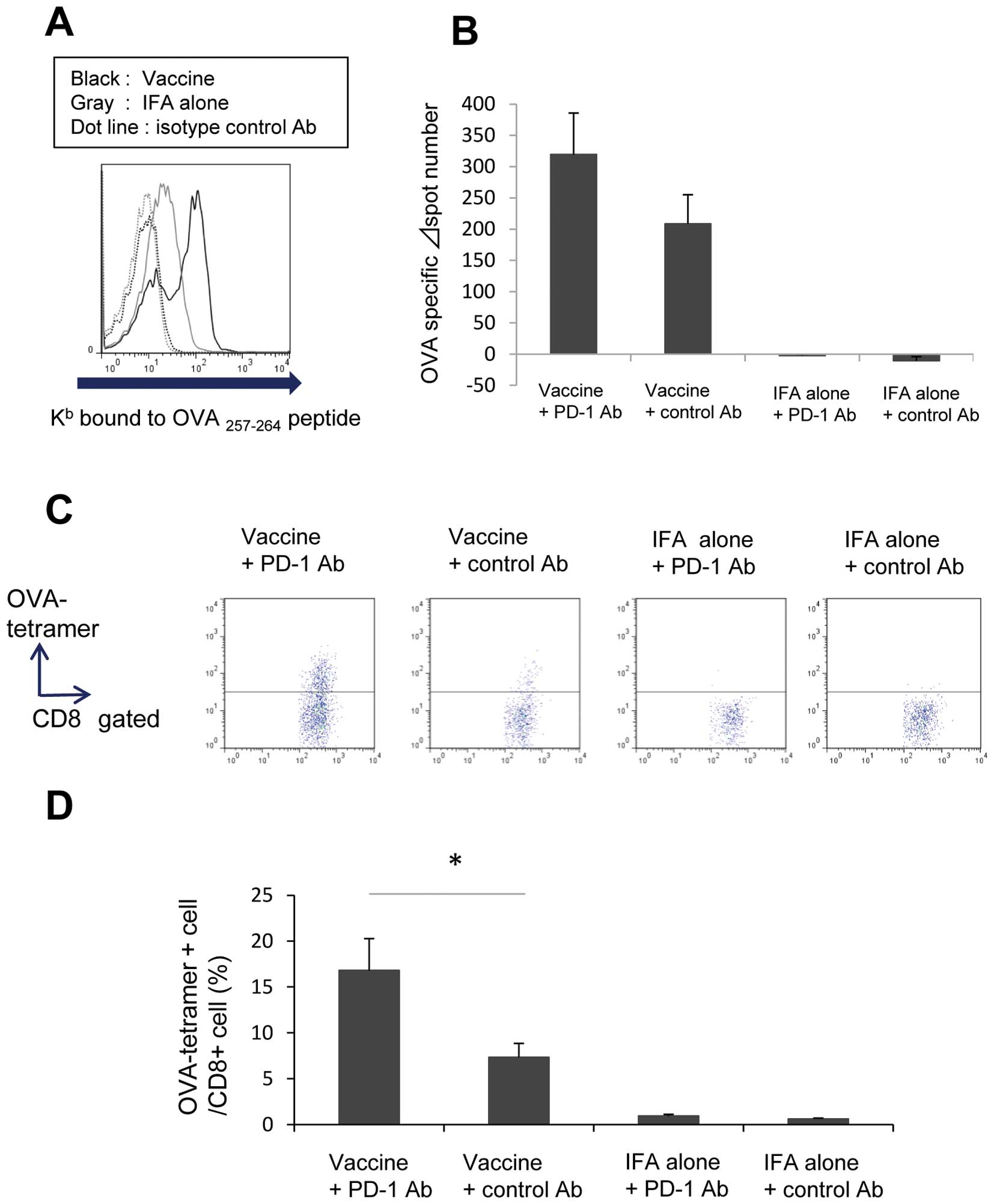
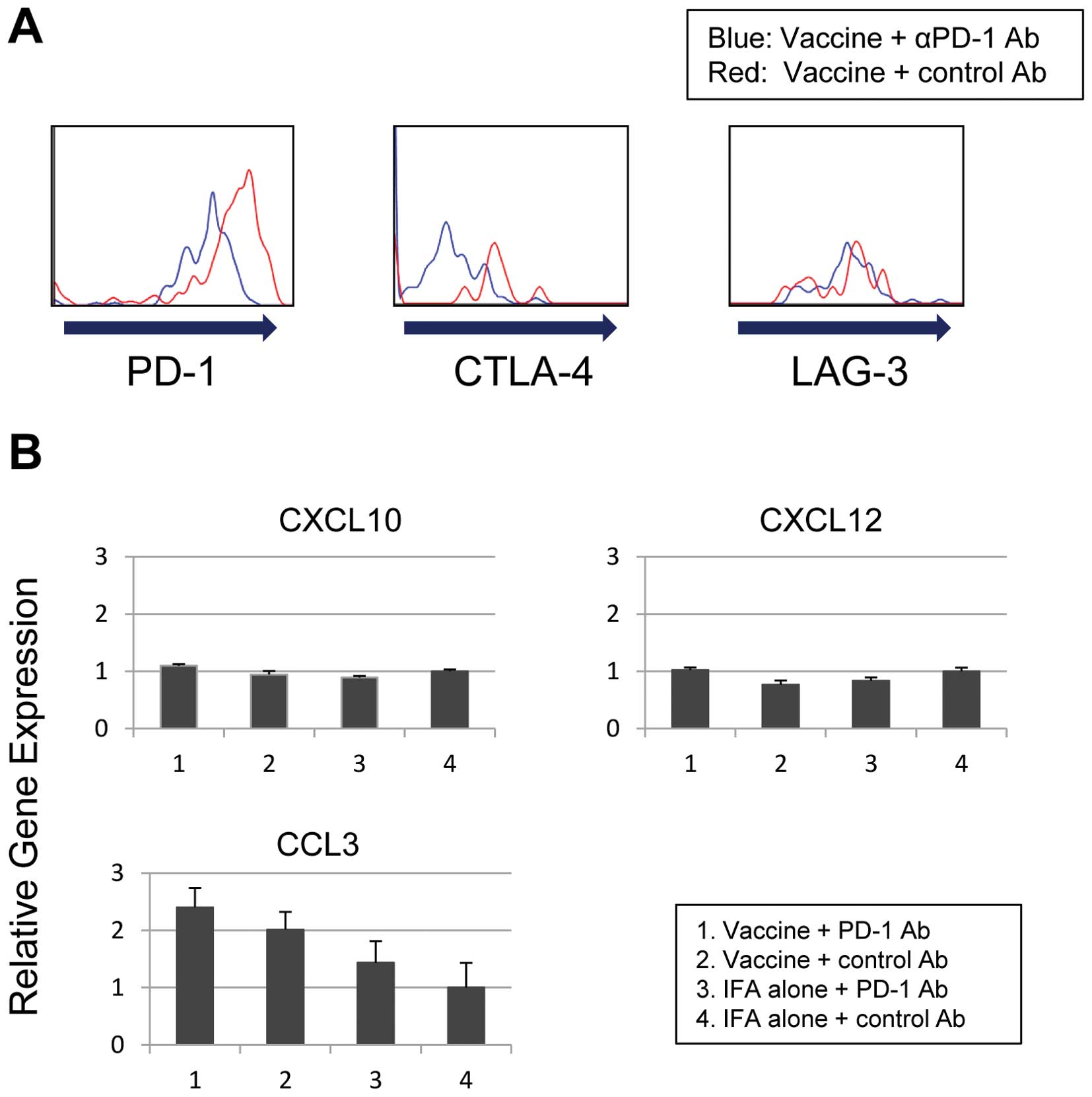
|
1
|
Breous E and Thimme R: Potential of
immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 54:830–834.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Greten TF, Manns MP and Korangy F:
Immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 45:868–878.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nakatsura T, Yoshitake Y, Senju S, et al:
Glypican-3, overexpressed specifically in human hepatocellular
carcinoma, is a novel tumor marker. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
306:16–25. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Capurro M, Wanless IR, Sherman M, et al:
Glypican-3: a novel serum and histochemical marker for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 125:89–97. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nakatsura T, Komori H, Kubo T, et al:
Mouse homologue of a novel human oncofetal antigen, glypican-3,
evokes T-cell-mediated tumor rejection without autoimmune reactions
in mice. Clin Cancer Res. 10:8630–8640. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Komori H, Nakatsura T, Senju S, et al:
Identification of HLA-A2- or HLA-A24-restricted CTL epitopes
possibly useful for glypican-3-specific immunotherapy of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 12:2689–2697. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shirakawa H, Suzuki H, Shimomura M, et al:
Glypican-3 expression is correlated with poor prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 100:1403–1407. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sawada Y, Yoshikawa T, Nobuoka D, et al:
