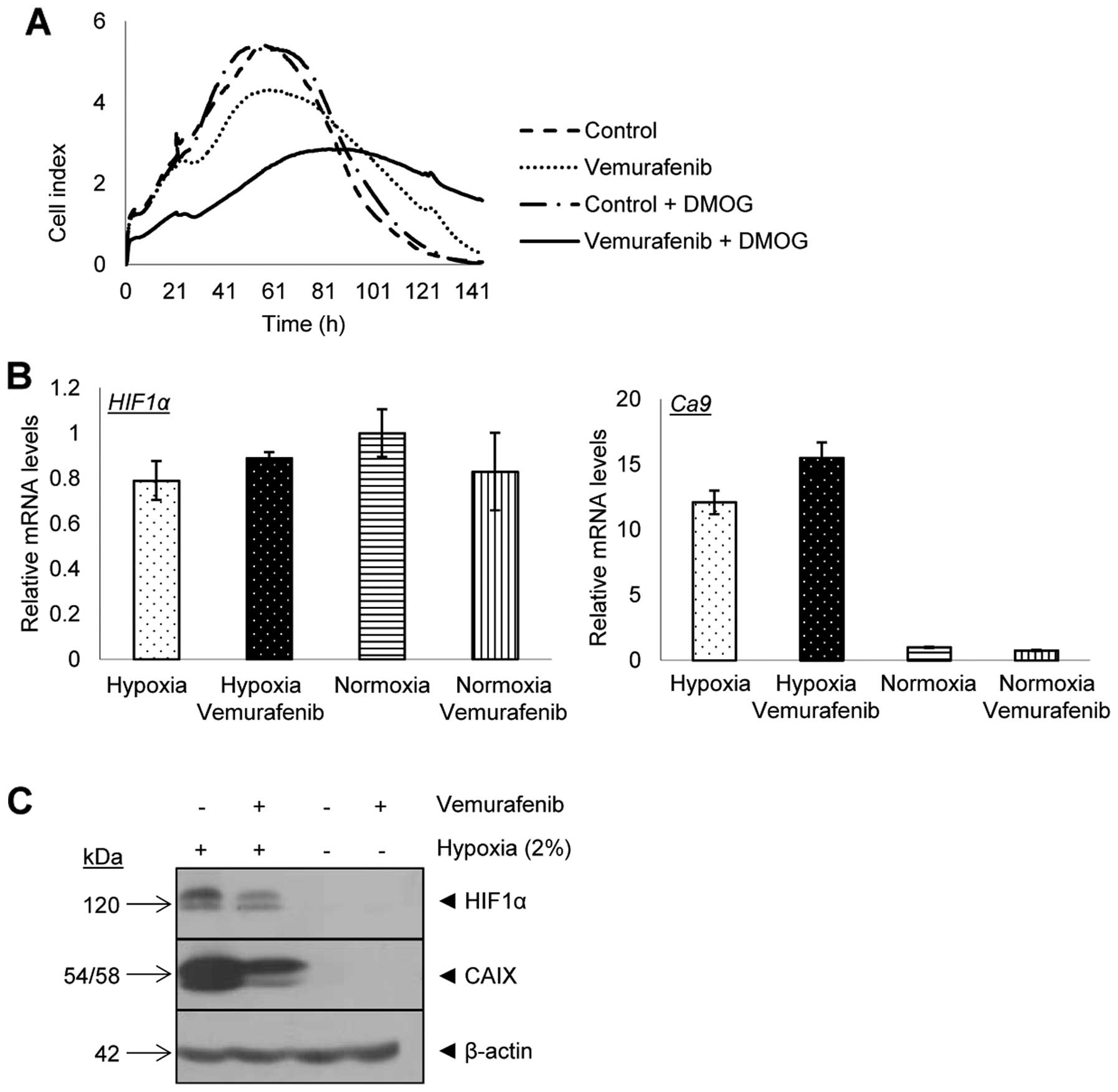
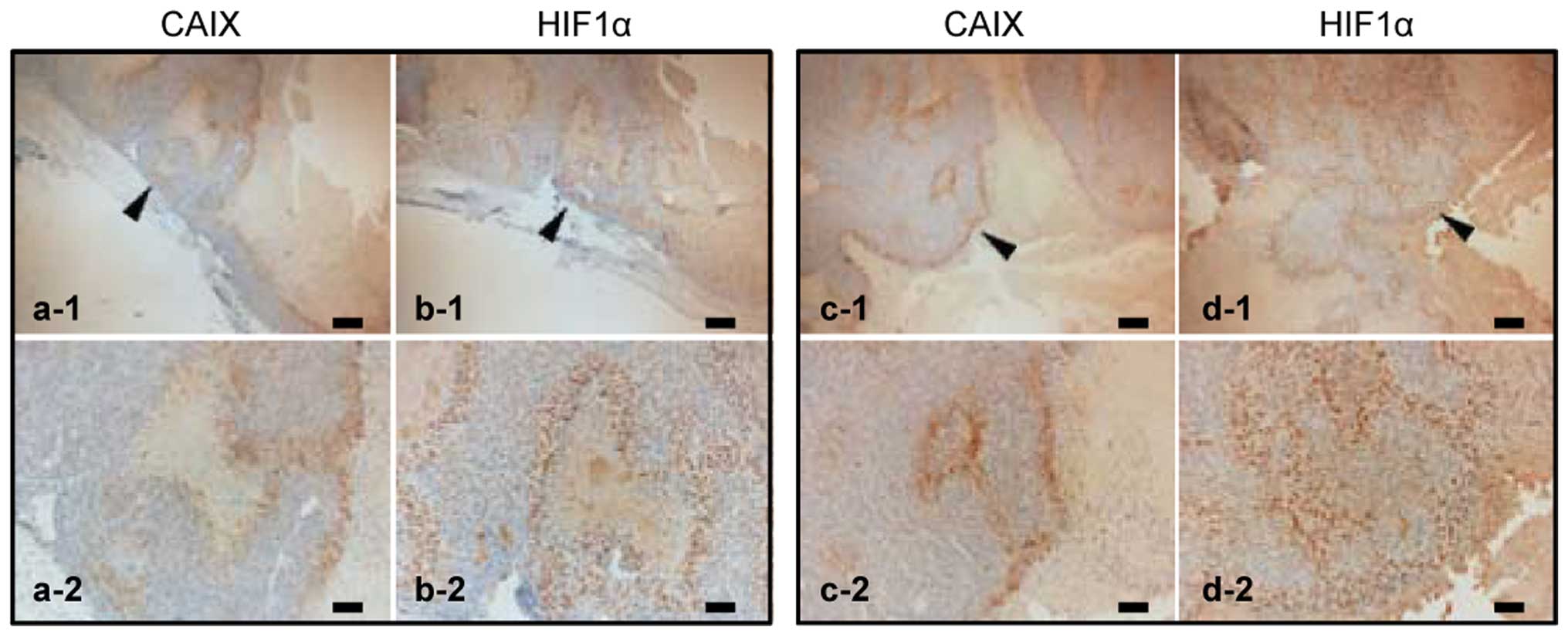
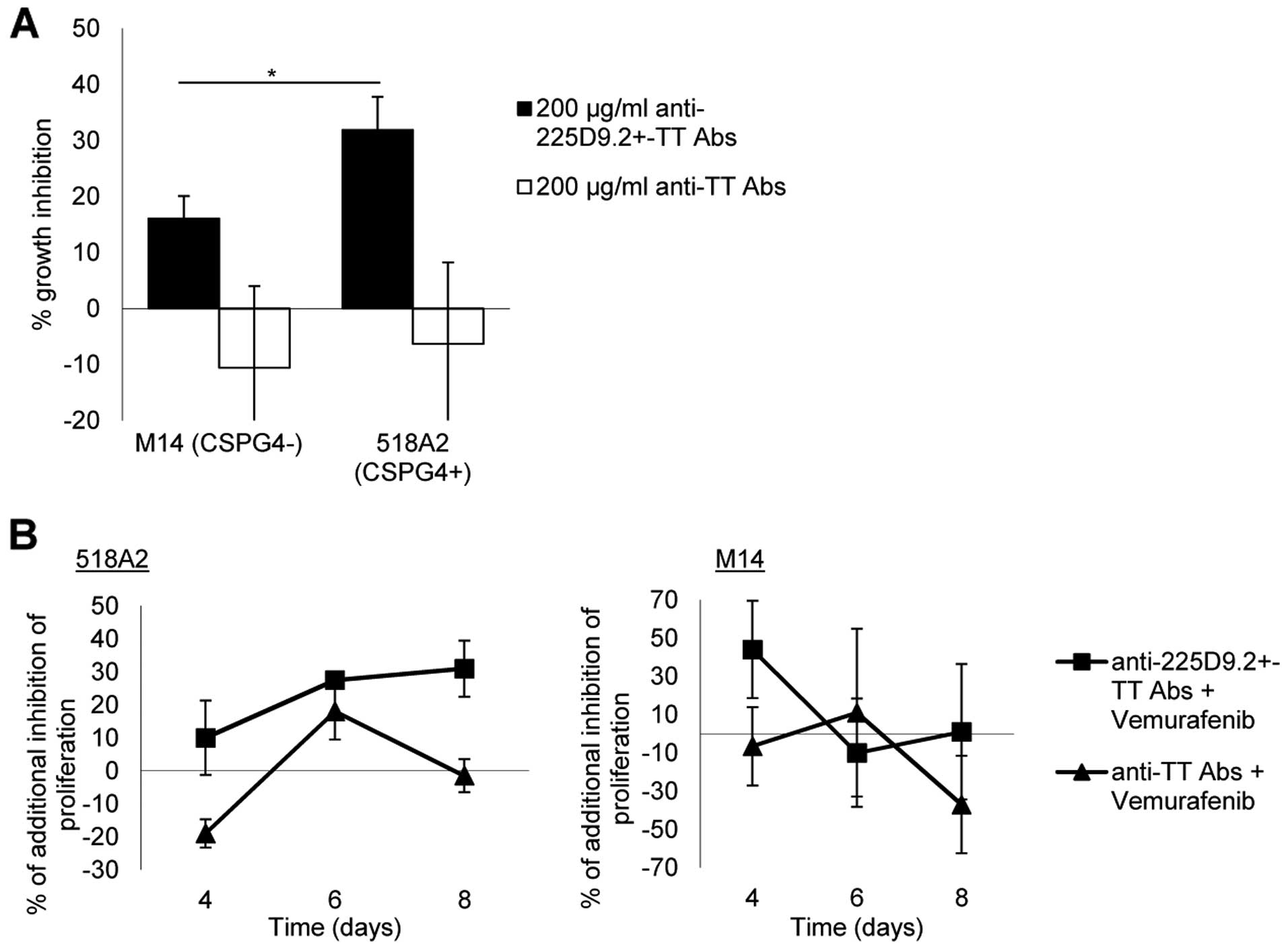
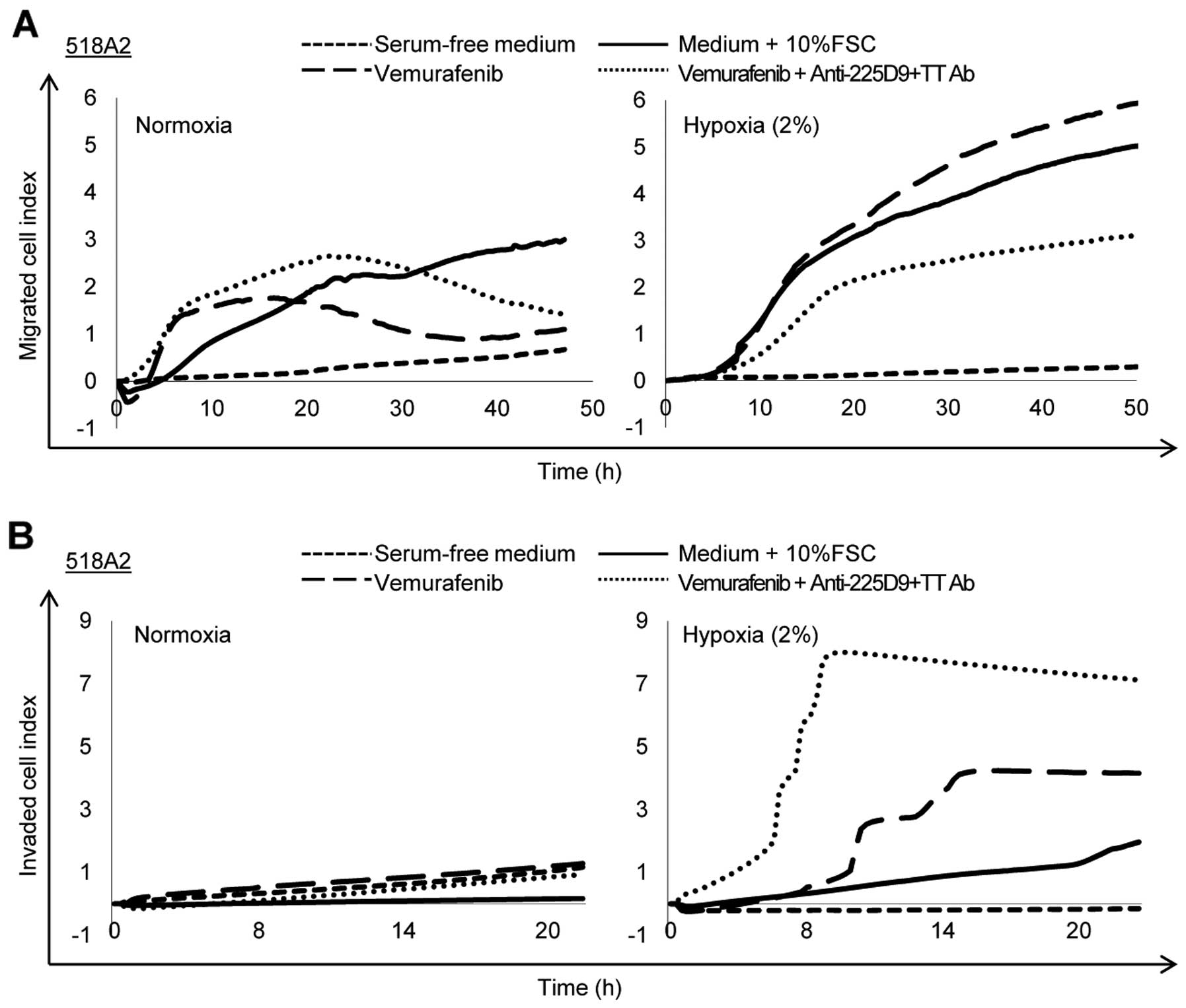
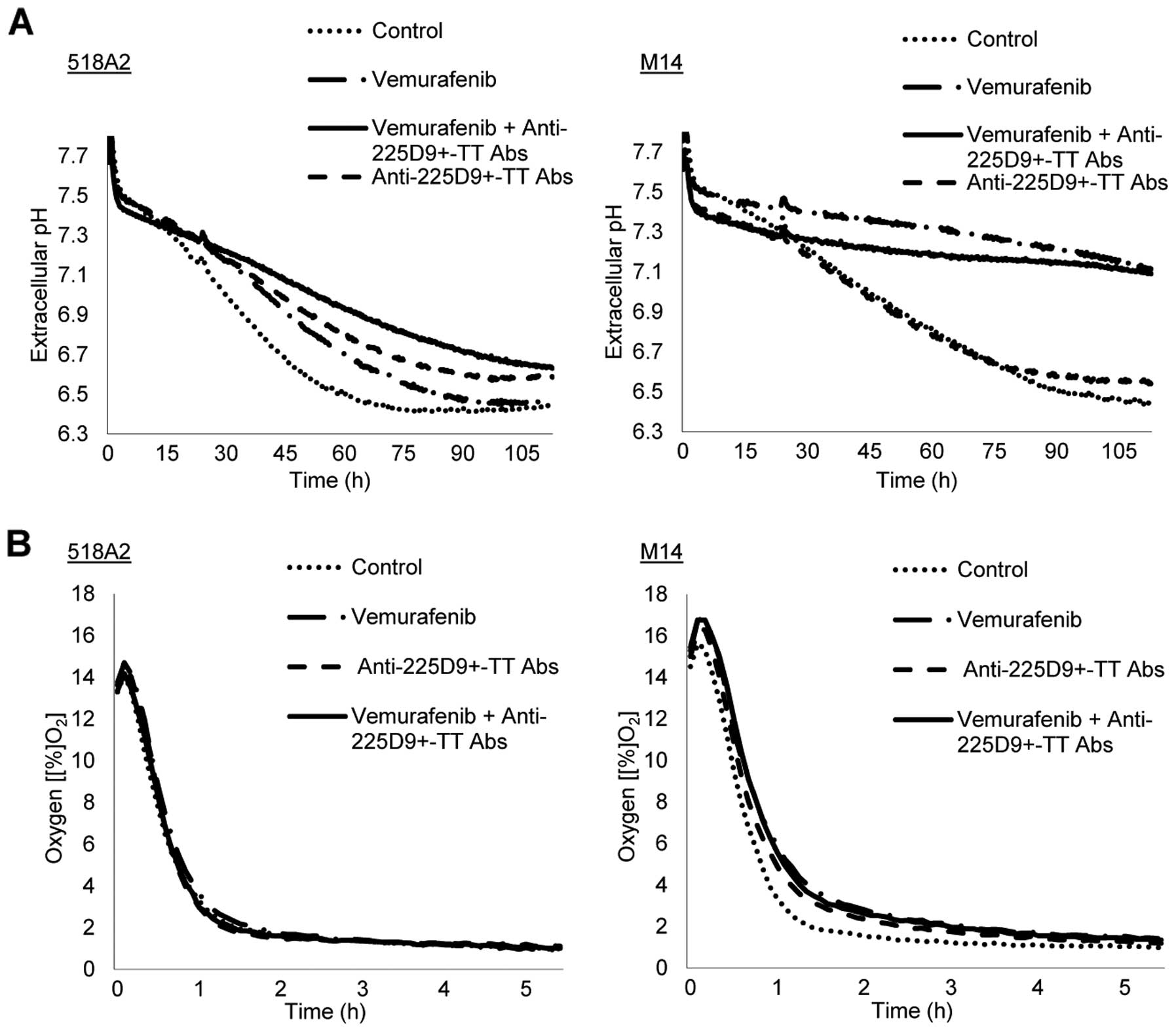
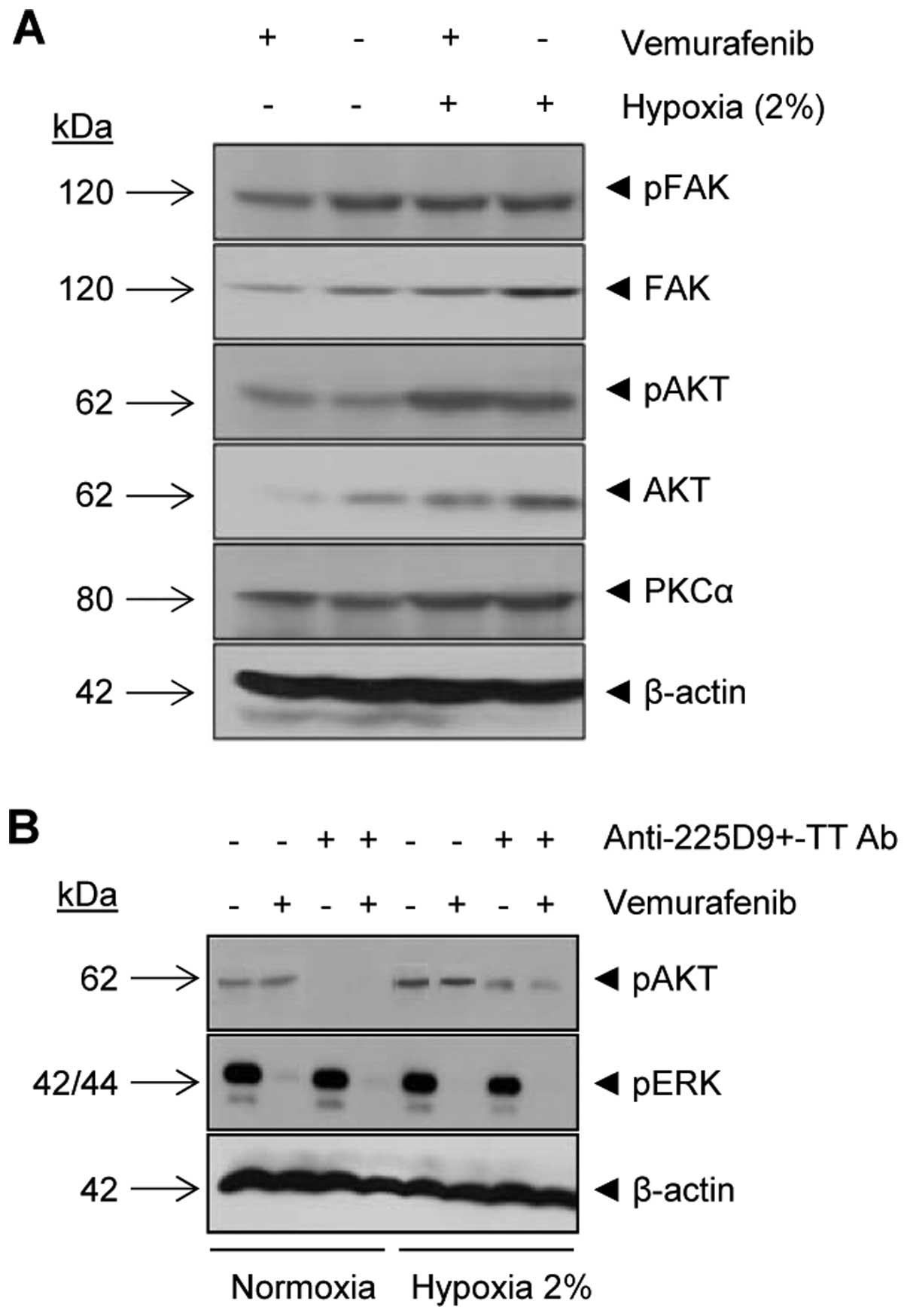
|
1
|
MacKie RM, Hauschild A and Eggermont AMM:
Epidemiology of invasive cutaneous melanoma. Ann Oncol. 20(Suppl
6): vi1–vi7. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Linos E, Swetter SM, Cockburn MG, Colditz
GA and Clarke CA: Increasing burden of melanoma in the United
States. J Invest Dermatol. 129:1666–1674. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Testori A, Rutkowski P, Marsden J,
