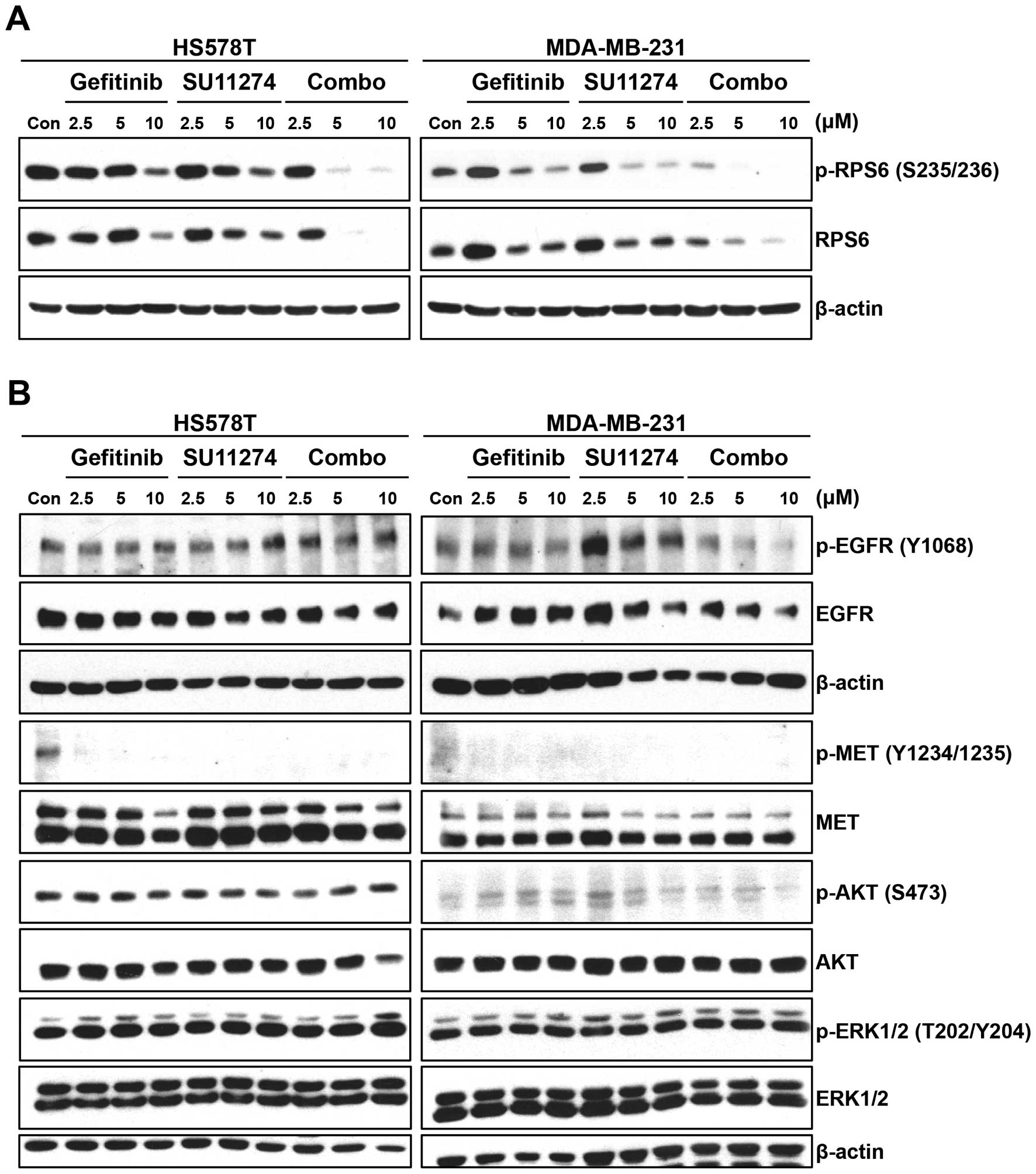
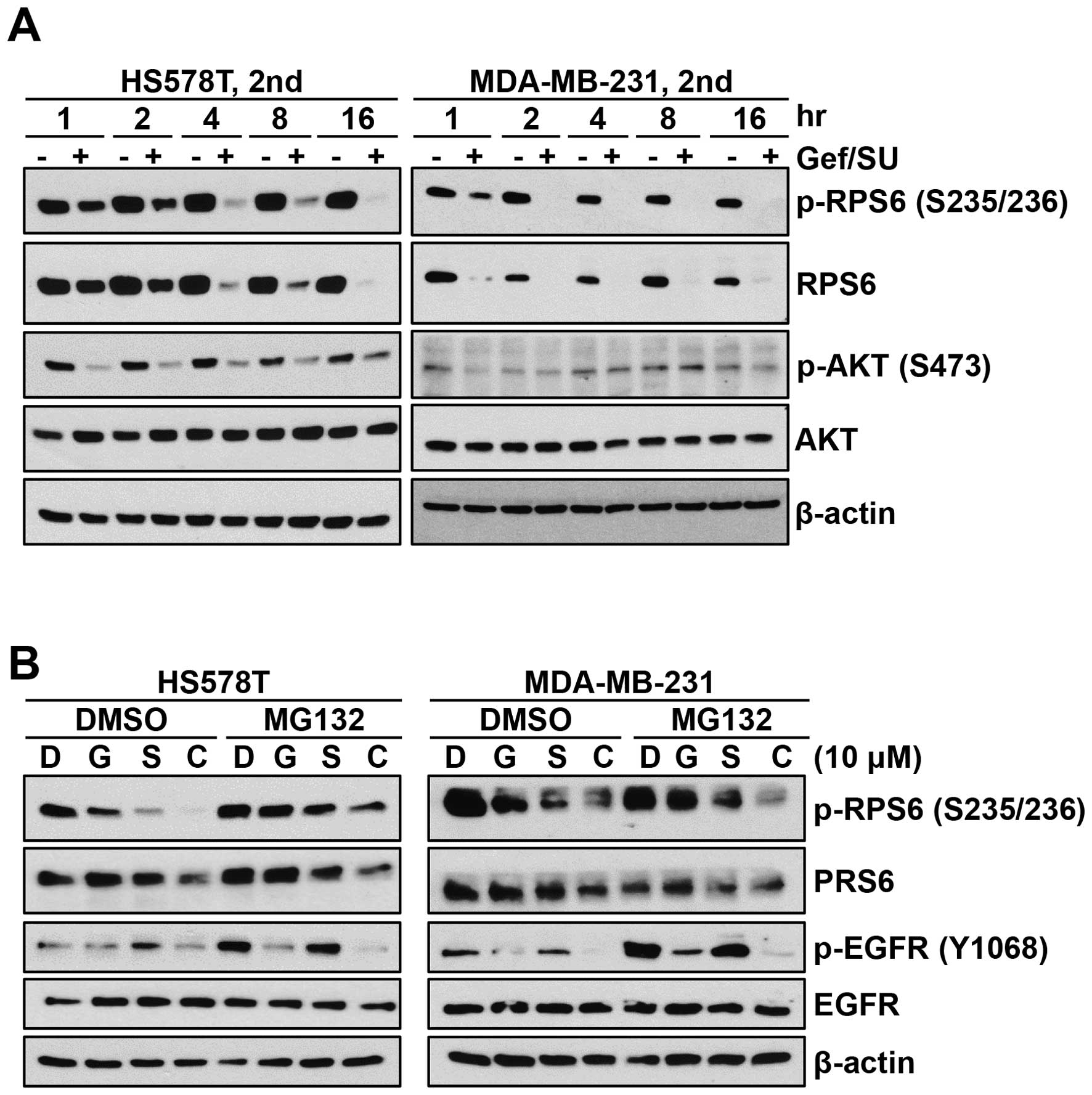
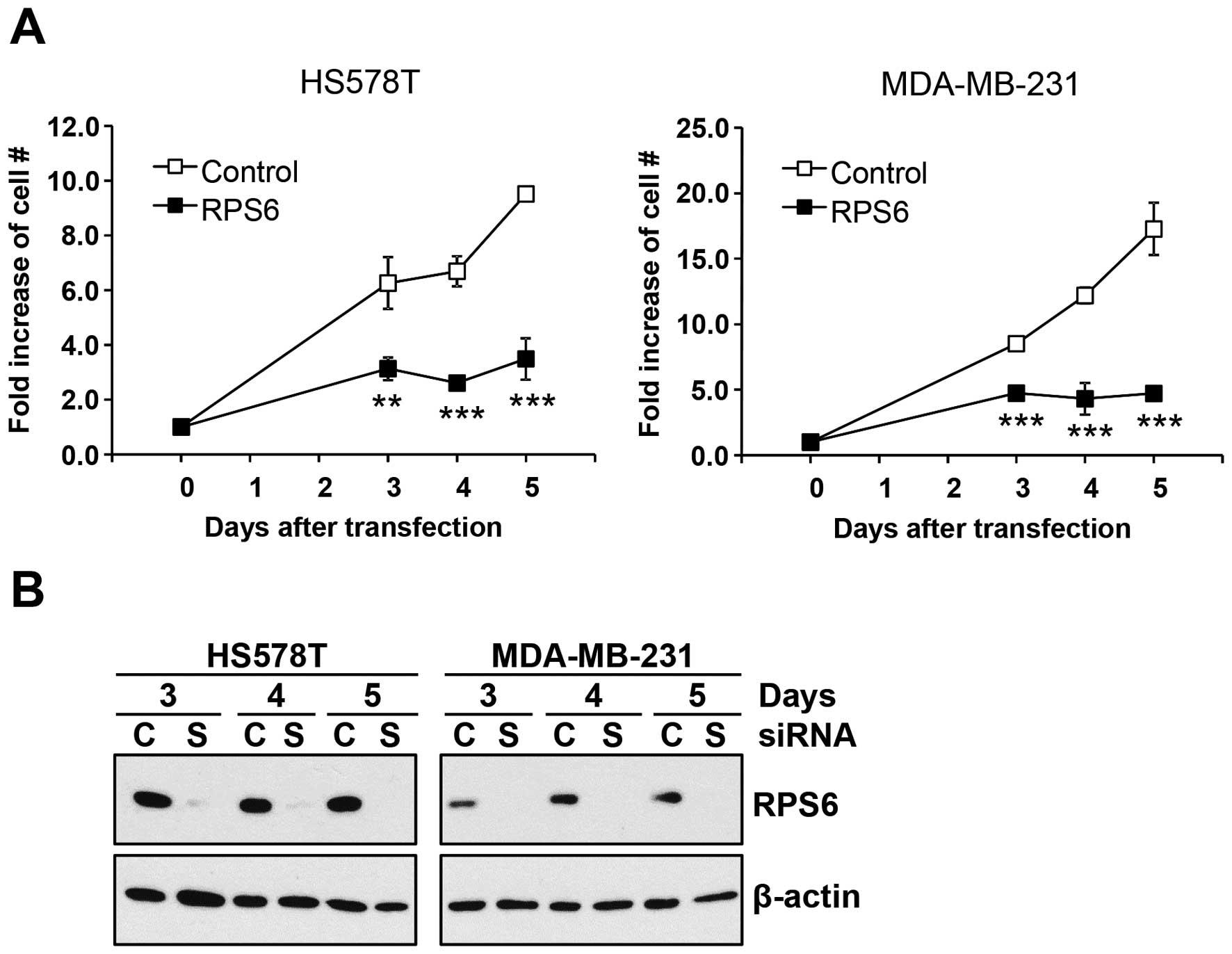
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lehmann BD, Bauer JA, Chen X, Sanders ME,
Chakravarthy AB, Shyr Y and Pietenpol JA: Identification of human
triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for
selection of targeted therapies. J Clin Invest. 121:2750–2767.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Morris GJ, Naidu S, Topham AK, Guiles F,
Xu Y, McCue P, Schwartz GF, Park PK, Rosenberg AL, Brill K, et al:
Differences in breast carcinoma characteristics in newly diagnosed
African-American and Caucasian patients: A single-institution
compilation compared with the National Cancer Institute’s
Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database. Cancer.
110:876–884. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Irvin WJ Jr and Carey LA: What is
triple-negative breast cancer? Eur J Cancer. 44:2799–2805. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, André F,
Tordai A, Mejia JA, Symmans WF, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hennessy B,
Green M, et al: Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term
survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 26:1275–1281. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Podo F, Buydens LM, Degani H, Hilhorst R,
Klipp E, Gribbestad IS, Van Huffel S, van Laarhoven HW, Luts J,
Monleon D, et al: FEMME Consortium: Triple-negative breast cancer:
Present challenges and new perspectives. Mol Oncol. 4:209–229.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Eccles SA: The epidermal growth factor
receptor/Erb-B/HER family in normal and malignant breast biology.
Int J Dev Biol. 55:685–696. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yarden Y and Pines G: The ERBB network: At
last, cancer therapy meets systems biology. Nat Rev Cancer.
