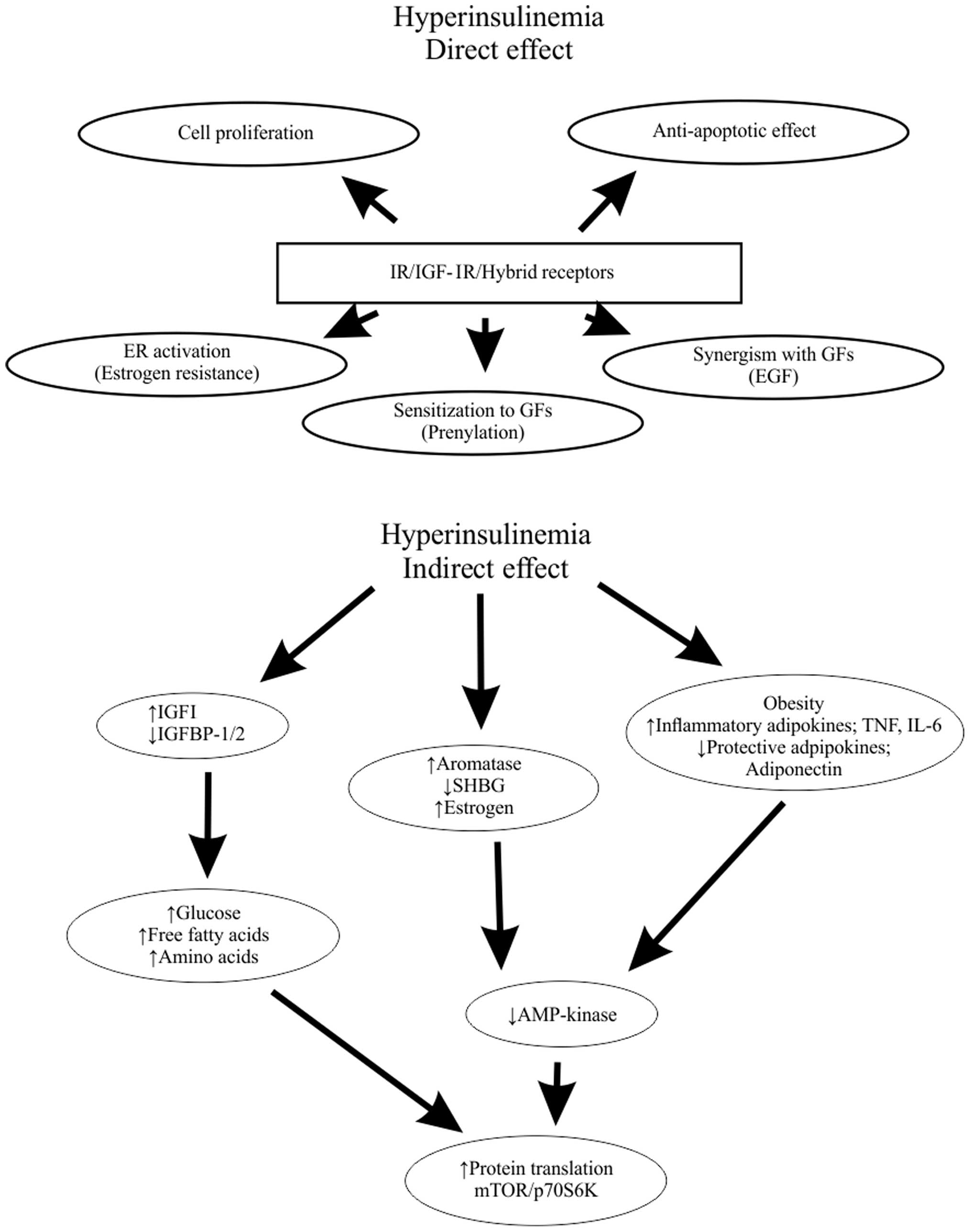
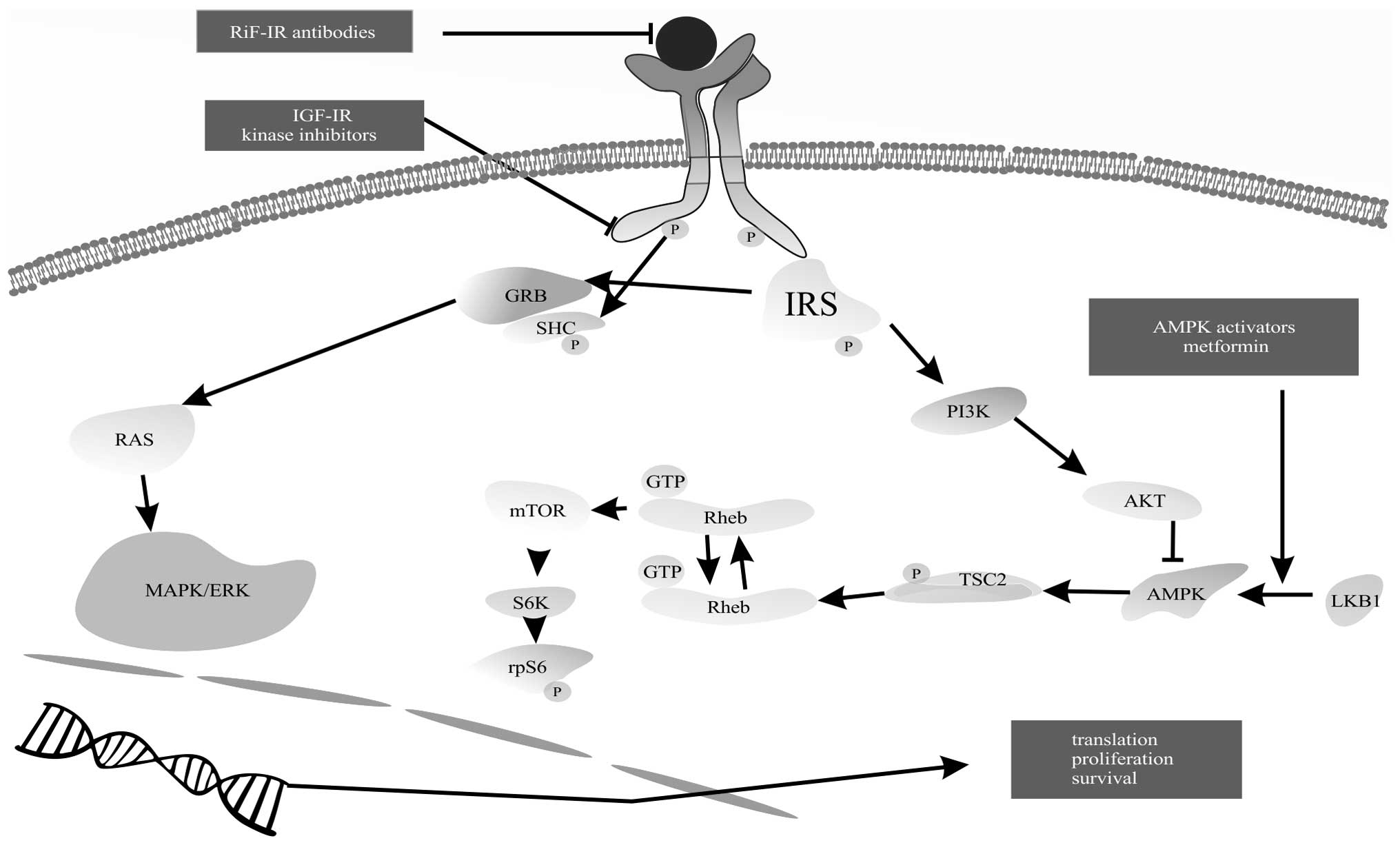
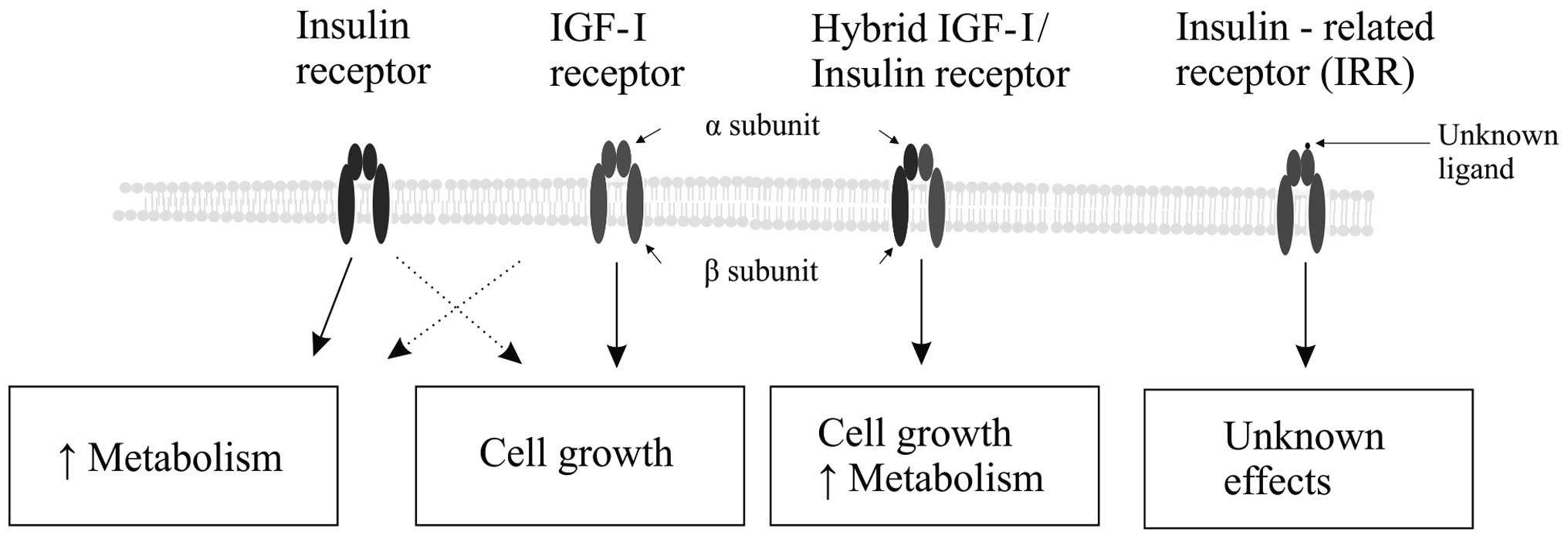
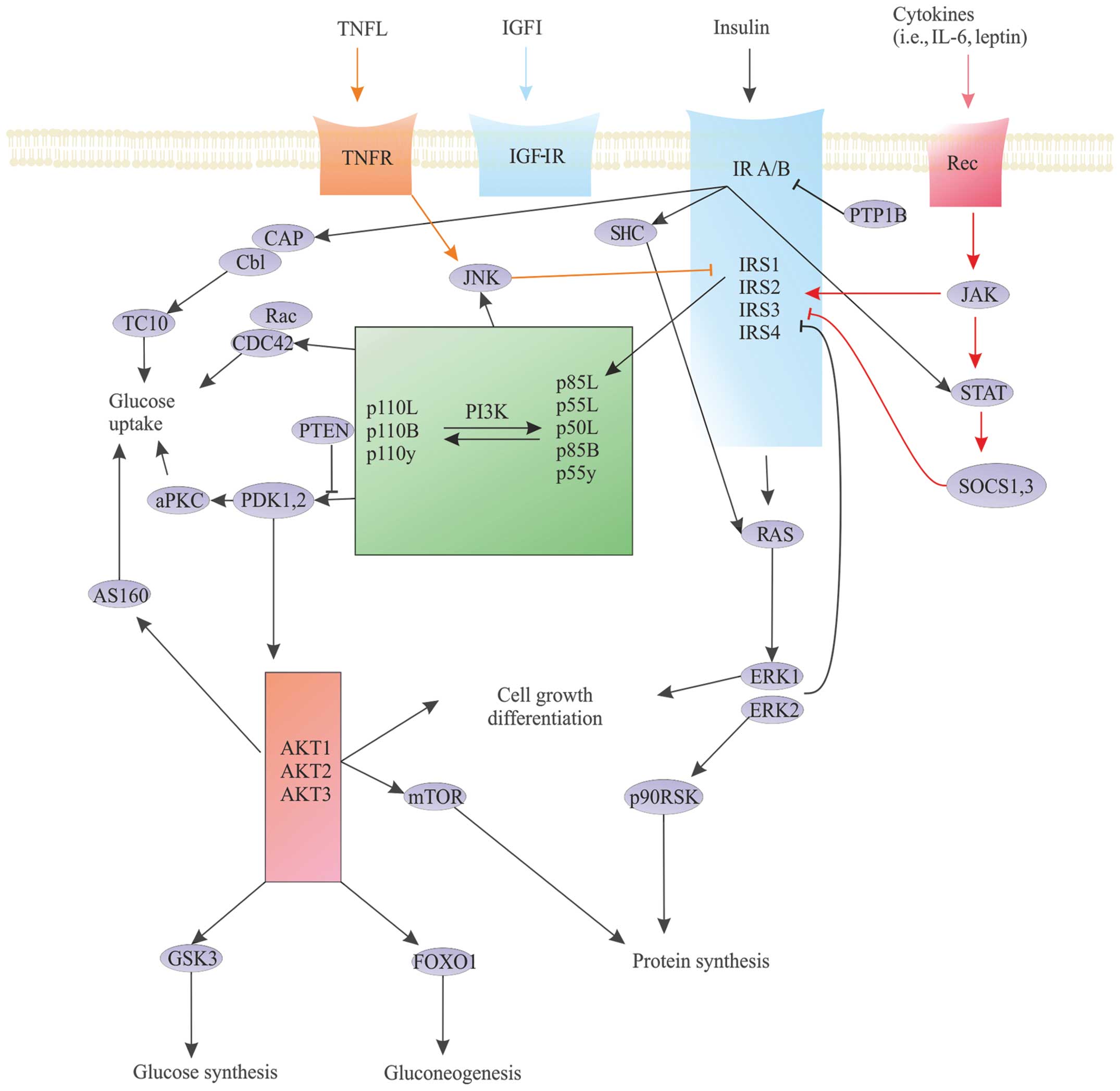
|
1
|
Piatkiewicz P and Czech A: Glucose
metabolism disorders and the risk of cancer. Arch Immunol Ther Exp
(Warsz). 59:215–230. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bergamini E, Cavallini G, Donati A and
Gori Z: The role of autophagy in aging: its essential part in the
anti-aging mechanism of caloric restriction. Ann NY Acad Sci.
1114:69–78. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
De Meyts P: The structural basis of
insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I receptor binding and
negative co-operativity, and its relevance to mitogenic versus
metabolic signalling. Diabetologia. 37(Suppl 2): S135–S148. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jensen M and De Meyts P: Molecular
mechanisms of differential intracellular signaling from the insulin
receptor. Vitam Horm. 80:51–75. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hermann C, Assmus B, Urbich C, Zeiher AM
and Dimmeler S: Insulin-mediated stimulation of protein kinase Akt:
A potent survival signaling cascade for endothelial cells.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 20:402–409. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hwa V, Oh Y and Rosenfeld RG: The
insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP) superfamily.
Endocr Rev. 20:761–787. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Holly J and Perks C: The role of
insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Neuroendocrinology.
83:154–160. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jones JI and Clemmons DR: Insulin-like
growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions.
