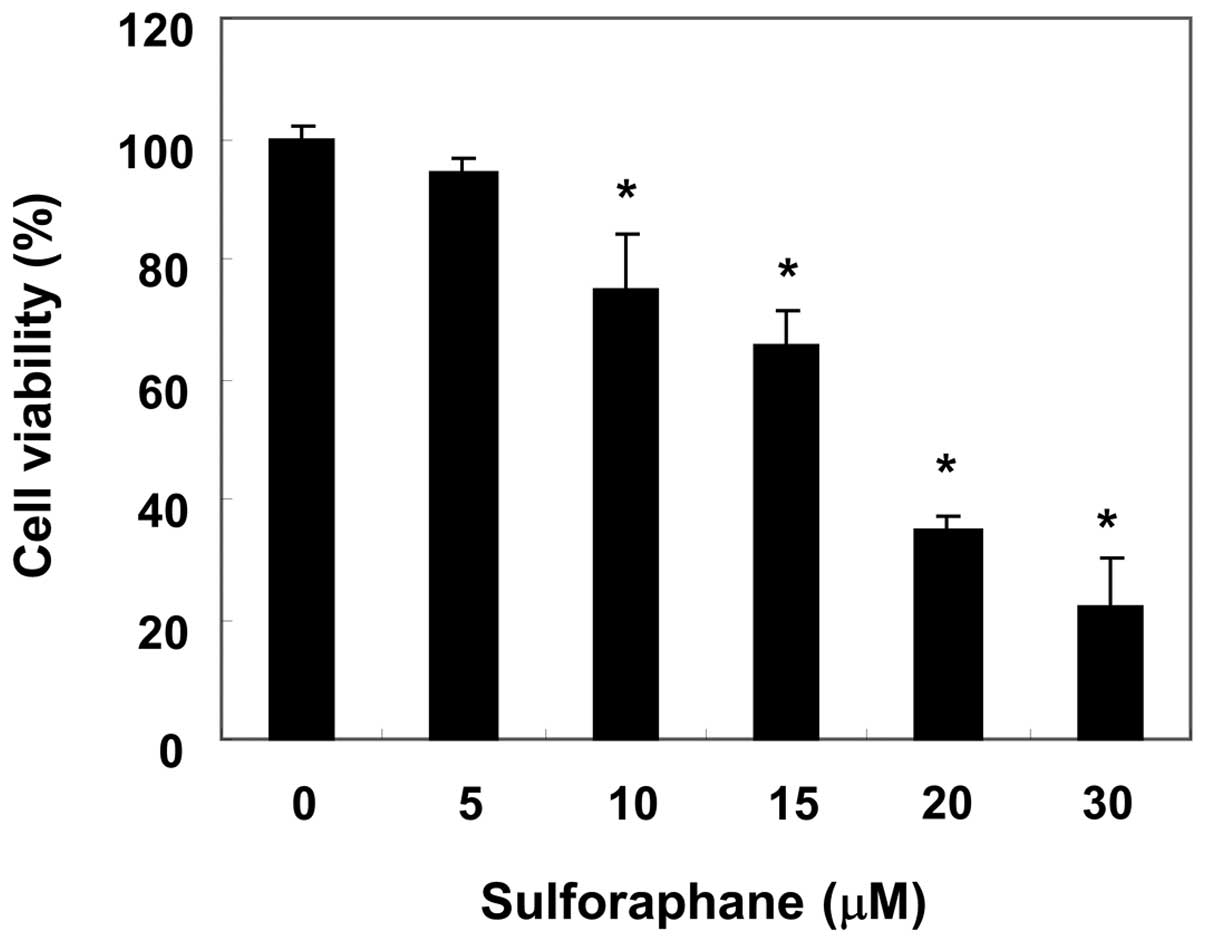
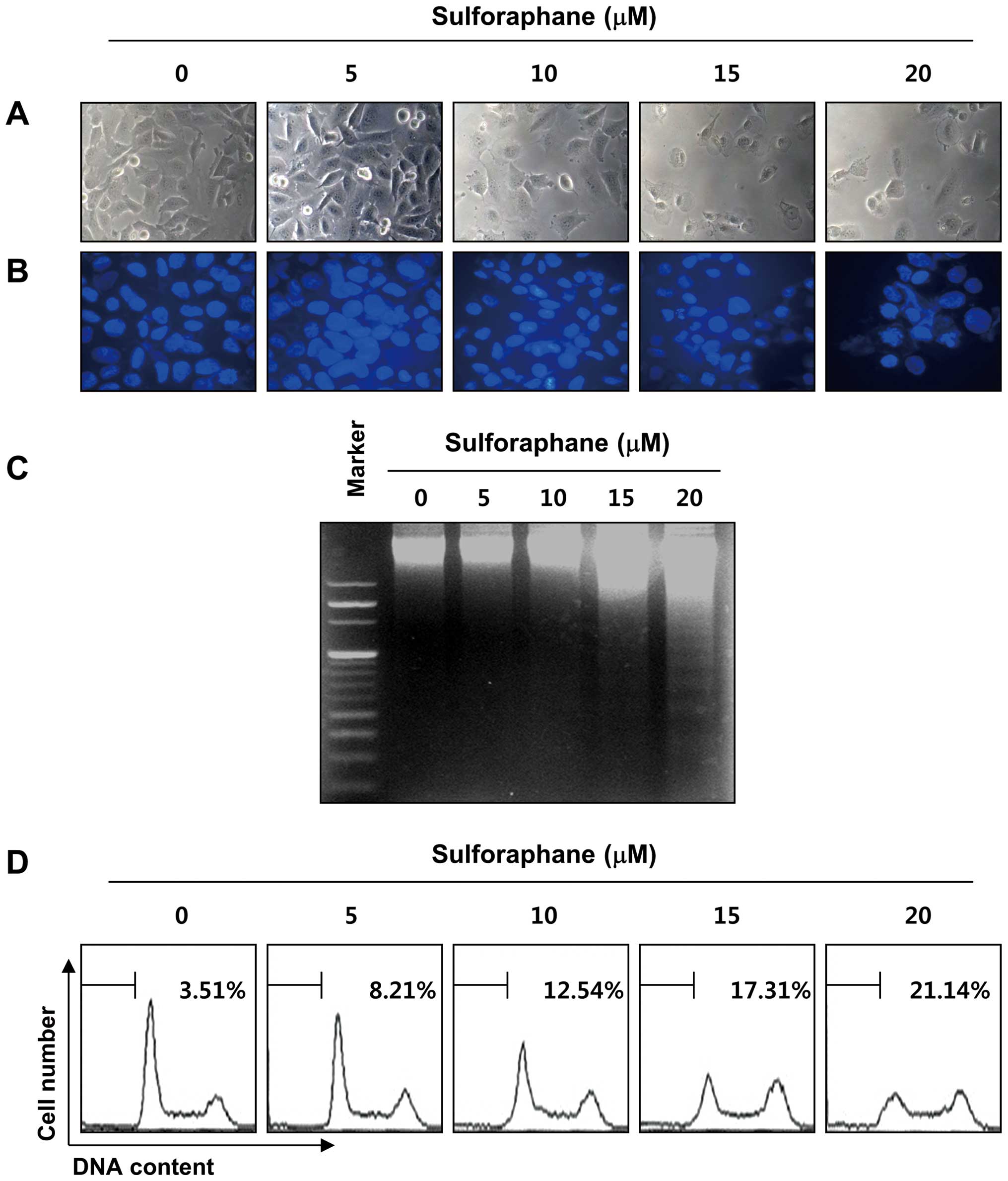
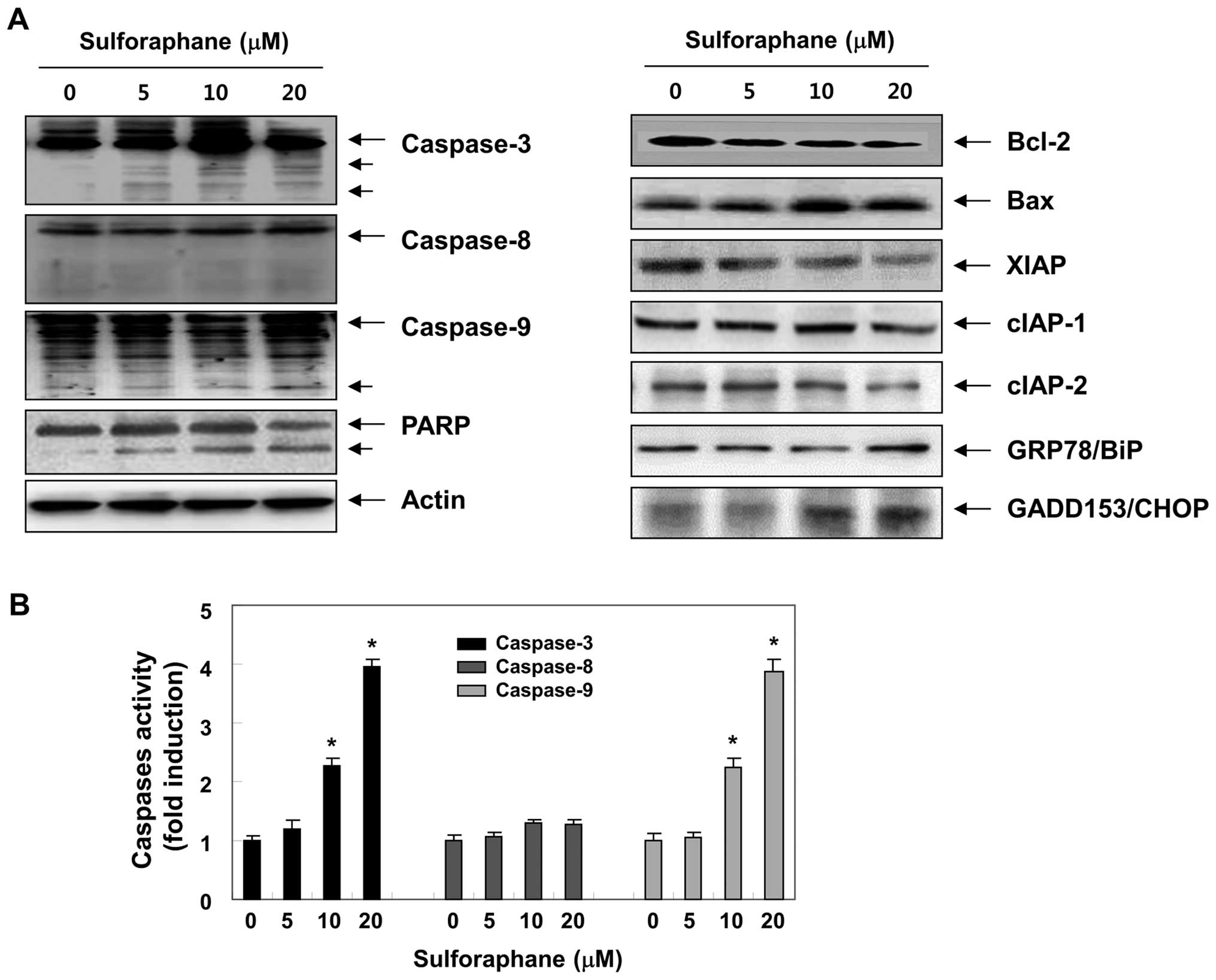
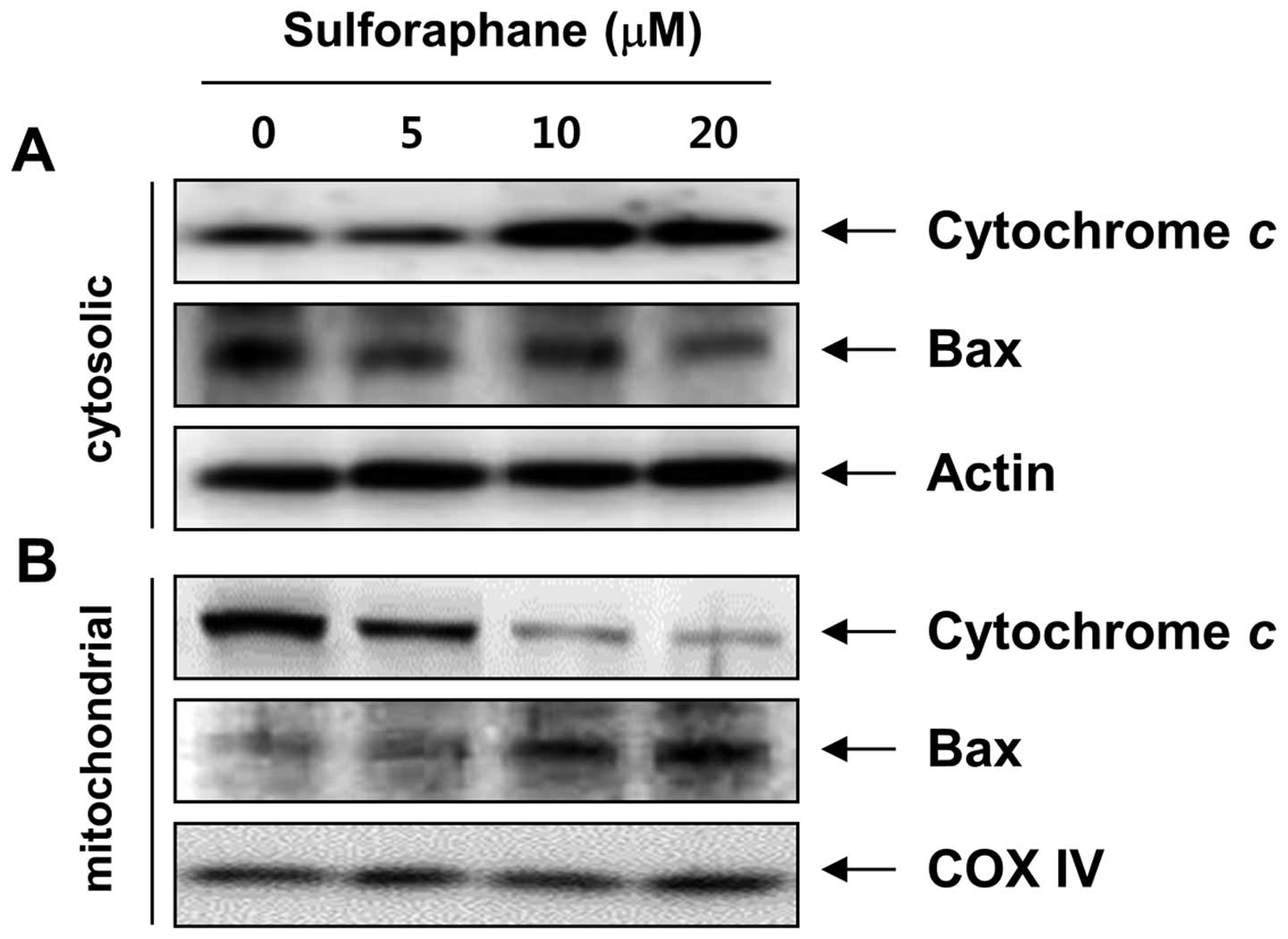
|
1
|
Cheung G, Sahai A, Billia M, Dasgupta P
and Khan MS: Recent advances in the diagnosis and treatment of
bladder cancer. BMC Med. 11:132013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Pinto-Leite R, Arantes-Rodrigues R,
Palmeira C, Colaço B, Lopes C, Colaço A, Costa C, da Silva VM,
Oliveira P and Santos L: Everolimus combined with cisplatin has a
potential role in treatment of urothelial bladder cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 67:116–121. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Black PC and Dinney CP: Bladder cancer
angiogenesis and metastasis-translation from murine model to
clinical trial. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 26:623–634. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chung KM and Yu SW: Interplay between
autophagy and programmed cell death in mammalian neural stem cells.
BMB Rep. 46:383–390. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: a review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jin Z and El-Deiry WS: Overview of cell
death signaling pathways. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:139–163.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Burz C, Berindan-Neagoe I, Balacescu O and
Irimie A: Apoptosis in cancer: key molecular signaling pathways and
therapy targets. Acta Oncol. 48:811–821. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fleury C, Mignotte B and Vayssière JL:
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in cell death signaling.
Biochimie. 84:131–141. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fruehauf JP and Meyskens FL Jr: Reactive
oxygen species: a breath of life or death? Clin Cancer Res.