Bastholt L, Chiarion-Sileni V, Hauschild A and Eggermont AM:
Surgery and radiotherapy in the treatment of cutaneous melanoma.
Ann Oncol. 20(Suppl 6): vi22–vi29. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kee D and McArthur G: Targeted therapies
for cutaneous melanoma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 28:491–505.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gogas H, Polyzos A and Kirkwood J:
Immunotherapy for advanced melanoma: Fulfilling the promise. Cancer
Treat Rev. 39:879–885. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, Haanen
JB, Ascierto P, Larkin J, Dummer R, Garbe C, Testori A, Maio M, et
al; BRIM-3 Study Group. Improved survival with vemurafenib in
melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N Engl J Med. 364:2507–2516.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Flaherty KT, Puzanov I, Kim KB, Ribas A,
McArthur GA, Sosman JA, O’Dwyer PJ, Lee RJ, Grippo JF, Nolop K, et
al: Inhibition of mutated, activated BRAF in metastatic melanoma. N
Engl J Med. 363:809–819. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fedorenko IV, Paraiso KH and Smalley KS:
Acquired and intrinsic BRAF inhibitor resistance in BRAF V600E
mutant melanoma. Biochem Pharmacol. 82:201–209. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun C, Wang L, Huang S, Heynen GJ,
Prahallad A, Robert C, Haanen J, Blank C, Wesseling J, Willems SM,
et al: Reversible and adaptive resistance to BRAF(V600E) inhibition
in melanoma. Nature. 508:118–122. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kugel CH III and Aplin AE: Adaptive
resistance to RAF inhibitors in melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma
Res. 27:1032–1038. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kudchadkar R, Paraiso KH and Smalley KS:
Targeting mutant BRAF in melanoma: Current status and future
development of combination therapy strategies. Cancer J.
18:124–131. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Price MA, Colvin Wanshura LE, Yang J,
Carlson J, Xiang B, Li G, Ferrone S, Dudek AZ, Turley EA and
McCarthy JB: CSPG4, a potential therapeutic target, facilitates
malignant progression of melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res.
24:1148–1157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mittelman A, Chen ZJ, Liu CC, Hirai S and
Ferrone S: Kinetics of the immune response and regression of
metastatic lesions following development of humoral anti-high
molecular weight-melanoma associated antigen immunity in three
patients with advanced malignant melanoma immunized with mouse
anti-idiotypic monoclonal antibody MK2-23. Cancer Res. 54:415–421.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ferris RL, Jaffee EM and Ferrone S: Tumor
antigen-targeted, monoclonal antibody-based immunotherapy: Clinical
response, cellular immunity, and immunoescape. J Clin Oncol.
28:4390–4399. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang X, Osada T, Wang Y, Yu L, Sakakura K,
Katayama A, McCarthy JB, Brufsky A, Chivukula M, Khoury T, et al:
CSPG4 protein as a new target for the antibody-based immunotherapy
of triple-negative breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst.