Endocr Rev. 16:3–34. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Werner H, Weinstein D and Bentov I:
Similarities and differences between insulin and IGF-I: structures,
receptors, and signalling pathways. Arch Physiol Biochem.
114:17–22. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee PD, Giudice LC, Conover CA and Powell
DR: Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1: recent findings
and new directions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 216:319–357. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gum RJ, Gaede LL, Koterski SL, et al:
Reduction of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B increases
insulin-dependent signaling in ob/ob mice. Diabetes. 52:21–28.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Taniguchi CM, Emanuelli B and Kahn CR:
Critical nodes in signalling pathways: insights into insulin
action. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:85–96. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ueki K, Kondo T and Kahn CR: Suppressor of
cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS-1) and SOCS-3 cause insulin resistance
through inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptor
substrate proteins by discrete mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol.
24:5434–5446. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ueki K, Kondo T, Tseng YH and Kahn CR:
Central role of suppressors of cytokine signaling proteins in
hepatic steatosis, insulin resistance, and the metabolic syndrome
in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:10422–10427. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Emanuelli B, Peraldi P, Filloux C,
Sawka-Verhelle D, Hilton D and Van Obberghen E: SOCS-3 is an
insulin-induced negative regulator of insulin signaling. J Biol
Chem. 275:15985–15991. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Emanuelli B, Peraldi P, Filloux C, et al:
SOCS-3 inhibits insulin signaling and is up-regulated in response
to tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the adipose tissue of obese mice.
J Biol Chem. 276:47944–47949. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wick KR, Werner ED, Langlais P, et al:
Grb10 inhibits insulin- stimulated insulin receptor substrate
(IRS)-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway by
disrupting the association of IRS-1/IRS-2 with the insulin
receptor. J Biol Chem. 278:8460–8467. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Dong H, Maddux BA, Altomonte J, et al:
Increased hepatic levels of the insulin receptor inhibitor,
PC-1/NPP1, induce insulin resistance and glucose intolerance.
Diabetes. 54:367–372. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kellerer M, von Eye Corleta H, Mühlhöfer
A, et al: Insulin- and insulin-like growth-factor-I receptor
tyrosine-kinase activities in human renal carcinoma. Int J Cancer.
62:501–507. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Corleta HE, Capp E and Corleta OC: Insulin
receptor tyrosine kinase activity in colon carcinoma. Braz J Med
Biol Res. 29:1593–1597. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Werner H and Le Roith D: New concepts in
regulation and function of the insulin-like growth factors:
implications for understanding normal growth and neoplasia. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 57:932–942. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yi HK, Hwang PH, Yang DH, Kang CW and Lee
DY: Expression of the insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and the
IGF-binding proteins (IGFBPs) in human gastric cancer cells. Eur J
Cancer. 37:2257–2263. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hudelist G, Wagner T, Rosner M, et al:
Intratumoral IGF-I protein expression is selectively upregulated in
breast cancer patients with BRCA1/2 mutations. Endocr Relat Cancer.
14:1053–1062. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim WY, Jin Q, Oh SH, et al: Elevated
epithelial insulin-like growth factor expression is a risk factor
for lung cancer development. Cancer Res. 69:7439–7448. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Werner H and Bruchim I: The insulin-like
growth factor-I receptor as an oncogene. Arch Physiol Biochem.
115:58–71. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vella V, Pandini G, Sciacca L, et al: A
novel autocrine loop involving IGF-II and the insulin receptor
isoform-A stimulates growth of thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 87:245–254. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Boulle N, Logié A, Gicquel C, Perin L and
Le Bouc Y: Increased levels of insulin-like growth factor II
(IGF-II) and IGF-binding protein-2 are associated with malignancy
in sporadic adreno-cortical tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
83:1713–1720. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Moorehead RA, Sanchez OH, Baldwin RM and
Khokha R: Transgenic overexpression of IGF-II induces spontaneous
lung tumors: a model for human lung adenocarcinoma. Oncogene.