13:789–794. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Saeidnia S and Abdollahi M: Toxicological
and pharmacological concerns on oxidative stress and related
diseases. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 273:442–455. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dorai T and Aggarwal BB: Role of
chemopreventive agents in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 215:129–140.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shu L, Cheung KL, Khor TO, Chen C and Kong
AN: Phytochemicals: cancer chemoprevention and suppression of tumor
onset and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 29:483–502. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vinod BS, Maliekal TT and Anto RJ:
Phytochemicals as chemosensitizers: from molecular mechanism to
clinical significance. Antioxid Redox Signal. 18:1307–1348. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fimognari C and Hrelia P: Sulforaphane as
a promising molecule for fighting cancer. Mutat Res. 635:90–104.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Clarke JD, Dashwood RH and Ho E:
Multi-targeted prevention of cancer by sulforaphane. Cancer Lett.
269:291–304. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cheung KL and Kong AN: Molecular targets
of dietary phenethyl isothiocyanate and sulforaphane for cancer
chemoprevention. AAPS J. 12:87–97. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shan Y, Wang X, Wang W, He C and Bao Y:
p38 MAPK plays a distinct role in sulforaphane-induced
up-regulation of ARE-dependent enzymes and down-regulation of COX-2
in human bladder cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 23:1133–1138.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ding Y, Paonessa JD, Randall KL, Argoti D,
Chen L, Vouros P and Zhang Y: Sulforaphane inhibits
4-aminobiphenyl-induced DNA damage in bladder cells and tissues.
Carcinogenesis. 31:1999–2003. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shan Y, Zhang L, Bao Y, Li B, He C, Gao M,
Feng X, Xu W, Zhang X and Wang S: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition, a novel target of sulforaphane via COX-2/MMP2, 9/Snail,
ZEB1 and miR-200c/ZEB1 pathways in human bladder cancer cells. J
Nutr Biochem. 24:1062–1069. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park HS, Han MH, Kim GY, Moon SK, Kim WJ,
Hwang HJ, Park KY and Choi YH: Sulforaphane induces reactive oxygen
species-mediated mitotic arrest and subsequent apoptosis in human
bladder cancer 5637 cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 64:157–165. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim NH, Hong BK, Choi SY, Moo Kwon H, Cho
CS, Yi EC and Kim WU: Reactive oxygen species regulate
context-dependent inhibition of NFAT5 target genes. Exp Mol Med.
45:e322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
MacKenzie SH and Clark AC: Targeting cell
death in tumors by activating caspases. Curr Cancer Drug Targets.
8:98–109. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wen X, Lin ZQ, Liu B and Wei YQ:
Caspase-mediated programmed cell death pathways as potential
therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Prolif. 45:217–224. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Susnow N, Zeng L, Margineantu D and
Hockenbery DM: Bcl-2 family proteins as regulators of oxidative
stress. Semin Cancer Biol. 19:42–49. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ola MS, Nawaz M and Ahsan H: Role of Bcl-2
family proteins and caspases in the regulation of apoptosis. Mol
Cell Biochem. 351:41–58. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shore GC, Papa FR and Oakes SA: Signaling
cell death from the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 23:143–149. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Logue SE, Cleary P, Saveljeva S and Samali
A: New directions in ER stress-induced cell death. Apoptosis.
18:537–546. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li N and Nel AE: Role of the Nrf2-mediated
signaling pathway as a negative regulator of inflammation:
implications for the impact of particulate pollutants on asthma.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 8:88–98. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Keum YS: Regulation of the Keap1/Nrf2
system by chemopreventive sulforaphane: implications of
posttranslational modifications. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1229:184–189.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kansanen E, Kuosmanen SM, Leinonen H and
Levonen AL: The Keap1-Nrf2 pathway: mechanisms of activation and
dysregulation in cancer. Redox Biol. 1:45–49. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Paine A, Eiz-Vesper B, Blasczyk R and
Immenschuh S: Signaling to heme oxygenase-1 and its
anti-inflammatory therapeutic potential. Biochem Pharmacol.
80:1895–1903. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Na HK and Surh YJ: Oncogenic potential of
Nrf2 and its principal target protein heme oxygenase-1. Free Radic
Biol Med. 67C:353–365. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Roy SK, Srivastava RK and Shankar S:
Inhibition of PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways causes activation of
FOXO transcription factor, leading to cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis in pancreatic cancer. J Mol Signal. 5:102010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bryant CS, Kumar S, Chamala S, Shah J, Pal
J, Haider M, Seward S, Qazi AM, Morris R, Semaan A, Shammas MA,
Steffes C, Potti RB, Prasad M, Weaver DW and Batchu RB:
Sulforaphane induces cell cycle arrest by protecting RB-E2F-1
complex in epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 9:472010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Choi WY, Choi BT, Lee WH and Choi YH:
Sulforaphane generates reactive oxygen species leading to
mitochondrial perturbation for apoptosis in human leukemia U937
cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 62:637–644. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Moon DO, Kang SH, Kim KC, Kim MO, Choi YH
and Kim GY: Sulforaphane decreases viability and telomerase
activity in hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells through the
reactive oxygen species-dependent pathway. Cancer Lett.