12:553–563. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Reis-Filho JS, Milanezi F, Carvalho S,
Simpson PT, Steele D, Savage K, Lambros MB, Pereira EM, Nesland JM,
Lakhani SR, et al: Metaplastic breast carcinomas exhibit EGFR, but
not HER2, gene amplification and overexpression:
Immunohistochemical and chromogenic in situ hybridization analysis.
Breast Cancer Res. 7:R1028–R1035. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Reis-Filho JS, Pinheiro C, Lambros MB,
Milanezi F, Carvalho S, Savage K, Simpson PT, Jones C, Swift S,
Mackay A, et al: EGFR amplification and lack of activating
mutations in metaplastic breast carcinomas. J Pathol. 209:445–453.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livasy CA, Karaca G, Nanda R, Tretiakova
MS, Olopade OI, Moore DT and Perou CM: Phenotypic evaluation of the
basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Mod Pathol.
19:264–271. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Nielsen TO, Hsu FD, Jensen K, Cheang M,
Karaca G, Hu Z, Hernandez-Boussard T, Livasy C, Cowan D, Dressler
L, et al: Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the
basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
10:5367–5374. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lehmann BD and Pietenpol JA:
Identification and use of biomarkers in treatment strategies for
triple-negative breast cancer subtypes. J Pathol. 232:142–150.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Dawson SJ, Provenzano E and Caldas C:
Triple negative breast cancers: Clinical and prognostic
implications. Eur J Cancer. 45(Suppl 1): 27–40. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lakhani SR, Reis-Filho JS, Fulford L,
Penault-Llorca F, van der Vijver M, Parry S, Bishop T, Benitez J,
Rivas C, Bignon YJ, et al: Prediction of BRCA1 status in patients
with breast cancer using estrogen receptor and basal phenotype.
Clin Cancer Res. 11:5175–5180. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cheang MC, Voduc D, Bajdik C, Leung S,
McKinney S, Chia SK, Perou CM and Nielsen TO: Basal-like breast
cancer defined by five biomarkers has superior prognostic value
than triple-negative phenotype. Clin Cancer Res. 14:1368–1376.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rakha EA, El-Sayed ME, Green AR, Lee AH,
Robertson JF and Ellis IO: Prognostic markers in triple-negative
breast cancer. Cancer. 109:25–32. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Tischkowitz M, Brunet JS, Bégin LR,
Huntsman DG, Cheang MC, Akslen LA, Nielsen TO and Foulkes WD: Use
of immunohistochemical markers can refine prognosis in triple
negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 7:1342007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Baselga J, Gómez P, Greil R, Braga S,
Climent MA, Wardley AM, Kaufman B, Stemmer SM, Pêgo A, Chan A, et
al: Randomized phase II study of the anti-epidermal growth factor
receptor monoclonal antibody cetuximab with cisplatin versus
cisplatin alone in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 31:2586–2592. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bernsdorf M, Ingvar C, Jörgensen L, Tuxen
MK, Jakobsen EH, Saetersdal A, Kimper-Karl ML, Kroman N, Balslev E
and Ejlertsen B: Effect of adding gefitinib to neoadjuvant
chemotherapy in estrogen receptor negative early breast cancer in a
randomized phase II trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 126:463–470.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Carey LA, Rugo HS, Marcom PK, Mayer EL,
Esteva FJ, Ma CX, Liu MC, Storniolo AM, Rimawi MF, Forero-Torres A,
et al: TBCRC 001: Randomized phase II study of cetuximab in
combination with carboplatin in stage IV triple-negative breast
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 30:2615–2623. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Anderson NG, Ahmad T, Chan K, Dobson R and
Bundred NJ: ZD1839 (Iressa), a novel epidermal growth factor
receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor, potently inhibits the
growth of EGFR-positive cancer cell lines with or without erbB2
overexpression. Int J Cancer. 94:774–782. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ciardiello F, Caputo R, Bianco R, Damiano
V, Pomatico G, De Placido S, Bianco AR and Tortora G: Antitumor
effect and potentiation of cytotoxic drugs activity in human cancer
cells by ZD-1839 (Iressa), an epidermal growth factor
receptor-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res.
