|
1
|
Farazi PA and DePinho RA: Hepatocellular
carcinoma pathogenesis: From genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:674–687. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Villanueva A, Savic R and Llovet JM:
Lymphotoxins: New targets for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer
Cell. 16:272–273. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang Z, Inuzuka H, Fukushima H, Wan L, Gao
D, Shaik S, Sarkar FH and Wei W: Emerging roles of the FBW7 tumour
suppressor in stem cell differentiation. EMBO Rep. 13:36–43. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
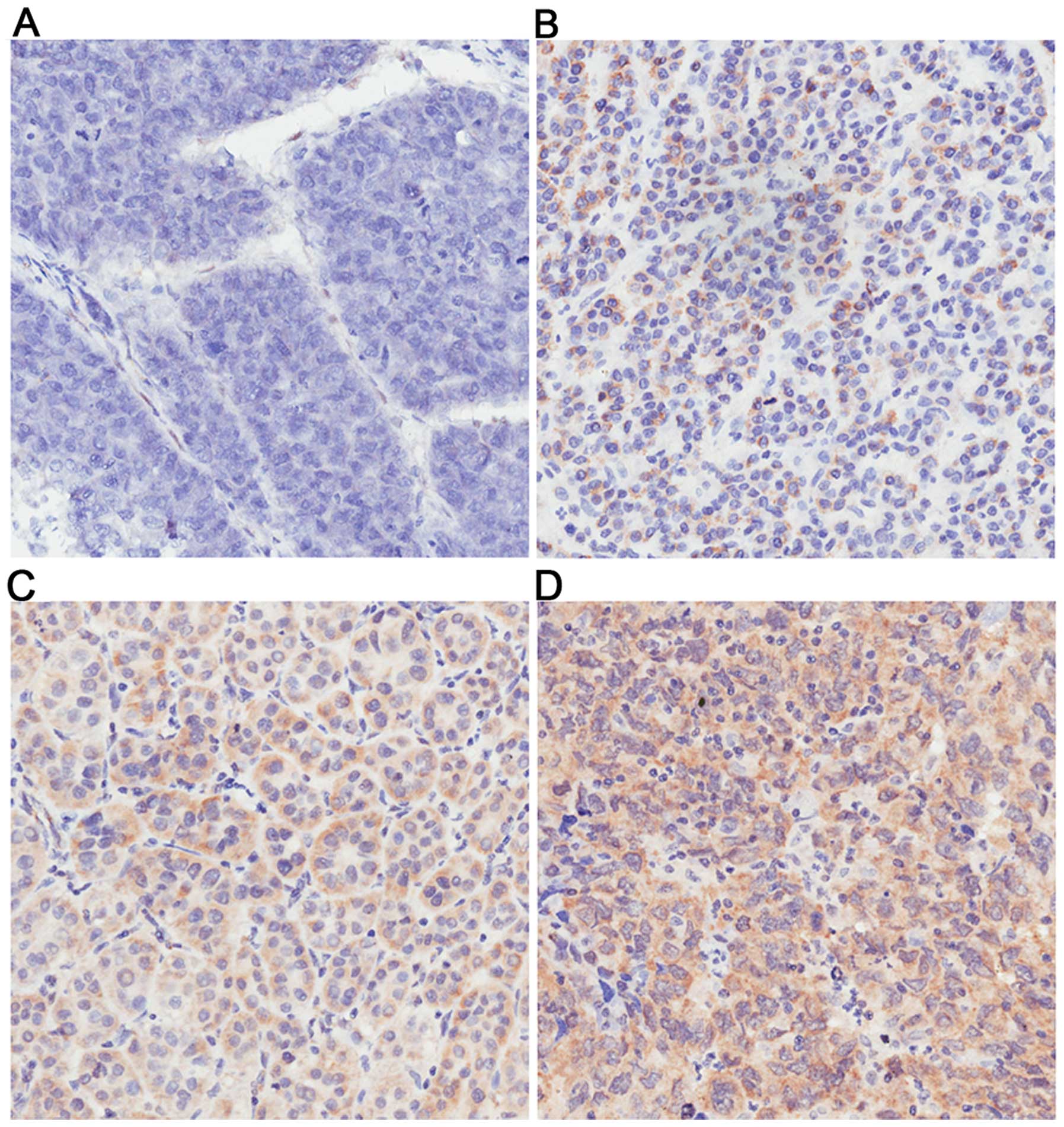
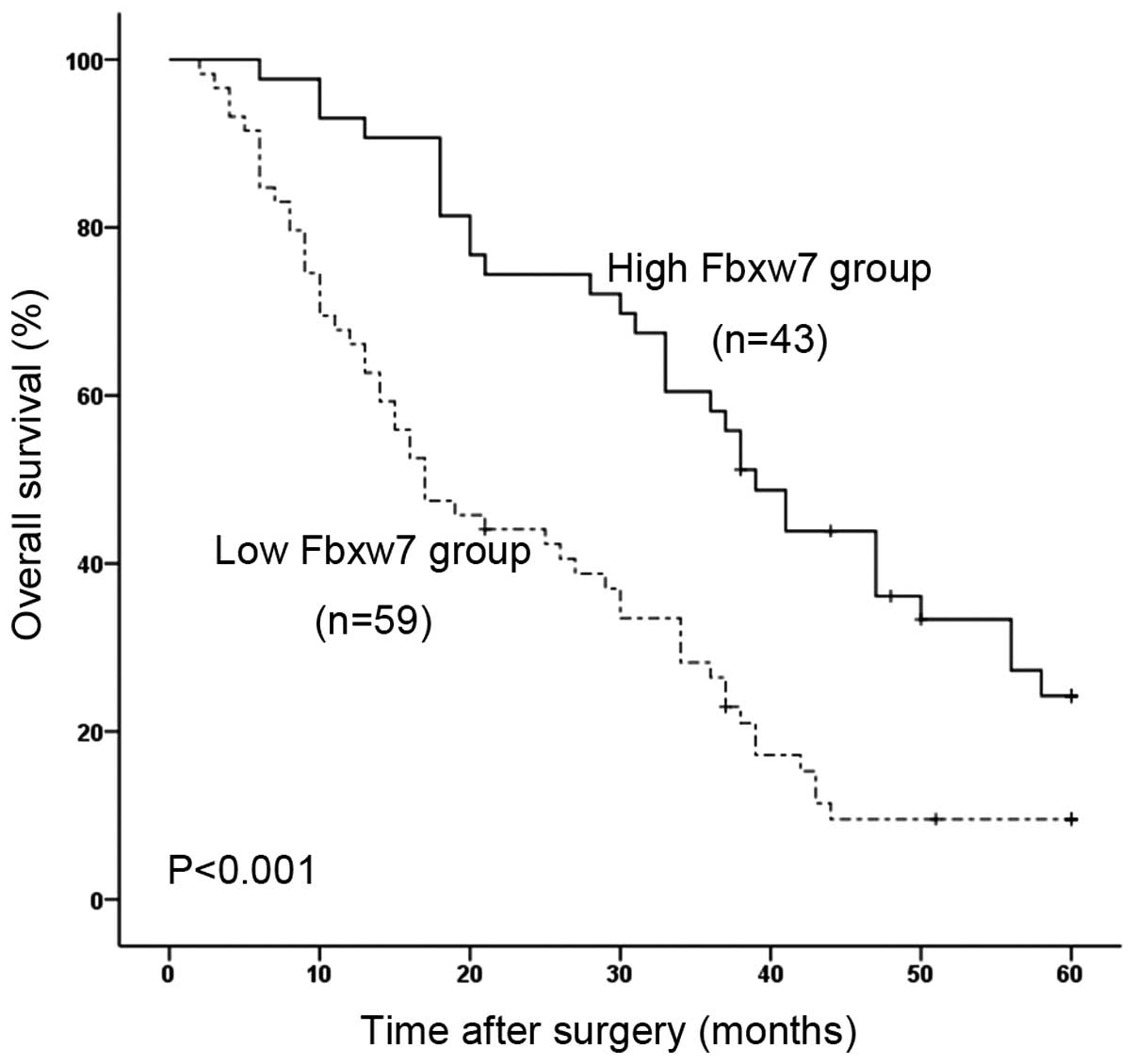
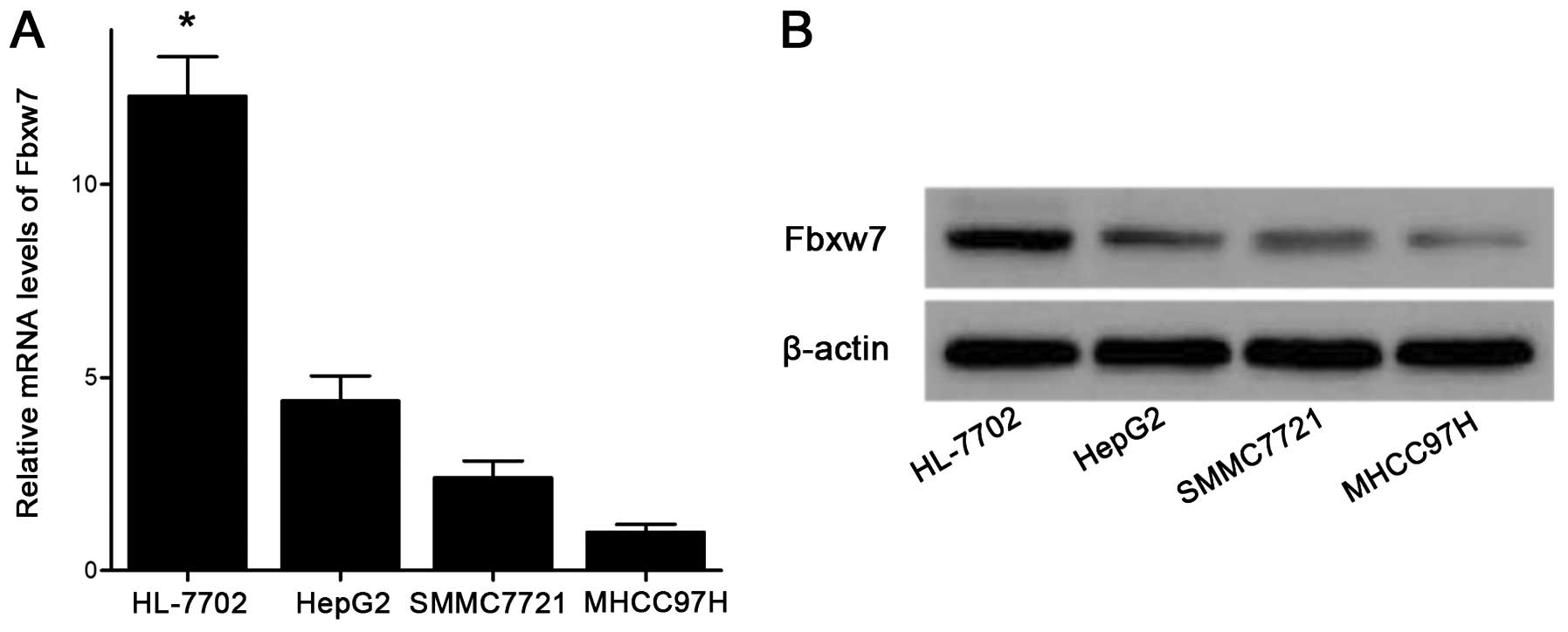
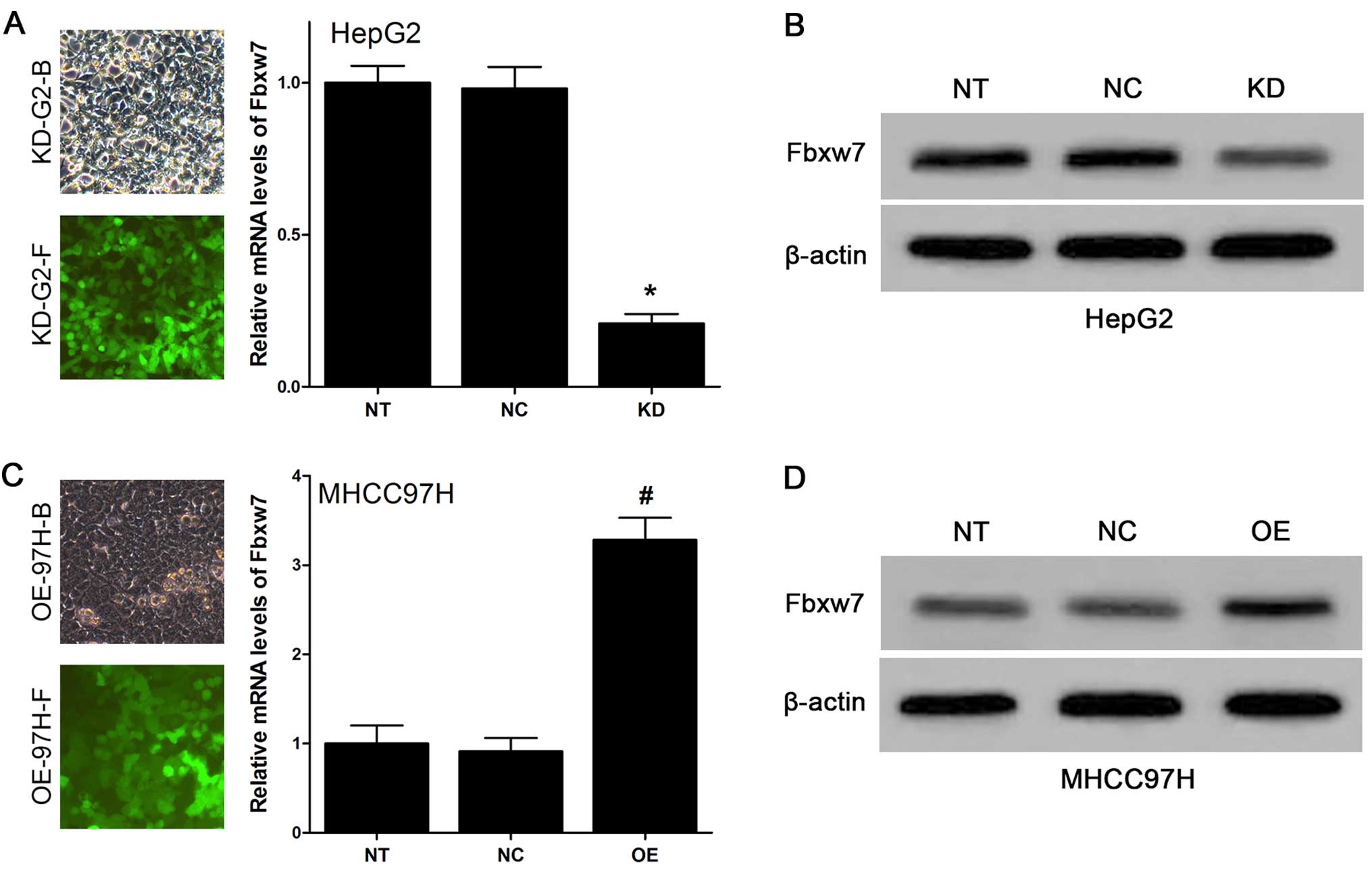
|
4
|
Welcker M and Clurman BE: FBW7 ubiquitin
ligase: A tumour suppressor at the crossroads of cell division,
growth and differentiation. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:83–93. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wang Z, Inuzuka H, Zhong J, Wan L,
Fukushima H, Sarkar FH and Wei W: Tumor suppressor functions of
FBW7 in cancer development and progression. FEBS Lett.
586:1409–1418. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Koepp DM, Schaefer LK, Ye X, Keyomarsi K,
Chu C, Harper JW and Elledge SJ: Phosphorylation-dependent
ubiquitination of cyclin E by the SCFFbw7 ubiquitin ligase.
Science. 294:173–177. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Welcker M, Orian A, Jin J, Grim JE, Harper
JW, Eisenman RN and Clurman BE: The Fbw7 tumor suppressor regulates
glycogen synthase kinase 3 phosphorylation-dependent c-Myc protein
degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:9085–9090. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu G, Lyapina S, Das I, Li J, Gurney M,
Pauley A, Chui I, Deshaies RJ and Kitajewski J: SEL-10 is an
inhibitor of notch signaling that targets notch for
ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation. Mol Cell Biol.
21:7403–7415. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tu K, Zheng X, Yin G, Zan X, Yao Y and Liu
Q: Evaluation of Fbxw7 expression and its correlation with
expression of SREBP-1 in a mouse model of NAFLD. Mol Med Rep.
