|
1
|
Malvezzi M, Bertuccio P, Levi F, La
Vecchia C and Negri E: European cancer mortality predictions for
the year 2013. Ann Oncol. 24:792–800. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rutkowski MR, Stephen TL and Conejo-Garcia
JR: Anti-tumor immunity: myeloid leukocytes control the immune
landscape. Cell Immunol. 278:21–26. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schiavoni G, Gabriele L and Mattei F: The
tumor microenvironment: a pitch for multiple players. Front Oncol.
3:902013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mantovani A: Cancer: inflaming metastasis.
Nature. 457:36–37. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
McLean MH, Murray GI, Stewart KN, et al:
The inflammatory microenvironment in colorectal neoplasia. PLoS
One. 6:e153662011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou Q, Peng RQ, Wu XJ, et al: The density
of macrophages in the invasive front is inversely correlated to
liver metastasis in colon cancer. J Transl Med. 8:132010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Forssell J, Oberg A, Henriksson ML,
Stenling R, Jung A and Palmqvist R: High macrophage infiltration
along the tumor front correlates with improved survival in colon
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:1472–1479. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mosser DM and Edwards JP: Exploring the
full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:958–969.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena
P, Vecchi A and Locati M: The chemokine system in diverse forms of
macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 25:677–686.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Biswas SK, Allavena P and Mantovani A:
Tumor-associated macrophages: functional diversity, clinical
significance, and open questions. Semin Immunopathol. 35:585–600.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ye Y, Huang X, Zhang Y, et al: Calcium
influx blocked by SK&F 96365 modulates the LPS plus
IFN-γ-induced inflammatory response in murine peritoneal
macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol. 12:384–393. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Weisser SB, McLarren KW, Kuroda E and Sly
LM: Generation and characterization of murine alternatively
activated macrophages. Methods Mol Biol. 946:225–239. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen PC, Cheng HC, Wang J, et al: Prostate
cancer-derived CCN3 induces M2 macrophage infiltration and
contributes to angiogenesis in prostate cancer microenvironment.
Oncotarget. 5:1595–1608. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xiao X, Gaffar I, Guo P, et al: M2
macrophages promote beta-cell proliferation by up-regulation of
SMAD7. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:E1211–E1220. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Edin S, Wikberg ML, Dahlin AM, et al: The
distribution of macrophages with a M1 or M2 phenotype in relation
to prognosis and the molecular characteristics of colorectal
cancer. PLoS One. 7:e470452012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kang JC, Chen JS, Lee CH, Chang JJ and
Shieh YS: Intratumoral macrophage counts correlate with tumor
progression in colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 102:242–248. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pancione M, Forte N, Sabatino L, et al:
Reduced beta-catenin and peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor-gamma expression levels are associated with colorectal
cancer metastatic progression: correlation with tumor-associated
macrophages, cyclooxygenase 2, and patient outcome. Hum Pathol.
40:714–725. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bailey C, Negus R, Morris A, et al:
Chemokine expression is associated with the accumulation of tumour
associated macrophages (TAMs) and progression in human colorectal
cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis. 24:121–130. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cui YL, Li HK, Zhou HY, Zhang T and Li Q:
Correlations of tumor-associated macrophage subtypes with liver
metastases of colorectal cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
14:1003–1007. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Andre T, Boni C, Navarro M, et al:
Improved overall survival with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and
leucovorin as adjuvant treatment in stage II or III colon cancer in
the MOSAIC trial. J Clin Oncol. 27:3109–3116. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Graham JS and Cassidy J: Adjuvant therapy
in colon cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 12:99–109. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
McDonald GT, Sullivan R, Paré GC and
Graham CH: Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase promotes
tumor cell resistance to chemotherapeutic agents via a mechanism
involving delay in cell cycle progression. Exp Cell Res.