Phase I trial of a glypican-3-derived peptide vaccine for advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma: immunologic evidence and potential for
improving overall survival. Clin Cancer Res. 18:3686–3696. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yoshikawa T, Nakatsugawa M, Suzuki S, et
al: HLA-A2-restricted glypican-3 peptide-specific CTL clones
induced by peptide vaccine show high avidity and antigen-specific
killing activity against tumor cells. Cancer Sci. 102:918–925.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Agata Y, Kawasaki A, Nishimura H, et al:
Expression of the PD-1 antigen on the surface of stimulated mouse T
and B lymphocytes. Int Immunol. 8:765–772. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, et al:
Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7
family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte
activation. J Exp Med. 192:1027–1034. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Iwai Y, Ishida M, Tanaka Y, Okazaki T,
Honjo T and Minato N: Invovement of PD-L1 on tumor cells in the
escape from host immune system and tumor immunotherapy by PD-L1
blockade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:12294–12297. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Iwai Y, Terawaki S and Honjo T: PD-1
blockade inhibits hematogenous spread of poorly immunogenic tumor
cells by enhanced recruitment of effector T cells. Int Immunol.
17:133–144. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, et al:
Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in
cancer. N Engl J Med. 366:2443–2454. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wolchok JD, Kluger H, Callahan MK, et al:
Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med.
369:122–133. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shi F, Shi M, Zeng Z, et al: PD-1 and
PD-L1 upregulation promotes CD8(+) T-cell apoptosis and
postoperative recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Int
J Cancer. 128:887–896. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gao Q, Wang XY, Qiu SJ, et al:
Overexpression of PD-L1 significantly associates with tumor
aggressiveness and postoperative recurrence in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:971–979. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
McGray AJ, Bernard D, Hallett R, et al:
Combined vaccination and immunostimulatory antibodies provides
durable cure of murine melanoma and induces transcriptional changes
associated with positive outcome in human melanoma patients.
Oncoimmunology. 1:419–431. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Mkrtichyan M, Najjar YG, Raulfs EC, et al:
Anti-PD-1 synergizes with cyclophosphamide to induce potent
antitumor vaccine effects through novel mechanisms. Eur J Immunol.
41:2977–2986. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Duraiswamy J, Kaluza KM, Freeman GJ and
Coukos G: Dual blockade of PD-1 and CTLA-4 combined with tumor
vaccine efficacy restorres T cell rejection function in tumors.
Cancer Res. 73:3591–3603. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fourcade J, Sun Z, Pagliano O, et al: PD-1
and Tim-3 regulate the expansion of tumor antigen-specific
CD8+ T cells induced by melanoma vaccines. Cancer Res.
