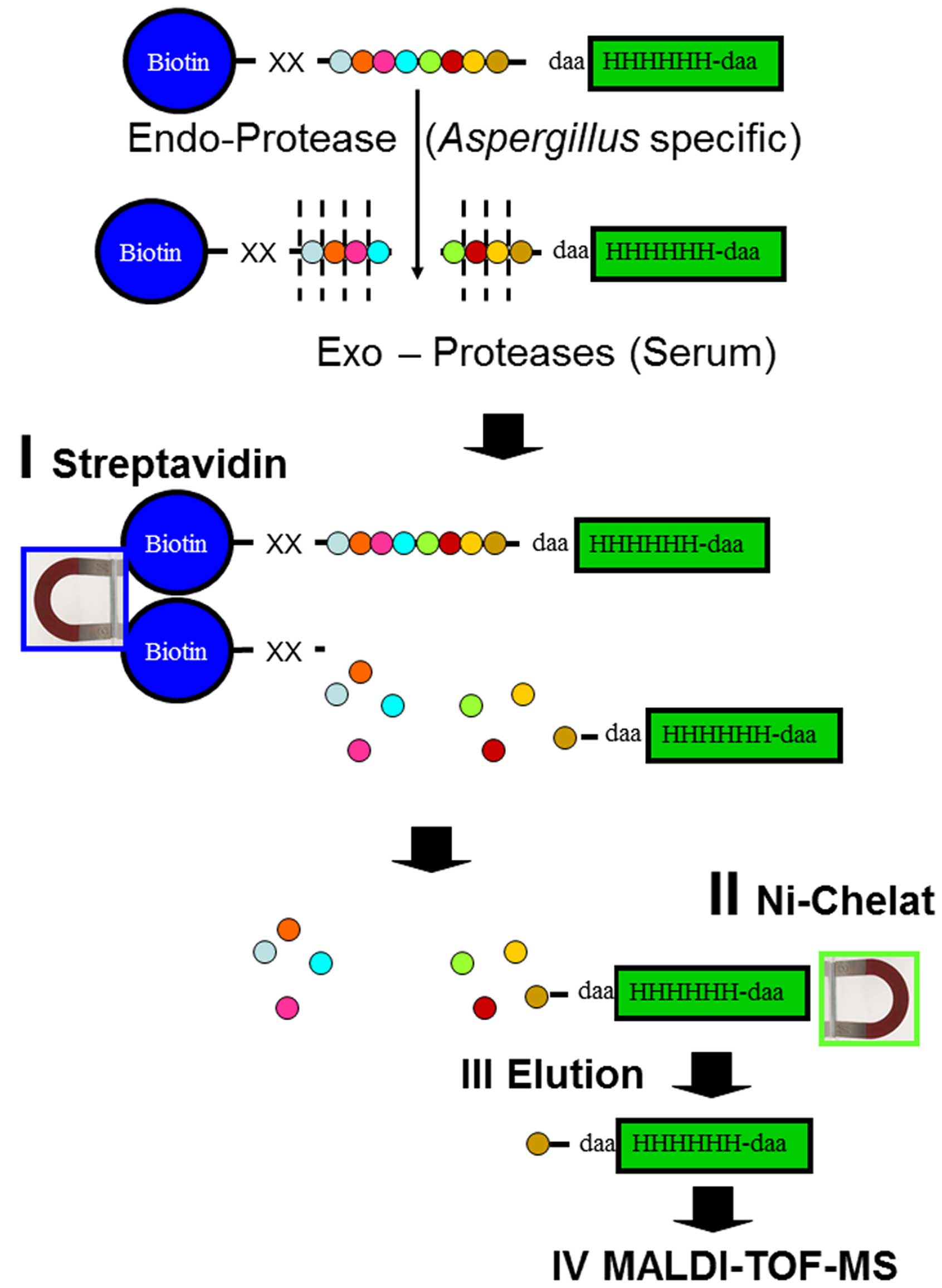
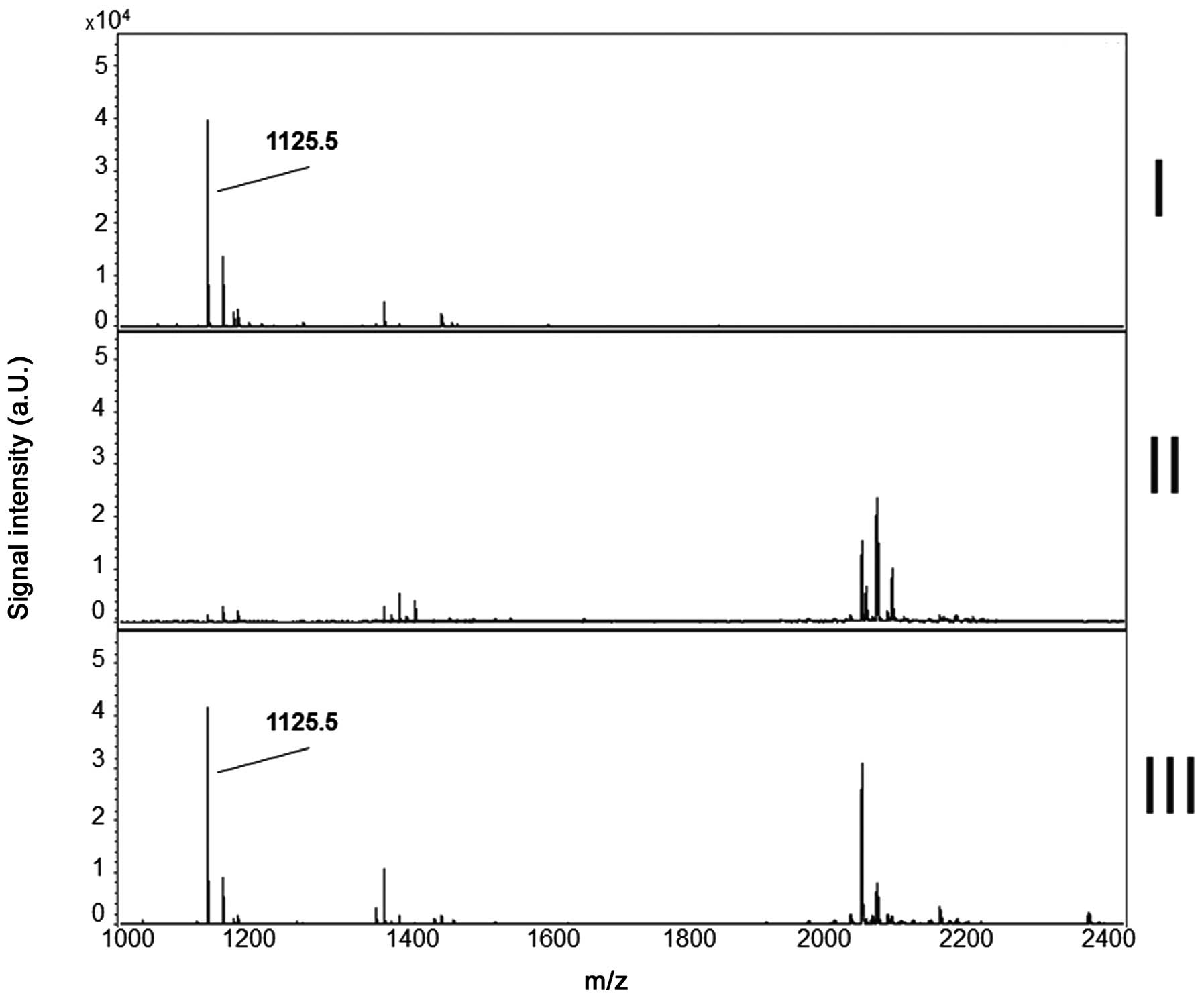