6:2053–2063. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wakeling AE, Guy SP, Woodburn JR, Ashton
SE, Curry BJ, Barker AJ and Gibson KH: ZD1839 (Iressa): An orally
active inhibitor of epidermal growth factor signaling with
potential for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 62:5749–5754.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yi YW, Hong W, Kang HJ, Kim HJ, Zhao W,
Wang A, Seong YS and Bae I: Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT pathway
potentiates cytotoxicity of EGFR kinase inhibitors in
triple-negative breast cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med. 17:648–656.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jin Q and Esteva FJ: Cross-talk between
the ErbB/HER family and the type I insulin-like growth factor
receptor signaling pathway in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 13:485–498. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Karamouzis MV, Konstantinopoulos PA and
Papavassiliou AG: Targeting MET as a strategy to overcome
crosstalk-related resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Lancet Oncol.
10:709–717. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu P, Cheng H, Roberts TM and Zhao JJ:
Targeting the phos-phoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 8:627–644. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nahta R, Yu D, Hung MC, Hortobagyi GN and
Esteva FJ: Mechanisms of disease: Understanding resistance to
HER2-targeted therapy in human breast cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol.
3:269–280. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yamaguchi H, Chang SS, Hsu JL and Hung MC:
Signaling crosstalk in the resistance to HER family receptor
targeted therapy. Oncogene. 33:1073–1081. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Baselga J: Targeting tyrosine kinases in
cancer: The second wave. Science. 312:1175–1178. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Morgillo F, Kim WY, Kim ES, Ciardiello F,
Hong WK and Lee HY: Implication of the insulin-like growth
factor-IR pathway in the resistance of non-small cell lung cancer
cells to treatment with gefitinib. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2795–2803.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yi YW, Kang HJ, Kim HJ, Kong Y, Brown ML
and Bae I: Targeting mutant p53 by a SIRT1 activator YK-3-237
inhibits the proliferation of triple-negative breast cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 4:984–994. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Duong HQ, Yi YW, Kang HJ, Hong YB, Tang W,
Wang A, Seong YS and Bae I: Inhibition of NRF2 by PIK-75 augments
sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine. Int J Oncol.
44:959–969. 2014.
|
|
35
|
Hou S, Yi YW, Kang HJ, Zhang L, Kim HJ,
Kong Y, Liu Y, Wang K, Kong HS, Grindrod S, et al: Novel carbazole
inhibits phospho-STAT3 through induction of protein-tyrosine
phosphatase PTPN6. J Med Chem. 57:6342–6353. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lovly CM and Shaw AT: Molecular pathways:
resistance to kinase inhibitors and implications for therapeutic
strategies. Clin Cancer Res. 20:2249–2256. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Szakács G, Paterson JK, Ludwig JA,
Booth-Genthe C and Gottesman MM: Targeting multidrug resistance in
cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 5:219–234. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zagouri F, Bago-Horvath Z, Rössler F,
Brandstetter A, Bartsch R, Papadimitriou CA, Dimitrakakis C,
Tsigginou A, Papaspyrou I, Giannos A, et al: High MET expression is
an adverse prognostic factor in patients with triple-negative
breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 108:1100–1105. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang X, Le P, Liang C, Chan J, Kiewlich D,
Miller T, Harris D, Sun L, Rice A, Vasile S, et al: Potent and
selective inhibitors of the Met [hepatocyte growth factor/scatter
factor (HGF/SF) receptor] tyrosine kinase block HGF/SF-induced
tumor cell growth and invasion. Mol Cancer Ther. 2:1085–1092.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ma PC, Maulik G, Christensen J and Salgia
R: c-Met: Structure, functions and potential for therapeutic
inhibition. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 22:309–325. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Christensen JG, Schreck R, Burrows J,
Kuruganti P, Chan E, Le P, Chen J, Wang X, Ruslim L, Blake R, et
al: A selective small molecule inhibitor of c-Met kinase inhibits
c-Met-dependent phenotypes in vitro and exhibits cytoreductive
antitumor activity in vivo. Cancer Res. 63:7345–7355.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sierra JR and Tsao MS: c-MET as a
potential therapeutic target and biomarker in cancer. Ther Adv Med
Oncol. 3(Suppl): S21–S35. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Trusolino L and Comoglio PM:
Scatter-factor and semaphorin receptors: Cell signalling for
invasive growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:289–300. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mueller KL, Madden JM, Zoratti GL,
Kuperwasser C, List K and Boerner JL: Fibroblast-secreted
hepatocyte growth factor mediates epidermal growth factor receptor
tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in triple-negative breast
cancers through paracrine activation of Met. Breast Cancer Res.
