|
1
|
Schneider-Stock R: Death-associated kinase
(DAPK): a cancer ‘gene chameleon’. Apoptosis. 19:2852014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ivanovska J, Tregubova A, Mahadevan V,
Chakilam S, Gandesiri M, Benderska N, Ettle B, Hartmann A, Söder S,
Ziesché E, et al: Identification of DAPK as a scaffold protein for
the LIMK/cofilin complex in TNF-induced apoptosis. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 45:1720–1729. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cohen O, Inbal B, Kissil JL, Raveh T,
Berissi H, Spivak-Kroizaman T, Feinstein E and Kimchi A: DAP-kinase
participates in TNF-alpha- and Fas-induced apoptosis and its
function requires the death domain. J Cell Biol. 146:141–148. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bialik S and Kimchi A: The
death-associated protein kinases: Structure, function, and beyond.
Annu Rev Biochem. 75:189–210. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gautel M: Cytoskeletal protein kinases:
Titin and its relations in mechanosensing. Pflugers Arch.
462:119–134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brenner H, Kloor M and Pox CP: Colorectal
cancer. Lancet. 383:1490–1502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wu WK, Wang XJ, Cheng AS, Luo MX, Ng SS,
To KF, Chan FK, Cho CH, Sung JJ and Yu J: Dysregulation and
crosstalk of cellular signaling pathways in colon carcinogenesis.
Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 86:251–277. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jass JR: Classification of colorectal
cancer based on correlation of clinical, morphological and
molecular features. Histopathology. 50:113–130. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Draht MX, Riedl RR, Niessen H, Carvalho B,
Meijer GA, Herman JG, van Engeland M, Melotte V and Smits KM:
Promoter CpG island methylation markers in colorectal cancer: The
road ahead. Epigenomics. 4:179–194. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
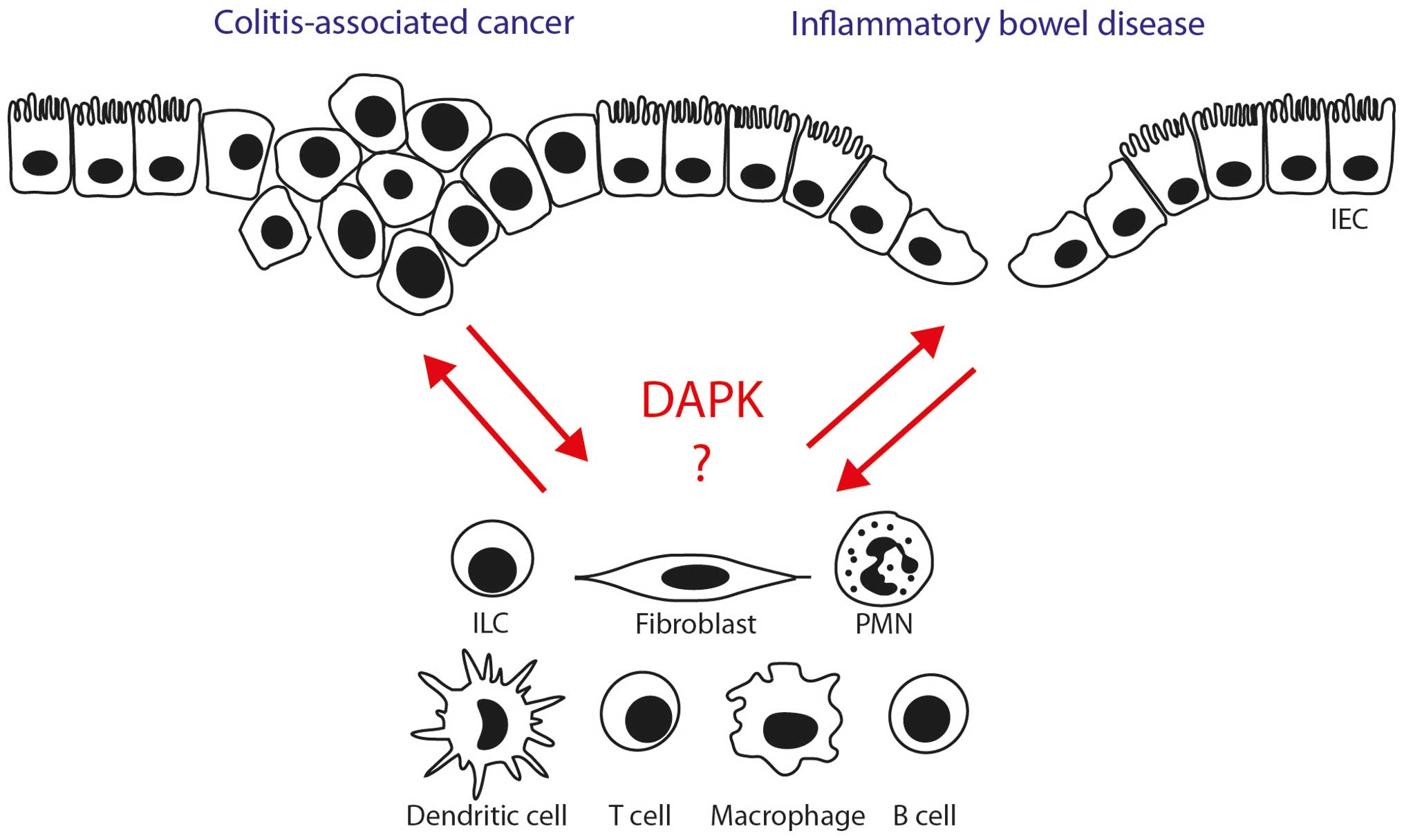
|
10
|
Feagins LA, Souza RF and Spechler SJ:
Carcinogenesis in IBD: Potential targets for the prevention of
colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 6:297–305. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Itzkowitz SH and Yio X: Inflammation and
cancer IV. Colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease: The
role of inflammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
287:G7–G17. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
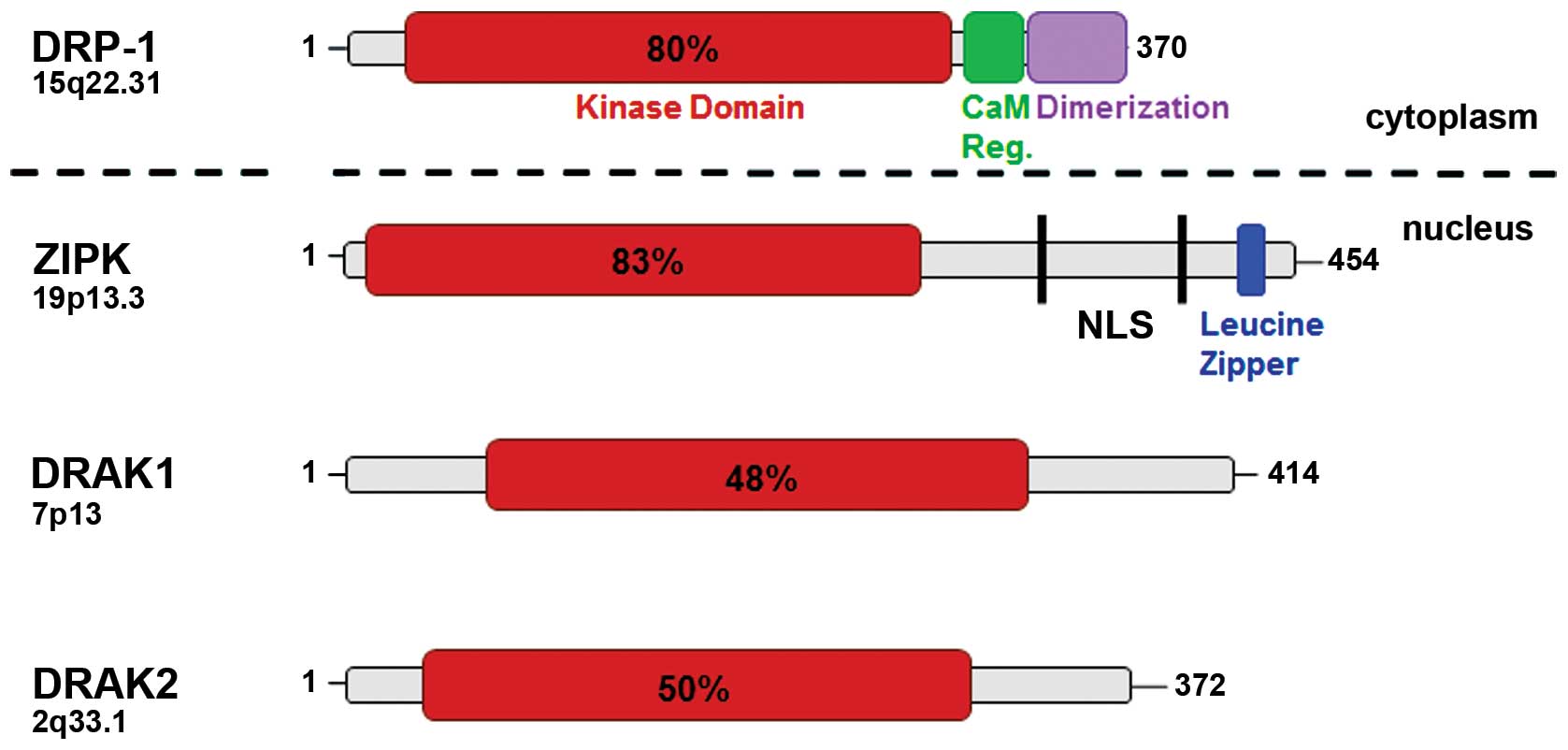
|
12
|
Mittag F, Kuester D, Vieth M, Peters B,
Stolte B, Roessner A and Schneider-Stock R: DAPK promotor
methylation is an early event in colorectal carcinogenesis. Cancer
Lett. 240:69–75. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chen HY, Lee YR and Chen RH: The functions
and regulations of DAPK in cancer metastasis. Apoptosis.
