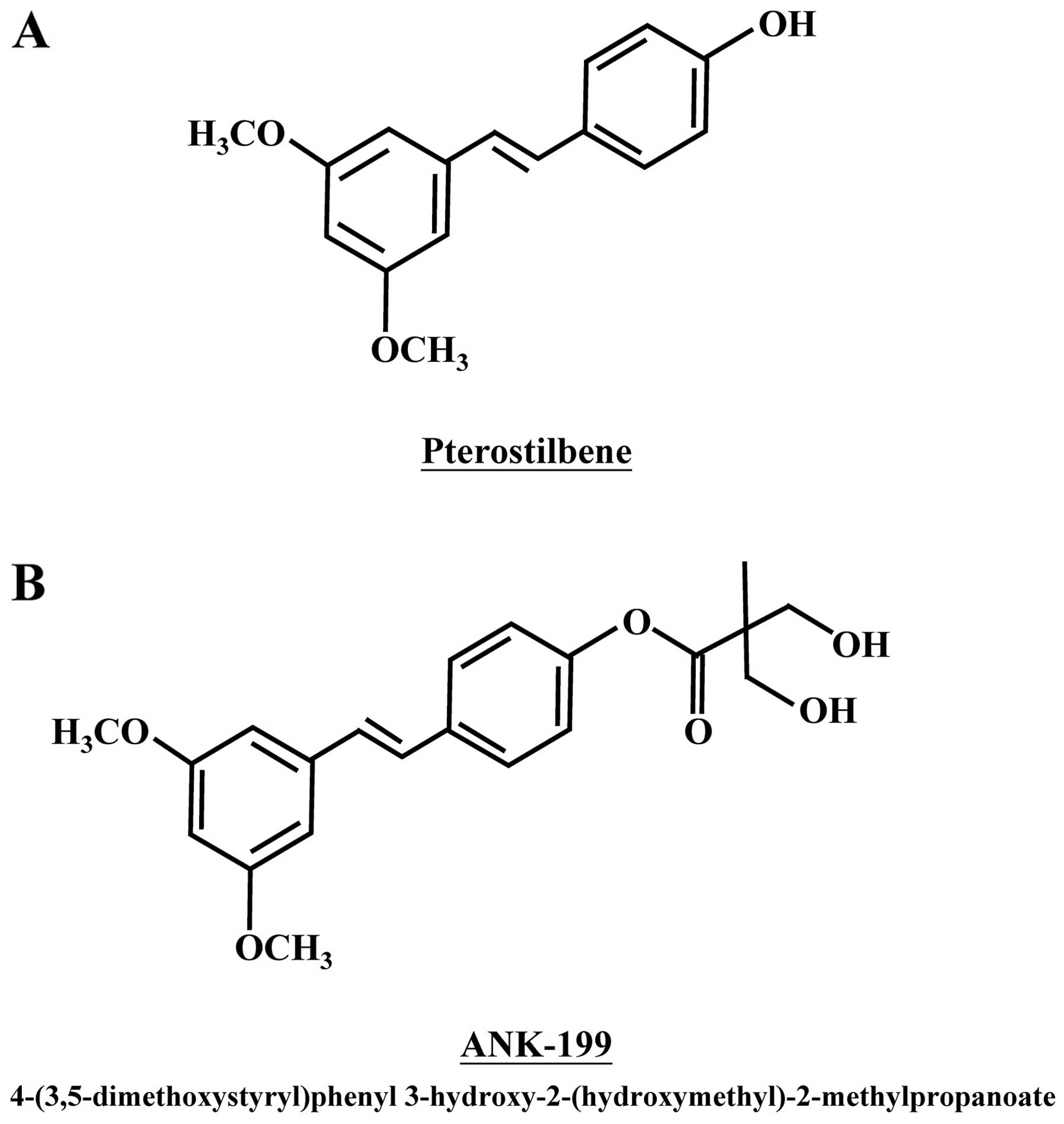
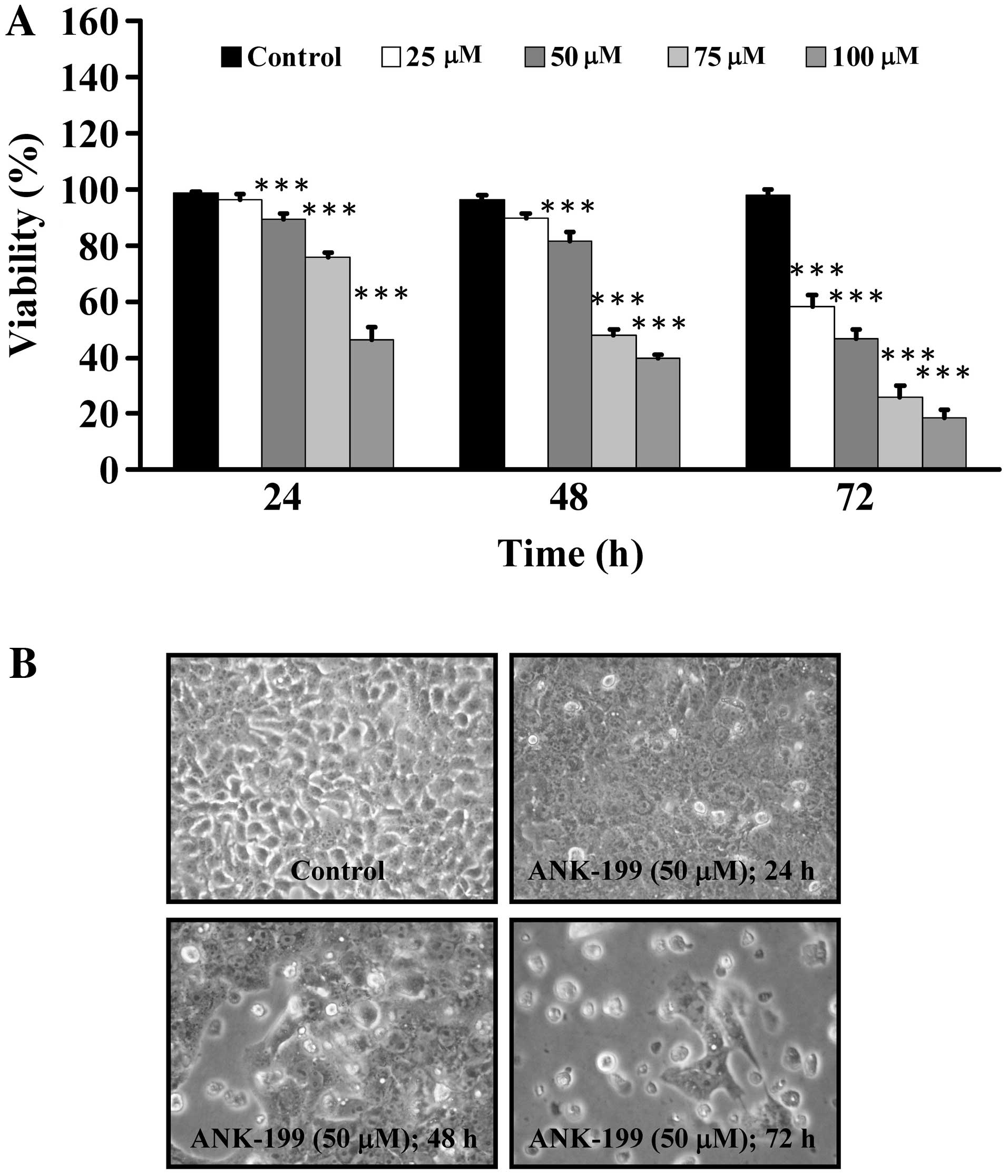
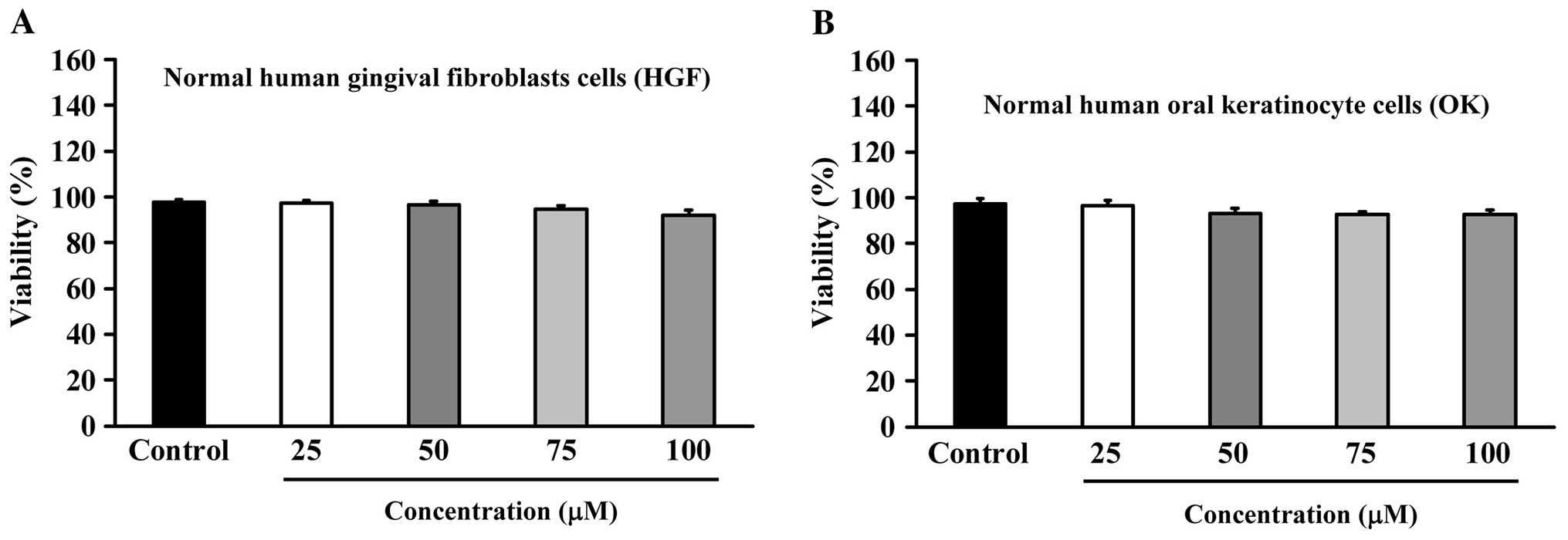
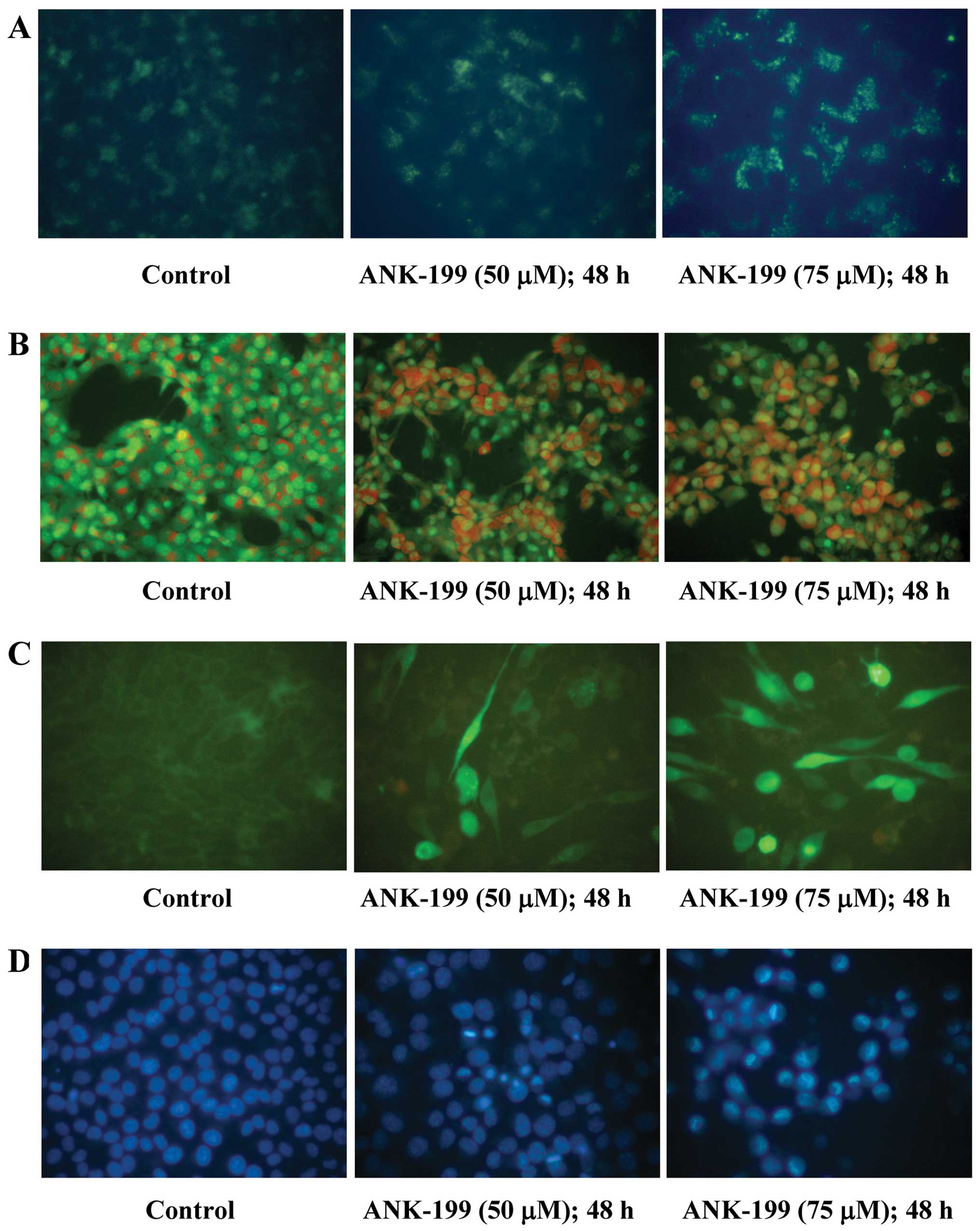
|
1
|
Estrela JM, Ortega A, Mena S, Rodriguez ML
and Asensi M: Pterostilbene: Biomedical applications. Crit Rev Clin
Lab Sci. 50:65–78. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
McCormack D and McFadden D: A review of
pterostilbene antioxidant activity and disease modification. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2013:5754822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cherniack EP: A berry thought-provoking
idea: the potential role of plant polyphenols in the treatment of
age-related cognitive disorders. Br J Nutr. 108:794–800. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
McCormack D and McFadden D: Pterostilbene
and cancer: current review. J Surg Res. 173:e53–e61. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mikstacka R and Ignatowicz E:
Chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic effect of trans-resveratrol
and its analogues in cancer. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 28:496–500.
2010.(In Polish).
|
|
6
|
Rimando AM and Suh N:
Biological/chemopreventive activity of stilbenes and their effect
on colon cancer. Planta Med. 74:1635–1643. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li N, Ma Z, Li M, Xing Y and Hou Y:
Natural potential therapeutic agents of neurodegenerative diseases
from the traditional herbal medicine Chinese Dragons Blood. J
Ethnopharmacol. 152:508–521. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Paul S, Rimando AM, Lee HJ, Ji Y, Reddy BS
and Suh N: Anti-inflammatory action of pterostilbene is mediated
through the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in colon
cancer cells. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2:650–657. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pan MH, Chang YH, Tsai ML, et al:
Pterostilbene suppressed lipopolysaccharide-induced up-expression
of iNOS and COX-2 in murine macrophages. J Agric Food Chem.
