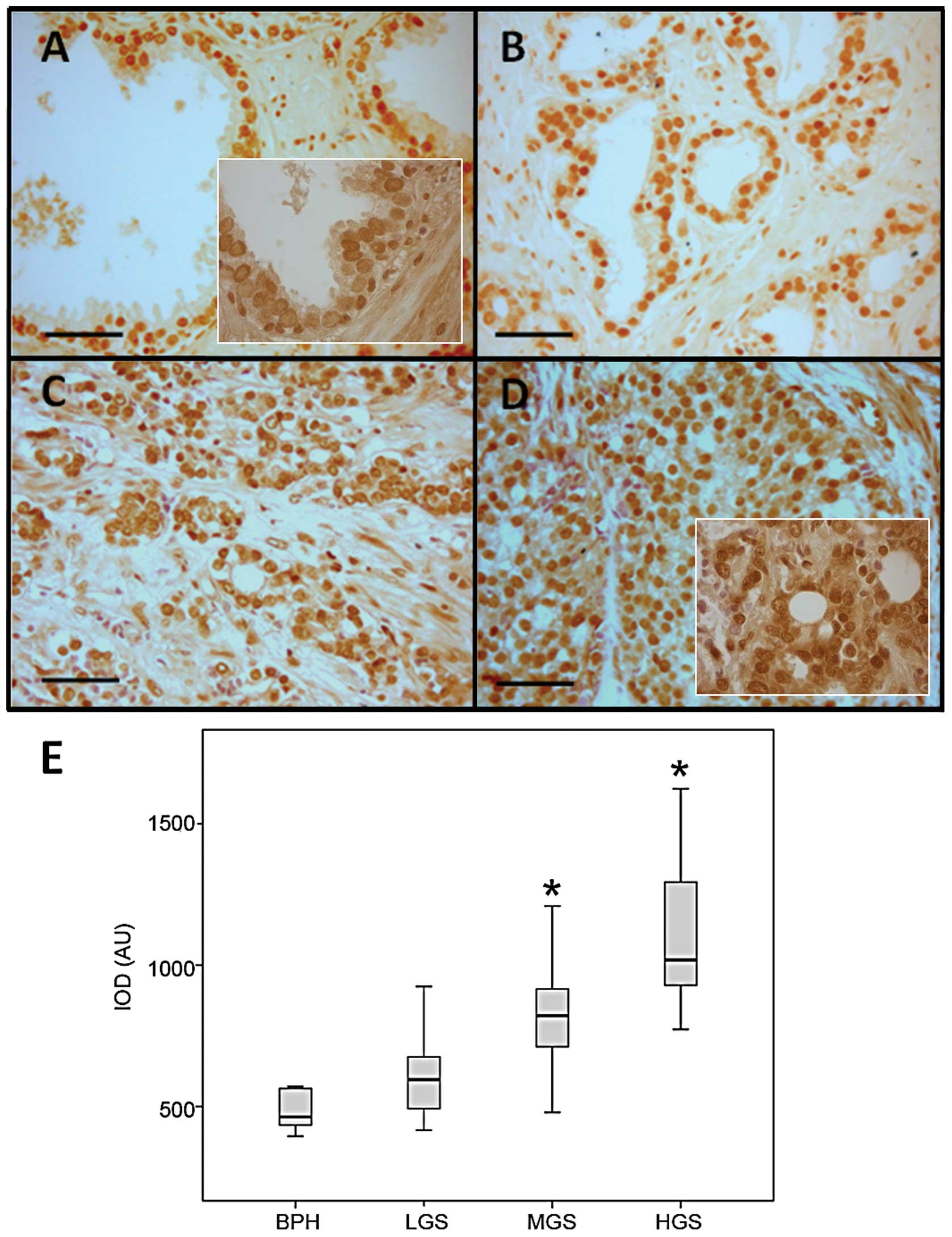
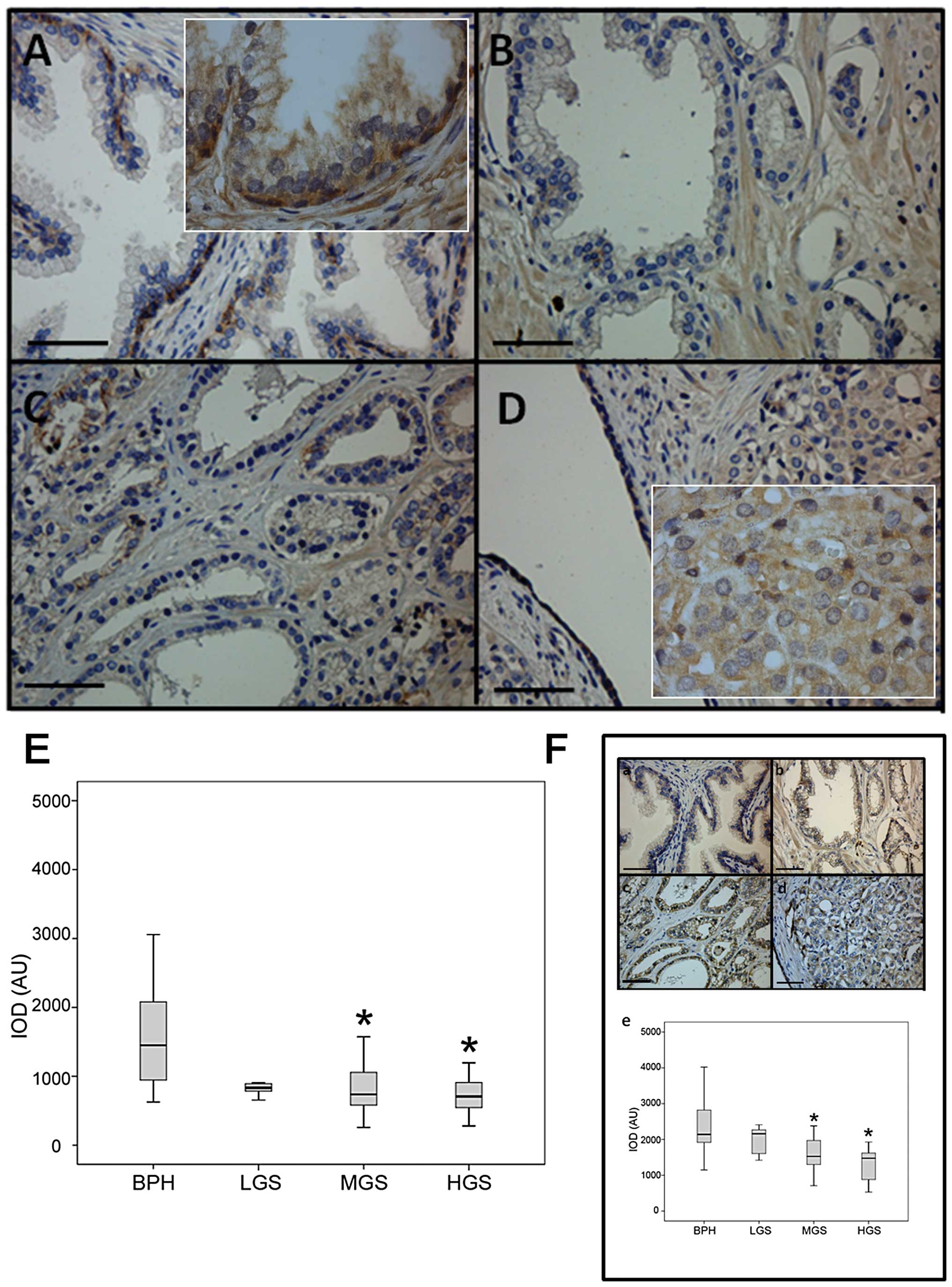
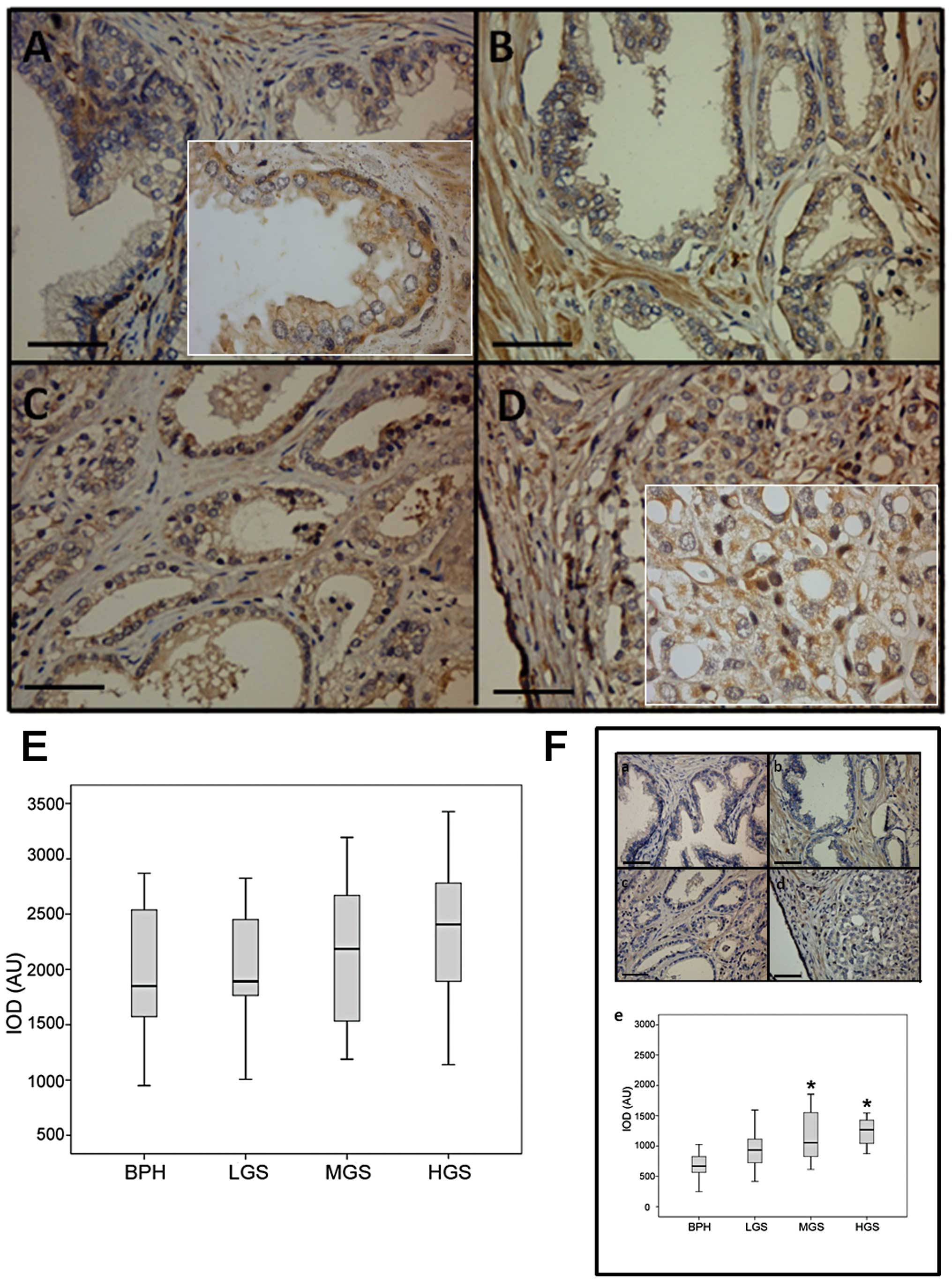
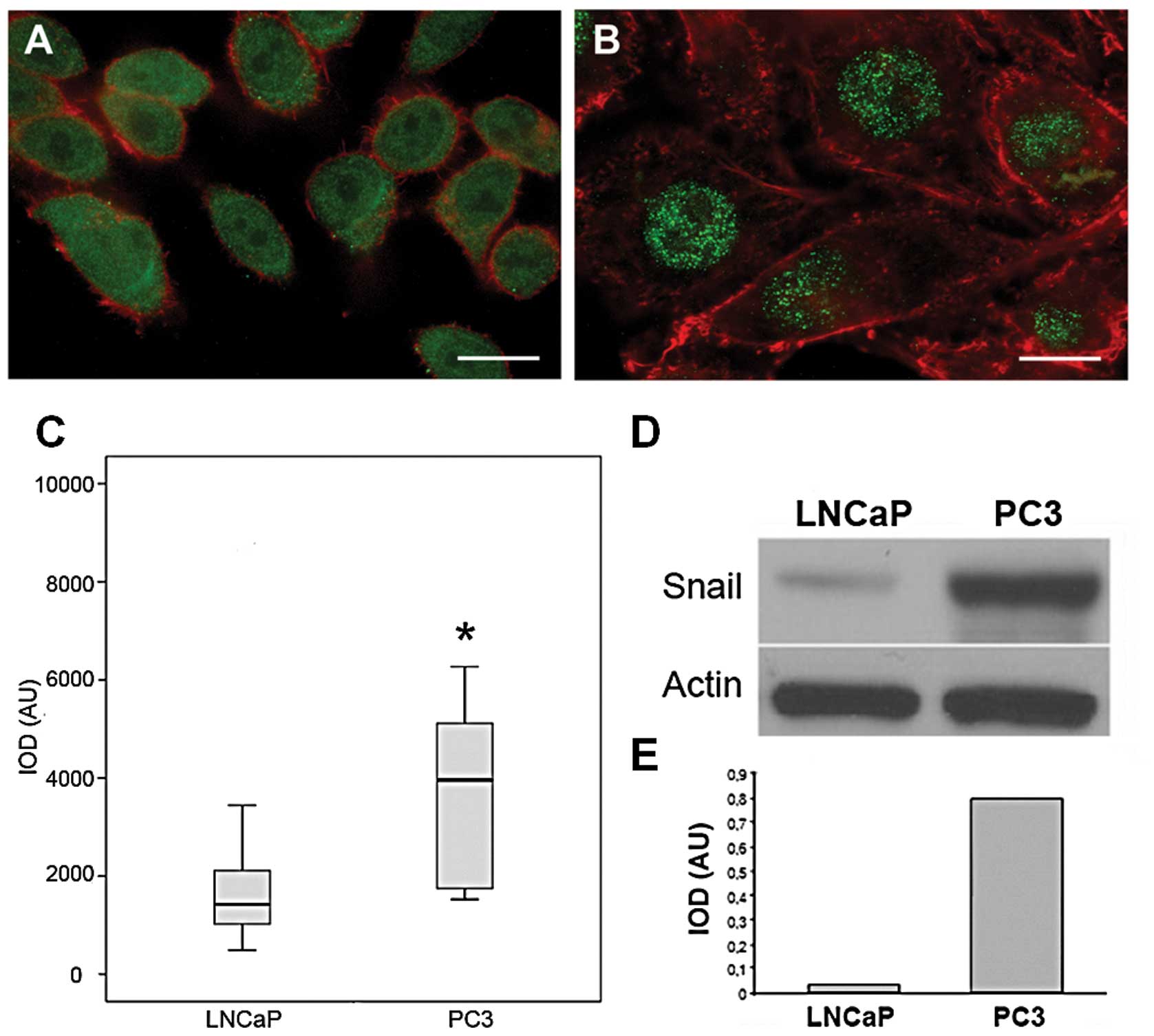
|
1.
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al: Global
Cancer Statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Kufe DW, Pollock RE, Weichselbaum RR, Bast
RC Jr, Gansler TS, Holland JF and Frei E III: Neoplasms of the
prostate. Cancer Medicine. Decker BC: ISBN: ISBN
1-55009-113-12003
|
|
3.
|
Long RM, Morrissey C, Fitzpatrick JM and
Watson WG: Prostate epithelial cell differentiation and its
relevance to the understanding of prostate cancer therapies. Clin
Sci (Lond). 108:1–11. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
