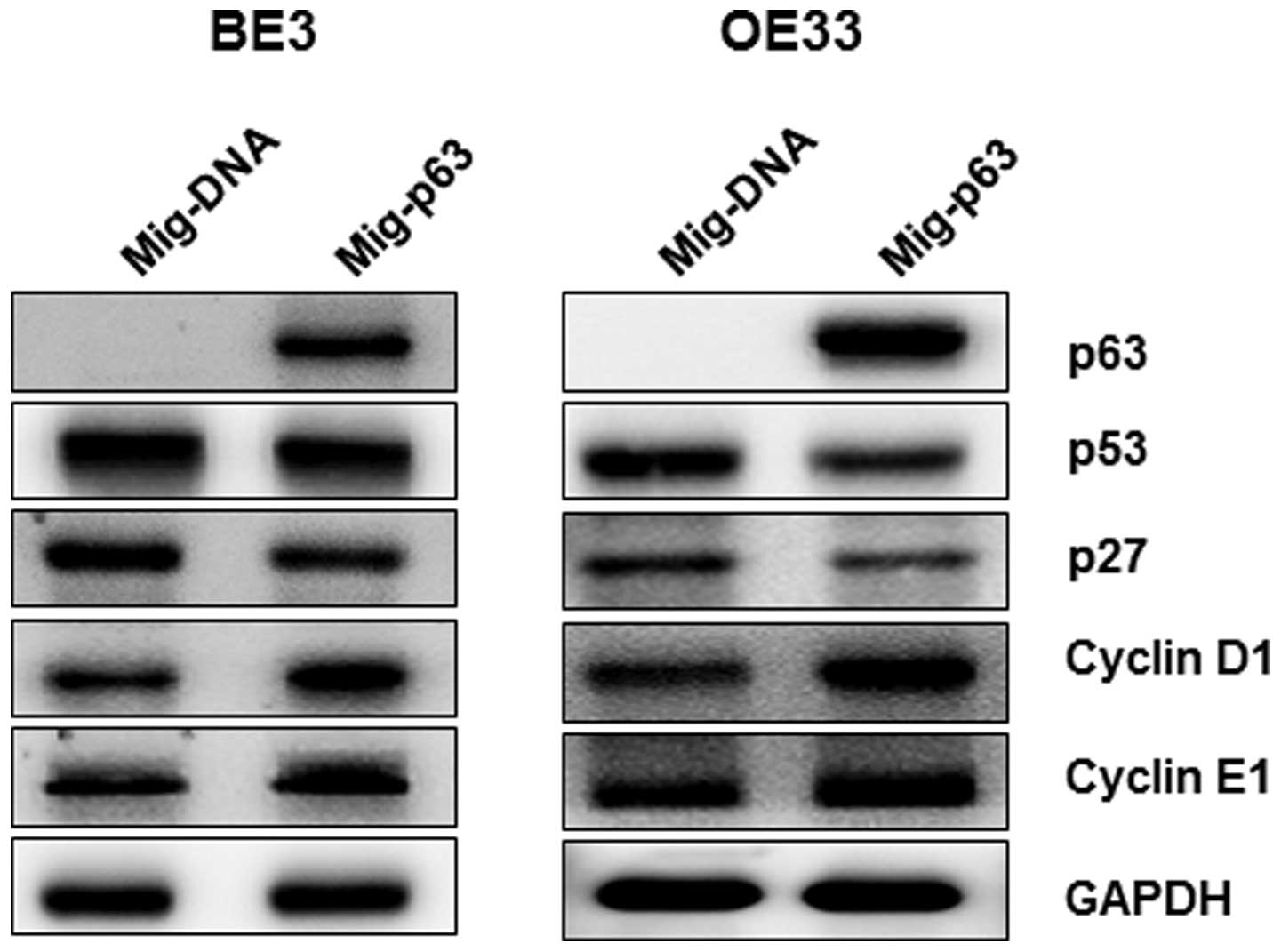
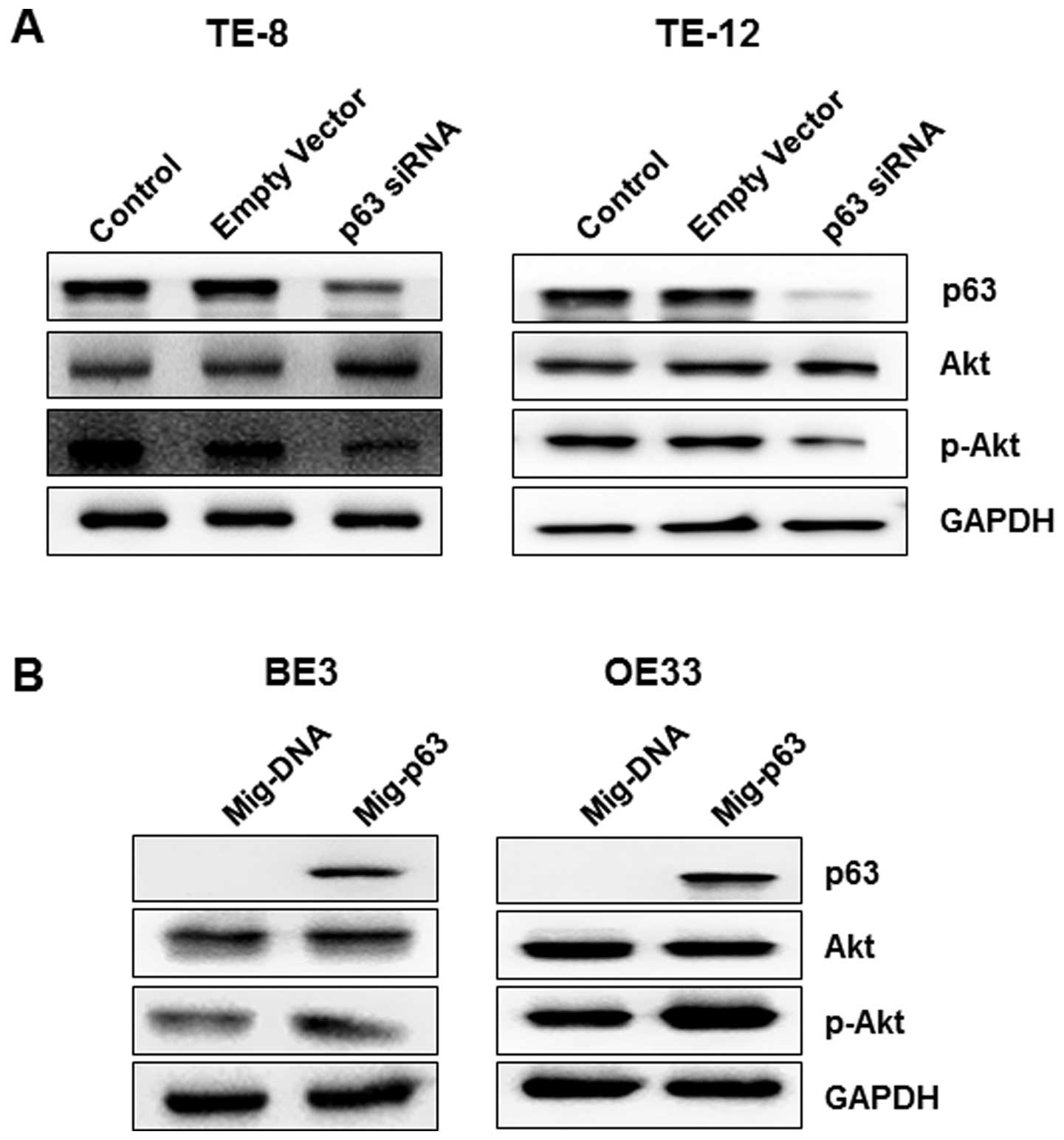
|
1.
|
Guo W and Jiang YG: Current gene
expression studies in esophageal carcinoma. Curr Genomics.
10:534–539. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Scott RB, Harrison J, Boulton C, et al:
Global attentional-executive sequelae following surgical lesions to
globus pallidus interna. Brain. 125:562–574. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Enzinger PC and Mayer RJ: Esophageal
cancer. N Engl J Med. 349:2241–2252. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Bergholz J and Xiao ZX: Role of p63 in
development, tumorigenesis and cancer progression. Cancer
Microenviron. 5:311–322. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Wu N, Rollin J, Masse I, Lamartine J and
Gidrol X: p63 regulates human keratinocyte proliferation via
MYC-regulated gene network and differentiation commitment through
cell adhesion-related gene network. J Biol Chem. 287:5627–5638.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Celli J, Duijf P, Hamel BC, et al:
Heterozygous germline mutations in the p53 homolog p63 are the
cause of EEC syndrome. Cell. 99:143–153. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Mills AA, Zheng B, Wang XJ, Vogel H, Roop
DR and Bradley A: p63 is a p53 homologue required for limb and
epidermal morphogenesis. Nature. 398:708–713. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Yang A, Schweitzer R, Sun D, et al: p63 is
essential for regenerative proliferation in limb, craniofacial and
epithelial development. Nature. 398:714–718. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Higashikawa K, Yoneda S, Tobiume K, Taki
M, Shigeishi H and Kamata N: Snail-induced down-regulation of