56:7502–7509. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Perecko T, Drabikova K, Rackova L, et al:
Molecular targets of the natural antioxidant pterostilbene: effect
on protein kinase C, caspase-3 and apoptosis in human neutrophils
in vitro. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 31(Suppl 2): 84–90.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Perecko T, Jancinova V, Drabikova K, Nosal
R and Harmatha J: Structure-efficiency relationship in derivatives
of stilbene. Comparison of resveratrol, pinosylvin and
pterostilbene. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 29:802–805. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rossi M, Caruso F, Antonioletti R, et al:
Scavenging of hydroxyl radical by resveratrol and related natural
stilbenes after hydrogen peroxide attack on DNA. Chem Biol
Interact. 206:175–185. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Acharya JD and Ghaskadbi SS: Protective
effect of pterostilbene against free radical mediated oxidative
damage. BMC Complement Altern Med. 13:2382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rimando AM, Cuendet M, Desmarchelier C,
Mehta RG, Pezzuto JM and Duke SO: Cancer chemopreventive and
antioxidant activities of pterostilbene, a naturally occurring
analogue of resveratrol. J Agric Food Chem. 50:3453–3457. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pan MH, Chang YH, Badmaev V, Nagabhushanam
K and Ho CT: Pterostilbene induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest
in human gastric carcinoma cells. J Agric Food Chem. 55:7777–7785.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ferrer P, Asensi M, Priego S, et al:
Nitric oxide mediates natural polyphenol-induced Bcl-2
down-regulation and activation of cell death in metastatic B16
melanoma. J Biol Chem. 282:2880–2890. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Siedlecka-Kroplewska K, Jozwik A,
Boguslawski W, et al: Pterostilbene induces accumulation of
autophagic vacuoles followed by cell death in HL60 human leukemia
cells. J Physiol Pharmacol. 64:545–556. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hsieh MJ, Lin CW, Yang SF, et al: A
combination of pterostilbene with autophagy inhibitors exerts
efficient apoptotic characteristics in both chemosensitive and
chemoresistant lung cancer cells. Toxicol Sci. 137:65–75. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kapoor S: Pterostilbene and its emerging
antineoplastic effects: a prospective treatment option for systemic
malignancies. Am J Surg. 205:4832013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tippani R, Prakhya LJ, Porika M, Sirisha
K, Abbagani S and Thammidala C: Pterostilbene as a potential novel
telomerase inhibitor: Molecular docking studies and its in vitro
evaluation. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. Jan 12–2014.(Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
21
|
Li K, Dias SJ, Rimando AM, et al:
Pterostilbene acts through metastasis-associated protein 1 to
inhibit tumor growth, progression and metastasis in prostate
cancer. PLoS One. 8:e575422013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
McCormack DE, Mannal P, McDonald D, Tighe
S, Hanson J and McFadden D: Genomic analysis of pterostilbene
predicts its antiproliferative effects against pancreatic cancer in
vitro and in vivo. J Gastrointest Surg. 16:1136–1143. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mannal PW, Alosi JA, Schneider JG,
McDonald DE and McFadden DW: Pterostilbene inhibits pancreatic
cancer in vitro. J Gastrointest Surg. 14:873–879. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Moon D, McCormack D, McDonald D and
McFadden D: Pterostilbene induces mitochondrially derived apoptosis
in breast cancer cells in vitro. J Surg Res. 180:208–215. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pan MH, Lin YT, Lin CL, Wei CS, Ho CT and
Chen WJ: Suppression of heregulin-beta1/HER2-modulated invasive and
aggressive phenotype of breast carcinoma by pterostilbene via
inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9, p38 kinase cascade and
Akt activation. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2011:5621872011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang Y, Yan X, Duan W, et al:
Pterostilbene exerts antitumor activity via the Notch1 signaling
pathway in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. PLoS One. 8:e626522013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu Y, Wang L, Wu Y, et al: Pterostilbene
exerts antitumor activity against human osteosarcoma cells by
inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Toxicology.