19:364–370. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
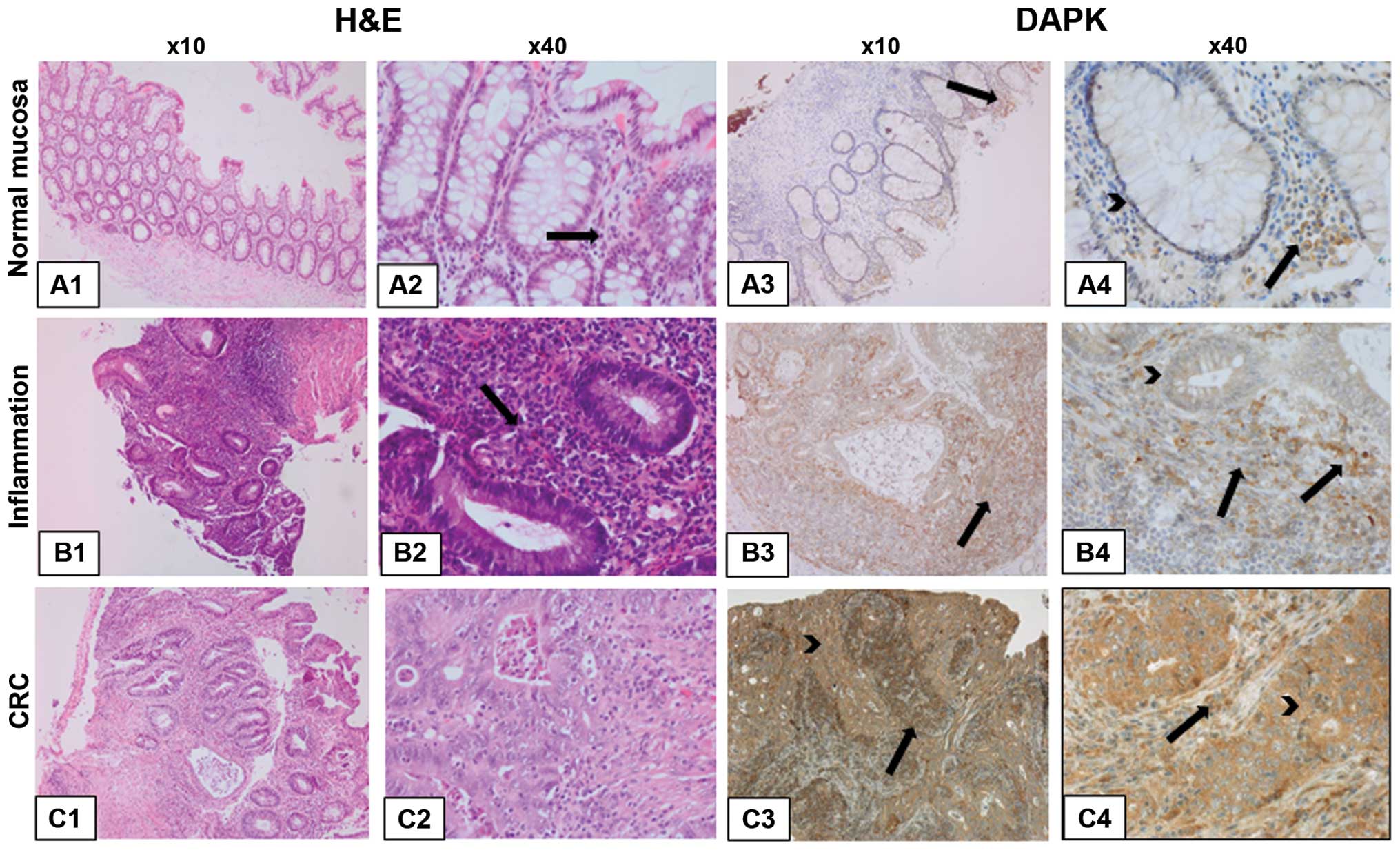
Bajbouj K, Poehlmann A, Kuester D, Drewes
T, Haase K, Hartig R, Teller A, Kliche S, Walluscheck D, Ivanovska
J, et al: Identification of phosphorylated p38 as a novel
DAPK-interacting partner during TNFalpha-induced apoptosis in
colorectal tumor cells. Am J Pathol. 175:557–570. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kuester D, Guenther T, Biesold S, Hartmann
A, Bataille F, Ruemmele P, Peters B, Meyer F, Schubert D, Bohr UR,
et al: Aberrant methylation of DAPK in long-standing ulcerative
colitis and ulcerative colitis-associated carcinoma. Pathol Res
Pract. 206:616–624. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chakilam S, Gandesiri M, Rau TT, Agaimy A,
Vijayalakshmi M, Ivanovska J, Wirtz RM, Schulze-Luehrmann J,
Benderska N, Wittkopf N, et al: Death-associated protein kinase
controls STAT3 activity in intestinal epithelial cells. Am J
Pathol. 182:1005–1020. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kawai T, Matsumoto M, Takeda K, Sanjo H
and Akira S: ZIP kinase, a novel serine/threonine kinase which
mediates apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 18:1642–1651. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kögel D, Plöttner O, Landsberg G,
Christian S and Scheidtmann KH: Cloning and characterization of
Dlk, a novel serine/threonine kinase that is tightly associated
with chromatin and phosphorylates core histones. Oncogene.
17:2645–2654. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Inbal B, Shani G, Cohen O, Kissil JL and
Kimchi A: Death-associated protein kinase-related protein 1, a
novel serine/threonine kinase involved in apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol.
20:1044–1054. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kawai T, Nomura F, Hoshino K, Copeland NG,
Gilbert DJ, Jenkins NA and Akira S: Death-associated protein kinase
2 is a new calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase that signals
apoptosis through its catalytic activity. Oncogene. 18:3471–3480.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Benderska N and Schneider-Stock R:
Transcription control of DAPK. Apoptosis. 19:298–305. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Dagher R, Peng S, Gioria S, Fève M, Zeniou
M, Zimmermann M, Pigault C, Haiech J and Kilhoffer MC: A general
strategy to characterize calmodulin-calcium complexes involved in
CaM-target recognition: DAPK and EGFR calmodulin binding domains
interact with different calmodulin-calcium complexes. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1813.1059–1067. 2011.
|
|
23
|
de Diego I, Kuper J, Bakalova N, Kursula P
and Wilmanns M: Molecular basis of the death-associated protein
kinase-calcium/calmodulin regulator complex. Sci Signal. 3:ra62010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang WJ, Kuo JC, Ku W, Lee YR, Lin FC,
Chang YL, Lin YM, Chen CH, Huang YP, Chiang MJ, et al: The tumor
suppressor DAPK is reciprocally regulated by tyrosine kinase Src
and phosphatase LAR. Mol Cell. 27:701–716. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bialik S and Kimchi A: Biochemical and
functional characterization of the ROC domain of DAPK establishes a
new paradigm of GTP regulation in ROCO proteins. Biochem Soc Trans.
40:1052–1057. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Carlessi R, Levin-Salomon V, Ciprut S,
Bialik S, Berissi H, Albeck S, Peleg Y and Kimchi A: GTP binding to
the ROC domain of DAP-kinase regulates its function through
intra-molecular signalling. EMBO Rep. 12:917–923. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim BM, You MH, Chen CH, Lee S, Hong Y,
Hong Y, Kimchi A, Zhou XZ and Lee TH: Death-associated protein
kinase 1 has a critical role in aberrant tau protein regulation and
function. Cell Death Dis. 5:e12372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stevens C, Lin Y, Harrison B, Burch L,
Ridgway RA, Sansom O and Hupp T: Peptide combinatorial libraries
identify TSC2 as a death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) death
domain-binding protein and reveal a stimulatory role for DAPK in
mTORC1 signaling. J Biol Chem. 284:334–344. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kissil JL, Feinstein E, Cohen O, Jones PA,
Tsai YC, Knowles MA, Eydmann ME and Kimchi A: DAP-kinase loss of
expression in various carcinoma and B-cell lymphoma cell lines:
Possible implications for role as tumor suppressor gene. Oncogene.