6:525–530. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nateri AS, Riera-Sans L, Da Costa C and
Behrens A: The ubiquitin ligase SCFFbw7 antagonizes apoptotic JNK
signaling. Science. 303:1374–1378. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mao JH, Kim IJ, Wu D, Climent J, Kang HC,
Del Rosario R and Balmain A: FBXW7 targets mTOR for degradation and
cooperates with PTEN in tumor suppression. Science. 321:1499–1502.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Inuzuka H, Shaik S, Onoyama I, Gao D,
Tseng A, Maser RS, Zhai B, Wan L, Gutierrez A, Lau AW, et al:
SCF(FBW7) regulates cellular apoptosis by targeting MCL1 for
ubiquitylation and destruction. Nature. 471:104–109. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cheng Y and Li G: Role of the ubiquitin
ligase Fbw7 in cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 31:75–87.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Akhoondi S, Sun D, von der Lehr N,
Apostolidou S, Klotz K, Maljukova A, Cepeda D, Fiegl H, Dafou D,
Marth C, et al: FBXW7/hCDC4 is a general tumor suppressor in human
cancer. Cancer Res. 67:9006–9012. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Onoyama I, Suzuki A, Matsumoto A, Tomita
K, Katagiri H, Oike Y, Nakayama K and Nakayama KI: Fbxw7 regulates
lipid metabolism and cell fate decisions in the mouse liver. J Clin
Invest. 121:342–354. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Maser RS, Choudhury B, Campbell PJ, Feng
B, Wong KK, Protopopov A, O’Neil J, Gutierrez A, Ivanova E, Perna
I, et al: Chromosomally unstable mouse tumours have genomic
alterations similar to diverse human cancers. Nature. 447:966–971.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee JW, Soung YH, Kim HJ, Park WS, Nam SW,
Kim SH, Lee JY, Yoo NJ and Lee SH: Mutational analysis of the hCDC4
gene in gastric carcinomas. Eur J Cancer. 42:2369–2373. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kemp Z, Rowan A, Chambers W, Wortham N,
Halford S, Sieber O, Mortensen N, von Herbay A, Gunther T, Ilyas M,
et al: CDC4 mutations occur in a subset of colorectal cancers but
are not predicted to cause loss of function and are not associated
with chromosomal instability. Cancer Res. 65:11361–11366. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hubalek MM, Widschwendter A, Erdel M,
Gschwendtner A, Fiegl HM, Müller HM, Goebel G, Mueller-Holzner E,
Marth C, Spruck CH, et al: Cyclin E dysregulation and chromosomal
instability in endometrial cancer. Oncogene. 23:4187–4192. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Koh MS, Ittmann M, Kadmon D, Thompson TC
and Leach FS: CDC4 gene expression as potential biomarker for
targeted therapy in prostate cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 5:78–83.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Li J, Guo Y, Liang X, Sun M, Wang G, De W
and Wu W: MicroRNA-223 functions as an oncogene in human gastric
cancer by targeting FBXW7/hCdc4. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
138:763–774. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cheng Y, Chen G, Martinka M, Ho V and Li
G: Prognostic significance of Fbw7 in human melanoma and its role
in cell migration. J Invest Dermatol. 133:1794–1802. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Imura S, Tovuu LO, Utsunomiya T, Morine Y,
Ikemoto T, Arakawa Y, Kanamoto M, Iwahashi S, Saito Y, Takasu C, et
al: The role of Fbxw7 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma and
adjacent non-tumor liver tissue. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
29:1822–1829. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tu K, Zheng X, Zan X, Han S, Yao Y and Liu
Q: Evaluation of Fbxw7 expression and its correlation with the
expression of c-Myc, cyclin E and p53 in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 42:904–910. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Z, Banerjee S, Li Y, Rahman KM, Zhang
Y and Sarkar FH: Down-regulation of notch-1 inhibits invasion by
inactivation of nuclear factor-kappaB, vascular endothelial growth
factor, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in pancreatic cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 66:2778–2784. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu B, Wei J, Qian X, Lei D, Ma Q and Liu
Y: Notch1 signaling pathway participates in cancer invasion by
regulating MMPs in lingual squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep.
27:547–552. 2012.
|
|
27
|
Wang J, Fu L, Gu F and Ma Y: Notch1 is
involved in migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells.
Oncol Rep. 26:1295–1303. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou L, Wang DS, Li QJ, Sun W, Zhang Y and
Dou KF: Downregulation of the Notch signaling pathway inhibits
hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion by inactivation of matrix
metalloproteinase-2 and -9 and vascular endothelial growth factor.