DeltaNp63alpha acquires invasive phenotype of human squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 67:9207–9213. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Deyoung MP and Ellisen LW: p63 and p73 in
human cancer: defining the network. Oncogene. 26:5169–5183. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Danilov AV, Neupane D, Nagaraja AS, et al:
DeltaNp63alpha-mediated induction of epidermal growth factor
receptor promotes pancreatic cancer cell growth and
chemoresistance. PloS One. 6:e268152011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Lee HH, Ye S, Li XJ, Lee KB, Park MH and
Kim SM: Combination treatment with paclitaxel and doxorubicin
inhibits growth of human esophageal squamous cancer cells by
inactivation of Akt. Oncol Rep. 31:183–188. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Kim AH, Khursigara G, Sun X, Franke TF and
Chao MV: Akt phosphorylates and negatively regulates apoptosis
signal-regulating kinase 1. Mol Cell Biol. 21:893–901. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Zhang HB, Lu P, Guo QY, Zhang ZH and Meng
XY: Baicalein induces apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma cells through modulation of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Oncol
Lett. 5:722–728. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Lin ML, Lu YC, Chen HY, Lee CC, Chung JG
and Chen SS: Suppressing the formation of lipid raft-associated
Rac1/PI3K/Akt signaling complexes by curcumin inhibits
SDF-1α-induced invasion of human esophageal carcinoma cells. Mol
Carcinog. 53:360–379. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Li XJ, Park ES, Park MH and Kim SM:
3,3′-Diindolylmethane suppresses the growth of gastric cancer cells
via activation of the Hippo signaling pathway. Oncol Rep.