22:853–857. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee JS, Weiss J, Martin JL and Scott CD:
Increased expression of the mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth
factor-II receptor in breast cancer cells alters tumorigenic
properties in vitro and in vivo. Int J Cancer. 107:564–570. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hebert E: Mannose-6-phosphate/insulin-like
growth factor II receptor expression and tumor development. Biosci
Rep. 26:7–17. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
El-Shewy HM and Luttrell LM: Insulin-like
growth factor-2/mannose-6 phosphate receptors. Vitam Horm.
80:667–697. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Larsson O, Girnita A and Girnita L: Role
of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signalling in cancer. Br J
Cancer. 92:2097–2101. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
LeRoith D and Roberts CT Jr: The
insulin-like growth factor system and cancer. Cancer Lett.
195:127–137. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Frasca F, Pandini G, Sciacca L, et al: The
role of insulin receptors and IGF-I receptors in cancer and other
diseases. Arch Physiol Biochem. 114:23–37. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Godsland IF: Insulin resistance and
hyperinsulinaemia in the development and progression of cancer.
Clin Sci (Lond). 118:315–332. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Renehan AG, Zwahlen M, Minder C, O’Dwyer
ST, Shalet SM and Egger M: Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF
binding protein-3, and cancer risk: systematic review and
meta-regression analysis. Lancet. 363:1346–1353. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ihle NT and Powis G: Take your PIK:
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors race through the clinic
and toward cancer therapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:1–9. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Robey RB and Hay N: Is Akt the ‘Warburg
kinase’? -Akt-energy metabolism interactions and oncogenesis. Semin
Cancer Biol. 19:25–31. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Courtney KD, Corcoran RB and Engelman JA:
The PI3K pathway as drug target in human cancer. J Clin Oncol.
28:1075–1083. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jenab M, Riboli E, Cleveland RJ, et al:
Serum C-peptide, IGFBP-1 and IGFBP-2 and risk of colon and rectal
cancers in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and
Nutrition. Int J Cancer. 121:368–376. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wei EK, Ma J, Pollak MN, et al: A
prospective study of C-peptide, insulin-like growth factor-I,
insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1, and the risk of
colorectal cancer in women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
14:850–855. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kaaks R, Toniolo P, Akhmedkhanov A, et al:
Serum C-peptide, insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF-binding
proteins, and colorectal cancer risk in women. J Natl Cancer Inst.
92:1592–1600. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ma J, Giovannucci E, Pollak M, et al: A
prospective study of plasma C-peptide and colorectal cancer risk in
men. J Natl Cancer Inst. 96:546–553. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Schoen RE, Tangen CM, Kuller LH, et al:
Increased blood glucose and insulin, body size, and incident
colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 91:1147–1154. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Le Marchand L, Wang H, Rinaldi S, et al:
Associations of plasma C-peptide and IGFBP-1 levels with risk of
colorectal adenoma in a multiethnic population. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 19:1471–1477. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wolpin BM, Meyerhardt JA, Chan AT, et al:
Insulin, the insulin-like growth factor axis, and mortality in
patients with nonmetastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol.