Oncol Rep. 28:874–882. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou L, Zhang N, Song W, You N, Li Q, Sun
W, Zhang Y, Wang D and Dou K: The significance of Notch1 compared
with Notch3 in high metastasis and poor overall survival in
hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e573822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Aydin IT, Melamed RD, Adams SJ,
Castillo-Martin M, Demir A, Bryk D, Brunner G, Cordon-Cardo C,
Osman I, Rabadan R, et al: FBXW7 mutations in melanoma and a new
therapeutic paradigm. J Natl Cancer Inst. 106:dju1072014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Barnes DM, Harris WH, Smith P, Millis RR
and Rubens RD: Immunohistochemical determination of oestrogen
receptor: Comparison of different methods of assessment of staining
and correlation with clinical outcome of breast cancer patients. Br
J Cancer. 74:1445–1451. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou L, Zhang N, Li QJ, Sun W, Zhang Y,
Wang DS and Dou KF: Associations between high levels of Notch1
expression and high invasion and poor overall survival in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 34:543–553. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yokobori T, Mimori K, Iwatsuki M, Ishii H,
Onoyama I, Fukagawa T, Kuwano H, Nakayama KI and Mori M:
p53-Altered FBXW7 expression determines poor prognosis in gastric
cancer cases. Cancer Res. 69:3788–3794. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Iwatsuki M, Mimori K, Ishii H, Yokobori T,
Takatsuno Y, Sato T, Toh H, Onoyama I, Nakayama KI, Baba H, et al:
Loss of FBXW7, a cell cycle regulating gene, in colorectal cancer:
Clinical significance. Int J Cancer. 126:1828–1837. 2010.
|
|
35
|
Hagedorn M, Delugin M, Abraldes I, Allain
N, Belaud-Rotureau MA, Turmo M, Prigent C, Loiseau H, Bikfalvi A
and Javerzat S: FBXW7/hCDC4 controls glioma cell proliferation in
vitro and is a prognostic marker for survival in glioblastoma
patients. Cell Div. 2:92007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhou ZY, Tu KS, Zhang J, Zheng X, Gao J,
Yao YM and Liu QG: Expression of Fbxw7 and its correlation with
cell proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Xi Bao Yu Fen
Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 28:1303–1306. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jandke A, Da Costa C, Sancho R, Nye E,
Spencer-Dene B and Behrens A: The F-box protein Fbw7 is required
for cerebellar development. Dev Biol. 358:201–212. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD and Lake RJ:
Notch signaling: Cell fate control and signal integration in
development. Science. 284:770–776. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bedogni B, Warneke JA, Nickoloff BJ,
Giaccia AJ and Powell MB: Notch1 is an effector of Akt and hypoxia
in melanoma development. J Clin Invest. 118:3660–3670. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Blair SS: Notch signaling: Fringe really
is a glycosyltransferase. Curr Biol. 10:R608–R612. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Minella AC and Clurman BE: Mechanisms of
tumor suppression by the SCF(Fbw7). Cell Cycle. 4:1356–1359. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lai EC: Protein degradation: Four E3s for
the notch pathway. Curr Biol. 12:R74–R78. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Oberg C, Li J, Pauley A, Wolf E, Gurney M
and Lendahl U: The Notch intracellular domain is ubiquitinated and
negatively regulated by the mammalian Sel-10 homolog. J Biol Chem.
276:35847–35853. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sun L, Hui AM, Su Q, Vortmeyer A,
Kotliarov Y, Pastorino S, Passaniti A, Menon J, Walling J, Bailey
R, et al: Neuronal and glioma-derived stem cell factor induces
angiogenesis within the brain. Cancer Cell. 9:287–300. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
D’Errico M, de Rinaldis E, Blasi MF, Viti
V, Falchetti M, Calcagnile A, Sera F, Saieva C, Ottini L, Palli D,
et al: Genomewide expression profile of sporadic gastric cancers
with microsatellite instability. Eur J Cancer. 45:461–469. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Landi MT, Dracheva T, Rotunno M, Figueroa
JD, Liu H, Dasgupta A, Mann FE, Fukuoka J, Hames M, Bergen AW, et
al: Gene expression signature of cigarette smoking and its role in
lung adenocarcinoma development and survival. PLoS One.
3:e16512008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Curtis C, Shah SP, Chin SF, Turashvili G,
Rueda OM, Dunning MJ, Speed D, Lynch AG, Samarajiwa S, Yuan Y, et
al; METABRIC Group. The genomic and transcriptomic architecture of
2,000 breast tumours reveals novel subgroups. Nature. 486:346–352.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Su BH, Qu J, Song M, Huang XY, Hu XM, Xie
J, Zhao Y, Ding LC, She L, Chen J, et al: NOTCH1 signaling
contributes to cell growth, anti-apoptosis and metastasis in
salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Oncotarget. 5:6885–6895.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Reedijk M, Odorcic S, Chang L, Zhang H,
Miller N, McCready DR, Lockwood G and Egan SE: High-level
coexpression of JAG1 and NOTCH1 is observed in human breast cancer
and is associated with poor overall survival. Cancer Res.
