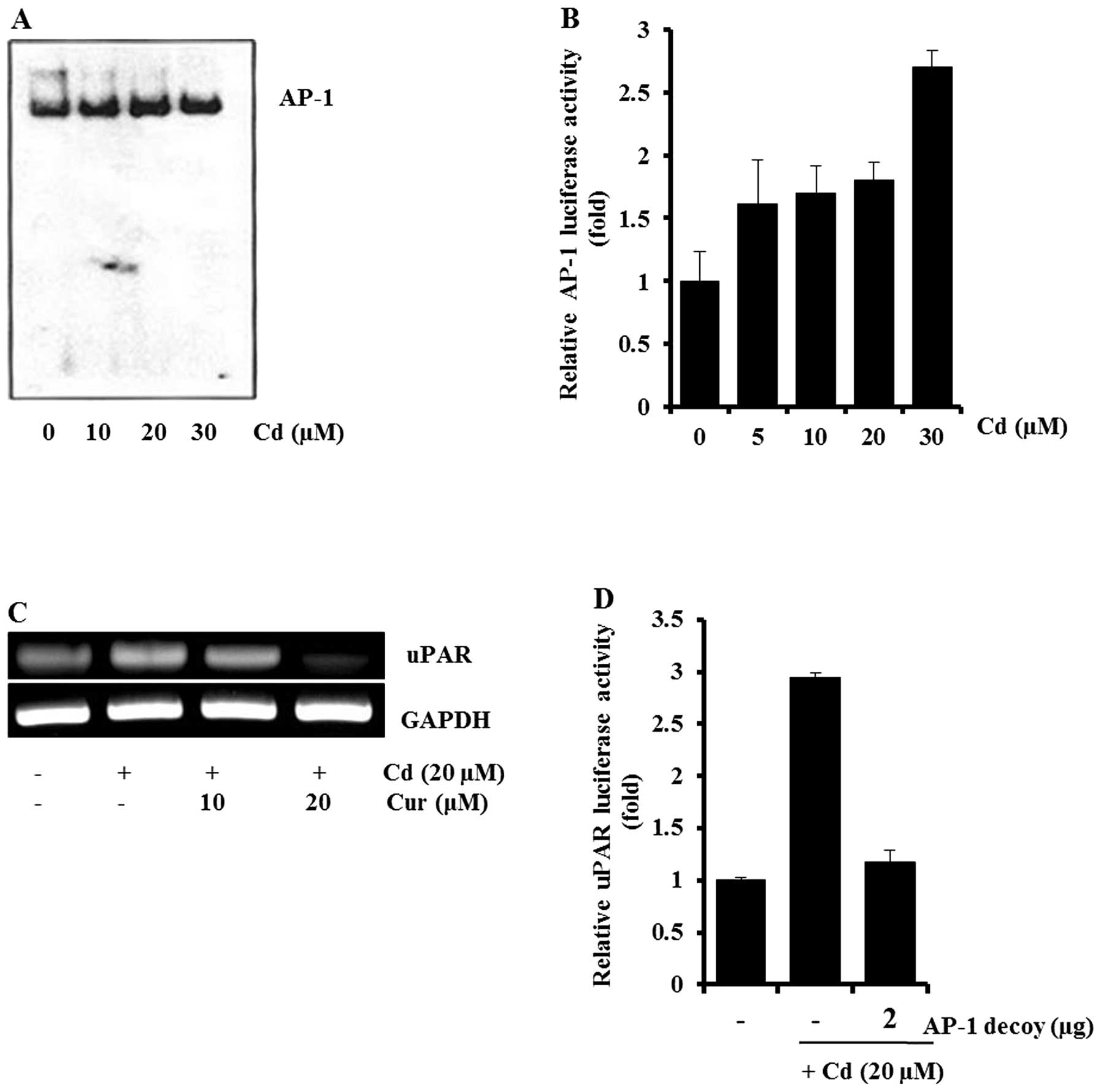
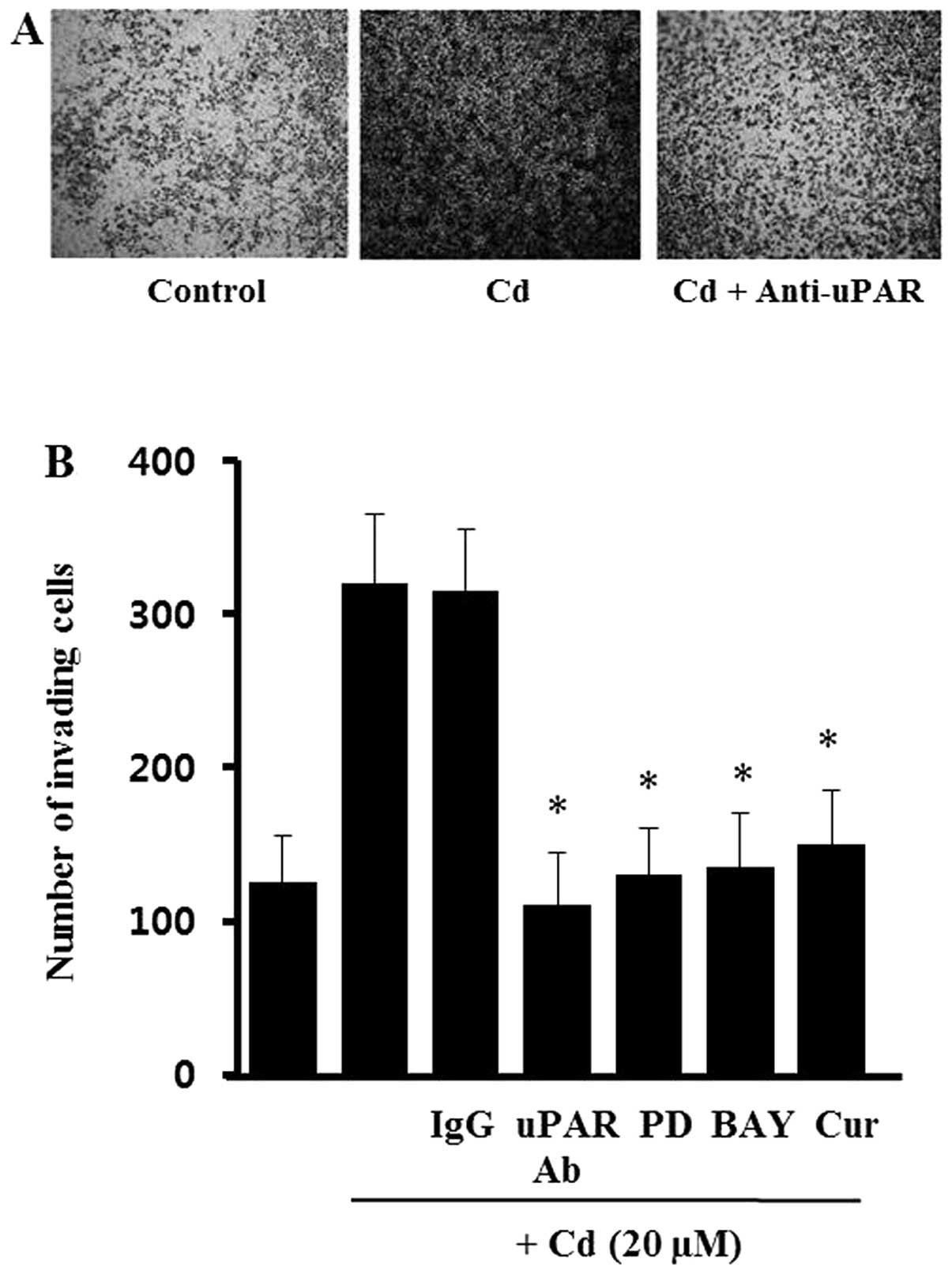
|
1
|
García-Esquinas E, Pollan M, Tellez-Plaza
M, Francesconi KA, Goessler W, Guallar E, Umans JG, Yeh J, Best LG
and Navas-Acien A: Cadmium exposure and cancer mortality in a
prospective cohort: the strong heart study. Environ Health
Perspect. 122:363–370. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang M, Song H, Chen WQ, Lu C, Hu Q, Ren
Z, Yang Y, Xu Y, Zhong A and Ling W: Cancer mortality in a Chinese
population surrounding a multi-metal sulphide mine in Guangdong
province: an ecologic study. BMC Public Health. 11:3192011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Engström KS, Vahter M, Johansson G, Lindh
CH, Teichert F, Singh R, Kippler M, Nermell B, Raqib R, Strömberg U
and Broberg K: Chronic exposure to cadmium and arsenic strongly
influences concentrations of 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2′-deoxyguanosine in
urine. Free Radic Biol Med. 48:1211–1217. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ochi T and Ohsawa M: Participation of
active oxygen species in the induction of chromosomal aberrations
by cadmium chloride in cultured Chinese hamster cells. Mutat Res.