De Marzo AM, Platz EA, Sutcliffe S, et al:
Inflammation in prostate carcinogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:256–269.
2007.
|
|
5.
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Gos M, Miloszewska J and Przybyszewska M:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer progression. Postepy
Biochem. 55:121–128. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Delahunt B, Miller RJ, Srigley JR, et al:
Gleason grading: past, present and future. Histopathology.
60:75–86. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Micalizzi DS, Farabaugh SM and Ford HL:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer: Parallels between
normal development and tumor progression. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 15:117–134. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Pecina-Slaus N: Tumor suppressor gene
E-cadherin and its role in normal and malignant cells. Cancer Cell
Int. 3:17–18. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Chan AO, Lam SK, Chu KM, et al: Soluble
E-cadherin is a valid prognostic marker in gastric carcinoma. Gut.
48:808–811. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Mell LK, Meyer JJ, Tretiakova M, et al:
Prognostic significance of E-cadherin protein expression in
pathological stage I–III endometrial cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
10:5546–5553. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Gould Rothberg B and Bracken M: E-cadherin
immunohistochemical expression as a prognostic factor in
infiltrating ductal carcinoma of the breast: a systematic review
and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 100:139–148.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Musial J, Sporny S and Nowicki A:
Prognostic significance of E-cadherin and ezrin immunohistochemical
expression in prostate cancer. Pol J Pathol. 58:235–243.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Zhou Q, Yan B, Hu X, et al: Luteolin
inhibits invasion of prostate cancer PC3 cells through E-cadherin.
