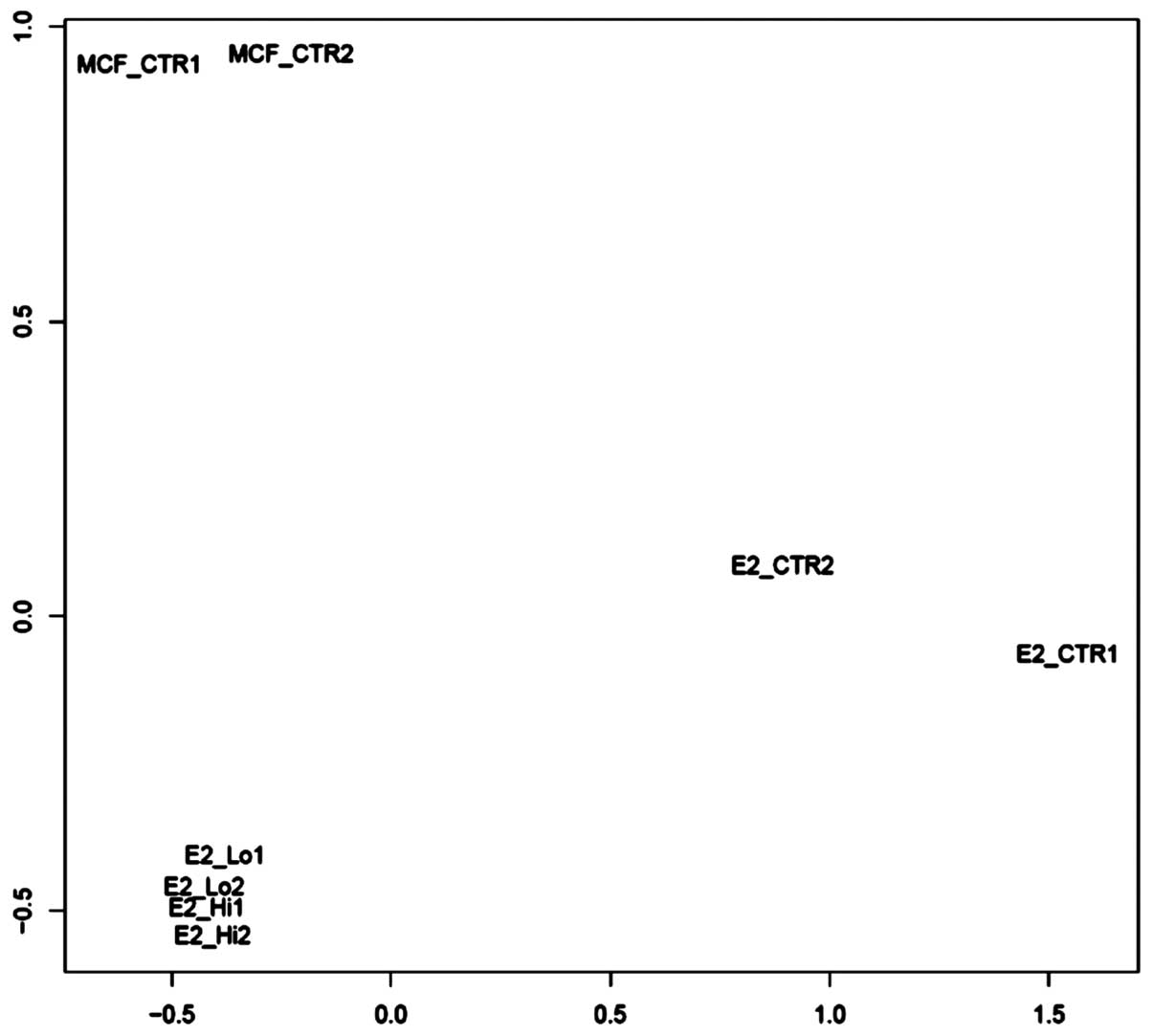
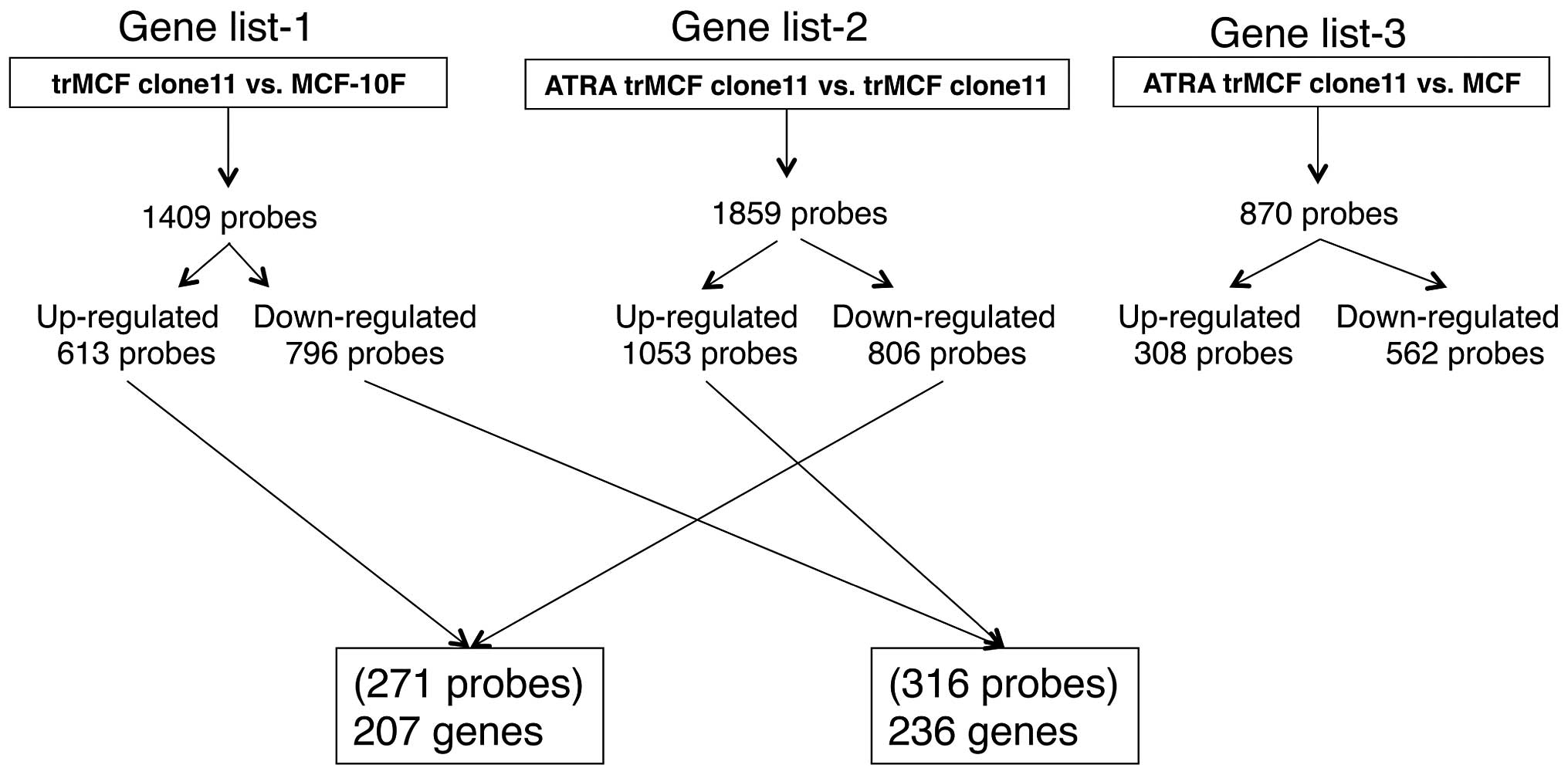
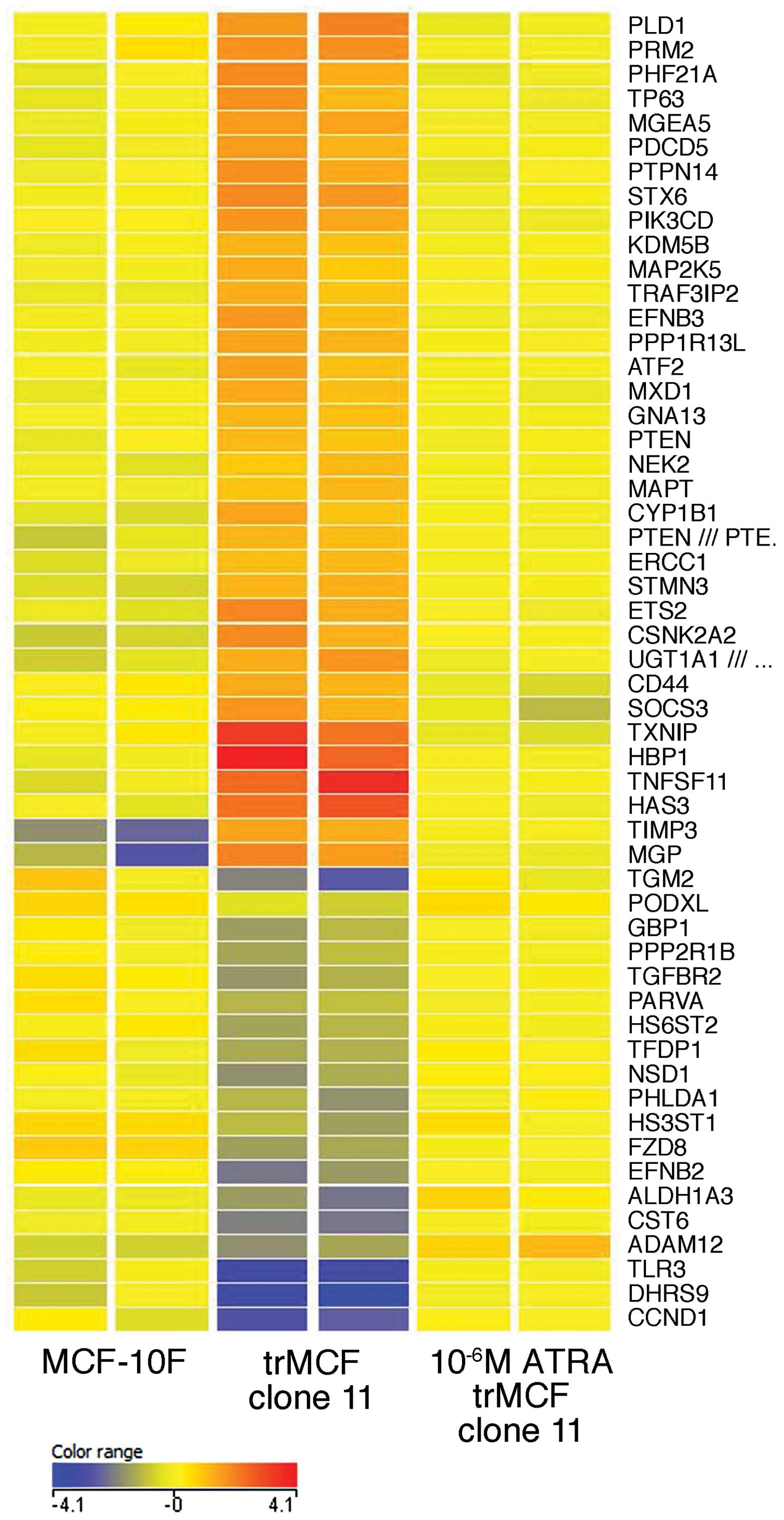
|
1.
|
Theodosiou M, Laudet V and Schubert M:
From carrot to clinic: an overview of the retinoic acid signaling
pathway. Cell Mol Life Sci. 67:1423–1445. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Duester G: Retinoic acid synthesis and
signaling during early organogenesis. Cell. 134:921–931. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Mongan NP and Gudas LJ: Diverse actions of
retinoid receptors in cancer prevention and treatment.