27:176–185. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
47
|
Michaud DS, Wolpin B, Giovannucci E, et
al: Prediagnostic plasma C-peptide and pancreatic cancer risk in
men and women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 16:2101–2109.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Balkau B, Kahn HS, Courbon D, Eschwège E
and Ducimetière P; Paris Prospective Study. Hyperinsulinemia
predicts fatal liver cancer but is inversely associated with fatal
cancer at some other sites: the Paris Prospective Study. Diabetes
Care. 24:843–849. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Eliassen AH, Tworoger SS, Mantzoros CS,
Pollak MN and Hankinson SE: Circulating insulin and c-peptide
levels and risk of breast cancer among predominately premenopausal
women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 16:161–164. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hirose K, Toyama T, Iwata H, Takezaki T,
Hamajima N and Tajima K: Insulin, insulin-like growth factor-I and
breast cancer risk in Japanese women. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
4:239–246. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Larsson SC, Mantzoros CS and Wolk A:
Diabetes mellitus and risk of breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Int J
Cancer. 121:856–862. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Cust AE, Allen NE, Rinaldi S, et al: Serum
levels of C-peptide, IGFBP-1 and IGFBP-2 and endometrial cancer
risk; results from the European prospective investigation into
cancer and nutrition. Int J Cancer. 120:2656–2664. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lukanova A, Lundin E, Micheli A, et al:
Risk of ovarian cancer in relation to prediagnostic levels of
C-peptide, insulin-like growth factor binding proteins-1 and -2
(USA, Sweden, Italy). Cancer Causes Control. 14:285–292. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lukanova A, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Lundin
E, et al: Prediagnostic levels of C-peptide, IGF-I, IGFBP -1, -2
and -3 and risk of endometrial cancer. Int J Cancer. 108:262–268.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Kasper JS and Giovannucci E: A
meta-analysis of diabetes mellitus and the risk of prostate cancer.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 15:2056–2062. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Borugian MJ, Spinelli JJ, Sun Z, et al:
Prediagnostic C-peptide and risk of prostate cancer. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 16:2164–2165. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Roddam AW, Allen NE, Appleby P, et al:
Insulin-like growth factors, their binding proteins, and prostate
cancer risk: analysis of individual patient data from 12
prospective studies. Ann Intern Med. 149:461–471. w83–w88. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ma J, Li H, Giovannucci E, et al:
Prediagnostic body-mass index, plasma C-peptide concentration, and
prostate cancer-specific mortality in men with prostate cancer: a
long-term survival analysis. Lancet Oncol. 9:1039–1047. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ahn J, Weinstein SJ, Snyder K, Pollak MN,
Virtamo J and Albanes D: No association between serum insulin-like
growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF-binding protein-3, and lung cancer risk.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 15:2010–2012. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lukanova A, Toniolo P, Akhmedkhanov A, et
al: A prospective study of insulin-like growth factor-I,
IGF-binding proteins-1, -2 and -3 and lung cancer risk in women.
Int J Cancer. 92:888–892. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
London SJ, Yuan JM, Travlos GS, et al:
Insulin-like growth factor I, IGF-binding protein 3, and lung
cancer risk in a prospective study of men in China. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 94:749–754. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Spitz MR, Barnett MJ, Goodman GE,
Thornquist MD, Wu X and Pollak M: Serum insulin-like growth factor
(IGF) and IGF-binding protein levels and risk of lung cancer: a
case-control study nested in the beta-Carotene and Retinol Efficacy
Trial Cohort. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 11:1413–1418.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Joshi N, Caputo GM, Weitekamp MR and
Karchmer AW: Infections in patients with diabetes mellitus. N Engl
J Med. 341:1906–1912. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Muller LM, Gorter KJ, Hak E, et al:
Increased risk of common infections in patients with type 1 and
type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Infect Dis. 41:281–288. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Takahashi K, Iwase M, Yamashita K, et al:
The elevation of natural killer cell activity induced by laughter
in a crossover designed study. Int J Mol Med. 8:645–650.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Li Q, Kobayashi M, Inagaki H, et al: A day
trip to a forest park increases human natural killer activity and
the expression of anti-cancer proteins in male subjects. J Biol
Regul Homeost Agents. 24:157–165. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Hayashi T, Tsujii S, Iburi T, et al:
Laughter up-regulates the genes related to NK cell activity in
diabetes. Biomed Res. 28:281–285. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Maes M, Meltzer HY, Stevens W, Calabrese J
and Cosyns P: Natural killer cell activity in major depression:
relation to circulating natural killer cells, cellular indices of
the immune response, and depressive phenomenology. Prog
Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 18:717–730. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Reiche EM, Nunes SO and Morimoto HK:
Stress, depression, the immune system, and cancer. Lancet Oncol.