304:120–131. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lin VC, Tsai YC, Lin JN, et al: Activation
of AMPK by pterostilbene suppresses lipogenesis and cell-cycle
progression in p53 positive and negative human prostate cancer
cells. J Agric Food Chem. 60:6399–6407. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chakraborty A, Gupta N, Ghosh K and Roy P:
In vitro evaluation of the cytotoxic, anti-proliferative and
anti-oxidant properties of pterostilbene isolated from
Pterocarpus marsupium. Toxicol In Vitro. 24:1215–1228. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Roslie H, Chan KM, Rajab NF, et al:
3,5-Dibenzyloxy-4′-hydroxystilbene induces early caspase-9
activation during apoptosis in human K562 chronic myelogenous
leukemia cells. J Toxicol Sci. 37:13–21. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tolomeo M, Grimaudo S, Di Cristina A, et
al: Pterostilbene and 3′-hydroxypterostilbene are effective
apoptosis-inducing agents in MDR and BCR-ABL-expressing leukemia
cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 37:1709–1726. 2005.
|
|
32
|
Mena S, Rodriguez ML, Ponsoda X, Estrela
JM, Jaattela M and Ortega AL: Pterostilbene-induced tumor
cytotoxicity: a lysosomal membrane permeabilization-dependent
mechanism. PLoS One. 7:e445242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Harun Z and Ghazali AR: Potential
chemoprevention activity of pterostilbene by enhancing the
detoxifying enzymes in the HT-29 cell line. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 13:6403–6407. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nutakul W, Sobers HS, Qiu P, et al:
Inhibitory effects of resveratrol and pterostilbene on human colon
cancer cells: a side-by-side comparison. J Agric Food Chem.
59:10964–10970. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang CS, Ho CT, Tu SH, et al: Long-term
ethanol exposure-induced hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration
and invasion through lysyl oxidase activation are attenuated by
combined treatment with pterostilbene and curcumin analogues. J
Agric Food Chem. 61:4326–4335. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Pan MH, Chiou YS, Chen WJ, Wang JM,
Badmaev V and Ho CT: Pterostilbene inhibited tumor invasion via
suppressing multiple signal transduction pathways in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis. 30:1234–1242. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Siedlecka-Kroplewska K, Jozwik A,
Kaszubowska L, Kowalczyk A and Boguslawski W: Pterostilbene induces
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in MOLT4 human leukemia cells.
Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 50:574–580. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen RJ, Tsai SJ, Ho CT, et al:
Chemopreventive effects of pterostilbene on urethane-induced lung
carcinogenesis in mice via the inhibition of EGFR-mediated pathways
and the induction of apoptosis and autophagy. J Agric Food Chem.
60:11533–11541. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chakraborty A, Bodipati N, Demonacos MK,
Peddinti R, Ghosh K and Roy P: Long term induction by pterostilbene
results in autophagy and cellular differentiation in MCF-7 cells
via ROS dependent pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 355:25–40. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen RJ, Ho CT and Wang YJ: Pterostilbene
induces autophagy and apoptosis in sensitive and chemoresistant
human bladder cancer cells. Mol Nutr Food Res. 54:1819–1832. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang L, Cui L, Zhou G, Jing H, Guo Y and
Sun W: Pterostilbene, a natural small-molecular compound, promotes
cytoprotective macroautophagy in vascular endothelial cells. J Nutr
Biochem. 24:903–911. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Riche DM, McEwen CL, Riche KD, et al:
Analysis of safety from a human clinical trial with pterostilbene.
J Toxicol. 2013:4635952013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shetty SR, Babu S, Kumari S, Prasad R,
Bhat S and Fazil KA: Salivary ascorbic acid levels in betel quid
chewers: A biochemical study. South Asian J Cancer. 2:142–144.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Arjungi KN: Areca nut: a review.
Arzneimittelforschung. 26:951–956. 1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chang PY, Peng SF, Lee CY, et al:
Curcumin-loaded nanoparticles induce apoptotic cell death through
regulation of the function of MDR1 and reactive oxygen species in
cisplatin-resistant CAR human oral cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
43:1141–1150. 2013.
|
|
46
|
Lin C, Tsai SC, Tseng MT, et al: AKT
serine/threonine protein kinase modulates baicalin-triggered
autophagy in human bladder cancer T24 cells. Int J Oncol.
42:993–1000. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tsai SC, Yang JS, Peng SF, et al: Bufalin
increases sensitivity to AKT/mTOR-induced autophagic cell death in
SK-HEP-1 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol.