Differentiation. 75:853–870. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Connolly R, Nguyen NK and Sukumar S:
Molecular pathways: current role and future directions of the
retinoic acid pathway in cancer prevention and treatment. Clin
Cancer Res. 19:1651–1659. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Bushue N and Wan YJ: Retinoid pathway and
cancer therapeutics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 62:1285–1298. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Aagaard MM, Siersbaek R and Mandrup S:
Molecular basis for gene-specific transactivation by nuclear
receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1812.824–835. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Tsai MJ and O’Malley BW: Molecular
mechanisms of action of steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily
members. Annu Rev Biochem. 63:451–486. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Rochette-Egly C and Germain P: Dynamic and
combinatorial control of gene expression by nuclear retinoic acid
receptors (RARs). Nucl Recept Signal. 7:e0052009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Heyman RA, Mangelsdorf DJ, Dyck JA, et al:
9-cis retinoic acid is a high affinity ligand for the retinoid X
receptor. Cell. 68:397–406. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Garattini E, Gianni M and Terao M:
Cytodifferentiation by retinoids, a novel therapeutic option in
oncology: rational combinations with other therapeutic agents.
Vitam Horm. 75:301–354. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Zanardi S, Serrano D, Argusti A, Barile M,
Puntoni M and Decensi A: Clinical trials with retinoids for breast
cancer chemoprevention. Endocr Relat Cancer. 13:51–68. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Seewaldt VL, Johnson BS, Parker MB,