102:1496–1512. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hafner C, Breiteneder H, Ferrone S,
Thallinger C, Wagner S, Schmidt WM, Jasinska J, Kundi M, Wolff K,
Zielinski CC, et al: Suppression of human melanoma tumor growth in
SCID mice by a human high molecular weight-melanoma associated
antigen (HMW-MAA) specific monoclonal antibody. Int J Cancer.
114:426–432. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yu L, Favoino E, Wang Y, Ma Y, Deng X and
Wang X: The CSPG4-specific monoclonal antibody enhances and
prolongs the effects of the BRAF inhibitor in melanoma cells.
Immunol Res. 50:294–302. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wagner S, Hafner C, Allwardt D, Jasinska
J, Ferrone S, Zielinski CC, Scheiner O, Wiedermann U, Pehamberger H
and Breiteneder H: Vaccination with a human high molecular weight
melanoma-associated antigen mimotope induces a humoral response
inhibiting melanoma cell growth in vitro. J Immunol. 174:976–982.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wagner S, Krepler C, Allwardt D, Latzka J,
Strommer S, Scheiner O, Pehamberger H, Wiedermann U, Hafner C and
Breiteneder H: Reduction of human melanoma tumor growth in severe
combined immunodeficient mice by passive transfer of antibodies
induced by a high molecular weight melanoma-associated antigen
mimotope vaccine. Clin Cancer Res. 14:8178–8183. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Walsh JC, Lebedev A, Aten E, Madsen K,
Marciano L and Kolb HC: The clinical importance of assessing tumor
hypoxia: Relationship of tumor hypoxia to prognosis and therapeutic
opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal. 21:1516–1554. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
O’Connell MP, Marchbank K, Webster MR,
Valiga AA, Kaur A, Vultur A, Li L, Herlyn M, Villanueva J, Liu Q,
et al: Hypoxia induces phenotypic plasticity and therapy resistance
in melanoma via the tyrosine kinase receptors ROR1 and ROR2. Cancer
Discov. 3:1378–1393. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Vergis R, Corbishley CM, Norman AR,
Bartlett J, Jhavar S, Borre M, Heeboll S, Horwich A, Huddart R,
Khoo V, et al: Intrinsic markers of tumour hypoxia and angiogenesis
in localised prostate cancer and outcome of radical treatment: A
retrospective analysis of two randomised radiotherapy trials and
one surgical cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 9:342–351. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mujcic H, Hill RP, Koritzinsky M and
Wouters BG: Hypoxia signaling and the metastatic phenotype. Curr
Mol Med. 14:565–579. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ghislin S, Deshayes F, Middendorp S,
Boggetto N and Alcaide-Loridan C: PHF19 and Akt control the switch
between proliferative and invasive states in melanoma. Cell Cycle.
11:1634–1645. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Erler JT, Bennewith KL, Nicolau M,
Dornhöfer N, Kong C, Le QT, Chi JT, Jeffrey SS and Giaccia AJ:
Lysyl oxidase is essential for hypoxia-induced metastasis. Nature.
440:1222–1226. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Widmer DS, Hoek KS, Cheng PF, Eichhoff OM,
Biedermann T, Raaijmakers MI, Hemmi S, Dummer R and Levesque MP:
Hypoxia contributes to melanoma heterogeneity by triggering
HIF1α-dependent phenotype switching. J Invest Dermatol.
133:2436–2443. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hanna SC, Krishnan B, Bailey ST, Moschos
SJ, Kuan PF, Shimamura T, Osborne LD, Siegel MB, Duncan LM, O’Brien
ET III, et al: HIF1α and HIF2α independently activate SRC to
promote melanoma metastases. J Clin Invest. 123:2078–2093. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mouriaux F, Sanschagrin F, Diorio C,
Landreville S, Comoz F, Petit E, Bernaudin M, Rousseau AP, Bergeron
D and Morcos M: Increased HIF-1α expression correlates with cell
proliferation and vascular markers CD31 and VEGF-A in uveal
melanoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 55:1277–1283. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ditte P, Dequiedt F, Svastova E, Hulikova
A, Ohradanova-Repic A, Zatovicova M, Csaderova L, Kopacek J,
Supuran CT, Pastorekova S, et al: Phosphorylation of carbonic
anhydrase IX controls its ability to mediate extracellular
acidification in hypoxic tumors. Cancer Res. 71:7558–7567. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kumar SM, Yu H, Edwards R, Chen L,
Kazianis S, Brafford P, Acs G, Herlyn M and Xu X: Mutant V600E BRAF
increases hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha expression in melanoma.
