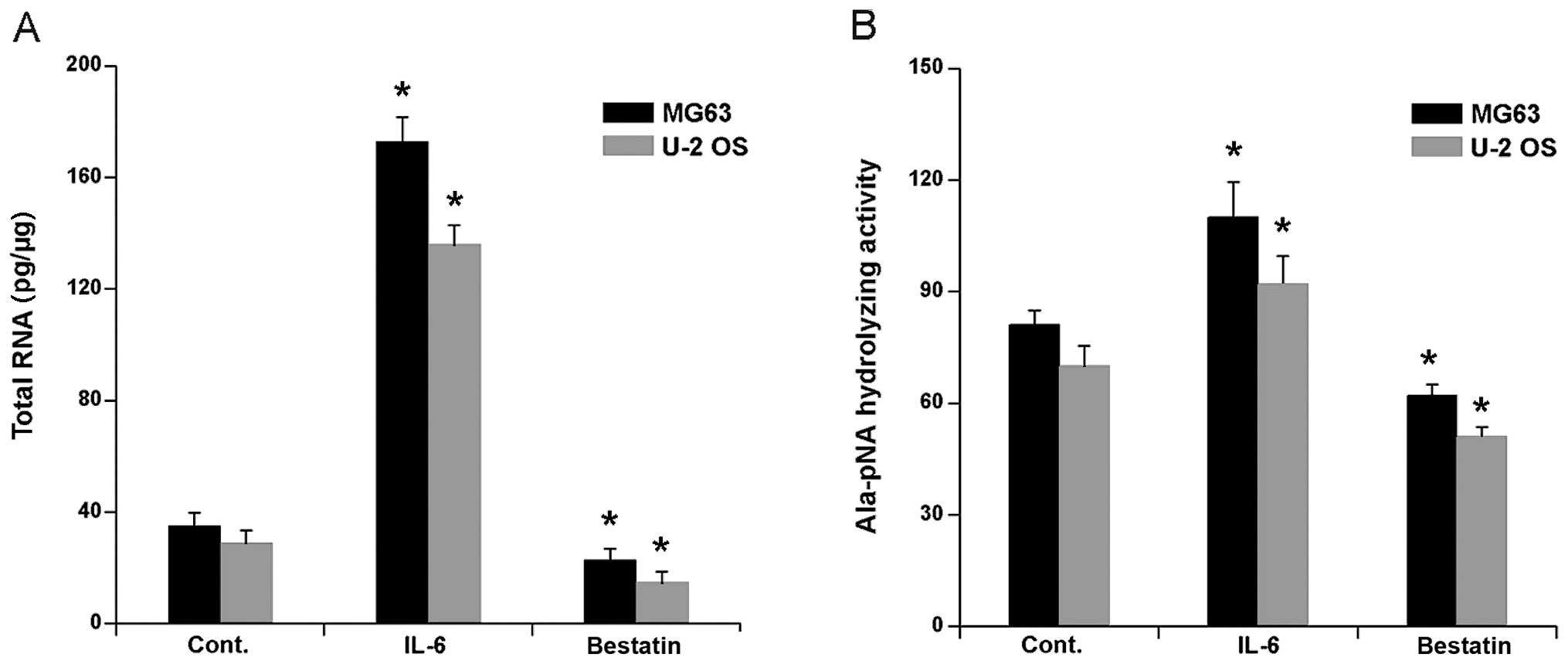
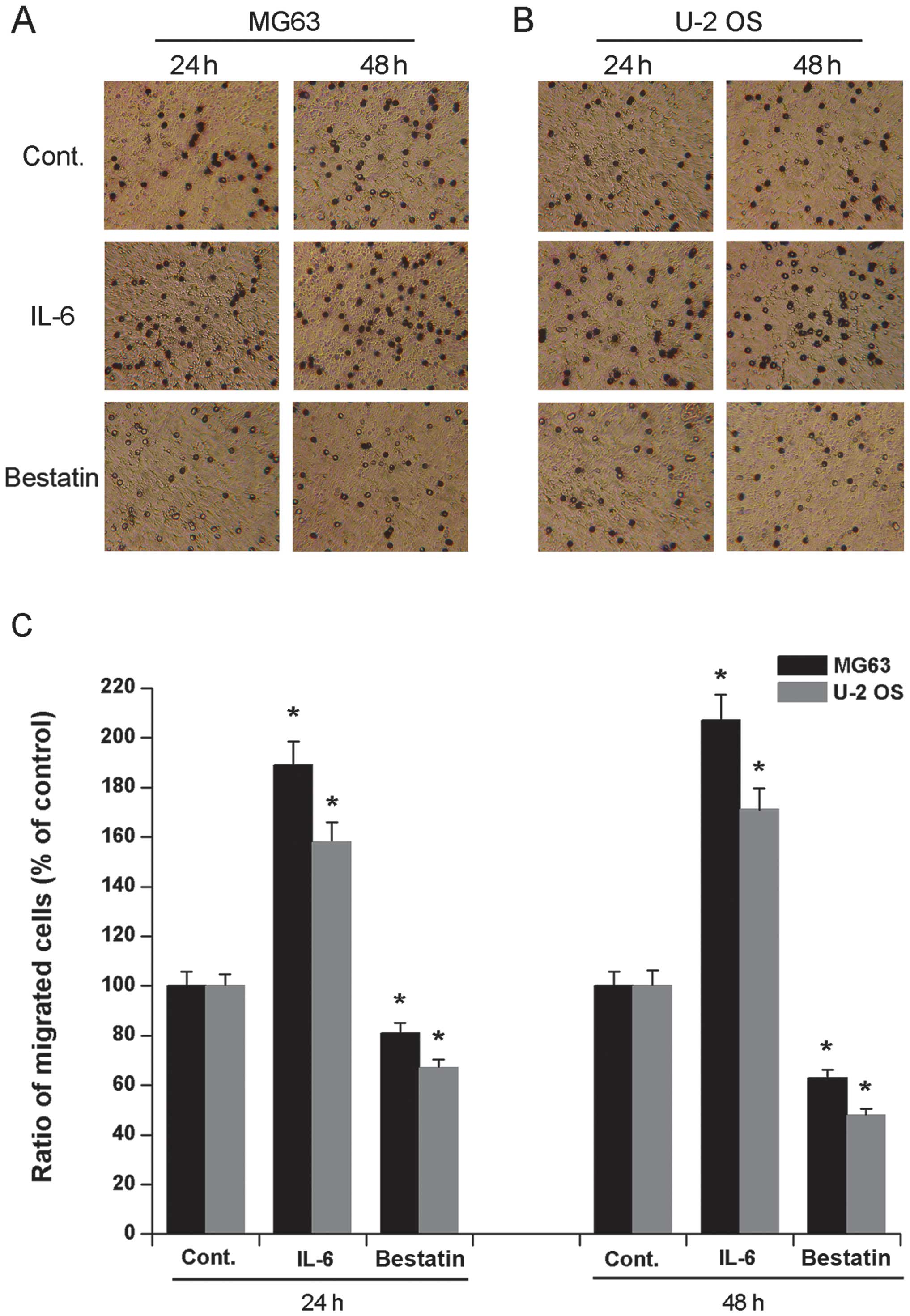
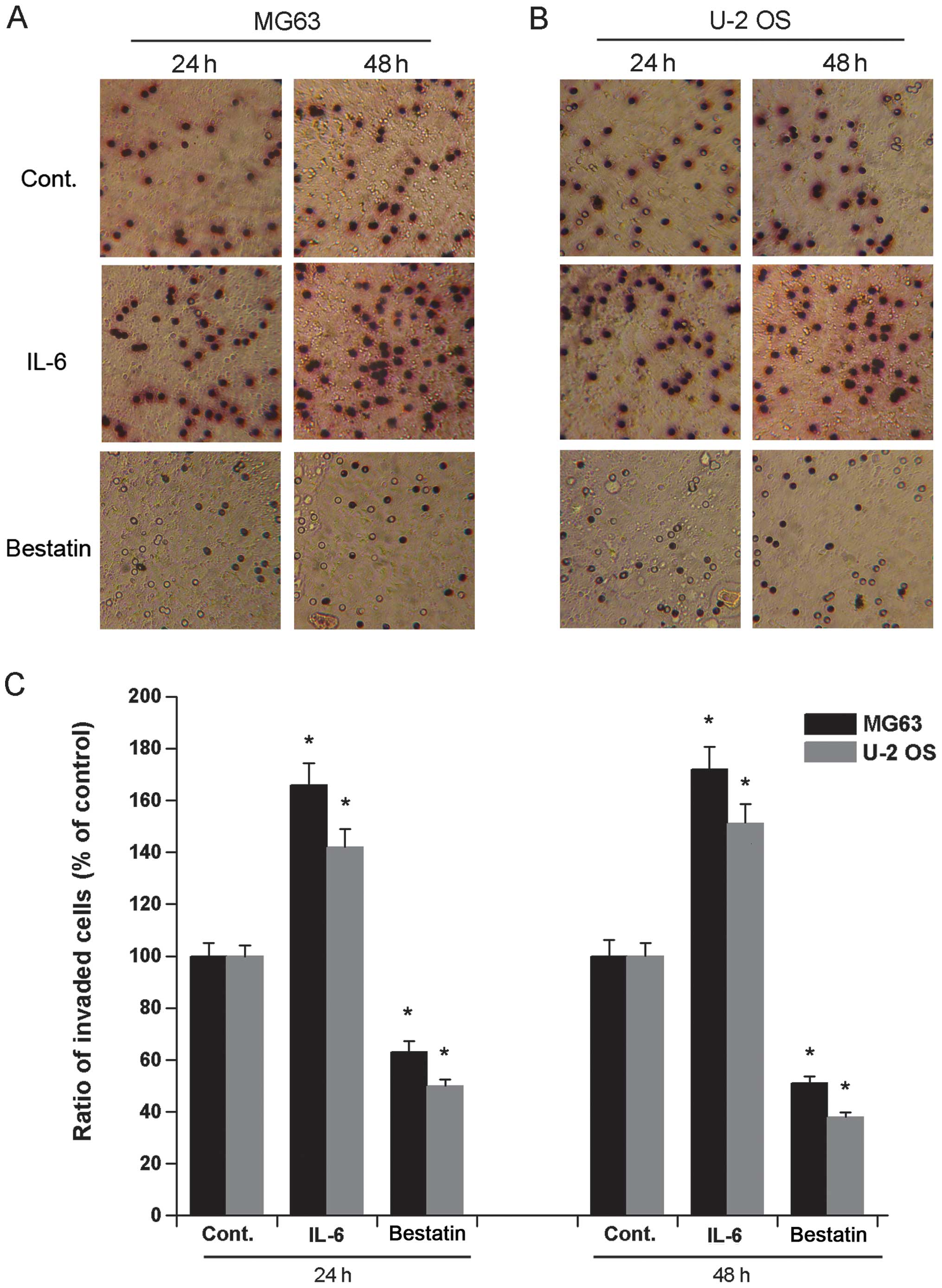
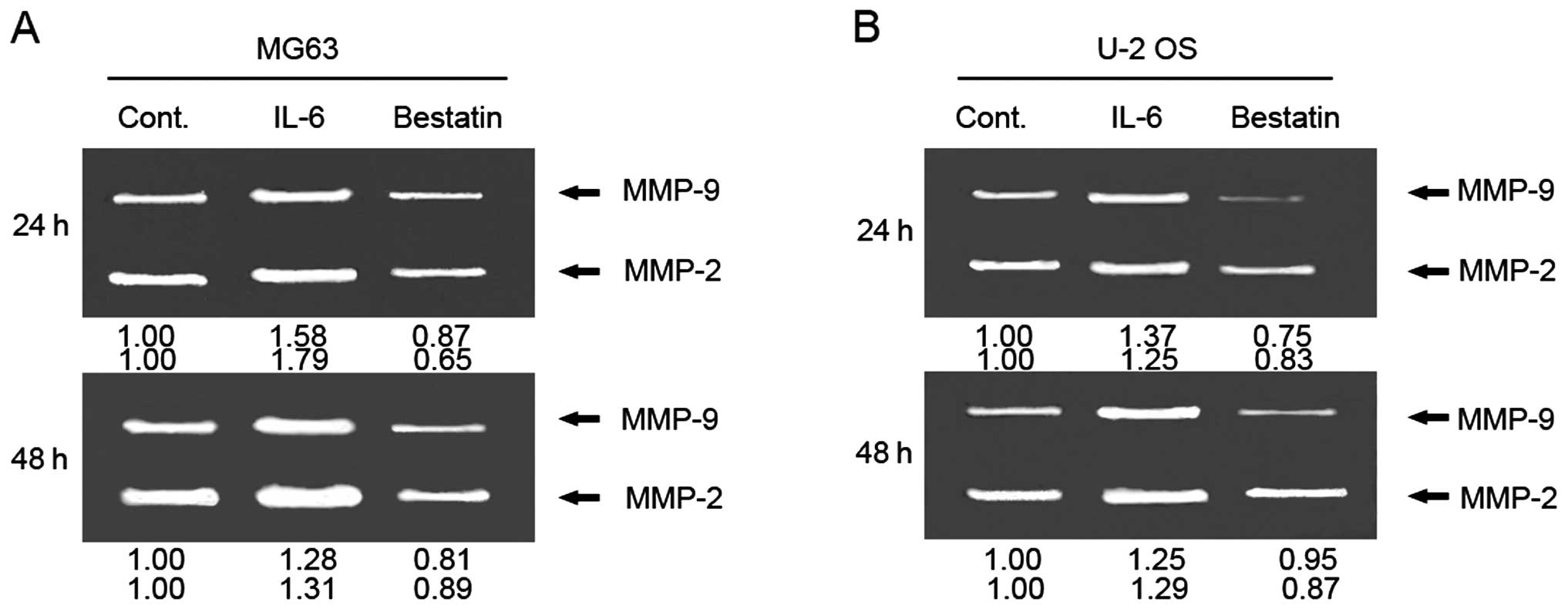
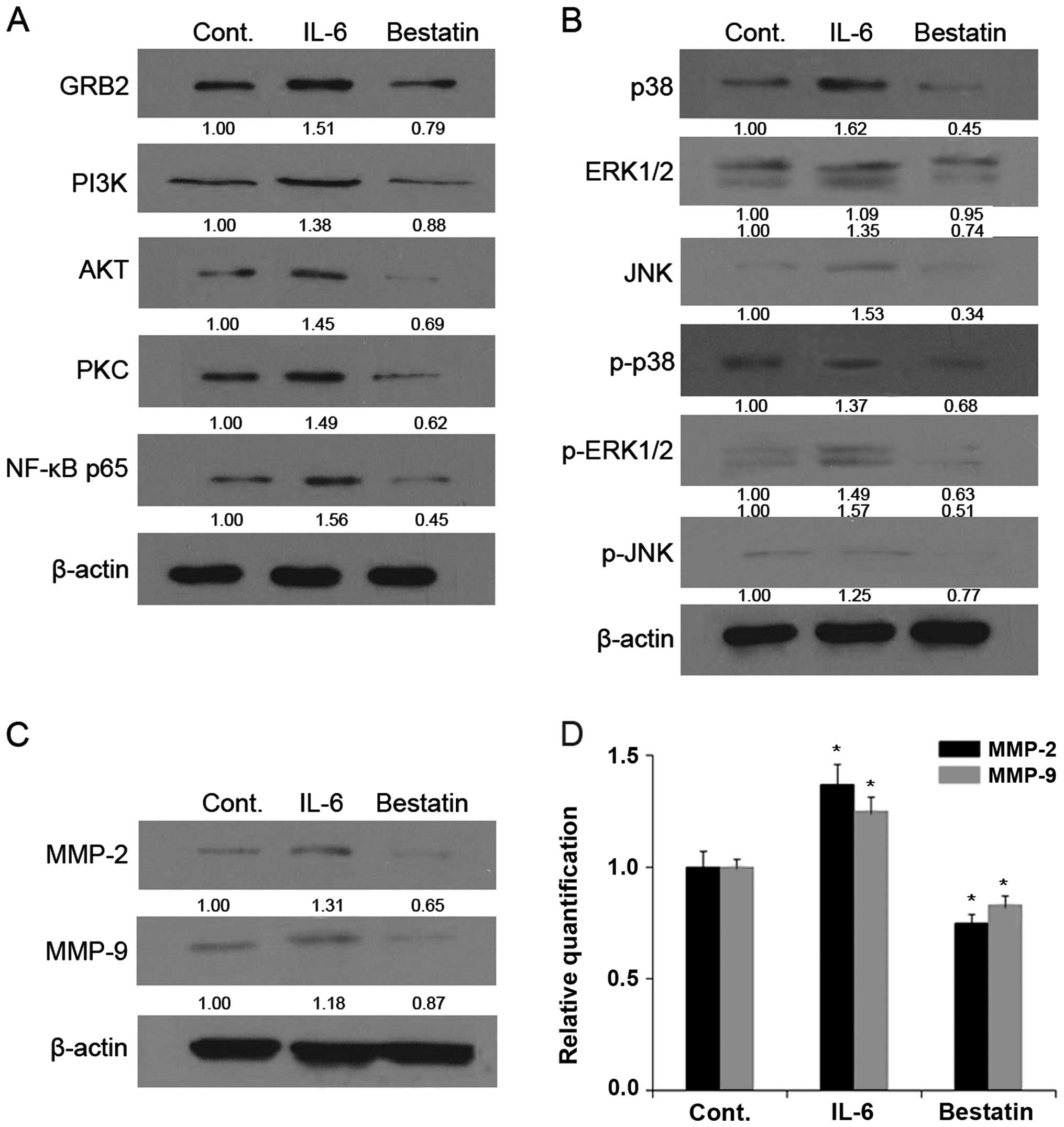
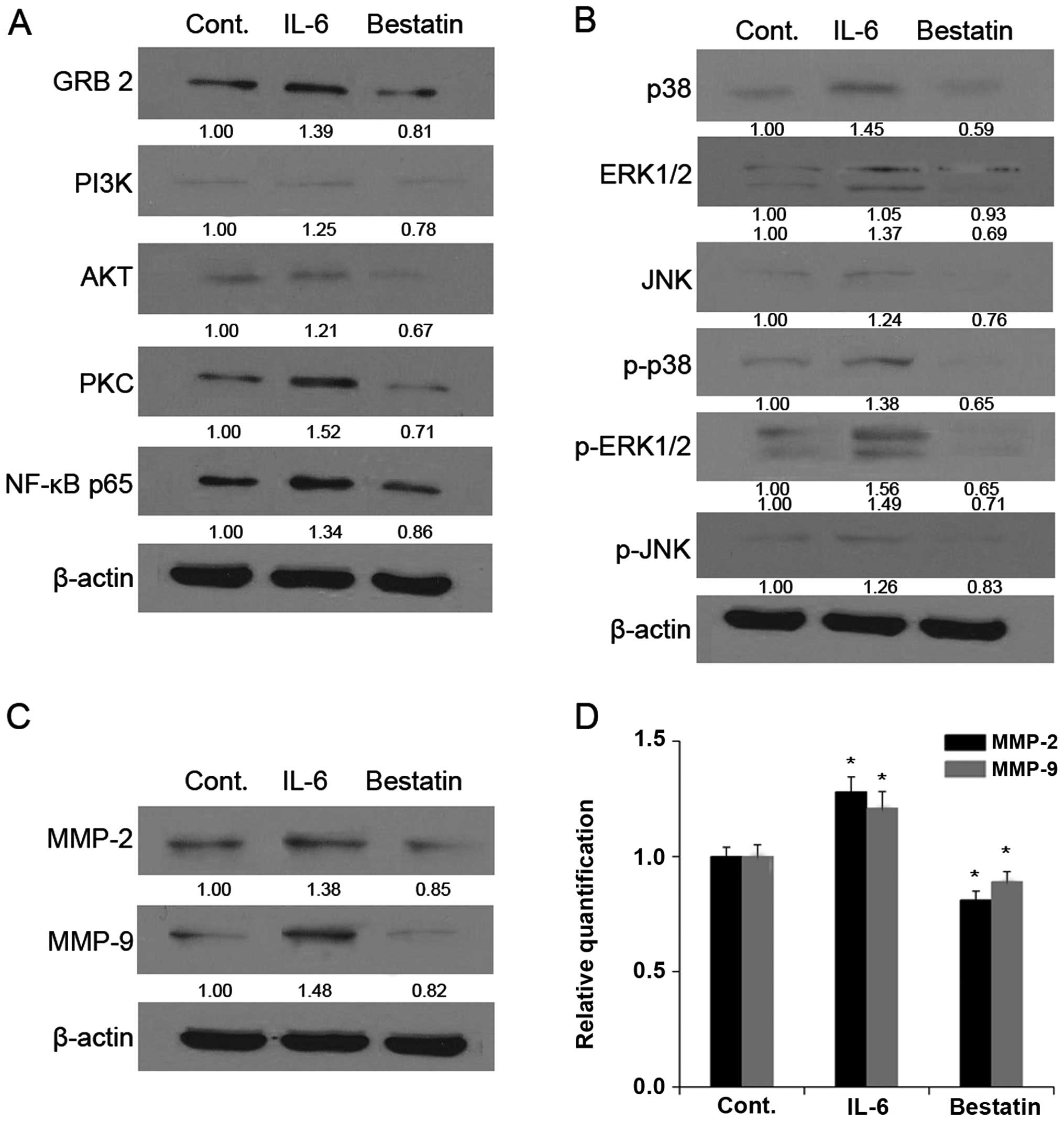
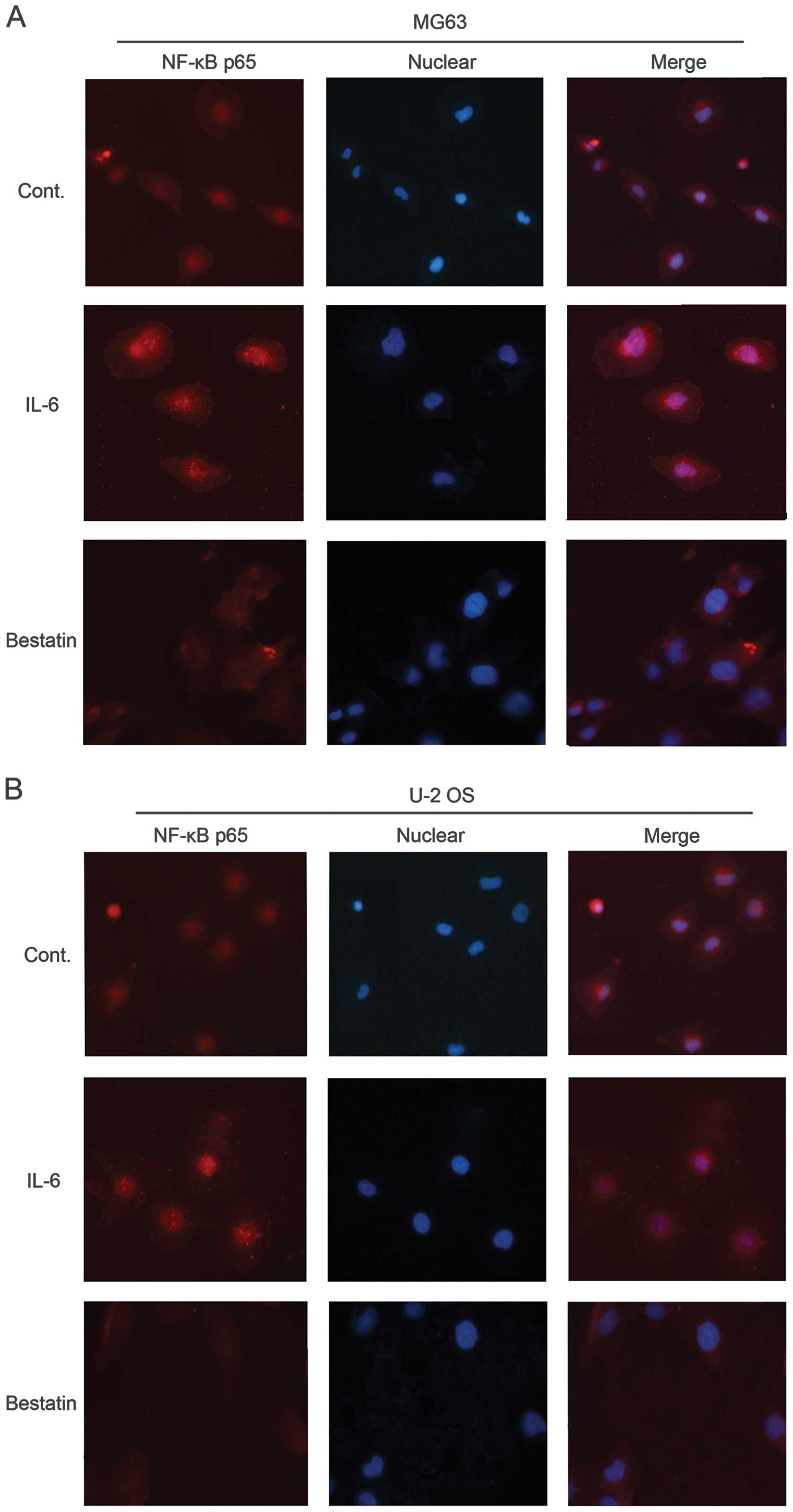
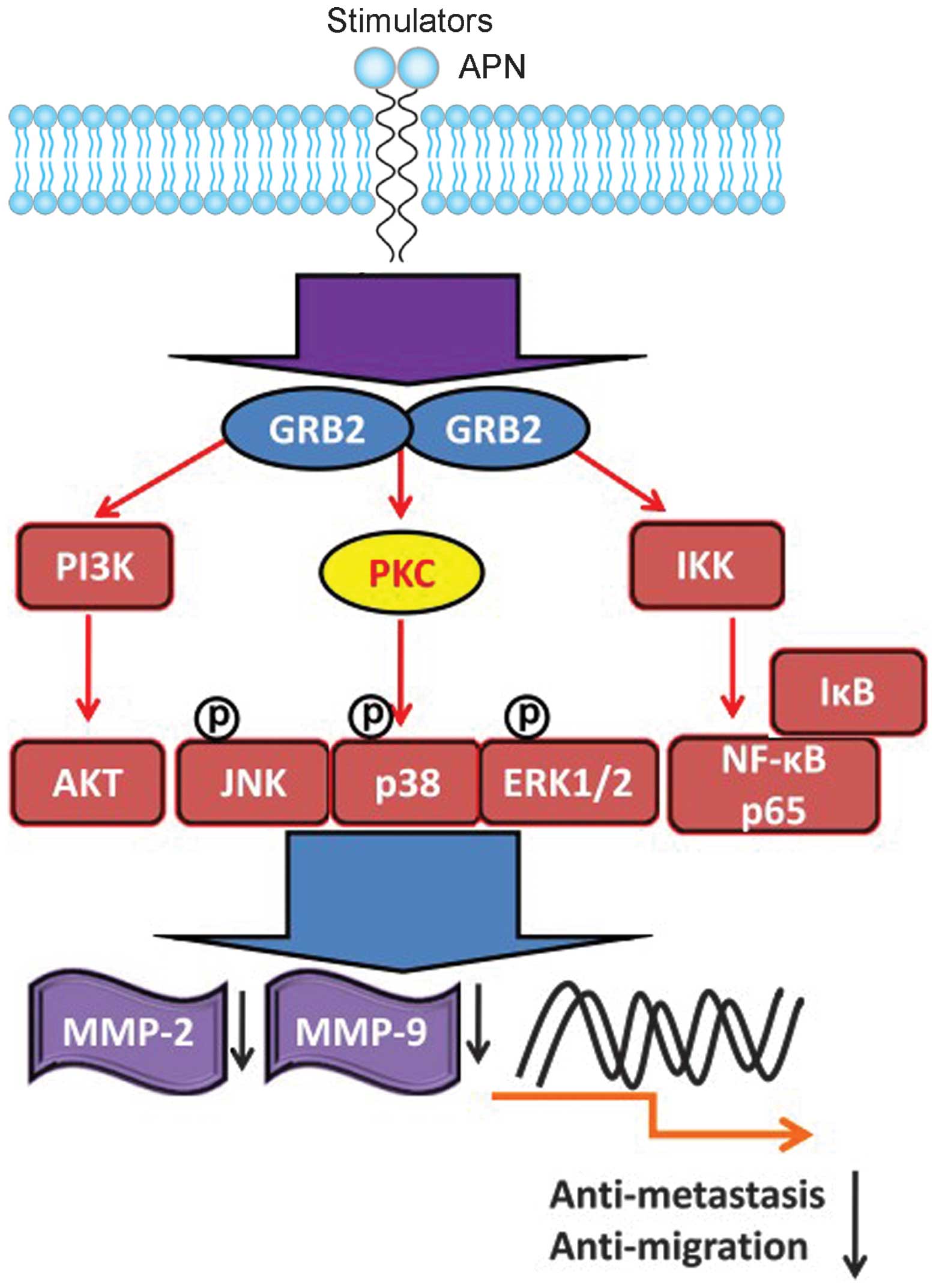
|
1
|
Ottaviani G and Jaffe N: The epidemiology