Collins SJ and Swisshelm K: Expression of retinoic acid receptor
beta mediates retinoic acid-induced growth arrest and apoptosis in
breast cancer cells. Cell Growth Differ. 6:1077–1088.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Swisshelm K, Ryan K, Lee X, Tsou HC,
Peacocke M and Sager R: Down-regulation of retinoic acid receptor
beta in mammary carcinoma cell lines and its up-regulation in
senescing normal mammary epithelial cells. Cell Growth Differ.
5:133–141. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Widschwendter M, Berger J, Muller HM,
Zeimet AG and Marth C: Epigenetic downregulation of the retinoic
acid receptor-beta2 gene in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 6:193–201. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
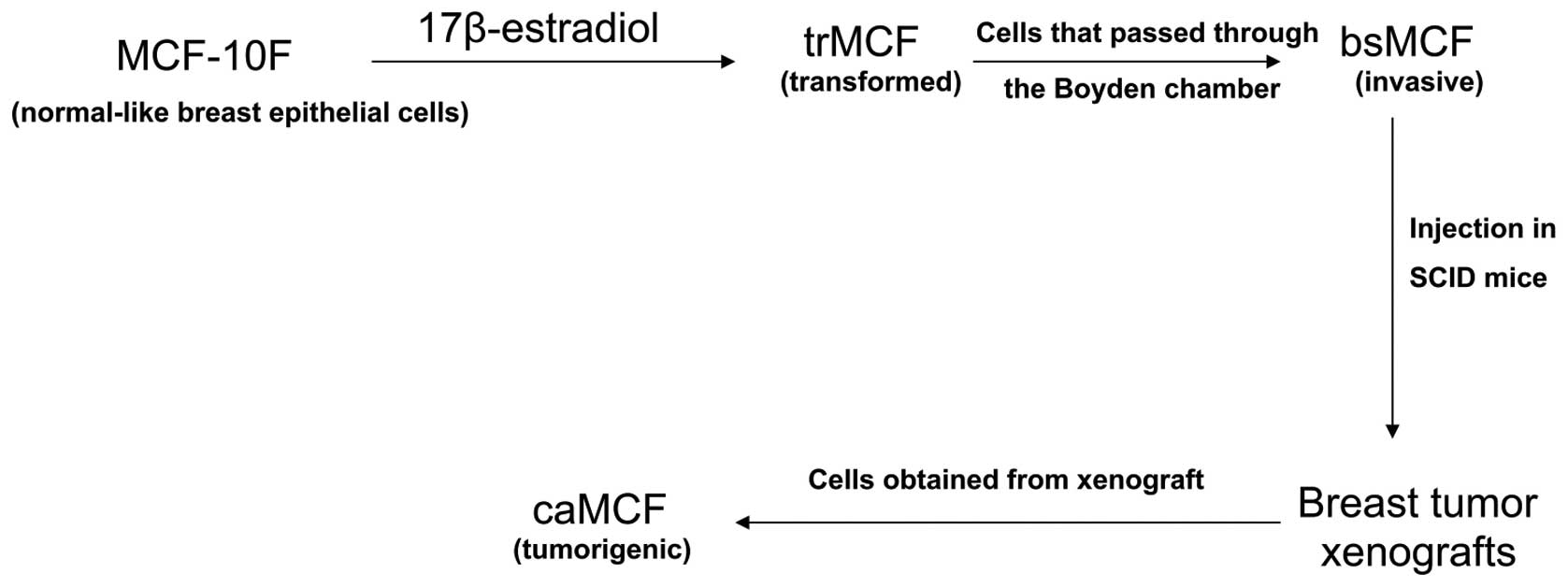
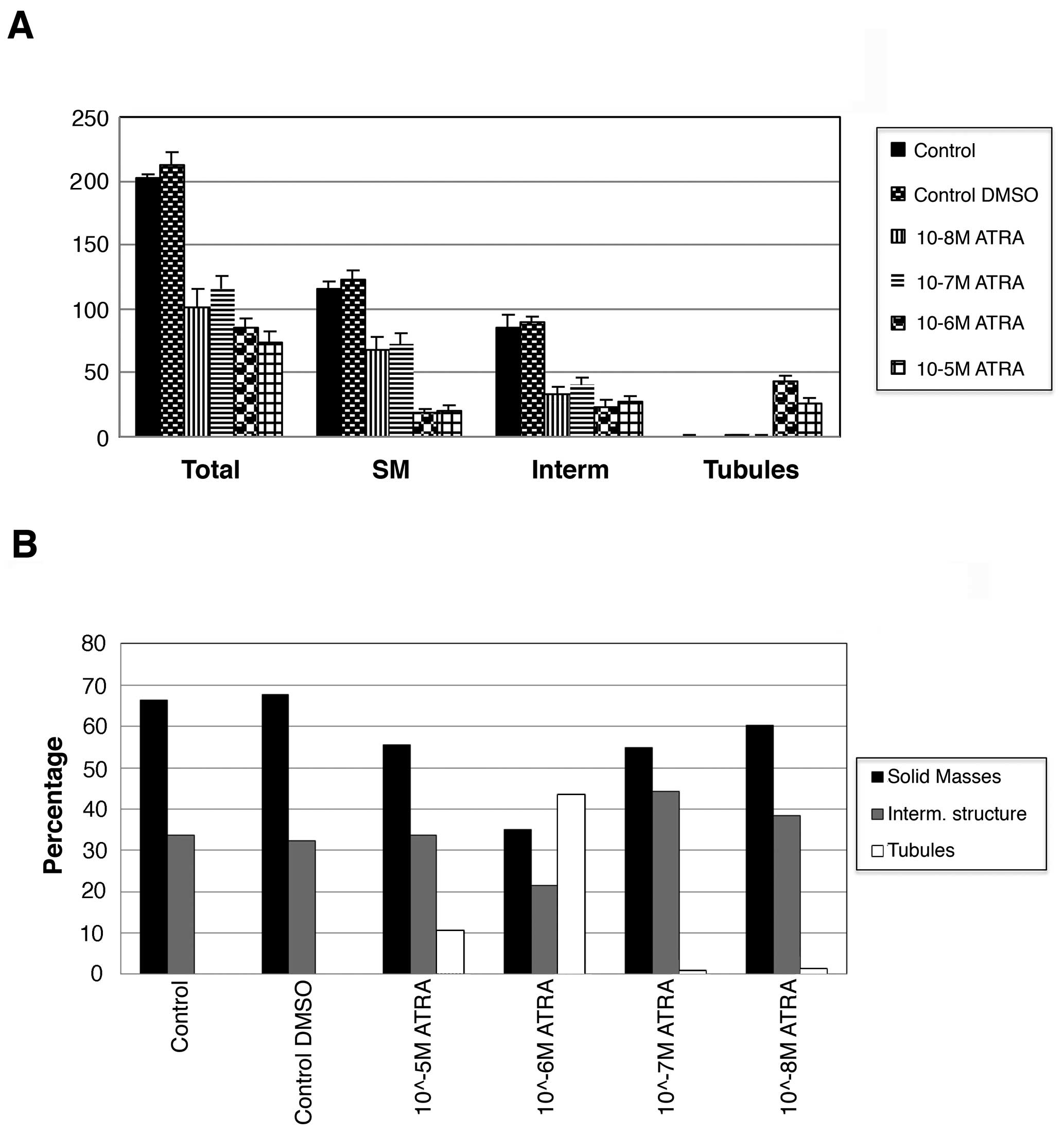
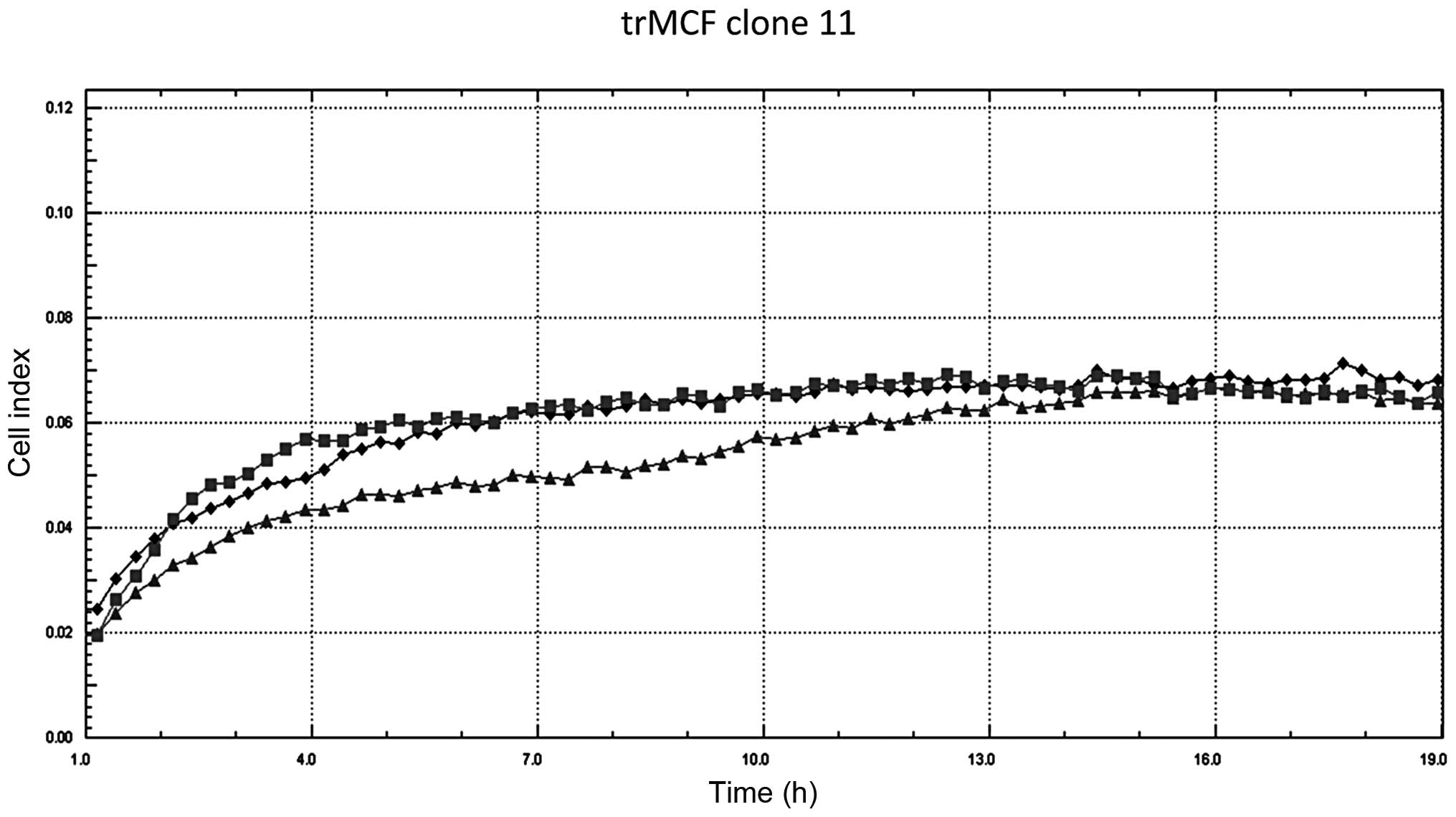
Russo J, Fernandez SV, Russo PA, et al:
17-Beta-estradiol induces transformation and tumorigenesis in human
breast epithelial cells. FASEB J. 20:1622–1634. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Huang Y, Fernandez SV, Goodwin S, et al:
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in human breast epithelial
cells transformed by 17beta-estradiol. Cancer Res. 67:11147–11157.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Fernandez SV and Russo J: Estrogen and
xenoestrogens in breast cancer. Toxicol Pathol. 38:110–122. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
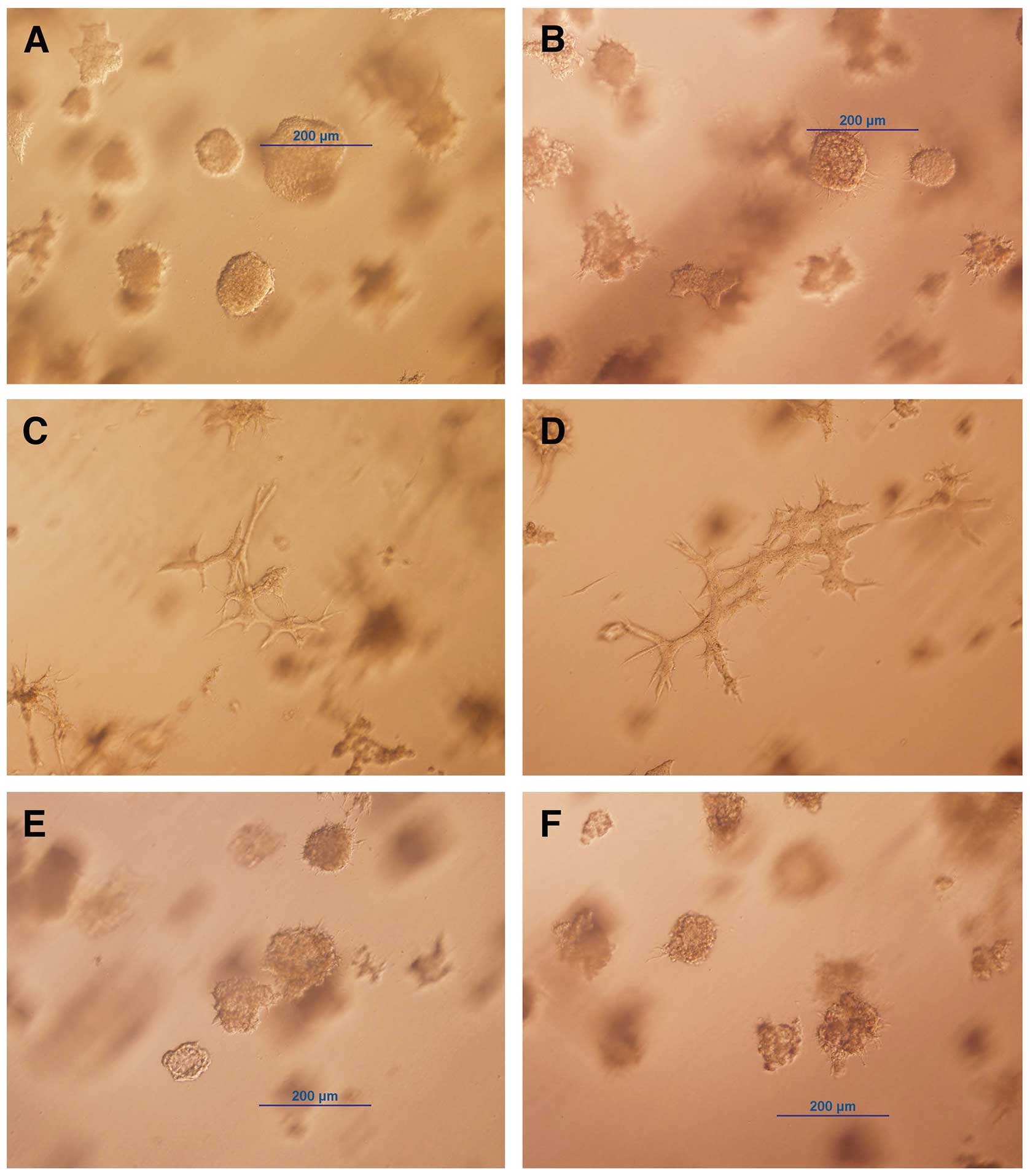
Hebner C, Weaver VM and Debnath J:
Modeling morphogenesis and oncogenesis in three-dimensional breast
epithelial cultures. Annu Rev Pathol. 3:313–339. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Snider KE, Ehya H, Russo J and Fernandez
SV: NRG1 and RARB hypermethylation in breast cancer progression.