65:8530–8537. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chu D, Li Y, Wang W, Zhao Q, Li J, Lu Y,
Li M, Dong G, Zhang H, Xie H, et al: High level of Notch1 protein
is associated with poor overall survival in colorectal cancer. Ann
Surg Oncol. 17:1337–1342. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Itoh Y and Nagase H: Matrix
metalloproteinases in cancer. Essays Biochem. 38:21–36.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nagase H, Visse R and Murphy G: Structure
and function of matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs. Cardiovasc
Res. 69:562–573. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kato Y, Yamashita T and Ishikawa M:
Relationship between expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and
matrix metalloproteinase-9 and invasion ability of cervical cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 9:565–569. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Giambernardi TA, Grant GM, Taylor GP, Hay
RJ, Maher VM, McCormick JJ and Klebe RJ: Overview of matrix
metalloproteinase expression in cultured human cells. Matrix Biol.
16:483–496. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Iwasaki M, Nishikawa A, Fujimoto T,
Akutagawa N, Manase K, Endo T, Yoshida K, Maekawa R, Yoshioka T and
Kudo R: Anti-invasive effect of MMI-166, a new selective matrix
metalloproteinase inhibitor, in cervical carcinoma cell lines.
Gynecol Oncol. 85:103–107. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Komatsu K, Nakanishi Y, Nemoto N, Hori T,
Sawada T and Kobayashi M: Expression and quantitative analysis of
matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in human gliomas. Brain Tumor
Pathol. 21:105–112. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Köhrmann A, Kammerer U, Kapp M, Dietl J
and Anacker J: Expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in
primary human breast cancer and breast cancer cell lines: New
findings and review of the literature. BMC Cancer. 9:1882009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Behrendt N, Rønne E and Danø K: The
structure and function of the urokinase receptor, a membrane
protein governing plasminogen activation on the cell surface. Biol
Chem Hoppe Seyler. 376:269–279. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Skrzydlewska E, Sulkowska M, Koda M and
Sulkowski S: Proteolytic-antiproteolytic balance and its regulation
in carcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 11:1251–1266. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Mason SD and Joyce JA: Proteolytic
networks in cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 21:228–237. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Shimizu M, Cohen B, Goldvasser P, Berman
H, Virtanen C and Reedijk M: Plasminogen activator uPA is a direct
transcriptional target of the JAG1-Notch receptor signaling pathway
in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 71:277–286. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Huang C, Jacobson K and Schaller MD: MAP
kinases and cell migration. J Cell Sci. 117:4619–4628. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Anand-Apte B, Zetter BR, Viswanathan A,
Qiu RG, Chen J, Ruggieri R and Symons M: Platelet-derived growth
factor and fibronectin-stimulated migration are differentially
regulated by the Rac and extracellular signal-regulated kinase
pathways. J Biol Chem. 272:30688–30692. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Duncia JV, Santella JB III, Higley CA,
Pitts WJ, Wityak J, Frietze WE, Rankin FW, Sun JH, Earl RA, Tabaka
AC, et al: MEK inhibitors: The chemistry and biological activity of
U0126, its analogs, and cyclization products. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
8:2839–2844. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Webb DJ, Nguyen DH and Gonias SL:
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase functions in the urokinase
receptor-dependent pathway by which neutralization of low density
lipoprotein receptor-related protein promotes fibrosarcoma cell
migration and matrigel invasion. J Cell Sci. 113:123–134. 2000.
|
|
66
|
Klemke RL, Cai S, Giannini AL, Gallagher
PJ, de Lanerolle P and Cheresh DA: Regulation of cell motility by
mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Cell Biol. 137:481–492. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Cheng YC, Chen LM, Chang MH, Chen WK, Tsai
FJ, Tsai CH, Lai TY, Kuo WW, Huang CY and Liu CJ:
Lipopolysaccharide upregulates uPA, MMP-2 and MMP-9 via ERK1/2
signaling in H9c2 cardiomyoblast cells. Mol Cell Biochem.
325:15–23. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Arai K, Lee SR and Lo EH: Essential role
for ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase in matrix
metalloproteinase-9 regulation in rat cortical astrocytes. Glia.
43:254–264. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|