of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 152:3–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sung L, Anderson JR, Donaldson SS, Spunt
SL, Crist WM and Pappo AS; Soft Tissue Sarcoma Committee of the
Children’s Oncology Group. Late events occurring five years or more
after successful therapy for childhood rhabdomyosarcoma: a report
from the Soft Tissue Sarcoma Committee of the Children’s Oncology
Group. Eur J Cancer. 40:1878–1885. 2004.
|
|
3
|
Cheng YY, Huang L, Lee KM, Li K and Kumta
SM: Alendronate regulates cell invasion and MMP-2 secretion in
human osteosarcoma cell lines. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 42:410–415.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cho HJ, Lee TS, Park JB, et al: Disulfiram
suppresses invasive ability of osteosarcoma cells via the
inhibition of MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression. J Biochem Mol Biol.
40:1069–1076. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xin ZF, Kim YK and Jung ST: Risedronate
inhibits human osteosarcoma cell invasion. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
28:1052009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fan DG, Dai JY, Tang J, et al: Silencing
of calpain expression reduces the metastatic potential of human
osteosarcoma cells. Cell Biol Int. 33:1263–1267. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dass CR, Nadesapillai AP, Robin D, et al:
Downregulation of uPAR confirms link in growth and metastasis of
osteosarcoma. Clin Exp Metastasis. 22:643–652. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wan X, Kim SY, Guenther LM, et al: Beta4
integrin promotes osteosarcoma metastasis and interacts with ezrin.
Oncogene. 28:3401–3411. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Haydon RC, Deyrup A, Ishikawa A, et al:
Cytoplasmic and/or nuclear accumulation of the beta-catenin protein
is a frequent event in human osteosarcoma. Int J Cancer.
