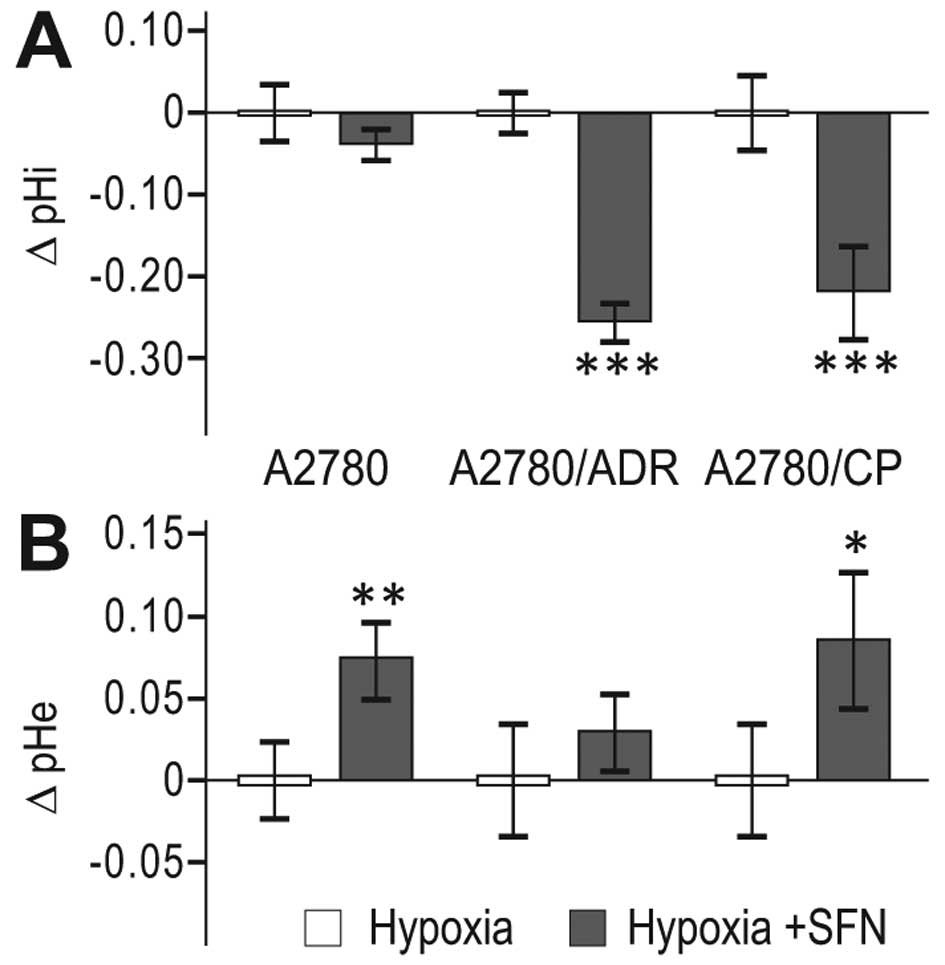
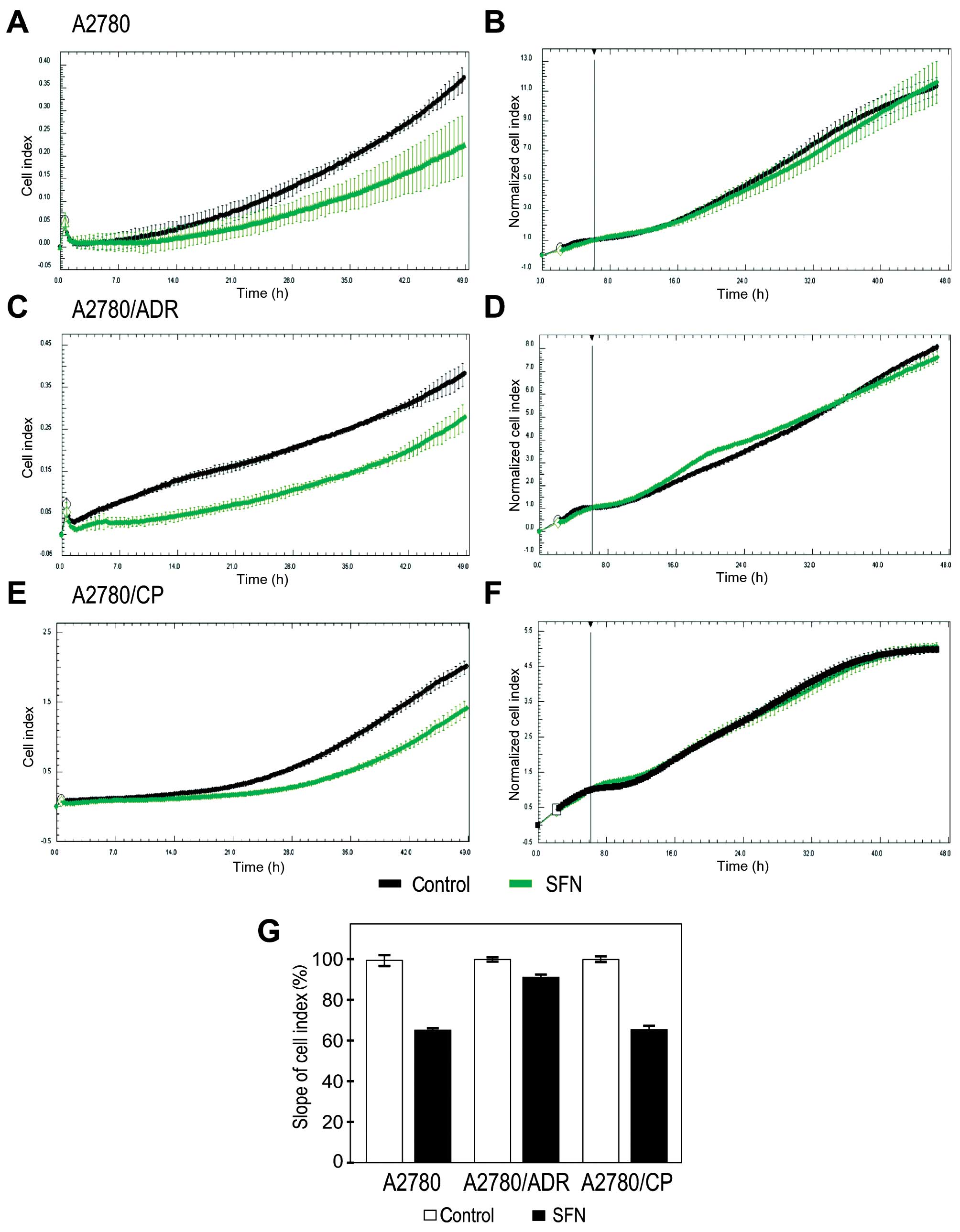
|
1
|
Harris AL: Hypoxia - a key regulatory
factor in tumor growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:38–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible factors:
mediators of cancer progression and targets for cancer therapy.
