|
1
|
Menendez D, Inga A and Resnick MA: The
expanding universe of p53 targets. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:724–737. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Reinhardt HC and Schumacher B: The p53
network: cellular and systemic DNA damage responses in aging and
cancer. Trends Genet. 28:128–136. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
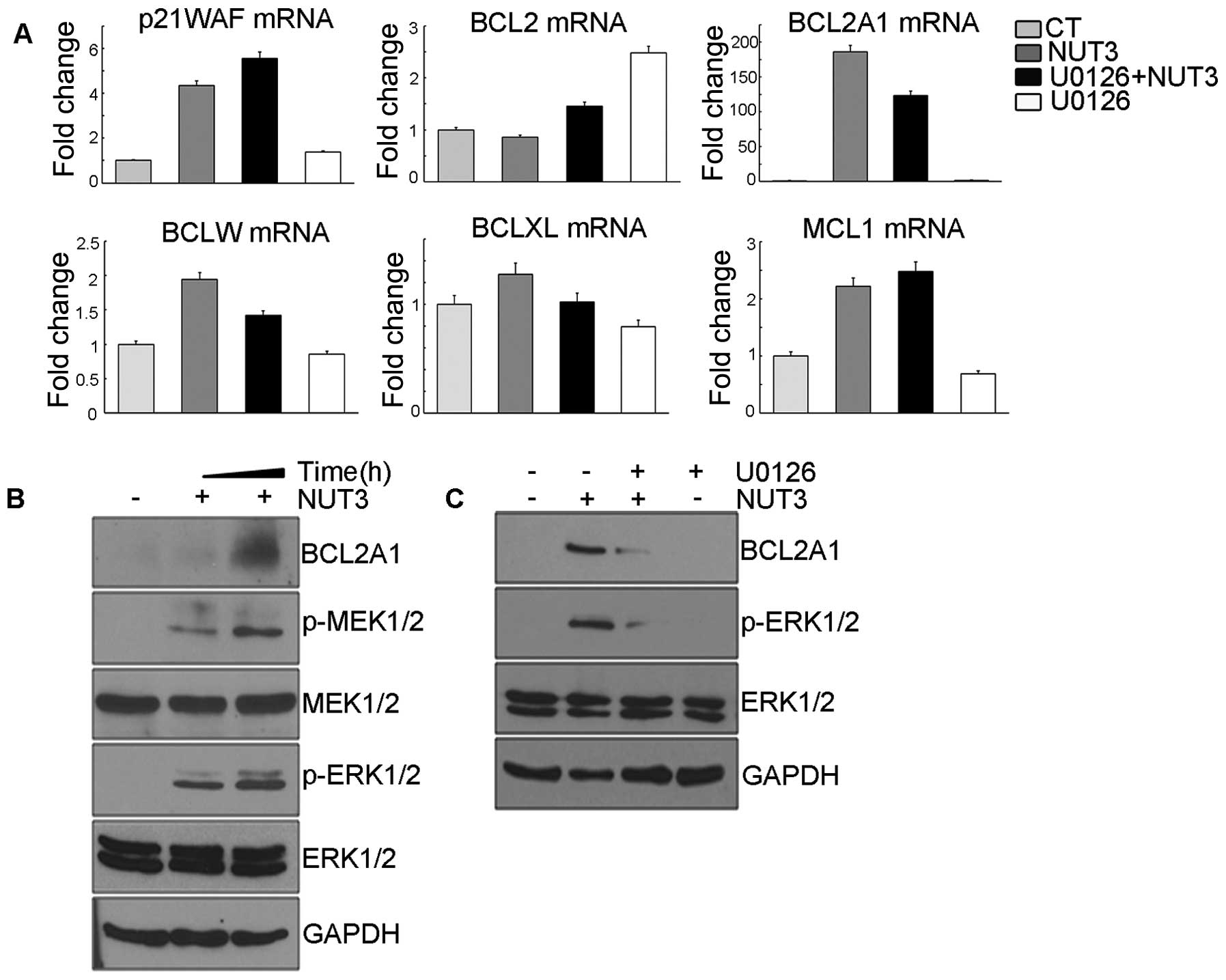
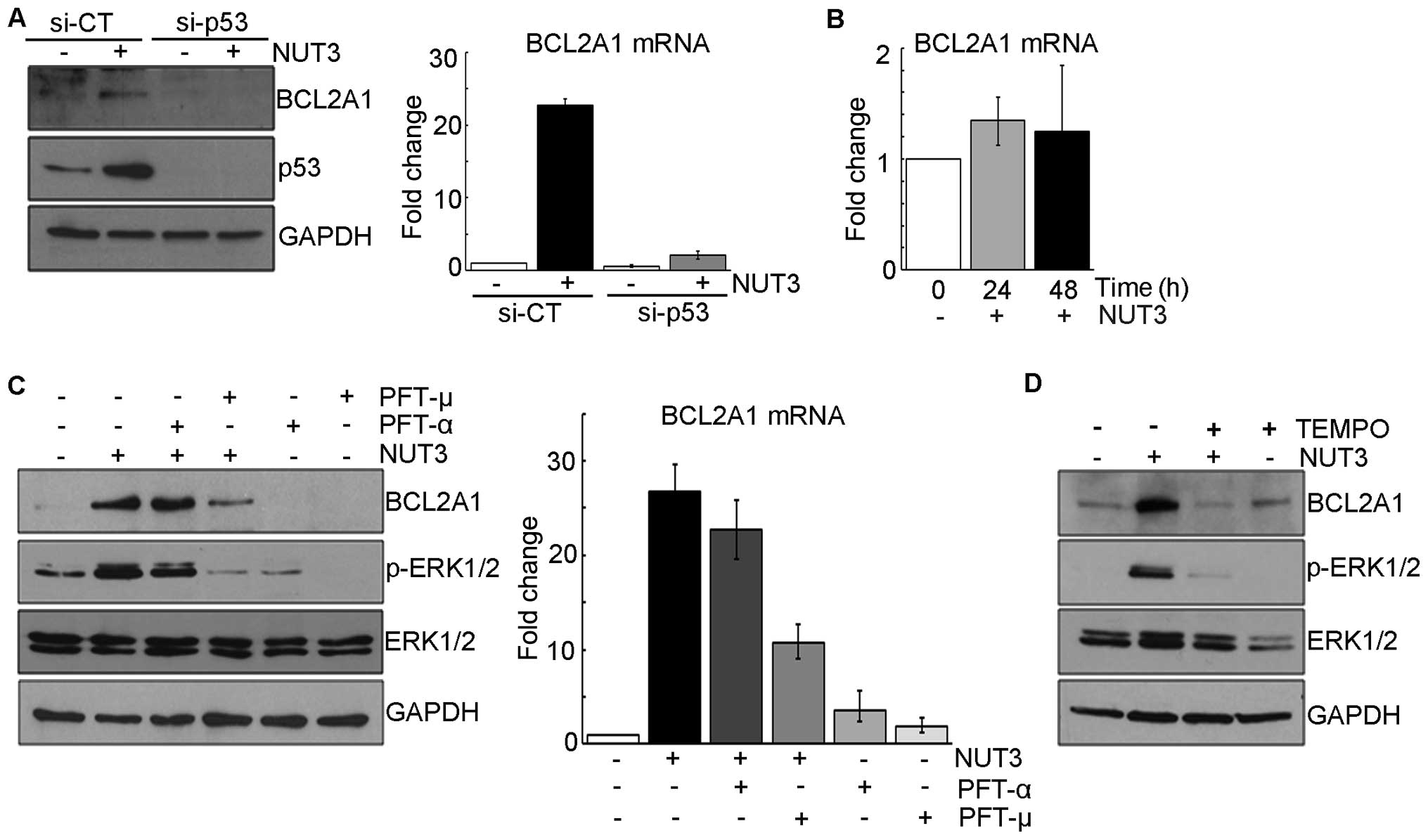
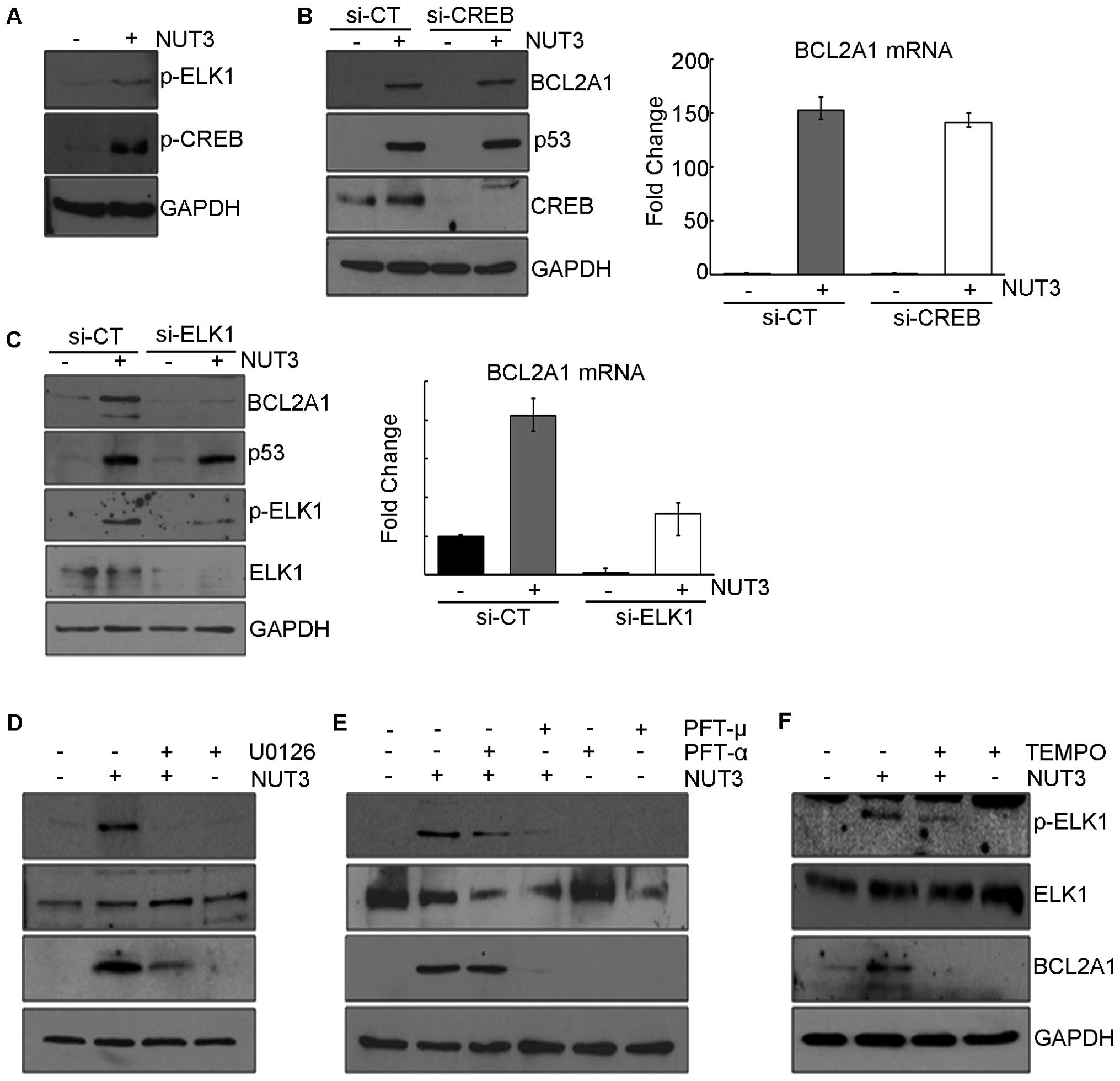