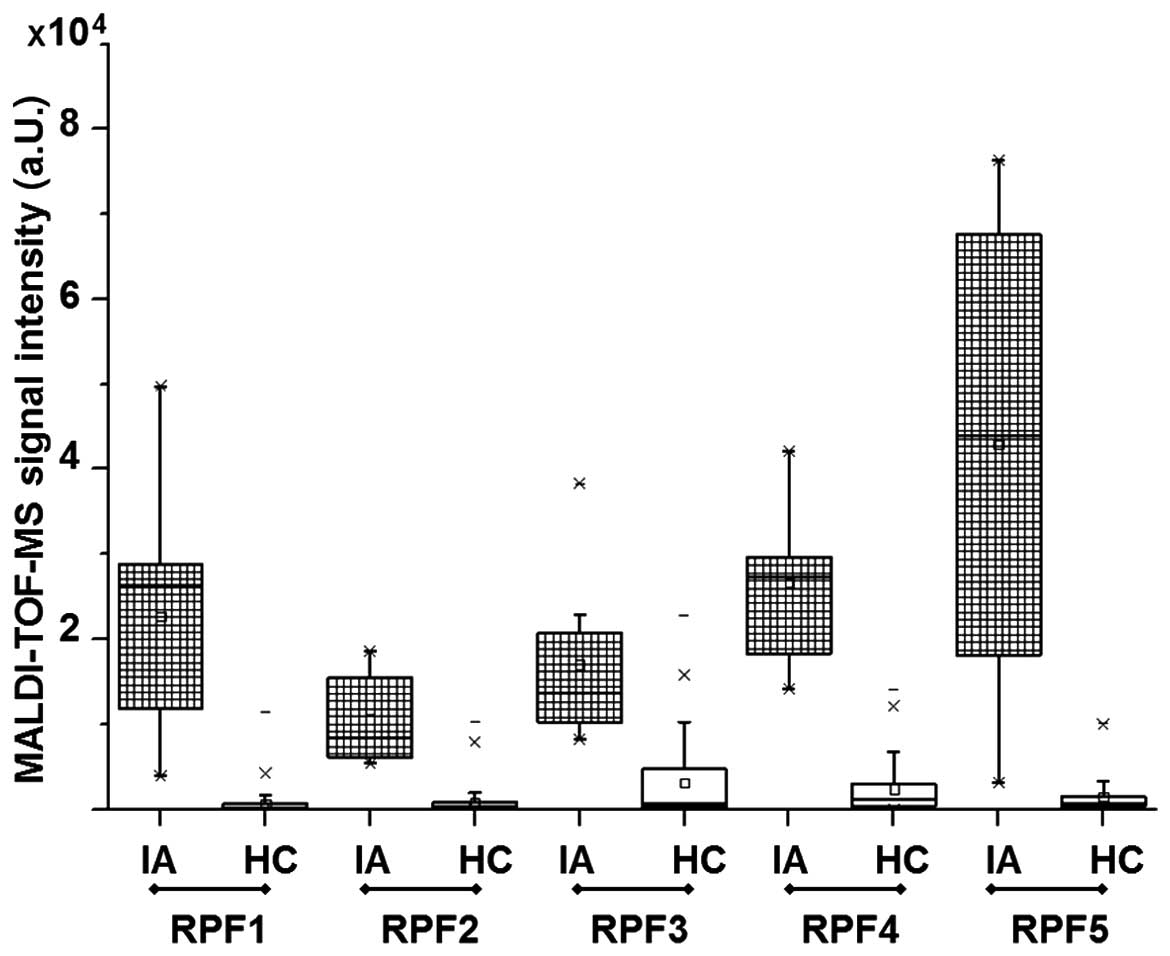
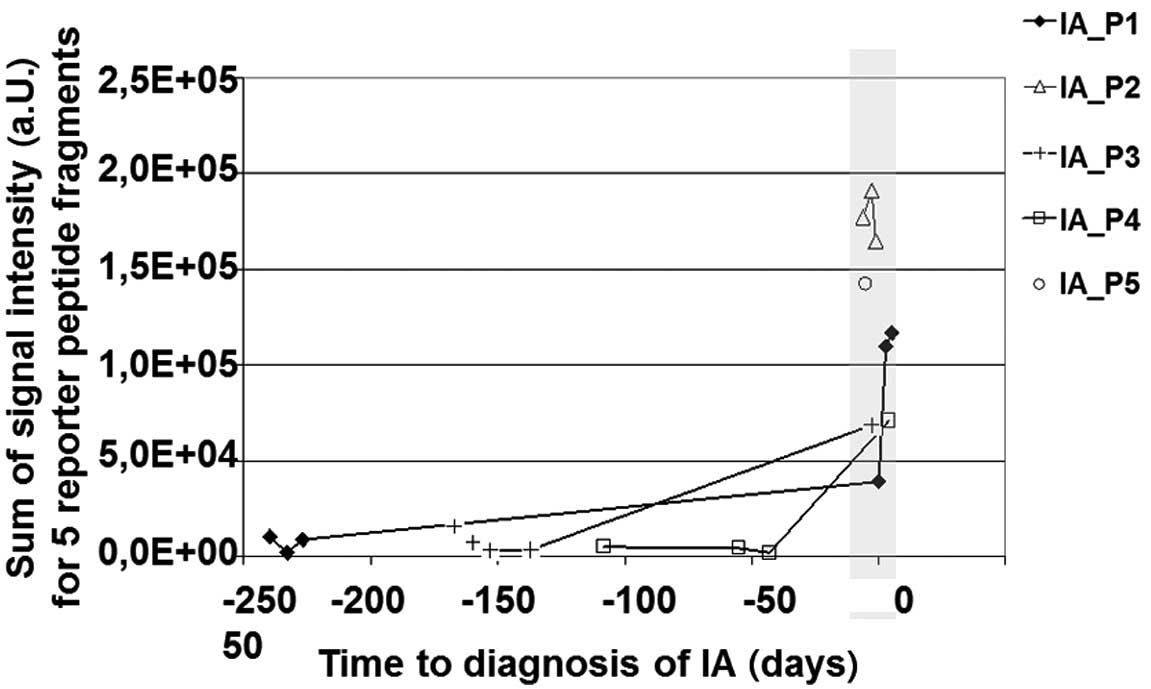