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 33:207–214. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brown JM and Wilson WR: Exploiting tumour
hypoxia in cancer treatment. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:437–447. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Birner P, Schindl M, Obermair A,
Breitenecker G and Oberhuber G: Expression of hypoxia-inducible
factor 1alpha in epithelial ovarian tumors: its impact on prognosis
and on response to chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 7:1661–1668.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rohwer N and Cramer T: Hypoxia-mediated
drug resistance: novel insights on the functional interaction of
HIFs and cell death pathways. Drug Resist Updat. 14:191–201. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Myzak MC, Dashwood WM, Orner GA, Ho E and
Dashwood RH: Sulforaphane inhibits histone deacetylase in vivo and
suppresses tumorigenesis in Apc-minus mice. FASEB J. 20:506–508.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chaudhuri D, Orsulic S and Ashok BT:
Antiproliferative activity of sulforaphane in Akt-overexpressing
ovarian cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:334–345. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bryant CS, Kumar S, Chamala S, Shah J, Pal
J, Haider M, Seward S, Qazi AM, Morris R, Semaan A, et al:
Sulforaphane induces cell cycle arrest by protecting RB-E2F-1
complex in epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 9:472010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chang CC, Hung CM, Yang YR, Lee MJ and Hsu
YC: Sulforaphane induced cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase via
the blockade of cyclin B1/CDC2 in human ovarian cancer cells. J
Ovarian Res. 6:412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou C, Poulton EJ, Grün F, Bammler TK,
Blumberg B, Thummel KE and Eaton DL: The dietary isothiocyanate
sulforaphane is an antagonist of the human steroid and xenobiotic
nuclear receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 71:220–229. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bertl E, Bartsch H and Gerhäuser C:
Inhibition of angiogenesis and endothelial cell functions are novel
sulforaphane-mediated mechanisms in chemoprevention. Mol Cancer
Ther. 5:575–585. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yao H, Wang H, Zhang Z, Jiang BH, Luo J
and Shi X: Sulforaphane inhibited expression of hypoxia-inducible
factor-1alpha in human tongue squamous cancer cells and prostate
cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 123:1255–1261. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jeong JK, Moon MH, Seo JS, Seol JW, Lee YJ
and Park SY: Sulforaphane blocks hypoxia-mediated resistance to
TRAIL-induced tumor cell death. Mol Med Rep. 4:325–330.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kaelin WG Jr and Ratcliffe PJ: Oxygen
sensing by metazoans: the central role of the HIF hydroxylase
pathway. Mol Cell. 30:393–402. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lendahl U, Lee KL, Yang H and Poellinger
L: Generating specificity and diversity in the transcriptional
response to hypoxia. Nat Rev Genet. 10:821–832. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pijnenborg JM, Wijnakker M, Hagelstein J,
Delvoux B and Groothuis PG: Hypoxia contributes to development of
recurrent endometrial carcinoma. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 17:897–904.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liang D, Ma Y, Liu J, Trope CG, Holm R,
Nesland JM and Suo Z: The hypoxic microenvironment upgrades
stem-like properties of ovarian cancer cells. BMC Cancer.
12:2012012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Williams E, Martin S, Moss R, Durrant L
and Deen S: Co-expression of VEGF and CA9 in ovarian high-grade
serous carcinoma and relationship to survival. Virchows Arch.
461:33–39. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sedlák J, Sedláková O, Hlavcák P, Hunáková
L, Bízik J, Grófová M and Chorváth B: Cell surface phenotype and
increased penetration of human multidrug-resistant ovarian
carcinoma cells into in vitro collagen-fibroblasts matrix.
Neoplasma. 43:389–395. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bodo J, Chovancova J, Hunakova L and
Sedlak J: Enhanced sensitivity of human ovarian carcinoma cell
lines A2780 and A2780/CP to the combination of cisplatin and
synthetic isothiocyanate ethyl 4-isothiocyanatobutanoate.
Neoplasma. 52:510–516. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Svastová E, Hulíková A, Rafajová M,
Zat’ovicová M, Gibadulinová A, Casini A, Cecchi A, Scozzafava A,
Supuran CT, Pastorek J, et al: Hypoxia activates the capacity of
tumor-associated carbonic anhydrase IX to acidify extracellular pH.
FEBS Lett. 577:439–445. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen H, Landen CN, Li Y, Alvarez RD and
Tollefsbol TO: Enhancement of cisplatin-mediated apoptosis in
ovarian cancer cells through potentiating G2/M arrest and p21
upregulation by combinatorial epigallocatechin gallate and
sulforaphane. J Oncol. 2013:8729572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Comerford KM, Cummins EP and Taylor CT:
c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation contributes to
hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha-dependent P-glycoprotein expression
in hypoxia. Cancer Res. 64:9057–9061. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
An J, Liu H, Magyar CE, Guo Y, Veena MS,
Srivatsan ES, Huang J and Rettig MB: Hyperactivated JNK is a
therapeutic target in pVHL-deficient renal cell carcinoma. Cancer
Res. 73:1374–1385. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gillies RJ and Gatenby RA: Hypoxia and
adaptive landscapes in the evolution of carcinogenesis. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 26:311–317. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sibhatu MB, Smitherman PK, Townsend AJ and
Morrow CS: Expression of MRP1 and GSTP1-1 modulate the acute
cellular response to treatment with the chemopreventive
isothiocyanate, sulforaphane. Carcinogenesis. 29:807–815. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rudolf E, Andelová H and Cervinka M:
Activation of several concurrent proapoptic pathways by
sulforaphane in human colon cancer cells SW620. Food Chem Toxicol.