102:338–342. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Iwaya K, Ogawa H, Kuroda M, Izumi M,
Ishida T and Mukai K: Cytoplasmic and/or nuclear staining of
beta-catenin is associated with lung metastasis. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 20:525–529. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Engin F, Bertin T, Ma O, et al: Notch
signaling contributes to the pathogenesis of human osteosarcomas.
Hum Mol Genet. 18:1464–1470. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hughes DP: How the NOTCH pathway
contributes to the ability of osteosarcoma cells to metastasize.
Cancer Treat Res. 152:479–496. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Leow PC, Tian Q, Ong ZY, Yang Z and Ee PL:
Antitumor activity of natural compounds, curcumin and PKF118-310,
as Wnt/β-catenin antagonists against human osteosarcoma cells.
Invest New Drugs. 28:766–782. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li Y, Zhang J, Ma D, et al: Curcumin
inhibits proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells through
inactivation of Notch-1 signaling. FEBS J. 279:2247–2259. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin YM, Chang ZL, Liao YY, Chou MC and
Tang CH: IL-6 promotes ICAM-1 expression and cell motility in human
osteosarcoma. Cancer Lett. 328:135–143. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Berdiaki A, Datsis GA, Nikitovic D, et al:
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) peptides through the regulation of
hyaluronan metabolism affect osteosarcoma cell migration. IUBMB
Life. 62:377–386. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang R, Hoang BH, Kubo T, et al:
Over-expression of parathyroid hormone Type 1 receptor confers an
aggressive phenotype in osteosarcoma. Int J Cancer. 121:943–954.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dobashi Y, Watanabe H, Matsubara M, et al:
Autocrine motility factor/glucose-6-phosphate isomerase is a
possible predictor of metastasis in bone and soft tissue tumours. J
Pathol. 208:44–53. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Niinaka Y, Harada K, Fujimuro M, et al:
Silencing of autocrine motility factor induces
mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition and suppression of
osteosarcoma pulmonary metastasis. Cancer Res. 70:9483–9493. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fromigue O, Hamidouche Z, Vaudin P, et al:
CYR61 downregulation reduces osteosarcoma cell invasion, migration,
and metastasis. J Bone Miner Res. 26:1533–1542. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bauvois B: Transmembrane proteases in cell
growth and invasion: new contributors to angiogenesis? Oncogene.
23:317–329. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Carl-McGrath S, Lendeckel U, Ebert M and
Röcken C: Ectopeptidases in tumour biology: a review. Histol
Histopathol. 21:1339–1353. 2006.
|
|
23
|
Hitzerd SM, Verbrugge SE, Ossenkoppele G,
Jansen G and Peters GJ: Positioning of aminopeptidase inhibitors in
next generation cancer therapy. Amino Acids. 46:793–808. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kido A, Krueger S, Haeckel C and Roessner
A: Possible contribution of aminopeptidase N (APN/CD13) to invasive
potential enhanced by interleukin-6 and soluble interleukin-6
receptor in human osteosarcoma cell lines. Clin Exp Metastasis.
17:857–863. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fujii H, Nakajima M, Saiki I, Yoneda J,
Azuma I and Tsuruo T: Human melanoma invasion and metastasis
enhancement by high expression of aminopeptidase N/CD13. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 13:337–344. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kehlen A, Lendeckel U, Dralle H, Langner J
and Hoang-Vu C: Biological significance of aminopeptidase N/CD13 in
thyroid carcinomas. Cancer Res. 63:8500–8506. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Petrovic N, Schacke W, Gahagan JR, et al:
CD13/APN regulates endothelial invasion and filopodia formation.
Blood. 110:142–150. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hong DY, Lee BJ, Lee JC, Choi JS, Wang SG
and Ro JH: Expression of VEGF, HGF, IL-6, IL-8, MMP-9, telomerase
in peripheral blood of patients with head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2:186–192. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Loo WT, Sasano H and Chow LW:
Pro-inflammatory cytokine, matrix metalloproteinases and TIMP-1 are
involved in wound healing after mastectomy in invasive breast
cancer patients. Biomed Pharmacother. 61:548–552. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Güllü IH, Kurdoğlu M and Akalin I: The
relation of gelatinase (MMP-2 and -9) expression with distant site
metastasis and tumour aggressiveness in colorectal cancer. Br J
Cancer. 82:2492000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mizutani K, Kofuji K and Shirouzu K: The
significance of MMP-1 and MMP-2 in peritoneal disseminated
metastasis of gastric cancer. Surg Today. 30:614–621. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Korpi JT, Hagström J, Lehtonen N, et al:
Expression of matrix metalloproteinases-2, −8, −13, −26, and tissue
inhibitors of metalloproteinase-1 in human osteosarcoma. Surg
Oncol. 20:e18–e22. 2011.