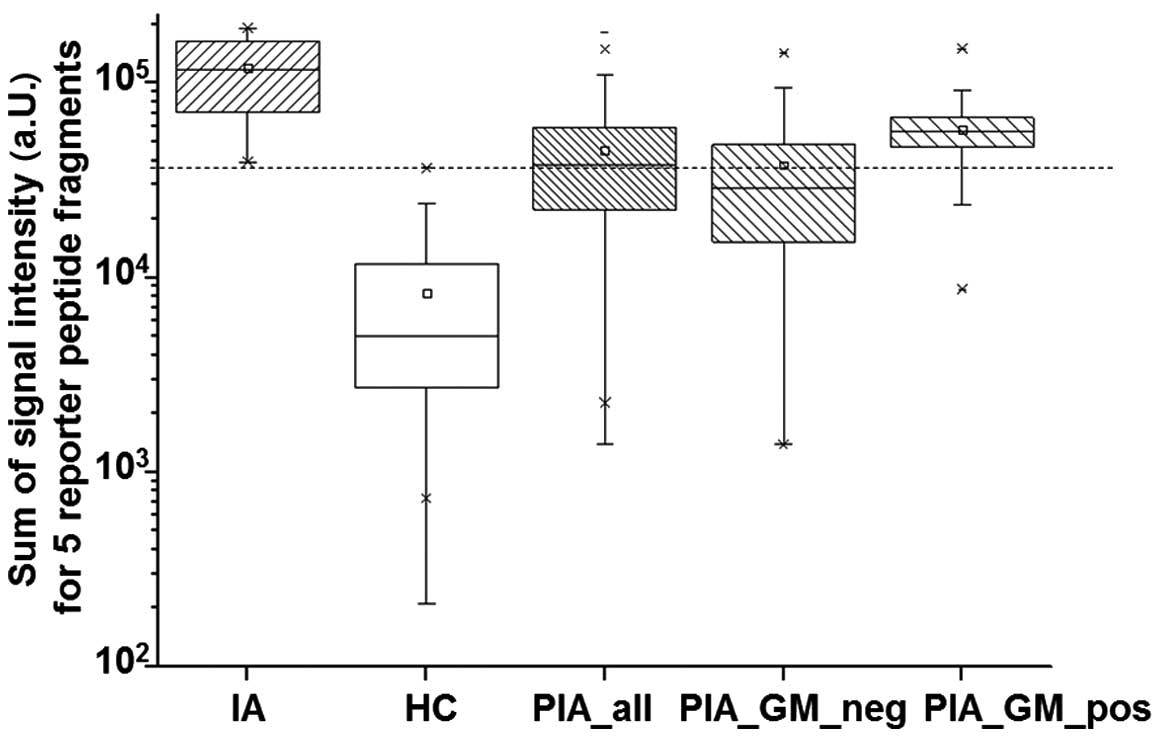
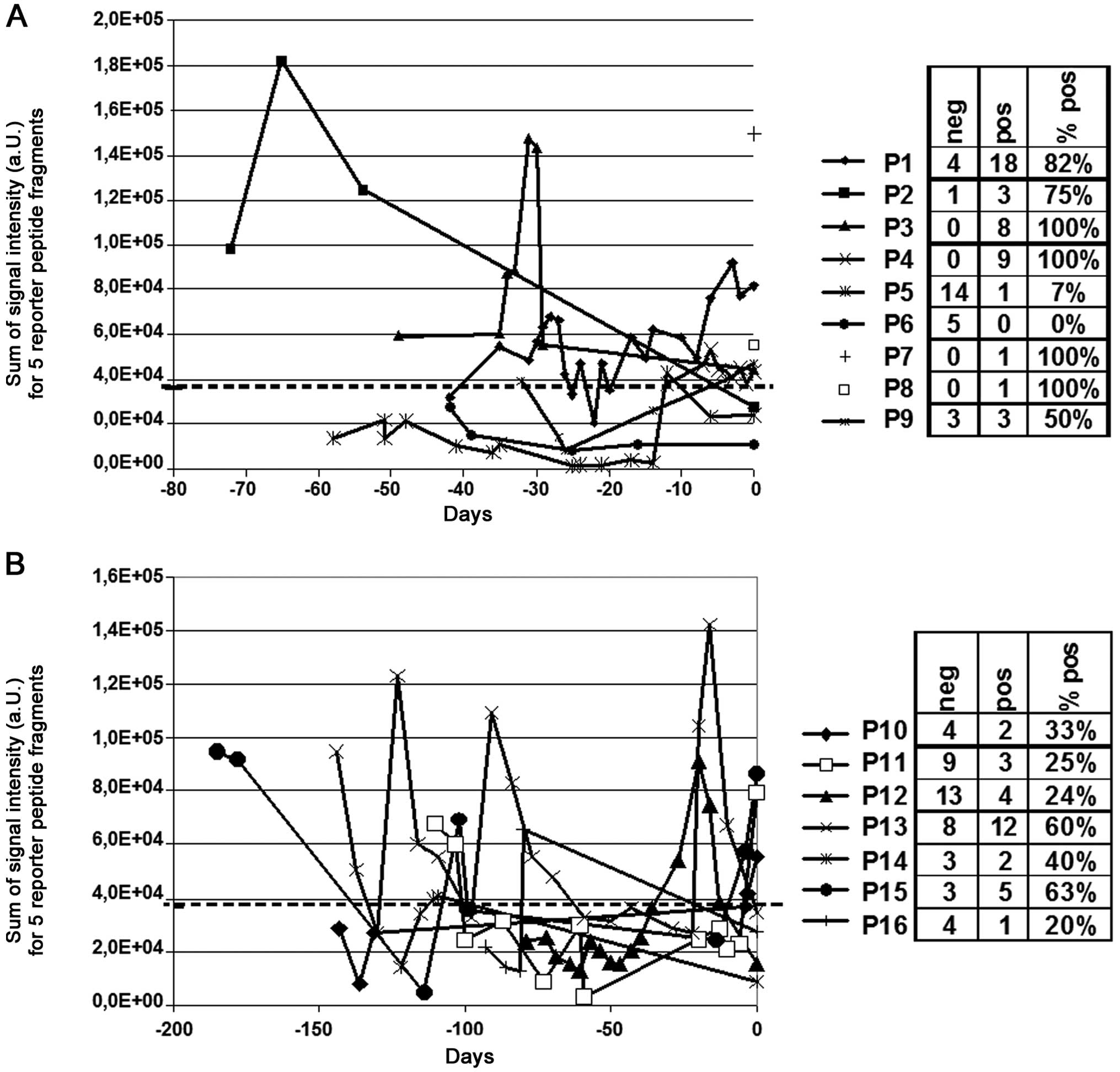
|
1
|
Denning DW: Invasive aspergillosis. Clin
Infect Dis. 26:781–803; quiz 804–805. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Segal BH: Aspergillosis. N Engl J Med.