15:403–407. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Leung RC, Liu SS, Chan KY, Tam KF, Chan
KL, Wong LC and Ngan HY: Promoter methylation of death-associated
protein kinase and its role in irradiation response in cervical
cancer. Oncol Rep. 19:1339–1345. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shanmugam R, Gade P, Wilson-Weekes A,
Sayar H, Suvannasankha A, Goswami C, Li L, Gupta S, Cardoso AA, Al
Baghdadi T, et al: A noncanonical Flt3ITD/NF-κB signaling pathway
represses DAPK1 in acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res.
18:360–369. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hayakawa J, Mittal S, Wang Y, Korkmaz KS,
Adamson E, English C, Ohmichi M, McClelland M and Mercola D:
Identification of promoters bound by c-Jun/ATF2 during rapid
large-scale gene activation following genotoxic stress. Mol Cell.
16:521–535. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Martoriati A, Doumont G, Alcalay M,
Bellefroid E, Pelicci PG and Marine JC: dapk1, encoding an
activator of a p19ARF-p53-mediated apoptotic checkpoint, is a
transcription target of p53. Oncogene. 24:1461–1466. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Gade P, Roy SK, Li H, Nallar SC and
Kalvakolanu DV: Critical role for transcription factor C/EBP-beta
in regulating the expression of death-associated protein kinase 1.
Mol Cell Biol. 28:2528–2548. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Benderska N, Ivanovska J, Rau TT,
Schulze-Luehrmann J, Mohan S, Chakilam S, Gandesiri M, Ziesché E,
Fischer T, Söder S, et al: DAPK-HSF1 interaction as a new positive
feedback loop for TNF-induced apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells.
J Cell Sci. 127:5273–5287. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Massagué J, Seoane J and Wotton D: Smad
transcription factors. Genes Dev. 19:2783–2810. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gandesiri M, Chakilam S, Ivanovska J,
Benderska N, Ocker M, Di Fazio P, Feoktistova M, Gali-Muhtasib H,
Rave-Fränk M, Prante O, et al: DAPK plays an important role in
panobinostat-induced autophagy and commits cells to apoptosis under
autophagy deficient conditions. Apoptosis. 17:1300–1315. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jin Y and Gallagher PJ: Antisense
depletion of death-associated protein kinase promotes apoptosis. J
Biol Chem. 278:51587–51593. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang L, Nephew KP and Gallagher PJ:
Regulation of death-associated protein kinase. Stabilization by
HSP90 hetero-complexes. J Biol Chem. 282:11795–11804. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jin Y, Blue EK, Dixon S, Shao Z and
Gallagher PJ: A death-associated protein kinase (DAPK)-interacting
protein, DIP-1, is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that promotes tumor
necrosis factor-induced apoptosis and regulates the cellular levels
of DAPK. J Biol Chem. 277:46980–46986. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee YR, Yuan WC, Ho HC, Chen CH, Shih HM
and Chen RH: The Cullin 3 substrate adaptor KLHL20 mediates DAPK
ubiquitination to control interferon responses. EMBO J.
29:1748–1761. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gallagher PJ and Blue EK:
Post-translational regulation of the cellular levels of DAPK.
Apoptosis. 19:306–315. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lin Y, Stevens C and Hupp T:
Identification of a dominant negative functional domain on DAPK-1
that degrades DAPK-1 protein and stimulates TNFR-1-mediated
apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 282:16792–16802. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lin Y, Hupp TR and Stevens C:
Death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) and signal transduction:
Additional roles beyond cell death. FEBS J. 277:48–57. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Benderska N, Chakilam S, Hugle M,
Ivanovska J, Gandesiri M, Schulze-Luhrmann J, Bajbouj K, Croner R
and Schneider-Stock R: Apoptosis signalling activated by TNF in the
lower gastrointestinal tract--review. Curr Pharm Biotechnol.
13:2248–2258. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Henshall DC, Araki T, Schindler CK,
Shinoda S, Lan JQ and Simon RP: Expression of death-associated
protein kinase and recruitment to the tumor necrosis factor
signaling pathway following brief seizures. J Neurochem.