316:3197–3206. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Miyazaki K, Shibahara T, Sato D, et al:
Influence of chemotherapeutic agents and cytokines on the
expression of 5-fluorouracil-associated enzymes in human colon
cancer cell lines. J Gastroenterol. 41:140–150. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Scartozzi M, Maccaroni E, Giampieri R, et
al: 5-Fluorouracil pharmacogenomics: still rocking after all these
years? Pharmacogenomics. 12:251–265. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
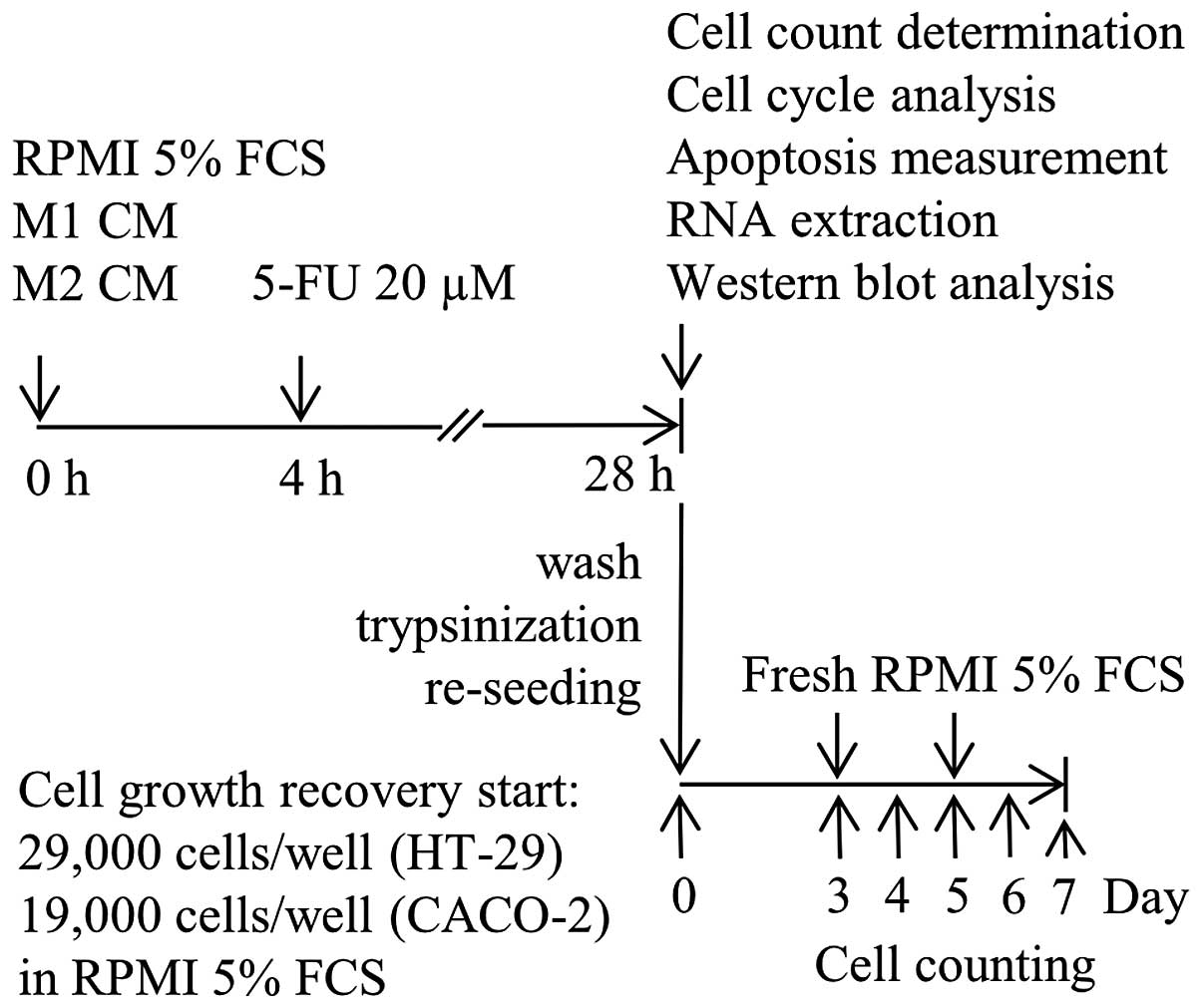
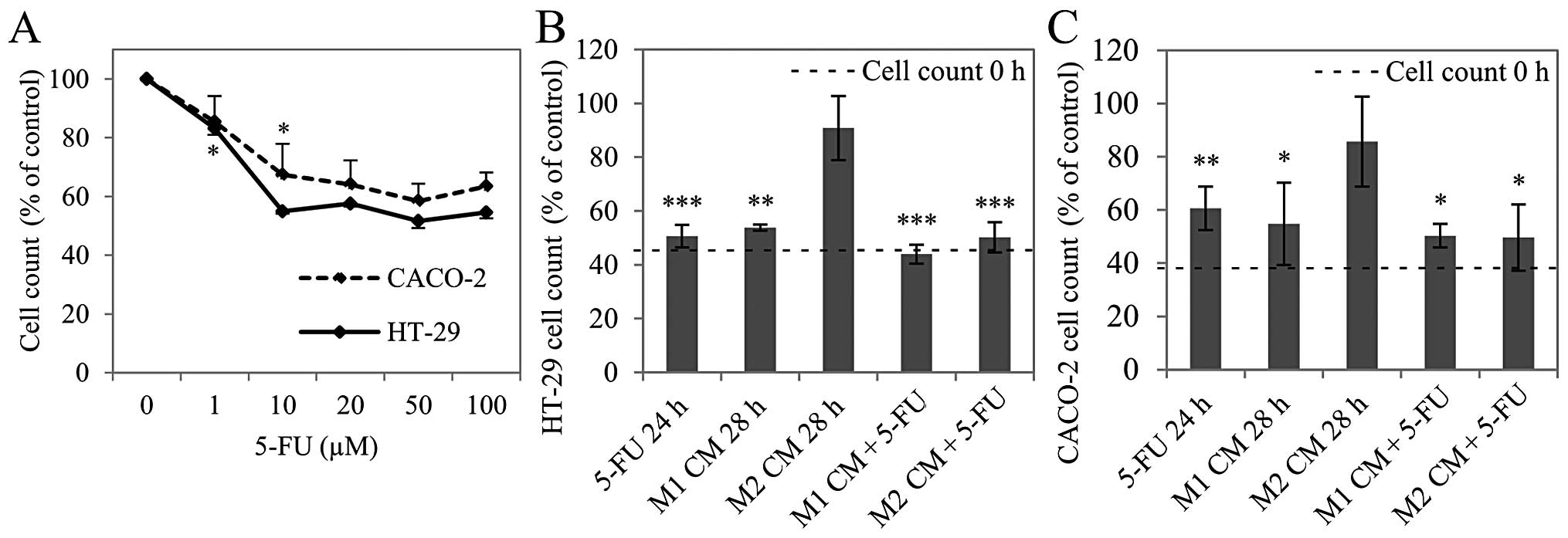
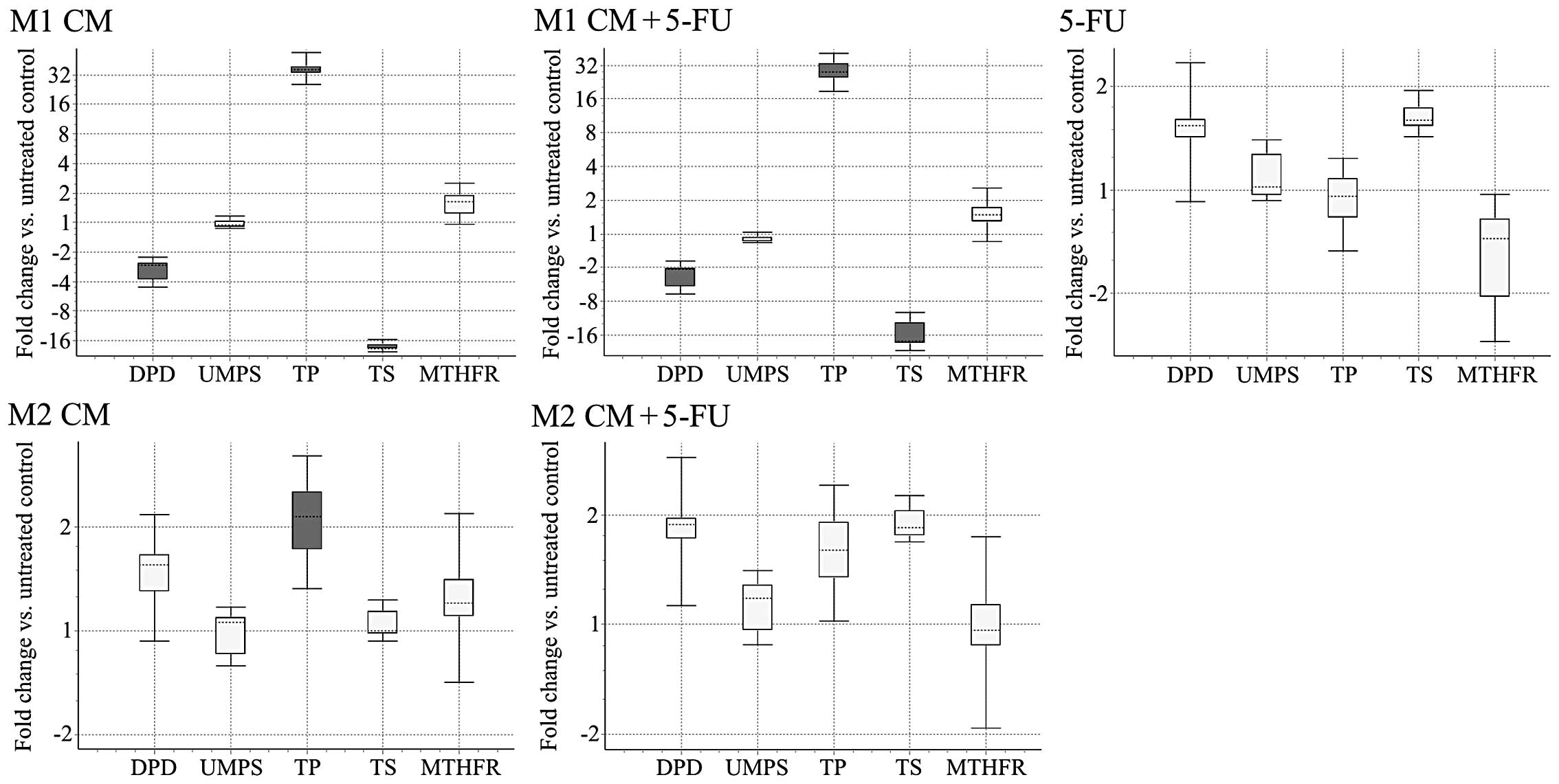
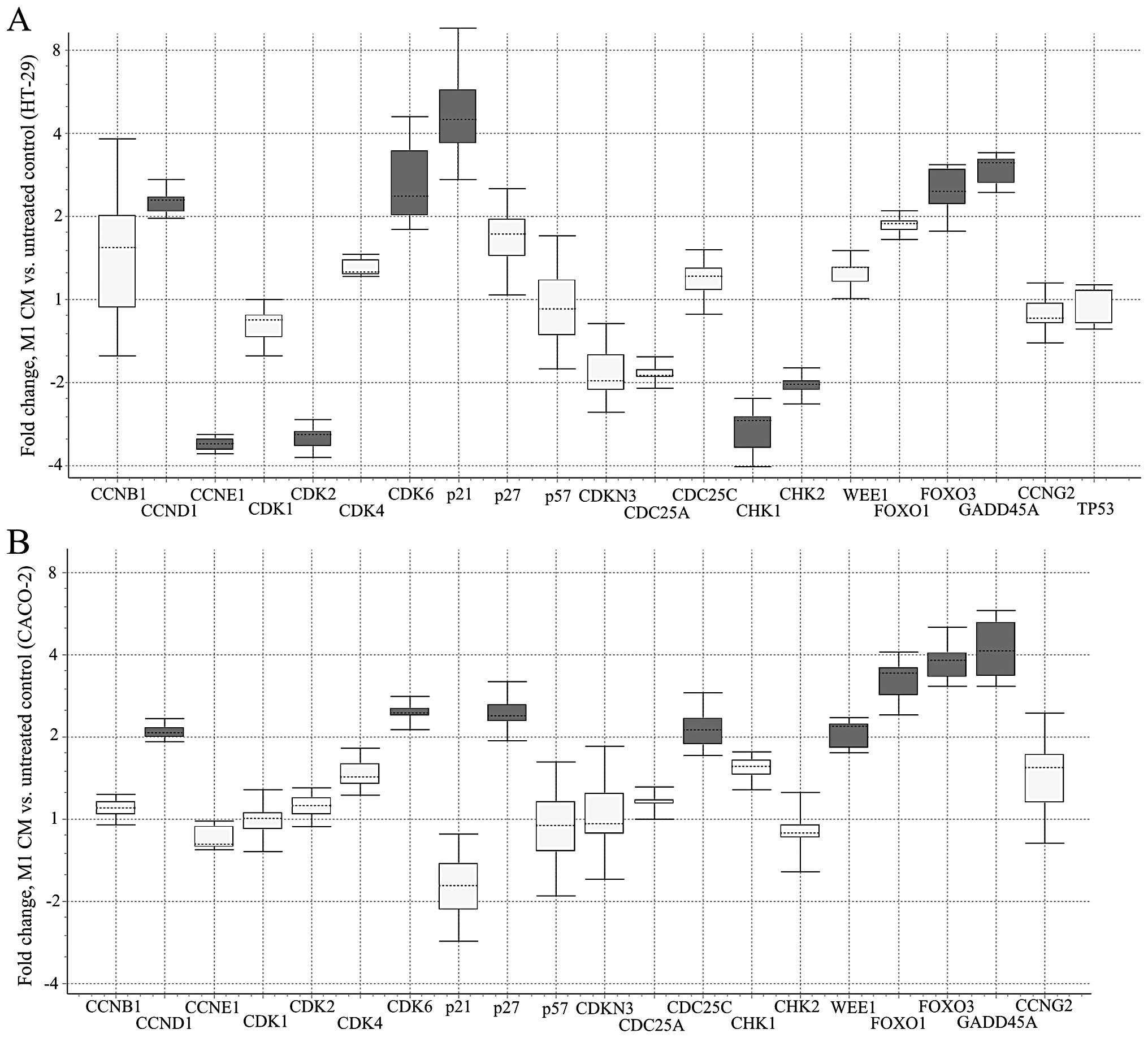
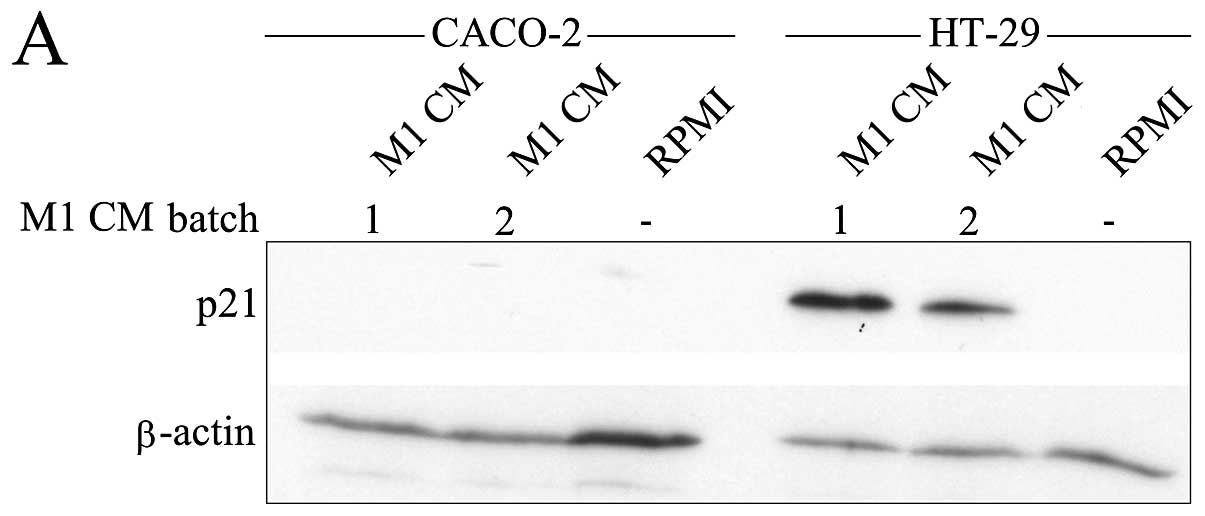
Engström A, Erlandsson A, Delbro D and
Wijkander J: Conditioned media from macrophages of M1, but not M2
phenotype, inhibit the proliferation of the colon cancer cell lines
HT-29 and CACO-2. Int J Oncol. 44:385–392. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW and Dempfle L:
Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison
and statistical analysis of relative expression results in
real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:e362002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ruijter JM, Ramakers C, Hoogaars WM, et
al: Amplification efficiency: linking baseline and bias in the
analysis of quantitative PCR data. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:e452009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bossi G, Lapi E, Strano S, Rinaldo C,
Blandino G and Sacchi A: Mutant p53 gain of function: reduction of
tumor malignancy of human cancer cell lines through abrogation of
mutant p53 expression. Oncogene. 25:304–309. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang N, Yin Y, Xu SJ and Chen WS:
5-Fluorouracil: mechanisms of resistance and reversal strategies.
