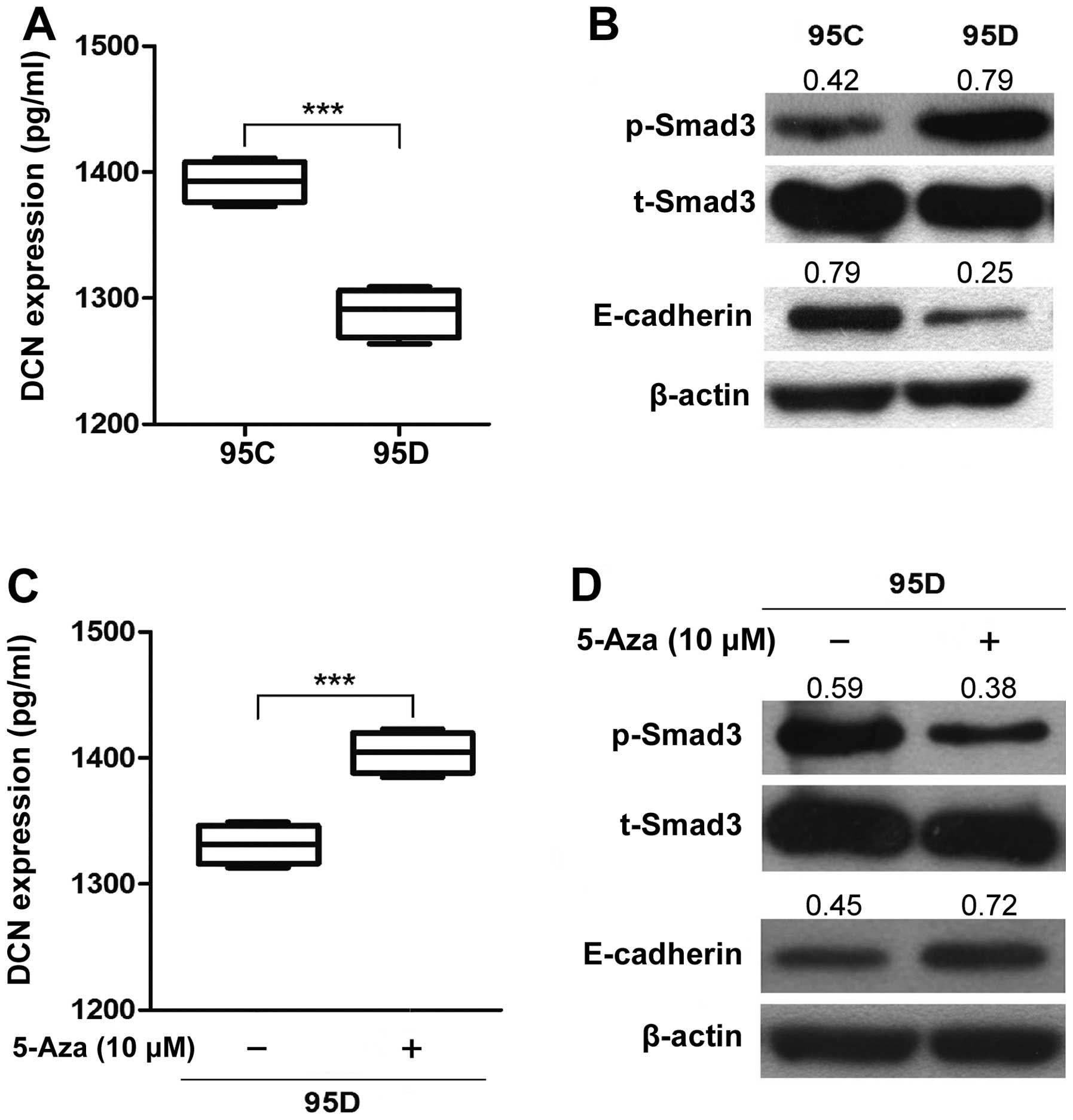
|
1.
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al: Cancer
statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 58:71–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Ramsey SD, Clarke L, Kamath TV and Lubeck
D: Evaluation of erlotinib in advanced non-small cell lung cancer:
impact on the budget of a U.S. health insurance plan. J Manag Care
Pharm. 12:472–478. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Feng J, Zhang X, Zhu H, Wang X, Ni S and
Huang J: High expression of FoxP1 is associated with improved
survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Am J Clin
Pathol. 138:230–235. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Gupta GP and Massague J: Cancer
metastasis: building a framework. Cell. 127:679–695. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Shi Y and Massague J: Mechanisms of
TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell.
113:685–700. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Toonkel RL, Borczuk AC and Powell CA:
TGF-beta signaling pathway in lung adenocarcinoma invasion. J
Thorac Oncol. 5:153–157. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Akhurst RJ and Derynck R: TGF-beta
signaling in cancer - a double-edged sword. Trends Cell Biol.
11:S44–S51. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Xu Y and Pasche B: TGF-beta signaling
alterations and susceptibility to colorectal cancer. Hum Mol Genet.