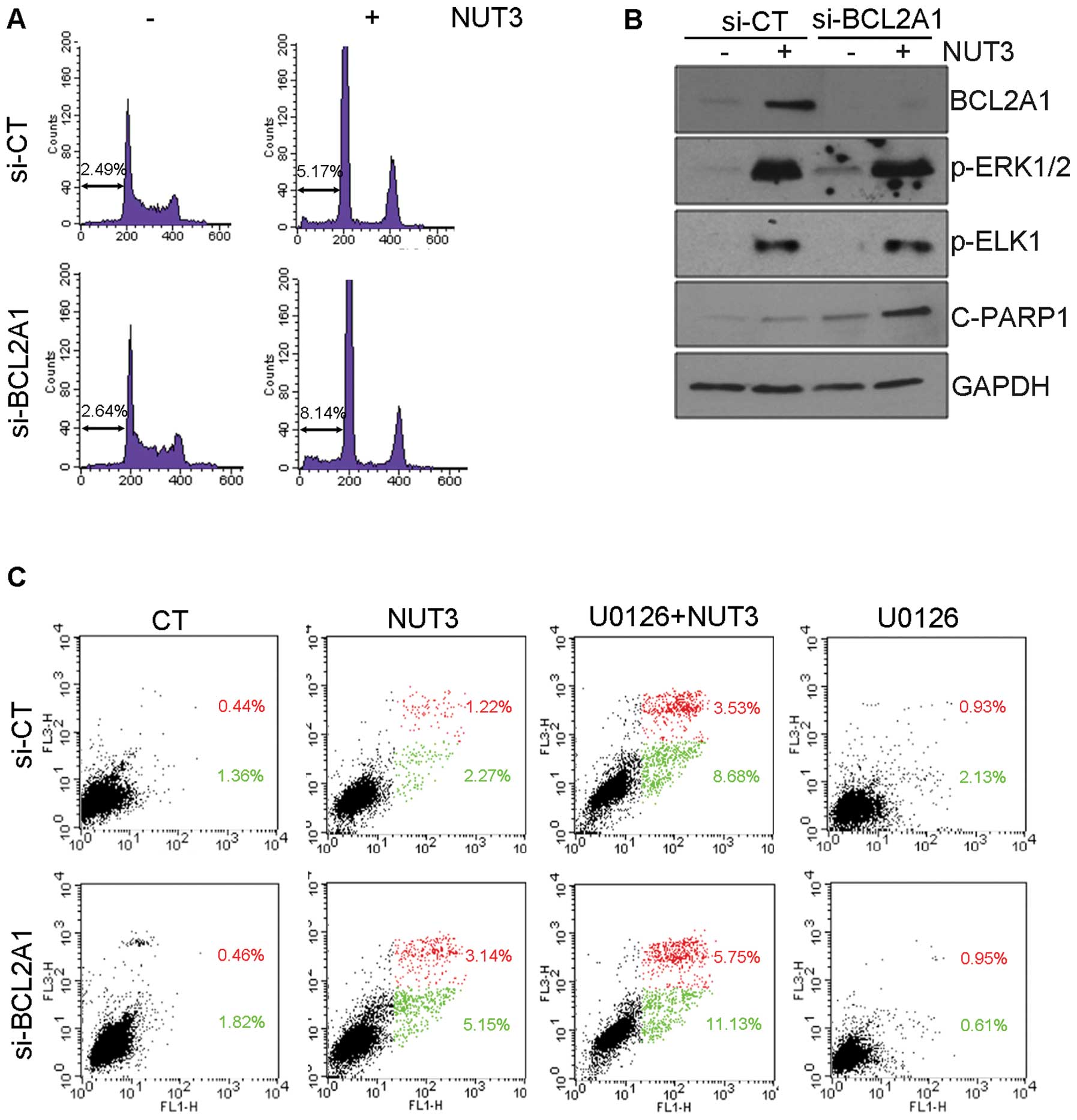
|
3
|
Chipuk JE and Green DR: Dissecting
p53-dependent apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 13:994–1002. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mihara M, Erster S, Zaika A, et al: p53
has a direct apoptogenic role at the mitochondria. Mol Cell.
11:577–590. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sot B, Freund SM and Fersht AR:
Comparative biophysical characterization of p53 with the
pro-apoptotic BAK and the anti-apoptotic BCL-xL. J Biol Chem.