360:1870–1884. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hohl TM and Feldmesser M: Aspergillus
fumigatus: Principles of pathogenesis and host defense. Eukaryot
Cell. 6:1953–1963. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thompson GR III and Patterson TF:
Pulmonary aspergillosis: Recent advances. Semin Respir Crit Care
Med. 32:673–681. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Latgé JP: Aspergillus fumigatus and
aspergillosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 12:310–350. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hope WW, Walsh TJ and Denning DW:
Laboratory diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis. Lancet Infect Dis.
5:609–622. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Adam O, Aupérin A, Wilquin F, Bourhis JH,
Gachot B and Chachaty E: Treatment with piperacillin-tazobactam and
false-positive Aspergillus galactomannan antigen test results for
patients with hematological malignancies. Clin Infect Dis.
38:917–920. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
McCulloch E, Ramage G, Rajendran R, Lappin
DF, Jones B, Warn P, Shrief R, Kirkpatrick WR, Patterson TF and
Williams C: Antifungal treatment affects the laboratory diagnosis
of invasive aspergillosis. J Clin Pathol. 65:83–86. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Barton RC: Laboratory diagnosis of
invasive aspergillosis: From diagnosis to prediction of outcome.
Scientifica Cairo. 2013:4594052013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pickering JW, Sant HW, Bowles CA, Roberts
WL and Woods GL: Evaluation of a (1–>3)-beta-D-glucan assay for
diagnosis of invasive fungal infections. J Clin Microbiol.
43:5957–5962. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mennink-Kersten MASH, Warris A and Verweij
PE: 1,3-β-D-glucan in patients receiving intravenous
amoxicillin-clavulanic acid. N Engl J Med. 354:2834–2835. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Einsele H and Loeffler J: Contribution of
new diagnostic approaches to antifungal treatment plans in
high-risk haematology patients. Clin Microbiol Infect. 14(Suppl 4):
37–45. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kogan TV, Jadoun J, Mittelman L,
Hirschberg K and Osherov N: Involvement of secreted Aspergillus
fumigatus proteases in disruption of the actin fiber cytoskeleton
and loss of focal adhesion sites in infected A549 lung pneumocytes.
J Infect Dis. 189:1965–1973. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jambunathan K, Watson DS, Najvar LK,
Wiederhold NP, Kirkpatrick WR, Patterson TF, Askew DS, Kodukula K
and Galande AK: Prolyl endopeptidase activity in bronchoalveolar
lavage fluid: A novel diagnostic biomarker in a guinea pig model of
invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Med Mycol. 51:592–602. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Findeisen P, Post S, Wenz F and Neumaier
M: Addition of exogenous reporter peptides to serum samples before
mass spectrometry-based protease profiling provides advantages over
profiling of endogenous peptides. Clin Chem. 53:1864–1866. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Peccerella T, Lukan N, Hofheinz R,
Schadendorf D, Kostrezewa M, Neumaier M and Findeisen P:
Endoprotease profiling with double-tagged peptide substrates: A new
diagnostic approach in oncology. Clin Chem. 56:272–280. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Findeisen P, Costina V, Yepes D, Hofheinz
R and Neumaier M: Functional protease profiling with reporter
peptides in serum specimens of colorectal cancer patients:
Demonstration of its routine diagnostic applicability. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 31:562012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
De Pauw B, Walsh TJ, Donnelly JP, Stevens
DA, Edwards JE, Calandra T, Pappas PG, Maertens J, Lortholary O,
Kauffman CA, et al: European Organization for Research and
Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group;
National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study
Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group: Revised definitions of invasive
fungal disease from the European Organization for Research and
Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group
and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group. Clin Infect Dis.
