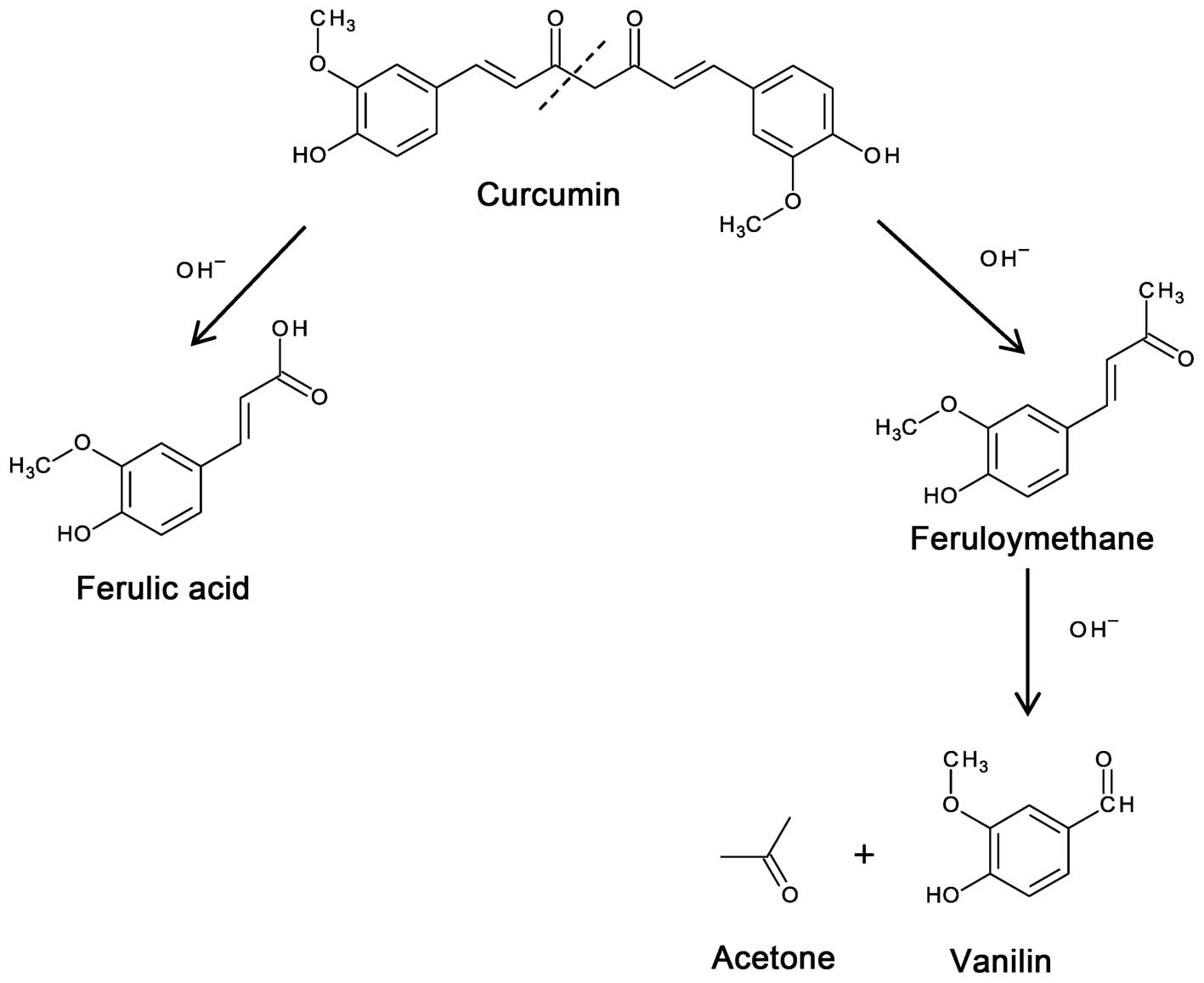
|
1
|
Edwards BK, Noone AM, Mariotto AB, Simard
EP, Boscoe FP, Henley SJ, Jemal A, Cho H, Anderson RN, Kohler BA,
et al: Annual Report to the Nation on the status of cancer,
1975–2010, featuring prevalence of comorbidity and impact on
survival among persons with lung, colorectal, breast, or prostate
cancer. Cancer. 120:1290–1314. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Nemoto RP, Victorino AA, Pessoa GB, da
Cunha LL, da Silva JA, Kanda JL and Matos LL: Oral cancer
preventive campaigns: are we reaching the real target? Braz J
Otorhinolaryngol. 81:44–49. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Toporcov TN, Znaor A, Zhang ZF, Yu GP,
Winn DM, Wei Q, Vilensky M, Vaughan T, Thomson P, Talamini R, et
al: Risk factors for head and neck cancer in young adults: A pooled
analysis in the INHANCE consortium. Int J Epidemiol. 44:169–185.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Walsh T, Liu JL, Brocklehurst P, Glenny
AM, Lingen M, Kerr AR, Ogden G, Warnakulasuriya S and Scully C:
Clinical assessment to screen for the detection of oral cavity
cancer and potentially malignant disorders in apparently healthy
adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 11:CD0101732013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chorostowska-Wynimko J, Swiercz R,
Skrzypczak-Jankun E, Wojtowicz A, Selman SH and Jankun J: A novel
form of the plasminogen activator inhibitor created by cysteine
mutations extends its half-life: Relevance to cancer and
angiogenesis. Mol Cancer Ther. 2:19–28. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jankun J and Skrzypczak-Jankun E: Yin and
yang of the plasminogen activator inhibitor. Pol Arch Med Wewn.