143:137–142. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fang MZ, Mar W and Cho MH: Cadmium affects
genes involved in growth regulation during two-stage transformation
of Balb/3T3 cells. Toxicology. 177:253–265. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jin P and Ringertz NR: Cadmium induces
transcription of proto-oncogenes c-jun and c-myc in rat L6
myoblasts. J Biol Chem. 265:14061–14064. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jing Y, Liu LZ, Jiang Y, Zhu Y, Guo NL,
Barnett J, Rojanasakul Y, Agani F and Jiang BH: Cadmium increases
HIF-1 and VEGF expression through ROS, ERK, and AKT signaling
pathways and induces malignant transformation of human bronchial
epithelial cells. Toxicol Sci. 125:10–19. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qu W, Fuquay R, Sakurai T and Waalkes MP:
Acquisition of apoptotic resistance in cadmium-induced malignant
transformation: specific perturbation of JNK signal transduction
pathway and associated metallothionein overexpression. Mol
Carcinog. 45:561–571. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Goldfarb RH and Liotta LA: Proteolytic
enzymes in cancer invasion and metastasis. Semin Thromb Hemost.
12:294–307. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Son YO, Wang L, Poyil P, Budhraja A,
Hitron JA, Zhang Z, Lee JC and Shi X: Cadmium induces
carcinogenesis in BEAS-2B cells through ROS-dependent activation of
PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
264:153–160. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Waltz DA, Fujita RM, Yang X, Natkin L,
Zhuo S, Gerard CJ, Rosenberg S and Chapman HA: Nonproteolytic role
for the urokinase receptor in cellular migration in vivo. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 22:316–322. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Baek MK, Kim MH, Jang HJ, Park JS, Chung
IJ, Shin BA, Ahn BW and Jung YD: EGF stimulates uPAR expression and
cell invasiveness through ERK, AP-1, and NF-kappaB signaling in
human gastric carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 20:1569–1575.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shariat SF, Semjonow A, Lilja H, Savage C,
Vickers AJ and Bjartell A: Tumor markers in prostate cancer I:
blood-based markers. Acta Oncol. 50(Suppl 1): 61–75. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Raghu H, Sodadasu PK, Malla RR, Gondi CS,
Estes N and Rao JS: Localization of uPAR and MMP-9 in lipid rafts
is critical for migration, invasion and angiogenesis in human
breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 10:6472010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Y1, Dang J, Johnson LK, Selhamer JJ
and Doe WF: Structure of the human urokinase receptor gene and its
similarity to CD59 and the Ly-6 family. Eur J Biochem. 227:116–122.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Person RJ, Tokar EJ, Xu Y, Orihuela R,
Ngalame NN and Waalkes MP: Chronic cadmium exposure in vitro
induces cancer cell characteristics in human lung cells. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 273:281–288. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hyder O, Chung M, Cosgrove D, Herman JM,
Li Z, Firoozmand A, Gurakar A, Koteish A and Pawlik TM: Cadmium
exposure and liver disease among US adults. J Gastrointest Surg.
17:1265–1273. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lubovac-Pilav Z, Borràs DM, Ponce E and
Louie MC: Using expression profiling to understand the effects of
chronic cadmium exposure on MCF-7 breast cancer cells. PLoS One.