|
|
33
|
Ferrari C, Benassi S, Ponticelli F, et al:
Role of MMP-9 and its tissue inhibitor TIMP-1 in human
osteosarcoma: findings in 42 patients followed for 1–16 years. Acta
Orthop Scand. 75:487–491. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Foukas AF, Deshmukh NS, Grimer RJ, Mangham
DC, Mangos EG and Taylor S: Stage-IIB osteosarcomas around the
knee. A study of MMP-9 in surviving tumour cells. J Bone Joint Surg
Br. 84:706–711. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Himelstein BP, Asada N, Carlton MR and
Collins MH: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) expression in
childhood osseous osteosarcoma. Med Pediatr Oncol. 31:471–474.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bellido T, O’Brien CA, Roberson PK and
Manolagas SC: Transcriptional activation of the p21(WAF1,CIP1,SDI1)
gene by interleukin-6 type cytokines. A prerequisite for their
pro-differentiating and anti-apoptotic effects on human
osteoblastic cells. J Biol Chem. 273:21137–21144. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Franchimont N, Gangji V, Durant D and
Canalis E: Interleukin-6 with its soluble receptor enhances the
expression of insulin-like growth factor-I in osteoblasts.
Endocrinology. 138:5248–5255. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jilka RL, Weinstein RS, Bellido T, Parfitt
AM and Manolagas SC: Osteoblast programmed cell death (apoptosis):
modulation by growth factors and cytokines. J Bone Miner Res.
13:793–802. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nishimura R, Moriyama K, Yasukawa K, Mundy
GR and Yoneda T: Combination of interleukin-6 and soluble
interleukin-6 receptors induces differentiation and activation of
JAK-STAT and MAP kinase pathways in MG-63 human osteoblastic cells.
J Bone Miner Res. 13:777–785. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kehlen A, Göhring B, Langner J and Riemann
D: Regulation of the expression of aminopeptidase A, aminopeptidase
N/CD13 and dipeptidylpeptidase IV/CD26 in renal carcinoma cells and
renal tubular epithelial cells by cytokines and cAMP-increasing
mediators. Clin Exp Immunol. 111:435–441. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Chen YY, Chiang SY, Lin JG, et al: Emodin,
aloe-emodin and rhein inhibit migration and invasion in human
tongue cancer SCC-4 cells through the inhibition of gene expression
of matrix metalloproteinase-9. Int J Oncol. 36:1113–1120.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lin CC, Chen JT, Yang JS, et al: Danthron
inhibits the migration and invasion of human brain glioblastoma
multiforme cells through the inhibition of mRNA expression of focal
adhesion kinase, Rho kinases-1 and metalloproteinase-9. Oncol Rep.
22:1033–1037. 2009.
|
|
43
|
Lai KC, Huang AC, Hsu SC, et al: Benzyl
isothiocyanate (BITC) inhibits migration and invasion of human
colon cancer HT29 cells by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9
and urokinase plasminogen (uPA) through PKC and MAPK signaling
pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 58:2935–2942. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Liu KC, Huang AC, Wu PP, et al: Gallic
acid suppresses the migration and invasion of PC-3 human prostate
cancer cells via inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9
signaling pathways. Oncol Rep. 26:177–184. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chiang JH, Yang JS, Ma CY, et al:
Danthron, an anthraquinone derivative, induces DNA damage and
caspase cascades-mediated apoptosis in SNU-1 human gastric cancer
cells through mitochondrial permeability transition pores and
Bax-triggered pathways. Chem Res Toxicol. 24:20–29. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Wen YF, Yang JS, Kuo SC, et al:
Investigation of anti-leukemia molecular mechanism of ITR-284, a
carboxamide analog, in leukemia cells and its effects in WEHI-3
leukemia mice. Biochem Pharmacol. 79:389–398. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hennessy BT, Smith DL, Ram PT, Lu Y and
Mills GB: Exploiting the PI3K/AKT pathway for cancer drug
discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 4:988–1004. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Qi M and Elion EA: MAP kinase pathways. J
Cell Sci. 118:3569–3572. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Bond M, Chase AJ, Baker AH and Newby AC:
Inhibition of transcription factor NF-kappaB reduces matrix
metalloproteinase-1, -3 and -9 production by vascular smooth muscle
cells. Cardiovasc Res. 50:556–565. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bauvois B and Dauzonne D:
Aminopeptidase-N/CD13 (EC 3.4.11.2) inhibitors: chemistry,
biological evaluations, and therapeutic prospects. Med Res Rev.
26:88–130. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Balkwill F, Charles KA and Mantovani A:
Smoldering and polarized inflammation in the initiation and
promotion of malignant disease. Cancer Cell. 7:211–217. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lo CW, Chen MW, Hsiao M, et al: IL-6
trans-signaling in formation and progression of malignant ascites
in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 71:424–434. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tang CH, Chen CF, Chen WM and Fong YC:
IL-6 increases MMP-13 expression and motility in human
chondrosarcoma cells. J Biol Chem. 286:11056–11066. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Tu B, Du L, Fan QM, Tang Z and Tang TT:
STAT3 activation by IL-6 from mesenchymal stem cells promotes the
proliferation and metastasis of osteosarcoma. Cancer Lett.
325:80–88. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Mina-Osorio P: The moonlighting enzyme
CD13: old and new functions to target. Trends Mol Med. 14:361–371.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liao CL, Lai KC, Huang AC, et al: Gallic
acid inhibits migration and invasion in human osteosarcoma U-2 OS
cells through suppressing the matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9,
protein kinase B (PKB) and PKC signaling pathways. Food Chem
Toxicol. 50:1734–1740. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|