119:410–417. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lein M, Jung K, Ortel B, Stephan C,
Rothaug W, Juchem R, Johannsen M, Deger S, Schnorr D, Loening S, et
al: The new synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor (Roche
28-2653) reduces tumor growth and prolongs survival in a prostate
cancer standard rat model. Oncogene. 21:2089–2096. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Al-Horani RA: Serpin regulation of
fibrinolytic system: Implications for therapeutic applications in
cardiovascular diseases. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem.
12:91–125. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Iishi H, Tatsuta M, Baba M, Yano H, Uehara
H and Nakaizumi A: Suppression by amiloride of bombesin-enhanced
peritoneal metastasis of intestinal adenocarcinomas induced by
azoxy-methane. Int J Cancer. 63:716–719. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wyganowska-Świątkowska M, Surdacka A,
Skrzypczak-Jankun E and Jankun J: The plasminogen activation system
in periodontal tissue (Review). Int J Mol Med. 33:763–768.
2014.
|
|
11
|
Jankun J and Skrzypczak-Jankun E:
Plasminogen activator inhibitor with very long half-life (VLHL
PAI-1) can reduce bleeding in PAI-1-deficient patients. Cardiovasc
Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 13:144–150. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fortenberry YM: Plasminogen activator
inhibitor-1 inhibitors: a patent review (2006-present). Expert Opin
Ther Pat. 23:801–815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ghosh AK and Vaughan DE: PAI-1 in tissue
fibrosis. J Cell Physiol. 227:493–507. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lindberg P, Larsson A and Nielsen BS:
Expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, urokinase receptor
and laminin gamma-2 chain is an early coordinated event in
incipient oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer.
118:2948–2956. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stewart CE and Sayers I: Urokinase
receptor orchestrates the plasminogen system in airway epithelial
cell function. Lung. 191:215–225. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tang L and Han X: The urokinase
plasminogen activator system in breast cancer invasion and
metastasis. Biomed Pharmacother. 67:179–182. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Gershtein ES and Kushlinskii NE: Clinical
prospects of tumor-associated proteases and their tissue inhibitors
investigation in oncologic patient. Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk.
16–27. 2013.(In Russian).
|
|
18
|
Weng CJ, Lin CW, Chung TT, Tsai CM, Chen
MK and Yang SF: Impact of uPA system gene polymorphisms on the
susceptibility of environmental factors to carcinogenesis and the
development of clinicopathology of oral cancer. Ann Surg Oncol.
18:805–812. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Duong HS, Le AD, Zhang Q and Messadi DV: A
novel 3-dimensional culture system as an in vitro model for
studying oral cancer cell invasion. Int J Exp Pathol. 86:365–374.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yoshizawa K, Nozaki S, Kitahara H, Kato K,
Noguchi N, Kawashiri S and Yamamoto E: Expression of urokinase-type
plasminogen activator/urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor
and maspin in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Association with mode
of invasion and clinicopathological factors. Oncol Rep.
26:1555–1560. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lescaille G, Menashi S, Cavelier-Balloy B,
Khayati F, Quemener C, Podgorniak MP, Naïmi B, Calvo F, Lebbe C and
Mourah S: EMMPRIN/CD147 up-regulates urokinase-type plasminogen
activator: Implications in oral tumor progression. BMC Cancer.
12:1152012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang Z, Pan J, Li L, Wang Z, Xiao W and
Li N: Survey of risk factors contributed to lymphatic metastasis in
patients with oral tongue cancer by immunohistochemistry. J Oral
Pathol Med. 40:127–134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Curino A, Patel V, Nielsen BS, Iskander
AJ, Ensley JF, Yoo GH, Holsinger FC, Myers JN, El-Nagaar A, Kellman
RM, et al: Detection of plasminogen activators in oral cancer by
laser capture microdissection combined with zymography. Oral Oncol.