30:2419–2426. 2013.
|
|
17.
|
Li XJ, Leem SH, Park MH and Kim SM:
Regulation of YAP through an Akt-dependent process by
3,3′-diindolylmethane in human colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
43:1992–1998. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Yang A, Kaghad M, Wang Y, et al: p63, a
p53 homolog at 3q27–29, encodes multiple products with
transactivating, death-inducing, and dominant-negative activities.
Mol Cell. 2:305–316. 1998.
|
|
19.
|
Di Como CJ, Urist MJ, Babayan I, et al:
p63 expression profiles in human normal and tumor tissues. Clin
Cancer Res. 8:494–501. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Parsa R, Yang A, McKeon F and Green H:
Association of p63 with proliferative potential in normal and
neoplastic human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 113:1099–1105.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Leonard MK, Kommagani R, Payal V, Mayo LD,
Shamma HN and Kadakia MP: DeltaNp63alpha regulates keratinocyte
proliferation by controlling PTEN expression and localization. Cell
Death Differ. 18:1924–1933. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Hara T, Kijima H, Yamamoto S, et al:
Ubiquitous p63 expression in human esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 14:169–173. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, et al:
Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 406:747–752.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Matos I, Dufloth R, Alvarenga M, Zeferino
LC and Schmitt F: p63, cytokeratin 5, and P-cadherin: three
molecular markers to distinguish basal phenotype in breast
carcinomas. Virchows Arch. 447:688–694. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Hu H, Xia SH, Li AD, et al: Elevated
expression of p63 protein in human esophageal squamous cell
carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 102:580–583. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Sniezek JC, Matheny KE, Westfall MD and
Pietenpol JA: Dominant negative p63 isoform expression in head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 114:2063–2072. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Massion PP, Taflan PM, Jamshedur Rahman
SM, et al: Significance of p63 amplification and overexpression in
lung cancer development and prognosis. Cancer Res. 63:7113–7121.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Weber A, Bellmann U, Bootz F, Wittekind C
and Tannapfel A: Expression of p53 and its homologues in primary
and recurrent squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Int J
Cancer. 99:22–28. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Chatterjee A, Chang X, Sen T, Ravi R, Bedi
A and Sidransky D: Regulation of p53 family member isoform
DeltaNp63alpha by the nuclear factor-kappaB targeting kinase
IkappaB kinase beta. Cancer Res. 70:1419–1429. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Westfall MD, Mays DJ, Sniezek JC and
Pietenpol JA: The Delta Np63 alpha phosphoprotein binds the p21 and
14-3-3 sigma promoters in vivo and has transcriptional repressor
activity that is reduced by Hay-Wells syndrome-derived mutations.
Mol Cell Biol. 23:2264–2276. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31.
|
Truong AB, Kretz M, Ridky TW, Kimmel R and
Khavari PA: p63 regulates proliferation and differentiation of
developmentally mature keratinocytes. Genes Dev. 20:3185–3197.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
DeYoung MP, Johannessen CM, Leong CO,
Faquin W, Rocco JW and Ellisen LW: Tumor-specific p73 up-regulation
mediates p63 dependence in squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res.
66:9362–9368. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Ha L, Ponnamperuma RM, Jay S, Ricci MS and
Weinberg WC: Dysregulated DeltaNp63alpha inhibits expression of
Ink4a/arf, blocks senescence, and promotes malignant conversion of
keratinocytes. PloS One. 6:e218772011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|