14:R1042012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Meyer AS, Miller MA, Gertler FB and
Lauffenburger DA: The receptor AXL diversifies EGFR signaling and
limits the response to EGFR-targeted inhibitors in triple-negative
breast cancer cells. Sci Signal. 6:ra662013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang S, Chung WC, Miele L and Xu K:
Targeting Met and Notch in the Lfng-deficient, Met-amplified
triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 15:633–642. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kim YJ, Choi JS, Seo J, Song JY, Lee SE,
Kwon MJ, Kwon MJ, Kundu J, Jung K, Oh E, et al: MET is a potential
target for use in combination therapy with EGFR inhibition in
triple-negative/ basal-like breast cancer. Int J Cancer.
134:2424–2436. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Meyuhas O: Physiological roles of
ribosomal protein S6: One of its kind. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol.
268:1–37. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Barrows BD, Rutkowski MJ, Gültekın SH,
Parsa AT and Tıhan T: Evidence of ambiguous differentiation and
mTOR pathway dysregulation in subependymal giant cell astrocytoma.
Turk Patoloji Derg. 28:95–103. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bellizzi AM, Bloomston M, Zhou XP, Iwenofu
OH and Frankel WL: The mTOR pathway is frequently activated in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and chronic pancreatitis. Appl
Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 18:442–447. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chaisuparat R, Rojanawatsirivej S and
Yodsanga S: Ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation is associated with
epithelial dysplasia and squamous cell carcinoma of the oral
cavity. Pathol Oncol Res. 19:189–193. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Chaisuparat R, Yodsanga S, Montaner S and
Jham BC: Activation of the Akt/mTOR pathway in dentigerous cysts,
odontogenic keratocysts, and ameloblastomas. Oral Surg Oral Med
Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 116:336–342. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chakraborty S, Mohiyuddin SM, Gopinath KS
and Kumar A: Involvement of TSC genes and differential expression
of other members of the mTOR signaling pathway in oral squamous
cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 8:1632008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chen W, Drakos E, Grammatikakis I,
Schlette EJ, Li J, Leventaki V, Staikou-Drakopoulou E, Patsouris E,
Panayiotidis P, Medeiros LJ, et al: mTOR signaling is activated by
FLT3 kinase and promotes survival of FLT3-mutated acute myeloid
leukemia cells. Mol Cancer. 9:2922010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chiang DY, Villanueva A, Hoshida Y, Peix
J, Newell P, Minguez B, LeBlanc AC, Donovan DJ, Thung SN, Solé M,
et al: Focal gains of VEGFA and molecular classification of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 68:6779–6788. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Golfinopoulos V, Pentheroudakis G, Goussia
A, Siozopoulou V, Bobos M, Krikelis D, Cervantes A, Ciuleanu T,
Marselos M, Fountzilas G, et al: Intracellular signalling via the
AKT axis and downstream effectors is active and prognostically
significant in cancer of unknown primary (CUP): a study of 100 CUP
cases. Ann Oncol. 23:2725–2730. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Hagner PR, Mazan-Mamczarz K, Dai B, Balzer
EM, Corl S, Martin SS, Zhao XF and Gartenhaus RB: Ribosomal protein
S6 is highly expressed in non-Hodgkin lymphoma and associates with
mRNA containing a 5′ terminal oligopyrimidine tract. Oncogene.
30:1531–1541. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
58
|
Iwenofu OH, Lackman RD, Staddon AP,
Goodwin DG, Haupt HM and Brooks JS: Phospho-S6 ribosomal protein: a
potential new predictive sarcoma marker for targeted mTOR therapy.
Mod Pathol. 21:231–237. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Kouvaraki MA, Liakou C, Paraschi A, Dimas
K, Patsouris E, Tseleni-Balafouta S, Rassidakis GZ and Moraitis D:
Activation of mTOR signaling in medullary and aggressive papillary
thyroid carcinomas. Surgery. 150:1258–1265. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Villanueva A, Chiang DY, Newell P, Peix J,
Thung S, Alsinet C, Tovar V, Roayaie S, Minguez B, Sole M, et al:
Pivotal role of mTOR signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 135:1972–1983. 1983 e1971–1911. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Qian ZR, Ter-Minassian M, Chan JA, Imamura
Y, Hooshmand SM, Kuchiba A, Morikawa T, Brais LK, Daskalova A,
Heafield R, et al: Prognostic significance of MTOR pathway
component expression in neuroendocrine tumors. J Clin Oncol.