5:617–625. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Kiessling R, Klein E, Pross H and Wigzell
H: ‘Natural’ killer cells in the mouse. II Cytotoxic cells with
specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells Characteristics of the
killer cell. Eur J Immunol. 5:117–121. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Kiessling R, Petranyi G, Kärre K, Jondal
M, Tracey D and Wigzell H: Killer cells: a functional comparison
between natural, immune T-cell and antibody-dependent in vitro
systems. J Exp Med. 143:772–780. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Roder JC, Kiessling R, Biberfeld P and
Andersson B: Target-effector interaction in the natural killer (NK)
cell system. II The isolation of NK cells and studies on the
mechanism of killing. J Immunol. 121:2509–2517. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Moretta L, Bottino C, Pende D, Vitale M,
Mingari MC and Moretta A: Human natural killer cells: molecular
mechanisms controlling NK cell activation and tumor cell lysis.
Immunol Lett. 100:7–13. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Waldhauer I and Steinle A: NK cells and
cancer immunosurveillance. Oncogene. 27:5932–5943. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Furue H, Matsuo K, Kumimoto H, et al:
Decreased risk of colorectal cancer with the high natural killer
cell activity NKG2D genotype in Japanese. Carcinogenesis.
29:316–320. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Szkaradkiewicz A, Karpiński TM, Drews M,
Borejsza-Wysocki M, Majewski P and Andrzejewska E: Natural killer
cell cytotoxicity and immunosuppressive cytokines (IL-10,
TGF-beta1) in patients with gastric cancer. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2010:9015642010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Hammond KJ, Pelikan SB, Crowe NY, et al:
NKT cells are phenotypically and functionally diverse. Eur J
Immunol. 29:3768–3781. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Jerud ES, Bricard G and Porcelli SA:
CD1d-restricted natural killer t cells: roles in tumor
immunosurveillance and tolerance. Transfus Med Hemother. 33:18–36.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Montoya CJ, Pollard D, Martinson J, et al:
Characterization of human invariant natural killer T subsets in
health and disease using a novel invariant natural killer T
cell-clonotypic monoclonal antibody, 6B11. Immunology. 122:1–14.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Balato A, Unutmaz D and Gaspari AA:
Natural killer T cells: an unconventional T-cell subset with
diverse effector and regulatory functions. J Invest Dermatol.
129:1628–1642. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Chan AC, Serwecinska L, Cochrane A,
Harrison LC, Godfrey DI and Berzins SP: Immune characterization of
an individual with an exceptionally high natural killer T cell
frequency and her immediate family. Clin Exp Immunol. 156:238–245.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Smyth MJ, Thia KY, Street SE, et al:
Differential tumor surveillance by natural killer (NK) and NKT
cells. J Exp Med. 191:661–668. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Mercer JC, Ragin MJ and August A: Natural
killer T cells: rapid responders controlling immunity and disease.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 37:1337–1343. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Bendelac A, Savage PB and Teyton L: The
biology of NKT cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 25:297–336. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Berzofsky JA and Terabe M: The contrasting
roles of NKT cells in tumor immunity. Curr Mol Med. 9:667–672.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Swann JB, Uldrich AP, van Dommelen S, et
al: Type I natural killer T cells suppress tumors caused by p53
loss in mice. Blood. 113:6382–6385. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
O’Shea D, Cawood TJ, O’Farrelly C and
Lynch L: Natural killer cells in obesity: impaired function and
increased susceptibility to the effects of cigarette smoke. PLoS
One. 5:e86602010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
88
|
Lynch LA, O’Connell JM, Kwasnik AK, Cawood
TJ, O’Farrelly C and O’Shea DB: Are natural killer cells protecting
the metabolically healthy obese patient? Obesity (Silver Spring).
17:601–605. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Lynch L, O’Shea D, Winter DC, Geoghegan J,
Doherty DG and O’Farrelly C: Invariant NKT cells and CD1d(+) cells
amass in human omentum and are depleted in patients with cancer and
obesity. Eur J Immunol. 39:1893–1901. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|