Mol Cancer Ther. 8:1684–1691. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Heebøll S, Borre M, Ottosen PD, et al:
Snail1 is over-expressed in prostate cancer. APMIS. 117:196–204.
2009.
|
|
16.
|
Smith B and Odero-Marah V: The role of
Snail in prostate cancer. Cell Adh Migr. 6:433–441. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Edwards IJ: Proteoglycans in prostate
cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 21:196–206. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18.
|
Contreras HR, Ledezma RA, Vergara J, et
al: The expression of syndecan-1 and -2 is associated with Gleason
score and epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers E-cadherin and
beta-catenin, in prostate cancer. Urol Oncol. 28:534–540. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Shimada K, Nakamura M, De Velasco MA, et
al: Syndecan-1, a new target molecule involved in progression of
androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Sci. 100:1248–1254.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Popović A, Demirović A, Spajić B, et al:
Expression and prognostic role of syndecan-2 in prostate cancer.
Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 13:78–82. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Ledezma R, Cifuentes F, Gallegos I, et al:
Altered expression patterns of syndecan-1 and -2 predict
biochemical recurrence in prostate cancer. Asian J Androl.
13:476–480. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Vihinen T, Määttä A, Jaakkola P, et al:
Functional characterization of mouse syndecan-1 promoter. J Biol
Chem. 271:12532–12541. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Nackaerts K, Verbeken E, Deneffe G, et al:
Heparan sulfate proteoglycan expression in human lung-cancer cells.
Int J Cancer. 74:335–345. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Contreras HR, Fabre M, Granés F, et al:
Syndecan-2 expression in colorectal cancer-derived HT-29 M6
epithelial cells induces a migratory phenotype. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 286:742–751. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Behnsawy HM, Miyake H, Harada K and
Fujisawa M: Expression patterns of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition markers in localized prostate cancer: significance in
clinicopathological outcomes following radical prostatectomy. BJU
Int. 111:30–37. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Kiviniemi J, Kallajoki M, Kujala I, et al:
Altered expression of syndecan-1 in prostate cancer. APMIS.
112:89–97. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Mennerich D, Vogel A, Klaman I, et al:
Shift of syndecan-1 expression from epithelial to stromal cells
during progression of solid tumours. Eur J Cancer. 40:1373–1382.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Shariat SF, Svatek RS, Kabbani W, et al:
Prognostic value of syndecan-1 expression in patients treated with
radical prostatectomy. BJU Int. 101:232–237. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Brimo F, Vollmer RT, Friszt M, et al:
Syndecan-1 expression in prostate cancer and its value as biomarker
for disease progression. BJU Int. 106:418–423. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Zong F, Fthenou E, Mundt F, et al:
Syndecan-1 domains regulate mesenchymal tumor cell adhesion,
motility and migration. PLoS One. 6:e148162011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Manon-Jensen T, Itoh Y and Couchman JR:
Proteoglycans in health and disease: the multiple roles of syndecan
shedding. FEBS J. 277:3876–3889. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Choi S, Lee H, Choi JR and Oh ES:
Shedding; towards a new paradigm of syndecan function in cancer.
BMB Rep. 43:305–310. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Fears C, Gladson C and Woods A: Syndecan-2
is expressed in the microvasculature of gliomas and regulates
angiogenic processes in microvascular endothelial cells. J Biol
Chem. 281:14533–14536. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Talbot L, Bhattacharya S and Kuo P:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition, the tumor microenvironment, and
metastatic behavior of epithelial malignancies. Int J Biochem Mol
Biol. 3:117–136. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Cano A, Pérez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I, et al:
The transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol.
2:76–83. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Nieto M and Cano A: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition under control: Global programs to
regulate epithelial plasticity. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:361–368.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Emadi Baygi M, Soheili ZS, Schmitz I, et
al: Snail regulates cell survival and inhibits cellular senescence
in human metastatic prostate cancer cell lines. Cell Biol Toxicol.
26:553–567. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Baritaki S, Chapman A, Yeung K, et al:
Inhibition of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in metastatic
prostate cancer cells by the novel proteasome inhibitor, NPI-0052:
pivotal roles of Snail repression and RKIP induction. Oncogene.
28:3573–3585. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39.
|
Wang H, Fang R, Wang XF, et al:
Stabilization of Snail through AKT/GSK-3β signaling pathway is
required for TNF-α-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
prostate cancer PC3 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 714:48–55.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|