8:e846462013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hartwig A: Mechanisms in cadmium-induced
carcinogenicity: recent insights. Biometals. 23:951–960. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Järup L: Hazards of heavy metal
contamination. Br Med Bull. 68:167–182. 2003.
|
|
21
|
Cormet-Boyaka E, Jolivette K,
Bonnegarde-Bernard A, Rennolds J, Hassan F, Mehta P, Tridandapani
S, Webster-Marketon J and Boyaka PN: An NF-κB-independent and
Erk1/2-dependent mechanism controls CXCL8/IL-8 responses of airway
epithelial cells to cadmium. Toxicol Sci. 125:418–429. 2012.
|
|
22
|
Park YK, Hong H and Jang BC:
Transcriptional and translational regulation of COX-2 expression by
cadmium in C6 glioma cells. Int J Mol Med. 30:960–966.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Choi YK, Yoon BI, Kook YH, Won YS, Kim JH,
Lee CH, Hyun BH, Oh GT, Sipley J and Kim DY: Overexpression of
urokinase-type plasminogen activator in human gastric cancer cell
line (AGS) induces tumorigenicity in severe combined
immunodeficient mice. Jpn J Cancer Res. 93:151–156. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Festuccia C, Dolo V, Guerra F, Violini S,
Muzi P, Pavan A and Bologna M: Plasminogen activator system
modulates invasive capacity and proliferation in prostatic tumor
cells. Clin Exp Metastasis. 16:513–528. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Carpenter RL and Jiang BH: Roles of EGFR,
PI3K, AKT, and mTOR in heavy metal-induced cancer (Review). Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 13:252–266. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mukhin YV, Garnovskaya MN, Collinsworth G,
Grewal JS, Pendergrass D, Nagai T, Pinckney S, Greene EL and
Raymond JR: 5-Hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor/Gibetagamma stimulates
mitogen-activated protein kinase via NAD(P)H oxidase and reactive
oxygen species upstream of src in chinese hamster ovary
fibroblasts. Biochem J. 347:61–67. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lee K and Esselman WJ: Inhibition of PTPs
by H(2)O(2) regulates the activation of distinct MAPK pathways.
Free Radic Biol Med. 33:1121–1132. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Valko M, Morris H and Cronin MT: Metals,
toxicity and oxidative stress (Review). Curr Med Chem. 12:1161–208.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Freitas M and Fernandes E: Zinc, cadmium
and nickel increase the activation of NF-κB and the release of
cytokines from THP-1 monocytic cells. Metallomics. 3:1238–1243.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Napolitano JR, Liu MJ, Bao S, Crawford M,
Nana-Sinkam P, Cormet-Boyaka E and Knoell DL: Cadmium-mediated
toxicity of lung epithelia is enhanced through NF-κB-mediated
transcriptional activation of the human zinc transporter ZIP8. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 302:L909–L918. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Thévenod F, Friedmann JM, Katsen AD and
Hauser IA: Up-regulation of multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein via
nuclear factor-kappaB activation protects kidney proximal tubule
cells from cadmium- and reactive oxygen species-induced apoptosis.
J Biol Chem. 275:1887–1896. 2000.
|
|
32
|
Li Q and Engelhardt JF: Interleukin-1beta
induction of NFkappaB is partially regulated by
H2O2-mediated activation of NFkappaB-inducing
kinase. J Biol Chem. 281:1495–1505. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Storz P and Toker A: NF-kappaB signaling -
an alternate pathway for oxidative stress responses. Cell Cycle.
2:9–10. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fan C, Li Q, Ross D and Engelhardt JF:
Tyrosine phosphorylation of I kappa B alpha activates NF kappa B
through a redox-regulated and c-Src-dependent mechanism following
hypoxia/reoxygenation. J Biol Chem. 278:2072–2080. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
del Escobar MC, Souza V, Bucio L,
Hernández E, Gómez-Quiroz LE and Gutiérrez Ruiz MC: MAPK activation
is involved in cadmium-induced Hsp70 expression in HepG2 cells.
Toxicol Mech Methods. 19:503–509. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang C, Zhang Q, Li J, Shi X, Castranova
V, Ju G, Costa M and Dong Z: Involvement of Erks activation in
cadmium-induced AP-1 transactivation in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cell
Biochem. 222:141–147. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Juang HH, Chung LC, Sung HC, Feng TH, Lee
YH, Chang PL and Tsui KH: Metallothionein 3: an
androgen-upregulated gene enhances cell invasion and tumorigenesis
of prostate carcinoma cells. Prostate. 73:1495–1506. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|