47:2366–2373. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Horiuchi A, Hayashi T, Kikuchi N, Hayashi
A, Fuseya C, Shiozawa T and Konishi I: Hypoxia upregulates ovarian
cancer invasiveness via the binding of HIF-1α to a hypoxia-induced,
methylation-free hypoxia response element of S100A4 gene. Int J
Cancer. 131:1755–1767. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Selvendiran K, Bratasz A, Kuppusamy ML,
Tazi MF, Rivera BK and Kuppusamy P: Hypoxia induces chemoresistance
in ovarian cancer cells by activation of signal transducer and
activator of transcription 3. Int J Cancer. 125:2198–2204. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Milane L, Duan Z and Amiji M: Role of
hypoxia and glycolysis in the development of multi-drug resistance
in human tumor cells and the establishment of an orthotopic
multi-drug resistant tumor model in nude mice using hypoxic
pre-conditioning. Cancer Cell Int. 11:32011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shimogai R, Kigawa J, Itamochi H, Iba T,
Kanamori Y, Oishi T, Shimada M, Sato S, Kawaguchi W, Sato S, et al:
Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha gene affects the
outcome in patients with ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer.
18:499–505. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wong C, Wellman TL and Lounsbury KM: VEGF
and HIF-1alpha expression are increased in advanced stages of
epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 91:513–517. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim K, Park WY, Kim JY, Sol MY, Shin DH,
Park do Y, Lee CH, Lee JH and Choi KU: Prognostic relevance of the
expression of CA IX, GLUT-1, and VEGF in ovarian epithelial
cancers. Korean J Pathol. 46:532–540. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Cheng JC, Klausen C and Leung PC:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha mediates epidermal growth
factor-induced down-regulation of E-cadherin expression and cell
invasion in human ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 329:197–206.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hynninen P, Vaskivuo L, Saarnio J,
Haapasalo H, Kivelä J, Pastoreková S, Pastorek J, Waheed A, Sly WS,
Puistola U, et al: Expression of transmembrane carbonic anhydrases
IX and XII in ovarian tumours. Histopathology. 49:594–602. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jeon YK, Yoo DR, Jang YH, Jang SY and Nam
MJ: Sulforaphane induces apoptosis in human hepatic cancer cells
through inhibition of
6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase4, mediated by
hypoxia inducible factor-1-dependent pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1814.1340–1348. 2011.
|
|
37
|
Sermeus A and Michiels C: Reciprocal
influence of the p53 and the hypoxic pathways. Cell Death Dis.
2:e1642011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chew YC, Adhikary G, Wilson GM, Xu W and
Eckert RL: Sulforaphane induction of p21(Cip1) cyclin-dependent
kinase inhibitor expression requires p53 and Sp1 transcription
factors and is p53-dependent. J Biol Chem. 287:16168–16178. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kolamunne RT, Dias IH, Vernallis AB, Grant
MM and Griffiths HR: Nrf2 activation supports cell survival during
hypoxia and hypoxia/reoxygenation in cardiomyoblasts; the roles of
reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Redox Biol. 1:418–426. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kensler TW, Egner PA, Agyeman AS,
Visvanathan K, Groopman JD, Chen JG, Chen TY, Fahey JW and Talalay
P: Keap1-nrf2 signaling: a target for cancer prevention by
sulforaphane. Top Curr Chem. 329:163–177. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Chan WK, Yao G, Gu YZ and Bradfield CA:
Cross-talk between the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and hypoxia
inducible factor signaling pathways. Demonstration of competition
and compensation. J Biol Chem. 274:12115–12123. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Takacova M, Holotnakova T, Vondracek J,
Machala M, Pencikova K, Gradin K, Poellinger L, Pastorek J,
Pastorekova S and Kopacek J: Role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in
modulation of the expression of the hypoxia marker carbonic
anhydrase IX. Biochem J. 419:419–425. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cavalli LR, Riggins RB, Wang A, Clarke R
and Haddad BR: Frequent loss of heterozygosity at the interferon
regulatory factor-1 gene locus in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 121:227–231. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
44
|
Wiczk A, Hofman D, Konopa G and
Herman-Antosiewicz A: Sulforaphane, a cruciferous vegetable-derived
isothiocyanate, inhibits protein synthesis in human prostate cancer
cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1823.1295–1305. 2012.