295:260–266. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Moon DO, Kim MO, Kang SH, Choi YH and Kim
GY: Sulforaphane suppresses TNF-alpha-mediated activation of
NF-kappaB and induces apoptosis through activation of reactive
oxygen species-dependent caspase-3. Cancer Lett. 274:132–142. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li J and Lee AS: Stress induction of
GRP78/BiP and its role in cancer. Curr Mol Med. 6:45–54. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Roller C and Maddalo D: The molecular
chaperone GRP78/BiP in the development of chemoresistance:
mechanism and possible treatment. Front Pharmacol. 4:102013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Oyadomari S and Mori M: Roles of
CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ.
11:381–389. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sano R and Reed JC: ER stress-induced cell
death mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:3460–3470. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cullinan SB and Diehl JA: Coordination of
ER and oxidative stress signaling: the PERK/Nrf2 signaling pathway.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 38:317–332. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xu H, Zhou YL, Zhang XY, Lu P and Li GS:
Activation of PERK signaling through fluoride-mediated endoplasmic
reticulum stress in OS732 cells. Toxicology. 277:1–5. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Miyamoto N, Izumi H, Miyamoto R, Bin H,
Kondo H, Tawara A, Sasaguri Y and Kohno K: Transcriptional
regulation of activating transcription factor 4 under oxidative
stress in retinal pigment epithelial ARPE-19/HPV-16 cells. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 52:1226–1234. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jeong WS, Keum YS, Chen C, Jain MR, Shen
G, Kim JH, Li W and Kong AN: Differential expression and stability
of endogenous nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) by natural
chemopreventive compounds in HepG2 human hepatoma cells. J Biochem
Mol Biol. 38:167–176. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Keum YS, Yu S, Chang PP, Yuan X, Kim JH,
Xu C, Han J, Agarwal A and Kong AN: Mechanism of action of
sulforaphane: inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
isoforms contributing to the induction of antioxidant response
element-mediated heme oxygenase-1 in human hepatoma HepG2 cells.
Cancer Res. 66:8804–8813. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Ping Z, Liu W, Kang Z, Cai J, Wang Q,
Cheng N, Wang S, Wang S, Zhang JH and Sun X: Sulforaphane protects
brains against hypoxic-ischemic injury through induction of
Nrf2-dependent phase 2 enzyme. Brain Res. 1343:178–185. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lee YJ, Jeong HY, Kim YB, Lee YJ, Won SY,
Shim JH, Cho MK, Nam HS and Lee SH: Reactive oxygen species and
PI3K/Akt signaling play key roles in the induction of Nrf2-driven
heme oxygenase-1 expression in sulforaphane-treated human
mesothelioma MSTO-211H cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:116–123. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Oh CJ, Kim JY, Min AK, Park KG, Harris RA,
Kim HJ and Lee IK: Sulforaphane attenuates hepatic fibrosis via
NF-E2-related factor 2-mediated inhibition of transforming growth
factor-β/Smad signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. 52:671–682.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Alfieri A, Srivastava S, Siow RC, Cash D,
Modo M, Duchen MR, Fraser PA, Williams SC and Mann GE: Sulforaphane
preconditioning of the Nrf2/HO-1 defense pathway protects the
cerebral vasculature against blood-brain barrier disruption and
neurological deficits in stroke. Free Radic Biol Med. 65:1012–1022.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Kleszczyński K, Ernst IM, Wagner AE, Kruse
N, Zillikens D, Rimbach G and Fischer TW: Sulforaphane and
phenylethyl isothiocyanate protect human skin against UVR-induced
oxidative stress and apoptosis: role of Nrf2-dependent gene
expression and antioxidant enzymes. Pharmacol Res. 78:28–40.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|