282:29193–29200. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhao Y, Chaiswing L, Velez JM, et al: p53
translocation to mitochondria precedes its nuclear translocation
and targets mitochondrial oxidative defense protein-manganese
superoxide dismutase. Cancer Res. 65:3745–3750. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Erster S, Mihara M, Kim RH, Petrenko O and
Moll UM: In vivo mitochondrial p53 translocation triggers a rapid
first wave of cell death in response to DNA damage that can precede
p53 target gene activation. Mol Cell Biol. 24:6728–6741. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Palacios G and Moll UM: Mitochondrially
targeted wild-type p53 suppresses growth of mutant p53 lymphomas in
vivo. Oncogene. 25:6133–6139. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vaseva AV, Marchenko ND, Ji K, Tsirka SE,
Holzmann S and Moll UM: p53 opens the mitochondrial permeability
transition pore to trigger necrosis. Cell. 149:1536–1548. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B, et al: In
vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of
MDM2. Science. 303:844–848. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Secchiero P, Bosco R, Celeghini C and
Zauli G: Recent advances in the therapeutic perspectives of
Nutlin-3. Curr Pharm Des. 17:569–577. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vaseva AV, Marchenko ND and Moll UM: The
transcription-independent mitochondrial p53 program is a major
contributor to nutlin-induced apoptosis in tumor cells. Cell Cycle.
8:1711–1719. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Saha MN, Jiang H and Chang H: Molecular
mechanisms of nutlin-induced apoptosis in multiple myeloma:
evidence for p53-transcription-dependent and -independent pathways.
Cancer Biol Ther. 10:567–578. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee SY, Shin SJ and Kim HS: ERK1/2
activation mediated by the nutlin-3-induced mitochondrial
translocation of p53. Int J Oncol. 42:1027–1035. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jang JY, Kim MK, Jeon YK, Joung YK, Park
KD and Kim CW: Adenovirus adenine nucleotide translocator-2 shRNA
effectively induces apoptosis and enhances chemosensitivity by the
down-regulation of ABCG2 in breast cancer stem-like cells. Exp Mol
Med. 44:251–259. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee K, Lee MH, Kang YW, Rhee KJ, Kim TU
and Kim YS: Parkin induces apoptotic cell death in
TNF-alpha-treated cervical cancer cells. BMB Rep. 45:526–531. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lau LM, Nugent JK, Zhao X and Irwin MS:
HDM2 antagonist Nutlin-3 disrupts p73-HDM2 binding and enhances p73
function. Oncogene. 27:997–1003. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Roberts PJ and Der CJ: Targeting the
Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the
treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 26:3291–3310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Johannessen M, Delghandi MP and Moens U:
What turns CREB on? Cell Signal. 16:1211–1227. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Choe YJ, Lee SY, Ko KW, Shin SJ and Kim
HS: Nutlin-3 induces HO-1 expression by activating JNK in a
transcription-independent manner of p53. Int J Oncol. 44:761–768.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Karsan A, Yee E, Kaushansky K and Harlan
JM: Cloning of human Bcl-2 homologue: inflammatory cytokines induce
human A1 in cultured endothelial cells. Blood. 87:3089–3096.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee HH, Dadgostar H, Cheng Q, Shu J and
Cheng G: NF-kappaB-mediated up-regulation of Bcl-x and Bfl-1/A1 is
required for CD40 survival signaling in B lymphocytes. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 96:9136–9141. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim H, Kim YN, Kim H and Kim CW: Oxidative
stress attenuates Fas-mediated apoptosis in Jurkat T cell line
through Bfl-1 induction. Oncogene. 24:1252–1261. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Karsan A, Yee E and Harlan JM: Endothelial
cell death induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha is inhibited by
the Bcl-2 family member, A1. J Biol Chem. 271:27201–27204. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim HR, Heo YM, Jeong KI, et al: FGF-2
inhibits TNF-alpha mediated apoptosis through upregulation of
Bcl2-A1 and Bcl-xL in ATDC5 cells. BMB Rep. 45:287–292. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Goncharenko-Khaider N, Matte I, Lane D,