Cancer Res. 67:3177–3184. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Limame R, Wouters A, Pauwels B, Fransen E,
Peeters M, Lardon F, De Wever O and Pauwels P: Comparative analysis
of dynamic cell viability, migration and invasion assessments by
novel real-time technology and classic endpoint assays. PLoS One.
7:e465362012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chiche J, Brahimi-Horn MC and Pouysségur
J: Tumour hypoxia induces a metabolic shift causing acidosis: A
common feature in cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 14:771–794. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Pastoreková S, Závadová Z, Kostál M,
Babusíková O and Závada J: A novel quasi-viral agent, MaTu, is a
two-component system. Virology. 187:620–626. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Trunzer K, Pavlick AC, Schuchter L,
Gonzalez R, McArthur GA, Hutson TE, Moschos SJ, Flaherty KT, Kim
KB, Weber JS, et al: Pharmacodynamic effects and mechanisms of
resistance to vemurafenib in patients with metastatic melanoma. J
Clin Oncol. 31:1767–1774. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cheng Y, Zhang G and Li G: Targeting MAPK
pathway in melanoma therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 32:567–584.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Irwin DC, McCord JM, Nozik-Grayck E,
Beckly G, Foreman B, Sullivan T, White M, T Crossno J Jr, Bailey D,
Flores SC, et al: A potential role for reactive oxygen species and
the HIF-1alpha-VEGF pathway in hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular
leak. Free Radic Biol Med. 47:55–61. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dewhirst MW: Relationships between cycling
hypoxia, HIF-1, angiogenesis and oxidative stress. Radiat Res.
172:653–665. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liao J, Qian F, Tchabo N,
Mhawech-Fauceglia P, Beck A, Qian Z, Wang X, Huss WJ, Lele SB,
Morrison CD, et al: Ovarian cancer spheroid cells with stem
cell-like properties contribute to tumor generation, metastasis and
chemotherapy resistance through hypoxia-resistant metabolism. PLoS
One. 9:e849412014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Azab AK, Hu J, Quang P, Azab F,
Pitsillides C, Awwad R, Thompson B, Maiso P, Sun JD, Hart CP, et
al: Hypoxia promotes dissemination of multiple myeloma through
acquisition of epithelial to mesenchymal transition-like features.
Blood. 119:5782–5794. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
McDonald PC, Winum JY, Supuran CT and
Dedhar S: Recent developments in targeting carbonic anhydrase IX
for cancer therapeutics. Oncotarget. 3:84–97. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ivanov S, Liao SY, Ivanova A,
Danilkovitch-Miagkova A, Tarasova N, Weirich G, Merrill MJ,
Proescholdt MA, Oldfield EH, Lee J, et al: Expression of
hypoxia-inducible cell-surface transmembrane carbonic anhydrases in
human cancer. Am J Pathol. 158:905–919. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chrastina A, Závada J, Parkkila S, Kaluz
S, Kaluzová M, Rajcáni J, Pastorek J and Pastoreková S:
Biodistribution and pharmacokinetics of 125I-labeled monoclonal
antibody M75 specific for carbonic anhydrase IX, an intrinsic
marker of hypoxia, in nude mice xenografted with human colorectal
carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 105:873–881. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Syrjänen L, Luukkaala T, Leppilampi M,
Kallioinen M, Pastorekova S, Pastorek J, Waheed A, Sly WS, Parkkila
S and Karttunen T: Expression of cancer-related carbonic anhydrases
IX and XII in normal skin and skin neoplasms. APMIS. 122:880–889.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Haass NK, Beaumont KA, Hill DS, Anfosso A,
Mrass P, Munoz MA, Kinjyo I and Weninger W: Real-time cell cycle
imaging during melanoma growth, invasion, and drug response.
Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 27:764–776. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Vultur A, Villanueva J, Krepler C, Rajan
G, Chen Q, Xiao M, Li L, Gimotty PA, Wilson M, Hayden J, et al: MEK
inhibition affects STAT3 signaling and invasion in human melanoma
cell lines. Oncogene. 33:1850–1861. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Sedlakova O, Svastova E, Takacova M,
Kopacek J, Pastorek J and Pastorekova S: Carbonic anhydrase IX, a
hypoxia-induced catalytic component of the pH regulating machinery
in tumors. Front Physiol. 4:4002014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|