41:1431–1442. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Huang WW, Tsai SC, Peng SF, et al:
Kaempferol induces autophagy through AMPK and AKT signaling
molecules and causes G2/M arrest via downregulation of CDK1/cyclin
B in SK-HEP-1 human hepatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
42:2069–2077. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Huang AC, Lien JC, Lin MW, et al:
Tetrandrine induces cell death in SAS human oral cancer cells
through caspase activation-dependent apoptosis and LC3-I and LC3-II
activation-dependent autophagy. Int J Oncol. 43:485–494. 2013.
|
|
50
|
Liu CY, Yang JS, Huang SM, et al: Smh-3
induces G(2)/M arrest and apoptosis through calcium-mediated
endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial signaling in human
hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells. Oncol Rep. 29:751–762.
2013.
|
|
51
|
Jin Z and El-Deiry WS: Overview of cell
death signaling pathways. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:139–163.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jin S and White E: Role of autophagy in
cancer: management of metabolic stress. Autophagy. 3:28–31. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Fink SL and Cookson BT: Apoptosis,
pyroptosis, and necrosis: mechanistic description of dead and dying
eukaryotic cells. Infect Immun. 73:1907–1916. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Lockshin RA and Zakeri Z: Apoptosis,
autophagy, and more. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 36:2405–2419. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Shimizu S, Yoshida T, Tsujioka M and
Arakawa S: Autophagic cell death and cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
15:3145–3153. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Mukhopadhyay S, Panda PK, Sinha N, Das DN
and Bhutia SK: Autophagy and apoptosis: where do they meet?
Apoptosis. 19:555–566. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ma Y, Galluzzi L, Zitvogel L and Kroemer
G: Autophagy and cellular immune responses. Immunity. 39:211–227.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Morselli E, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, et al:
Anti- and pro-tumor functions of autophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1793:1524–1532. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li LC, Liu GD, Zhang XJ and Li YB:
Autophagy, a novel target for chemotherapeutic intervention of
thyroid cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 73:439–449. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Meschini S, Condello M, Lista P and
Arancia G: Autophagy: Molecular mechanisms and their implications
for anticancer therapies. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 11:357–379.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Liu B, Bao JK, Yang JM and Cheng Y:
Targeting autophagic pathways for cancer drug discovery. Chin J
Cancer. 32:113–120. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ghavami S, Shojaei S, Yeganeh B, et al:
Autophagy and apoptosis dysfunction in neurodegenerative disorders.
Prog Neurobiol. 112:24–49. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Fu LL, Cheng Y and Liu B: Beclin-1:
autophagic regulator and therapeutic target in cancer. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 45:921–924. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Kang R, Zeh HJ, Lotze MT and Tang D: The
Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death
Differ. 18:571–580. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Parkes M: Evidence from genetics for a
role of autophagy and innate immunity in IBD pathogenesis. Dig Dis.
30:330–333. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Martinez-Lopez N and Singh R: ATGs:
Scaffolds for MAPK/ERK signaling. Autophagy. 10:535–537. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Tam BT and Siu PM: Autophagic cellular
responses to physical exercise in skeletal muscle. Sports Med.
44:625–640. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Jiang P and Mizushima N: Autophagy and
human diseases. Cell Res. 24:69–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Pottier M, Masclaux-Daubresse C, Yoshimoto
K and Thomine S: Autophagy as a possible mechanism for
micronutrient remobilization from leaves to seeds. Front Plant Sci.
5:112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Schmeisser H, Bekisz J and Zoon KC: New
function of type I IFN: Induction of autophagy. J Interferon
Cytokine Res. 34:71–78. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Mizushima N and Yoshimori T: How to
interpret LC3 immunoblotting. Autophagy. 3:542–545. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zhang W, Sviripa V, Kril LM, et al:
Fluorinated N,N-dialkylaminostilbenes for Wnt pathway inhibition
and colon cancer repression. J Med Chem. 54:1288–1297. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Fuendjiep V, Wandji J, Tillequin F, et al:
Chalconoid and stilbenoid glycosides from Guibourtia
tessmanii. Phytochemistry. 60:803–806. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|