86:1260–1270. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zalckvar E, Berissi H, Mizrachy L,
Idelchuk Y, Koren I, Eisenstein M, Sabanay H, Pinkas-Kramarski R
and Kimchi A: DAP-kinase-mediated phosphorylation on the BH3 domain
of beclin 1 promotes dissociation of beclin 1 from Bcl-XL and
induction of autophagy. EMBO Rep. 10:285–292. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen CH, Wang WJ, Kuo JC, Tsai HC, Lin JR,
Chang ZF and Chen RH: Bidirectional signals transduced by DAPK-ERK
interaction promote the apoptotic effect of DAPK. EMBO J.
24:294–304. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
49
|
Anjum R, Roux PP, Ballif BA, Gygi SP and
Blenis J: The tumor suppressor DAP kinase is a target of
RSK-mediated survival signaling. Curr Biol. 15:1762–1767. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Eisenberg-Lerner A and Kimchi A: DAP
kinase regulates JNK signaling by binding and activating protein
kinase D under oxidative stress. Cell Death Differ. 14:1908–1915.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Shani G, Marash L, Gozuacik D, Bialik S,
Teitelbaum L, Shohat G and Kimchi A: Death-associated protein
kinase phosphorylates ZIP kinase, forming a unique kinase hierarchy
to activate its cell death functions. Mol Cell Biol. 24:8611–8626.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kuo JC, Lin JR, Staddon JM, Hosoya H and
Chen RH: Uncoordinated regulation of stress fibers and focal
adhesions by DAP kinase. J Cell Sci. 116:4777–4790. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Houle F, Poirier A, Dumaresq J and Huot J:
DAP kinase mediates the phosphorylation of tropomyosin-1 downstream
of the ERK pathway, which regulates the formation of stress fibers
in response to oxidative stress. J Cell Sci. 120:3666–3677. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Bialik S, Berissi H and Kimchi A: A high
throughput proteomics screen identifies novel substrates of
death-associated protein kinase. Mol Cell Proteomics. 7:1089–1098.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Schumacher AM, Schavocky JP, Velentza AV,
Mirzoeva S and Watterson DM: A calmodulin-regulated protein kinase
linked to neuron survival is a substrate for the
calmodulin-regulated death-associated protein kinase. Biochemistry.
43:8116–8124. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Fraser JA and Hupp TR: Chemical genetics
approach to identify peptide ligands that selectively stimulate
DAPK-1 kinase activity. Biochemistry. 46:2655–2673. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Schumacher AM, Velentza AV, Watterson DM
and Dresios J: Death-associated protein kinase phosphorylates
mammalian ribosomal protein S6 and reduces protein synthesis.
Biochemistry. 45:13614–13621. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Tian JH, Das S and Sheng ZH:
Ca2+-dependent phosphorylation of syntaxin-1A by the
death-associated protein (DAP) kinase regulates its interaction
with Munc18. J Biol Chem. 278:26265–26274. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Danese S and Fiocchi C: Ulcerative
colitis. N Engl J Med. 365:1713–1725. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Baumgart DC and Sandborn WJ: Crohn’s
disease. Lancet. 380:1590–1605. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Atreya R and Neurath MF: IBD pathogenesis
in 2014: Molecular pathways controlling barrier function in IBD.
Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 12:67–68. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Strober W, Fuss I and Mannon P: The
fundamental basis of inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Invest.
117:514–521. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Jostins L, Ripke S, Weersma RK, Duerr RH,
McGovern DP, Hui KY, Lee JC, Schumm LP, Sharma Y, Anderson CA, et
al: International IBD Genetics Consortium (IIBDGC): Host-microbe
interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory
bowel disease. Nature. 491:119–124. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Neurath MF: Cytokines in inflammatory
bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:329–342. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Feagan BG, Rutgeerts P, Sands BE, Hanauer
S, Colombel JF, Sandborn WJ, Van Assche G, Axler J, Kim HJ, Danese
S, et al: GEMINI 1 Study Group: Vedolizumab as induction and
maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med.
369:699–710. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, Rutgeerts P,
Hanauer S, Colombel JF, Sands BE, Lukas M, Fedorak RN, Lee S,
Bressler B, et al: GEMINI 2 Study Group: Vedolizumab as induction
and maintenance therapy for Crohn’s disease. N Engl J Med.
369:711–721. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Atreya R, Zimmer M, Bartsch B, Waldner MJ,
Atreya I, Neumann H, Hildner K, Hoffman A, Kiesslich R, Rink AD, et
al: Antibodies against tumor necrosis factor (TNF) induce T-cell
apoptosis in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases via TNF
receptor 2 and intestinal CD14+ macrophages.