74:1045–1055. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nobuoka D, Yoshikawa T, Takahashi M, et
al: Intratumoral peptide injection enhances tumor cell antigenicity
recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes: a potential option for
improvement in antigen-specific cancer immunotherapy. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 62:639–652. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li B, VanRoey M, Wang C, Chen TH, Korman A
and Jooss K: Anti-programmed death-1 synergizes with granulocyte
macrophage colony-stimulating factor - secreting tumor cell
immunotherapy providing therapeutic benefit to mice with
established tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 15:1623–1634. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Iwama T, Horie K, Yoshikawa T, et al:
Identification of an H2-Kb or H2-Db
restricted and glypican-3-derived cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitope
peptide. Int J Oncol. 42:831–838. 2013.
|
|
25
|
Peng W, Liu C, Xu C, et al: PD-1 blockade
enhances T-cell migration to tumors by elevating IFN-γ inducible
chemokines. Cancer Res. 72:5209–5218. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tada Y, Yoshikawa T, Shimomura M, et al:
Analysis of cytotoxic T lymphocytes from a patient with
hepatocellular carcinoma who showed a clinical response to
vaccination with a glypican-3-derived peptide. Int J Oncol.
43:1019–1026. 2013.
|
|
27
|
Wong RM, Scotland RR, Lau RL, et al:
Programmed death-1 blockade enhances expansion and functional
capacity of human melanoma antigen-specific CTLs. Int Immunol.
19:1223–1234. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mizukoshi E, Nakamoto Y, Arai K, et al:
Comparative analysis of various tumor-associated antigen-specific
T-cell responses in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 53:1206–1216. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Butterfield LH, Ribas A, Meng WS, et al:
T-cell responses to HLA-A*0201 immunodominant peptides
derived from alpha-fetoprotein in patients with hepatocellular
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 9:5902–5908. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Butterfield LH, Ribas A, Dissette VB, et
al: A phase I/II trial testing immunization of hepatocellular
carcinoma patients with dendritic cells pulsed with four
alpha-fetoprotein peptides. Clin Cancer Res. 12:2817–2825. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Greten TF, Forner A, Korangy F, et al: A
phase II open trial evaluating safety and efficacy of a telomerase
peptide vaccination in patients with advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 10:2092010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Capurro MI, Xiang YY, Lobe C and Filmus J:
Glypican-3 promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by
stimulating canonical Wnt signaling. Cancer Res. 65:6245–6254.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Feng M, Gao W, Wang R, et al:
Therapeutically targeting glypican-3 via a conformation-specific
single-domain antibody in hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 110:E1083–E1091. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nagao M, Nakajima Y, Hisanaga M, et al:
The alteration of Fas receptor and ligand system in hepatocellular
carcinomas: how do hepatoma cells escape from the host immune
surveillance in vivo? Hepatology. 30:413–421. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen C, Zhang C, Zhuang G, et al: Decoy
receptor 3 overexpression and immunologic tolerance in
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development. Cancer Invest.
26:965–974. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xu Y, Li H, Gao RL, Adeyemo O, Itkin M and
Kaplan DE: Expansion of interferon-gamma-producing multifunctional
CD4+ T-cells and dysfunctional CD8+ T-cells
by glypican-3 peptide library in hepatocellular carcinoma patients.
Clin Immunol. 139:302–313. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hailemichael Y, Dai Z, Jaffarzad N, et al:
Persistent antigen at vaccination sites induces tumor-specific
CD8(+) T cell sequestration, dysfunction and deletion. Nat Med.
19:465–472. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Woo SR, Turnis ME, Goldberg MV, et al:
Immune inhibitory molecules LAG-3 and PD-1 synergistically regulate
T-cell function to promote tumoral immune escape. Cancer Res.
72:917–927. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Matsuzaki J, Gnjatic S, Mhawech-Fauceglia
P, et al: Tumor-infiltrating NY-ESO-1-specific CD8+ T
cells are negatively regulated by LAG-3 and PD-1 in human ovarian
cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:7875–7880. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sierro SR, Donda A, Perret R, et al:
Combination of lentivector immunization and low-dose chemotherapy
or PD-1/PD-L1 blocking primes self-reactive T cells and induces
antitumor immunity. Eur J Immunol. 41:2217–2228. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|