|
|
45
|
Wykoff CC, Beasley NJ, Watson PH, Turner
KJ, Pastorek J, Sibtain A, Wilson GD, Turley H, Talks KL, Maxwell
PH, et al: Hypoxia-inducible expression of tumor-associated
carbonic anhydrases. Cancer Res. 60:7075–7083. 2000.
|
|
46
|
Kaluz S, Kaluzová M, Opavský R,
Pastoreková S, Gibadulinová A, Dequiedt F, Kettmann R and Pastorek
J: Transcriptional regulation of the MN/CA 9 gene coding for the
tumor-associated carbonic anhydrase IX. Identification and
characterization of a proximal silencer element. J Biol Chem.
274:32588–32595. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kaluzová M, Kaluz S, Lerman MI and
Stanbridge EJ: DNA damage is a prerequisite for p53-mediated
proteasomal degradation of HIF-1alpha in hypoxic cells and
downregulation of the hypoxia marker carbonic anhydrase IX. Mol
Cell Biol. 24:5757–5766. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Pastorek J, Pastoreková S, Callebaut I,
Mornon JP, Zelník V, Opavský R, Zat’ovicová M, Liao S, Portetelle
D, Stanbridge EJ, et al: Cloning and characterization of MN, a
human tumor-associated protein with a domain homologous to carbonic
anhydrase and a putative helix-loop-helix DNA binding segment.
Oncogene. 9:2877–2888. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ditte P, Dequiedt F, Svastova E, Hulikova
A, Ohradanova-Repic A, Zatovicova M, Csaderova L, Kopacek J,
Supuran CT, Pastorekova S, et al: Phosphorylation of carbonic
anhydrase IX controls its ability to mediate extracellular
acidification in hypoxic tumors. Cancer Res. 71:7558–7567. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Fang JS, Gillies RD and Gatenby RA:
Adaptation to hypoxia and acidosis in carcinogenesis and tumor
progression. Semin Cancer Biol. 330–337. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gatenby RA and Gillies RJ: A
microenvironmental model of carcinogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer.
8:56–61. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Sedlakova O, Svastova E, Takacova M,
Kopacek J, Pastorek J and Pastorekova S: Carbonic anhydrase IX, a
hypoxia-induced catalytic component of the pH regulating machinery
in tumors. Front Physiol. 4:4002014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jakubikova J, Cervi D, Ooi M, Kim K, Nahar
S, Klippel S, Cholujova D, Leiba M, Daley JF, Delmore J, et al:
Anti-tumor activity and signaling events triggered by the
isothiocyanates, sulforaphane and phenethyl isothiocyanate, in
multiple myeloma. Haematologica. 96:1170–1179. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kaminski BM, Weigert A, Brüne B,
Schumacher M, Wenzel U, Steinhilber D, Stein J and Ulrich S:
Sulforaphane potentiates oxaliplatin-induced cell growth inhibition
in colorectal cancer cells via induction of different modes of cell
death. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 67:1167–1178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Mokhtari RB, Kumar S, Islam SS,
Yazdanpanah M, Adeli K, Cutz E and Yeger H: Combination of carbonic
anhydrase inhibitor, acetazolamide, and sulforaphane, reduces the
viability and growth of bronchial carcinoid cell lines. BMC Cancer.
13:3782013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|