Gastroenterology. 141:2026–2038. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Lai MZ and Chen RH: Regulation of
inflammation by DAPK. Apoptosis. 19:357–363. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Backert I, Koralov SB, Wirtz S, Kitowski
V, Billmeier U, Martini E, Hofmann K, Hildner K, Wittkopf N, Brecht
K, et al: STAT3 activation in Th17 and Th22 cells controls
IL-22-mediated epithelial host defense during infectious colitis. J
Immunol. 193:3779–3791. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Pickert G, Neufert C, Leppkes M, Zheng Y,
Wittkopf N, Warntjen M, Lehr HA, Hirth S, Weigmann B, Wirtz S, et
al: STAT3 links IL-22 signaling in intestinal epithelial cells to
mucosal wound healing. J Exp Med. 206:1465–1472. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Atreya R, Neumann H, Neufert C, Waldner
MJ, Billmeier U, Zopf Y, Willma M, App C, Münster T, Kessler H, et
al: In vivo imaging using fluorescent antibodies to tumor necrosis
factor predicts therapeutic response in Crohn’s disease. Nat Med.
20:313–318. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Jin Y, Blue EK and Gallagher PJ: Control
of death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) activity by
phosphorylation and proteasomal degradation. J Biol Chem.
281:39033–39040. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Yoo HJ, Byun HJ, Kim BR, Lee KH, Park SY
and Rho SB: DAPk1 inhibits NF-κB activation through TNF-α and
INF-γ-induced apoptosis. Cell Signal. 24:1471–1477. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Chuang YT, Fang LW, Lin-Feng MH, Chen RH
and Lai MZ: The tumor suppressor death-associated protein kinase
targets to TCR-stimulated NF-kappa B activation. J Immunol.
180:3238–3249. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Chuang YT, Lin YC, Lin KH, Chou TF, Kuo
WC, Yang KT, Wu PR, Chen RH, Kimchi A and Lai MZ: Tumor suppressor
death-associated protein kinase is required for full IL-1β
production. Blood. 117:960–970. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Turner-Brannen E, Choi KY, Arsenault R,
El-Gabalawy H, Napper S and Mookherjee N: Inflammatory cytokines
IL-32 and IL-17 have common signaling intermediates despite
differential dependence on TNF-receptor 1. J Immunol.
186:7127–7135. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Nakav S, Cohen S, Feigelson SW, Bialik S,
Shoseyov D, Kimchi A and Alon R: Tumor suppressor death-associated
protein kinase attenuates inflammatory responses in the lung. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 46:313–322. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Bauer C, Duewell P, Mayer C, Lehr HA,
Fitzgerald KA, Dauer M, Tschopp J, Endres S, Latz E and Schnurr M:
Colitis induced in mice with dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) is
mediated by the NLRP3 inflammasome. Gut. 59:1192–1199. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Schoultz I, Verma D, Halfvarsson J,
Törkvist L, Fredrikson M, Sjöqvist U, Lördal M, Tysk C, Lerm M,
Söderkvist P, et al: Combined polymorphisms in genes encoding the
inflammasome components NALP3 and CARD8 confer susceptibility to
Crohn’s disease in Swedish men. Am J Gastroenterol. 104:1180–1188.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Fantini MC, Rizzo A, Fina D, Caruso R,
Sarra M, Stolfi C, Becker C, Macdonald TT, Pallone F, Neurath MF
and Monteleone G: Smad7 controls resistance of colitogenic T cells
to regulatory T cell-mediated suppression. Gastroenterology.
136:1308–1316. e1–3. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Monteleone G, Fantini MC, Onali S, Zorzi
F, Sancesario G, Bernardini S, Calabrese E, Viti F, Monteleone I,
Biancone L and Pallone F: Phase I clinical trial of Smad7 knockdown
using antisense oligonucleotide in patients with active Crohn’s
disease. Mol Ther. 20:870–876. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Jang CW, Chen CH, Chen CC, Chen JY, Su YH
and Chen RH: TGF-beta induces apoptosis through Smad-mediated
expression of DAP-kinase. Nat Cell Biol. 4:51–58. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
MacDonald TT, Monteleone I, Fantini MC and
Monteleone G: Regulation of homeostasis and inflammation in the
intestine. Gastroenterology. 140:1768–1775. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Shiloh R, Bialik S and Kimchi A: The DAPK
family: a structure-function analysis. Apoptosis. 19:286–297. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Ekbom A, Helmick C, Zack M and Adami HO:
Ulcerative colitis and colorectal cancer. A population-based study.