Molecules. 13:1551–1569. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Song B, Wang Y, Xi Y, et al: Mechanism of
chemoresistance mediated by miR-140 in human osteosarcoma and colon
cancer cells. Oncogene. 28:4065–4074. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Harper JW, Elledge SJ, Keyomarsi K, et al:
Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases by p21. Mol Biol Cell.
6:387–400. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Choi YK, Seo HS, Choi HS, Kim SR, Shin YC
and Ko SG: Induction of Fas-mediated extrinsic apoptosis,
p21WAF1-related G2/M cell cycle arrest and ROS generation by
costunolide in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cells,
MDA-MB-231. Mol Cell Biochem. 363:119–128. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sturm I, Rau B, Schlag PM, et al: Genetic
dissection of apoptosis and cell cycle control in response of
colorectal cancer treated with preoperative radiochemotherapy. BMC
Cancer. 6:1242006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yoshiba S, Ito D, Nagumo T, Shirota T,
Hatori M and Shintani S: Hypoxia induces resistance to
5-fluorouracil in oral cancer cells via G(1) phase cell cycle
arrest. Oral Oncol. 45:109–115. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K
and Elledge SJ: The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent
inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 75:805–816. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rodrigues NR, Rowan A, Smith ME, et al:
p53 mutations in colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
87:7555–7559. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Seoane J, Le HV, Shen L, Anderson SA and
Massagué J: Integration of Smad and forkhead pathways in the
control of neuroepithelial and glioblastoma cell proliferation.
Cell. 117:211–223. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fu G and Peng C: Nodal enhances the
activity of FoxO3a and its synergistic interaction with Smads to
regulate cyclin G2 transcription in ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene.
30:3953–3966. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Stahl M, Dijkers PF, Kops GJ, et al: The
forkhead transcription factor FoxO regulates transcription of
p27Kip1 and Bim in response to IL-2. J Immunol. 168:5024–5031.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Notas G, Alexaki VI, Kampa M, et al: APRIL
binding to BCMA activates a JNK2-FOXO3-GADD45 pathway and induces a
G2/M cell growth arrest in liver cells. J Immunol. 189:4748–4758.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Doroshow JH, Multhauf P, Leong L, et al:
Prospective randomized comparison of fluorouracil versus
fluorouracil and high-dose continuous infusion leucovorin calcium
for the treatment of advanced measurable colorectal cancer in
patients previously unexposed to chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol.
8:491–501. 1990.
|
|
42
|
Schwartz EL, Baptiste N, Wadler S and
Makower D: Thymidine phosphorylase mediates the sensitivity of
human colon carcinoma cells to 5-fluorouracil. J Biol Chem.
270:19073–19077. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pritchard DM, Watson AJ, Potten CS,
Jackman AL and Hickman JA: Inhibition by uridine but not thymidine
of p53-dependent intestinal apoptosis initiated by 5-fluorouracil:
evidence for the involvement of RNA perturbation. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 94:1795–1799. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Peters GJ, van Groeningen CJ, Laurensse EJ
and Pinedo HM: A comparison of 5-fluorouracil metabolism in human
colorectal cancer and colon mucosa. Cancer. 68:1903–1909. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Etienne MC, Chéradame S, Fischel JL, et
al: Response to fluorouracil therapy in cancer patients: the role
of tumoral dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase activity. J Clin Oncol.
13:1663–1670. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Takagi K, Sowa Y, Cevik OM, Nakanishi R
and Sakai T: CDK inhibitor enhances the sensitivity to
5-fluorouracil in colorectal cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
32:1105–1110. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Matsushita S, Ikeda R, Nishizawa Y, et al:
The role of thymidine phosphorylase in the induction of early
growth response protein-1 and thrombospondin-1 by 5-fluorouracil in
human cancer carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 36:1193–1200. 2010.
|