In: Proceedings of the ACCR 102nd Anual Meeting; Orlando, FL..
Cancer Res. 71(Suppl 1): abs. 75. pp. 2011
|
|
20.
|
Glass CK and Rosenfeld MG: The coregulator
exchange in transcriptional functions of nuclear receptors. Genes
Dev. 14:121–141. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Hartman HB, Yu J, Alenghat T, Ishizuka T
and Lazar MA: The histone-binding code of nuclear receptor
co-repressors matches the substrate specificity of histone
deacetylase 3. EMBO Rep. 6:445–451. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Lefebvre B, Ozato K and Lefebvre P:
Phosphorylation of histone H3 is functionally linked to retinoic
acid receptor beta promoter activation. EMBO Rep. 3:335–340. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
McKenna NJ and O’Malley BW: Combinatorial
control of gene expression by nuclear receptors and coregulators.
Cell. 108:465–474. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Rochette-Egly C: Dynamic combinatorial
networks in nuclear receptor-mediated transcription. J Biol Chem.
280:32565–32568. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Chen H, Lin RJ, Xie W, Wilpitz D and Evans
RM: Regulation of hormone-induced histone hyperacetylation and gene
activation via acetylation of an acetylase. Cell. 98:675–686. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Bhat-Nakshatri P, Goswami CP, Badve S,
Sledge GW Jr and Nakshatri H: Identification of FDA-approved drugs
targeting breast cancer stem cells along with biomarkers of
sensitivity. Sci Rep. 3:25302013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Gudas LJ: Retinoids induce stem cell
differentiation via epigenetic changes. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
24:701–705. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Zhang XK, Liu Y and Lee MO: Retinoid
receptors in human lung cancer and breast cancer. Mutat Res.
350:267–277. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Hua S, Kittler R and White KP: Genomic
antagonism between retinoic acid and estrogen signaling in breast
cancer. Cell. 137:1259–1271. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Soprano DR and Soprano KJ: Pharmacological
doses of some synthetic retinoids can modulate both the aryl
hydrocarbon receptor and retinoid receptor pathways. J Nutr.
133:277S–281S. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Murphy KA, Quadro L and White LA: The
intersection between the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR)- and
retinoic acid-signaling pathways. Vitam Horm. 75:33–67. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Hail N Jr, Kim HJ and Lotan R: Mechanisms
of fenretinide-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis. 11:1677–1694. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33.
|
McCormick DL, Becci PJ and Moon RC:
Inhibition of mammary and urinary bladder carcinogenesis by a
retinoid and a maleic anhydride-divinyl ether copolymer (MVE-2).
Carcinogenesis. 3:1473–1476. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34.
|
McCormick DL and Moon RC: Antipromotional
activity of dietary N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide in two-stage skin
tumorigenesis in CD-1 and SENCAR mice. Cancer Lett. 31:133–138.
1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Moon RC, Pritchard JF, Mehta RG, Nomides
CT, Thomas CF and Dinger NM: Suppression of rat mammary cancer
development by N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide (4-HPR) following
surgical removal of first palpable tumor. Carcinogenesis.
10:1645–1649. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Pollard M, Luckert PH and Sporn MB:
Prevention of primary prostate cancer in Lobund-Wistar rats by
N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide. Cancer Res. 51:3610–3611.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|