N Engl J Med. 323:1228–1233. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Mathy C, Schneider K, Chen YY, Varma M,
Terdiman JP and Mahadevan U: Gross versus microscopic pancolitis
and the occurrence of neoplasia in ulcerative colitis. Inflamm
Bowel Dis. 9:351–355. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Rutter M, Saunders B, Wilkinson K, Rumbles
S, Schofield G, Kamm M, Williams C, Price A, Talbot I and Forbes A:
Severity of inflammation is a risk factor for colorectal neoplasia
in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 126:451–459. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Broomé U, Lindberg G and Löfberg R:
Primary sclerosing cholangitis in ulcerative colitis - a risk
factor for the development of dysplasia and DNA aneuploidy?
Gastroenterology. 102:1877–1880. 1992.
|
|
89
|
Van Assche G, Dignass A, Bokemeyer B,
Danese S, Gionchetti P, Moser G, Beaugerie L, Gomollón F, Häuser W,
Herrlinger K, et al: European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation:
Second European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and
management of ulcerative colitis part 3: Special situations. J
Crohn’s Colitis. 7:1–33. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Ullman TA and Itzkowitz SH: Intestinal
inflammation and cancer. Gastroenterology. 140:1807–1816. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Vogelstein B, Fearon ER, Hamilton SR, Kern
SE, Preisinger AC, Leppert M, Nakamura Y, White R, Smits AM and Bos
JL: Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N Engl
J Med. 319:525–532. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Fearon ER: Molecular genetics of
colorectal cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:479–507. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Hussain SP, Amstad P, Raja K, Ambs S,
Nagashima M, Bennett WP, Shields PG, Ham AJ, Swenberg JA, Marrogi
AJ, et al: Increased p53 mutation load in noncancerous colon tissue
from ulcerative colitis: A cancer-prone chronic inflammatory
disease. Cancer Res. 60:3333–3337. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Redston MS, Papadopoulos N, Caldas C,
Kinzler KW and Kern SE: Common occurrence of APC and K-ras gene
mutations in the spectrum of colitis-associated neoplasias.
Gastroenterology. 108:383–392. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Michie AM, McCaig AM, Nakagawa R and
Vukovic M: Death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) and signal
transduction: Regulation in cancer. FEBS J. 277:74–80. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Grivennikov S, Karin E, Terzic J, Mucida
D, Yu GY, Vallabhapurapu S, Scheller J, Rose-John S, Cheroutre H,
Eckmann L, et al: IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of
intestinal epithelial cells and development of colitis-associated
cancer. Cancer Cell. 15:103–113. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Neufert C, Becker C, Türeci Ö, Waldner MJ,
Backert I, Floh K, Atreya I, Leppkes M, Jefremow A, Vieth M, et al:
Tumor fibroblast-derived epiregulin promotes growth of
colitis-associated neoplasms through ERK. J Clin Invest.
123:1428–1443. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Salcedo R, Worschech A, Cardone M, Jones
Y, Gyulai Z, Dai RM, Wang E, Ma W, Haines D, O’hUigin C, et al:
MyD88-mediated signaling prevents development of adenocarcinomas of
the colon: Role of interleukin 18. J Exp Med. 207:1625–1636. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Popivanova BK, Kitamura K, Wu Y, Kondo T,
Kagaya T, Kaneko S, Oshima M, Fujii C and Mukaida N: Blocking
TNF-alpha in mice reduces colorectal carcinogenesis associated with
chronic colitis. J Clin Invest. 118:560–570. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
D’Incà R, Cardin R, Benazzato L, Angriman
I, Martines D and Sturniolo GC: Oxidative DNA damage in the mucosa
of ulcerative colitis increases with disease duration and
dysplasia. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 10:23–27. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Goel A and Boland CR: Epigenetics of
colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 143:1442–1460. e12012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Schneider-Stock R, Kuester D, Ullrich O,
Mittag F, Habold C, Boltze C, Peters B, Krueger S, Hintze C, Meyer
F, et al: Close localization of DAP-kinase positive
tumour-associated macrophages and apoptotic colorectal cancer
cells. J Pathol. 209:95–105. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Mukhopadhyay R, Ray PS, Arif A, Brady AK,
Kinter M and Fox PL: DAPK-ZIPK-L13a axis constitutes a
negative-feedback module regulating inflammatory gene expression.
Mol Cell. 32:371–382. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Kamal M, Pawlak A, BenMohamed F,
Valanciuté A, Dahan K, Candelier M, Lang P, Guellaën G and Sahali
D: C-mip interacts with the p85 subunit of PI3 kinase and exerts a
dual effect on ERK signaling via the recruitment of Dip1 and DAP
kinase. FEBS Lett. 584:500–506. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|