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Glassmeier G, Hempel K, Wulfsen I, Bauer
CK, Schumacher U and Schwarz JR: Inhibition of HERG1 K+
channel protein expression decreases cell proliferation of human
small cell lung cancer cells. Pflugers Arch. 463:365–376. 2012.
|