Rancourt C and Piche A: Ovarian cancer ascites increase Mcl-1
expression in tumor cells through ERK1/2-Elk-1 signaling to
attenuate TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Mol Cancer. 11:842012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang CY, Guttridge DC, Mayo MW and Baldwin
AS Jr: NF-kappaB induces expression of the Bcl-2 homologue A1/Bfl-1
to preferentially suppress chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell
Biol. 19:5923–5929. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Simmons MJ, Fan G, Zong WX, Degenhardt K,
White E and Gelinas C: Bfl-1/A1 functions, similar to Mcl-1, as a
selective tBid and Bak antagonist. Oncogene. 27:1421–1428. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kasza A: Signal-dependent Elk-1 target
genes involved in transcript processing and cell migration. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1829:1026–1033. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Booy EP, Henson ES and Gibson SB:
Epidermal growth factor regulates Mcl-1 expression through the
MAPK-Elk-1 signalling pathway contributing to cell survival in
breast cancer. Oncogene. 30:2367–2378. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sun NK, Huang SL, Chang TC and Chao CC:
Sorafenib induces endometrial carcinoma apoptosis by inhibiting
Elk-1-dependent Mcl-1 transcription and inducing
Akt/GSK3beta-dependent protein degradation. J Cell Biochem.
114:1819–1831. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shangary S, Qin D, McEachern D, et al:
Temporal activation of p53 by a specific MDM2 inhibitor is
selectively toxic to tumors and leads to complete tumor growth
inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:3933–3938. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Travis LB, Ng AK, Allan JM, et al: Second
malignant neoplasms and cardiovascular disease following
radiotherapy. Health Phys. 106:229–246. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tovar C, Rosinski J, Filipovic Z, et al:
Small-molecule MDM2 antagonists reveal aberrant p53 signaling in
cancer: implications for therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:1888–1893. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Moreno CS, Matyunina L, Dickerson EB, et
al: Evidence that p53-mediated cell-cycle-arrest inhibits
chemotherapeutic treatment of ovarian carcinomas. PLoS One.
2:e4412007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rinaldo C, Prodosmo A, Siepi F, et al:
HIPK2 regulation by MDM2 determines tumor cell response to the
p53-reactivating drugs nutlin-3 and RITA. Cancer Res. 69:6241–6248.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Enge M, Bao W, Hedstrom E, Jackson SP,
Moumen A and Selivanova G: MDM2-dependent downregulation of p21 and
hnRNP K provides a switch between apoptosis and growth arrest
induced by pharmacologically activated p53. Cancer Cell.
15:171–183. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Choi SS, Park IC, Yun JW, Sung YC, Hong SI
and Shin HS: A novel Bcl-2 related gene, Bfl-1, is overexpressed in
stomach cancer and preferentially expressed in bone marrow.
Oncogene. 11:1693–1698. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Riker AI, Enkemann SA, Fodstad O, et al:
The gene expression profiles of primary and metastatic melanoma
yields a transition point of tumor progression and metastasis. BMC
Med Genomics. 1:132008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Simpson LA, Burwell EA, Thompson KA,
Shahnaz S, Chen AR and Loeb DM: The antiapoptotic gene A1/BFL1 is a
WT1 target gene that mediates granulocytic differentiation and
resistance to chemotherapy. Blood. 107:4695–4702. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Brien G, Trescol-Biemont MC and
Bonnefoy-Berard N: Downregulation of Bfl-1 protein expression
sensitizes malignant B cells to apoptosis. Oncogene. 26:5828–5832.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Vogler M, Butterworth M, Majid A, et al:
Concurrent up-regulation of BCL-XL and BCL2A1 induces approximately
1000-fold resistance to ABT-737 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Blood. 113:4403–4413. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Haq R, Yokoyama S, Hawryluk EB, et al:
BCL2A1 is a lineage-specific antiapoptotic melanoma oncogene that
confers resistance to BRAF inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:4321–4326. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|