16(Spec No 1): R14–R20. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Liu X, Sun Y, Constantinescu S, Karam E,
Weinberg R and Lodish H: Transforming growth factor beta-induced
phosphorylation of Smad3 is required for growth inhibition and
transcriptional induction in epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 94:10669–10674. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Velden JL, Alcorn JF, Guala AS, Badura EC
and Janssen-Heininger YM: c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 promotes
transforming growth factor-beta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition via control of linker phosphorylation and
transcriptional activity of Smad3. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
44:571–581. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Yilmaz M, Christofori G and Lehembre F:
Distinct mechanisms of tumor invasion and metastasis. Trends Mol
Med. 13:535–541. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Goldoni S, Owens RT, McQuillan DJ, et al:
Biologically active decorin is a monomer in solution. J Biol Chem.
279:6606–6612. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Bi X, Pohl NM, Qian Z, et al:
Decorin-mediated inhibition of colorectal cancer growth and
migration is associated with E-cadherin in vitro and in mice.
Carcinogenesis. 33:326–330. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Bi XL and Yang W: Biological functions of
decorin in cancer. Chin J Cancer. 32:266–269. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Bi XL, Tong C, Dockendorff A, et al:
Genetic deficiency of decorin causes intestinal tumor formation
through disruption of intestinal cell maturation. Carcinogenesis.
29:1435–1440. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16.
|
Goldoni S, Seidler DG, Heath J, et al: An
antimetastatic role for decorin in breast cancer. Am J Pathol.
173:844–855. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Matsumine A, Shintani K, Kusuzaki K, et
al: Expression of decorin, a small leucine-rich proteoglycan, as a
prognostic factor in soft tissue tumors. J Surg Oncol. 96:411–418.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Nash MA, Deavers MT and Freedman RS: The
expression of decorin in human ovarian tumors. Clin Cancer Res.
8:1754–1760. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Reed CC, Gauldie J and Iozzo RV:
Suppression of tumorigenicity by adenovirus-mediated gene transfer
of decorin. Oncogene. 21:3688–3695. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Kresse H and Schonherr E: Proteoglycans of
the extracellular matrix and growth control. J Cell Physiol.
189:266–274. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Tralhao JG, Schaefer L, Micegova M, et al:
In vivo selective and distant killing of cancer cells, using
adenovirus-mediated decorin gene transfer. FASEB J. 17:464–466.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Yamaguchi Y, Mann DM and Ruoslahti E:
Negative regulation of transforming growth factor-beta by the
proteoglycan decorin. Nature. 346:281–284. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Biaoxue R, Xiguang C, Hua L, et al:
Decreased expression of decorin and p57(KIP2) correlates with poor
survival and lymphatic metastasis in lung cancer patients. Int J
Biol Markers. 26:9–21. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Liu Z, Zhao J, Chen XF, et al: CpG island
methylator phenotype involving tumor suppressor genes located on
chromosome 3p in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 62:15–22.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Liu Z, Li W, Lei Z, et al: CpG island
methylator phenotype involving chromosome 3p confers an increased
risk of non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 5:790–797.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Zhang HT, Chen XF, Wang MH, et al:
Defective expression of transforming growth factor beta receptor
type II is associated with CpG methylated promoter in primary
non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 10:2359–2367. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Doi A, Park IH, Wen B, et al: Differential
methylation of tissue-and cancer-specific CpG island shores
distinguishes human induced pluripotent stem cells, embryonic stem
cells and fibroblasts. Nat Genet. 41:1350–1353. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28.
|
Irizarry RA, Ladd-Acosta C, Wen B, et al:
The human colon cancer methylome shows similar hypo- and
hypermethylation at conserved tissue-specific CpG island shores.
Nat Genet. 41:178–186. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Lu YL, Huang JX, Li XH, et al: Spontaneous
metastasis of clonal cell subpopulations of human lung giant cell
carcinoma after subcutaneous inoculation in nude mice. Chin J
Oncol. 11:1–7. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Sun W, Guo C, Meng X, et al: Differential
expression of PAI-RBP1, C1orf142, and COTL1 in non-small cell lung
cancer cell lines with different tumor metastatic potential. J
Investig Med. 60:689–694. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Shang Y, Myers M and Brown M: Formation of
the androgen receptor transcription complex. Mol Cell. 9:601–610.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Sogawa K and Fujii-Kuriyama Y: Ah
receptor, a novel ligand-activated transcription factor. J Biochem.
122:1075–1079. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Zhao J, Sime PJ, Bringas P Jr, Gauldie J
and Warburton D: Adenovirus-mediated decorin gene transfer prevents
TGF-beta-induced inhibition of lung morphogenesis. Am J Physiol.
277:L412–L422. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Koninger J, Giese NA, di Mola FF, et al:
Overexpressed decorin in pancreatic cancer: potential tumor growth
inhibition and attenuation of chemotherapeutic action. Clin Cancer
Res. 10:4776–4783. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Cairns P: Gene methylation and early
detection of genitourinary cancer: the road ahead. Nat Rev Cancer.
7:531–543. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Lu F and Zhang HT: DNA methylation and
nonsmall cell lung cancer. Anat Rec. 294:1787–1795. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Luczak MW and Jagodzinski PP: The role of
DNA methylation in cancer development. Folia Histochem Cytobiol.
44:143–154. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Jeon HS and Jen J: TGF-beta signaling and
the role of inhibitory Smads in non-small cell lung cancer. J
Thorac Oncol. 5:417–419. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|