46:1813–1821. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ostrosky-Zeichner L: Invasive mycoses:
Diagnostic challenges. Am J Med. 125(Suppl): S14–S24. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schaal R, Kupfahl C, Buchheidt D, Neumaier
M and Findeisen P: Systematic identification of substrates for
profiling of secreted proteases from Aspergillus species. J
Microbiol Methods. 71:93–100. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Neustadt M, Costina V, Kupfahl C,
Buchheidt D, Eckerskorn C, Neumaier M and Findeisen P:
Characterization and identification of proteases secreted by
Aspergillus fumigatus using free flow electrophoresis and MS.
Electrophoresis. 30:2142–2150. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Watson DS, Feng X, Askew DS, Jambunathan
K, Kodukula K and Galande AK: Substrate specifity profiling of the
Aspergillus fumigatus proteolytic secretome reveals consensus
motifs with predominance of Ile/Leu and Phe/Tyr. PLoS One.
6:e210012011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rawlings ND, Morton FR, Kok CY, Kong J and
Barrett AJ: MEROPS: The peptidase database. Nucleic Acids Res.
36:Database. D320–D325. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Findeisen P, Costina V, Yepes D, Hofheinz
R and Neumaier M: Functional protease profiling with reporter
peptides in serum specimens of colorectal cancer patients:
Demonstration of its routine diagnostic applicability. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 31:562012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vaideeswar P, Prasad S, Deshpande JR and
Pandit SP: Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: A study of 39 cases at
autopsy. J Postgrad Med. 50:21–26. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Findeisen P and Neumaier M: Functional
protease profiling for diagnosis of malignant disease. Proteomics
Clin Appl. 6:60–78. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Witt I: Test systems with synthetic
peptide substrates in haemostaseology. Eur J Clin Chem Clin
Biochem. 29:355–374. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Powell MF, Grey H, Gaeta F, Sette A and
Colón S: Peptide stability in drug development: A comparison of
peptide reactivity in different biological media. J Pharm Sci.
81:731–735. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Walker JR, Altman RK, Warren JW and Altman
E: Using protein-based motifs to stabilize peptides. J Pept Res.
62:214–226. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Donnelly JP: Consensus definitions for
invasive fungal disease: Strengths, limitations, and revisions. Med
Mycol. 44(s1): 285–288. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Subirà M, Martino R, Franquet T, Puzo C,
Altés A, Sureda A, Brunet S and Sierra J: Invasive pulmonary
aspergillosis in patients with hematologic malignancies: Survival
and prognostic factors. Haematologica. 87:528–534. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Subirà M, Martino R, Rovira M, Vazquez L,
Serrano D and De La Cámara R: Clinical applicability of the new
EORTC/MSG classification for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in
patients with hematological malignancies and autopsy-confirmed
invasive aspergillosis. Ann Hematol. 82:80–82. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tsitsikas DA, Morin A, Araf S, Murtagh B,
Johnson G, Vinnicombe S, Ellis S, Suaris T, Wilks M, Doffman S, et
al: Impact of the revised (2008) EORTC/MSG definitions for invasive
fungal disease on the rates of diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis.
Med Mycol. 50:538–542. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Johnson G, Ferrini A, Dolan SK, Nolan T,
Agrawal S, Doyle S and Bustin SA: Biomarkers for invasive
aspergillosis: The challenges continue. Biomarkers Med. 8:429–451.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|