31:3418–3425. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Potratz JC, Saunders DN, Wai DH, Ng TL,
McKinney SE, Carboni JM, Gottardis MM, Triche TJ, Jürgens H, Pollak
MN, et al: Synthetic lethality screens reveal RPS6 and MST1R as
modifiers of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor inhibitor
activity in childhood sarcomas. Cancer Res. 70:8770–8781. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Khalaileh A, Dreazen A, Khatib A, Apel R,
Swisa A, Kidess-Bassir N, Maitra A, Meyuhas O, Dor Y and Zamir G:
Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 attenuates DNA damage and
tumor suppression during development of pancreatic cancer. Cancer
Res. 73:1811–1820. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Dephoure N, Zhou C, Villén J, Beausoleil
SA, Bakalarski CE, Elledge SJ and Gygi SP: A quantitative atlas of
mitotic phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:10762–10767.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Olsen JV, Vermeulen M, Santamaria A, Kumar
C, Miller ML, Jensen LJ, Gnad F, Cox J, Jensen TS, Nigg EA, et al:
Quantitative phosphoproteomics reveals widespread full
phosphorylation site occupancy during mitosis. Sci Signal.
3:ra32010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Rigbolt KT, Prokhorova TA, Akimov V,
Henningsen J, Johansen PT, Kratchmarova I, Kassem M, Mann M, Olsen
JV and Blagoev B: System-wide temporal characterization of the
proteome and phosphoproteome of human embryonic stem cell
differentiation. Sci Signal. 4:rs32011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Roux PP, Shahbazian D, Vu H, Holz MK,
Cohen MS, Taunton J, Sonenberg N and Blenis J: RAS/ERK signaling
promotes site-specific ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation via RSK
and stimulates cap-dependent translation. J Biol Chem.
282:14056–14064. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Schläfli P, Tröger J, Eckhardt K, Borter
E, Spielmann P and Wenger RH: Substrate preference and
phosphatidylinositol monophosphate inhibition of the catalytic
domain of the Per-Arnt-Sim domain kinase PASKIN. FEBS J.
278:1757–1768. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Stevens C, Lin Y, Harrison B, Burch L,
Ridgway RA, Sansom O and Hupp T: Peptide combinatorial libraries
identify TSC2 as a death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) death
domain-binding protein and reveal a stimulatory role for DAPK in
mTORC1 signaling. J Biol Chem. 284:334–344. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Falsone SF, Gesslbauer B, Tirk F,
Piccinini AM and Kungl AJ: A proteomic snapshot of the human heat
shock protein 90 interactome. FEBS Lett. 579:6350–6354. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Kim TS, Jang CY, Kim HD, Lee JY, Ahn BY
and Kim J: Interaction of Hsp90 with ribosomal proteins protects
from ubiquitination and proteasome-dependent degradation. Mol Biol
Cell. 17:824–833. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
72
|
Zou HY, Li Q, Lee JH, Arango ME, McDonnell
SR, Yamazaki S, Koudriakova TB, Alton G, Cui JJ, Kung PP, et al: An
orally available small-molecule inhibitor of c-Met, PF-2341066,
exhibits cytoreductive antitumor efficacy through antiproliferative
and antiangiogenic mechanisms. Cancer Res. 67:4408–4417. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Bonfils C, Beaulieu N, Fournel M,
Ste-Croix H, Besterman JM and Maroun CR: The combination of
MGCD265, a Met/VEGFR inhibitor in clinical development, and
erlotinib potently inhibits tumor growth by altering multiple
pathways including glycolysis. Cancer Res. 72(Suppl 8): S17902012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Qian F, Engst S, Yamaguchi K, Yu P, Won
KA, Mock L, Lou T, Tan J, Li C, Tam D, et al: Inhibition of tumor
cell growth, invasion, and metastasis by EXEL-2880 (XL880,
GSK1363089), a novel inhibitor of HGF and VEGF receptor tyrosine
kinases. Cancer Res. 69:8009–8016. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
You WK, Sennino B, Williamson CW, Falcón
B, Hashizume H, Yao LC, Aftab DT and McDonald DM: VEGF and c-Met
blockade amplify angiogenesis inhibition in pancreatic islet
cancer. Cancer Res. 71:4758–4768. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|