40:1026–1032. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gaarenstroom KN, Kenter GG, Bonfrer JM,
Korse CM, Van de Vijver MJ, Fleuren GJ and Trimbos JB: Can initial
serum cyfra 21-1, SCC antigen, and TPA levels in squamous cell
cervical cancer predict lymph node metastases or prognosis? Gynecol
Oncol. 77:164–170. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jankun J, Maher VM and McCormick JJ:
Malignant transformation of human fibroblasts correlates with
increased activity of receptor-bound plasminogen activator. Cancer
Res. 51:1221–1226. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jankun J, Merrick HW and Goldblatt PJ:
Expression and localization of elements of the plasminogen
activation system in benign breast disease and breast cancers. J
Cell Biochem. 53:135–144. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zubac DP, Wentzel-Larsen T, Seidal T and
Bostad L: Type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) in clear
cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC) and its impact on angiogenesis,
progression and patient survival after radical nephrectomy. BMC
Urol. 10:202010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Harbeck N, Schmitt M, Paepke S, Allgayer H
and Kates RE: Tumor-associated proteolytic factors uPA and PAI-1:
Critical appraisal of their clinical relevance in breast cancer and
their integration into decision-support algorithms. Crit Rev Clin
Lab Sci. 44:179–201. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schrohl AS, Holten-Andersen MN, Peters HA,
Look MP, Meijervan Gelder ME, Klijn JG, Brünner N and Foekens JA:
Tumor tissue levels of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 as a
prognostic marker in primary breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
10:2289–2298. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Borstnar S, Vrhovec I, Svetic B and Cufer
T: Prognostic value of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator,
and its inhibitors and receptor in breast cancer patients. Clin
Breast Cancer. 3:138–146. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Grøndahl-Hansen J, Christensen IJ, Briand
P, Pappot H, Mouridsen HT, Blichert-Toft M, Danø K and Brünner N:
Plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 in cytosolic tumor extracts
predicts prognosis in low-risk breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer
Res. 3:233–239. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Duggan C, Maguire T, McDermott E,
O’Higgins N, Fennelly JJ and Duffy MJ: Urokinase plasminogen
activator and urokinase plasminogen activator receptor in breast
cancer. Int J Cancer. 61:597–600. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
McMahon B and Kwaan HC: The plasminogen
activator system and cancer. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb.
36:184–194. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
McMahon GA, Petitclerc E, Stefansson S,
Smith E, Wong MK, Westrick RJ, Ginsburg D, Brooks PC and Lawrence
DA: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 regulates tumor growth and
angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 276:33964–33968. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Swiercz R, Keck RW, Skrzypczak-Jankun E,
Selman SH and Jankun J: Recombinant PAI-1 inhibits angiogenesis and
reduces size of LNCaP prostate cancer xenografts in SCID mice.
Oncol Rep. 8:463–470. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kwaan HC, Mazar AP and McMahon BJ: The
apparent uPA/ PAI-1 paradox in cancer: More than meets the eye.
Semin Thromb Hemost. 39:382–391. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Okumura Y, Kamikubo Y, Curriden SA, Wang
J, Kiwada T, Futaki S, Kitagawa K and Loskutoff DJ: Kinetic
analysis of the interaction between vitronectin and the urokinase
receptor. J Biol Chem. 277:9395–9404. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Czekay RP, Aertgeerts K, Curriden SA and
Loskutoff DJ: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 detaches cells from
extracellular matrices by inactivating integrins. J Cell Biol.
160:781–791. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Balsara RD and Ploplis VA: Plasminogen
activator inhibitor-1: The double-edged sword in apoptosis. Thromb
Haemost. 100:1029–1036. 2008.
|
|
40
|
Devy L, Blacher S, Grignet-Debrus C, Bajou
K, Masson V, Gerard RD, Gils A, Carmeliet G, Carmeliet P, Declerck
PJ, et al: The pro- or antiangiogenic effect of plasminogen
activator inhibitor 1 is dose dependent. FASEB J. 16:147–154. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lambert V, Munaut C, Carmeliet P, Gerard
RD, Declerck PJ, Gils A, Claes C, Foidart JM, Noël A and Rakic JM:
Dose-dependent modulation of choroidal neovascularization by
plasminogen activator inhibitor type I: Implications for clinical
trials. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 44:2791–2797. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bajou K, Masson V, Gerard RD, Schmitt PM,
Albert V, Praus M, Lund LR, Frandsen TL, Brunner N, Dano K, et al:
The plasminogen activator inhibitor PAI-1 controls in vivo tumor
vascularization by interaction with proteases, not vitronectin.
Implications for antiangiogenic strategies. J Cell Biol.
152:777–784. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nishioka N, Matsuoka T, Yashiro M,
Hirakawa K, Olden K and Roberts JD: Plasminogen activator inhibitor
1 RNAi suppresses gastric cancer metastasis in vivo. Cancer Sci.
103:228–232. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Stefansson S, McMahon GA, Petitclerc E and
Lawrence DA: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in tumor growth,
angiogenesis and vascular remodeling. Curr Pharm Des. 9:1545–1564.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zheng D, Chen H, Davids J, Bryant M and
Lucas A: Serpins for diagnosis and therapy in cancer. Cardiovasc
Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 13:123–132. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kohler HP and Grant PJ:
Plasminogen-activator inhibitor type 1 and coronary artery disease.
N Engl J Med. 342:1792–1801. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Vairaktaris E, Yapijakis C, Serefoglou Z,
Vylliotis A, Ries J, Nkenke E, Wiltfang J, Derka S, Vassiliou S,
Springer I, et al: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 polymorphism
is associated with increased risk for oral cancer. Oral Oncol.
42:888–892. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Grunnet M, Christensen IJ, Lassen U,
Jensen LH, Lydolph M, Lund IK, Thurison T, Høyer-Hansen G and
Mau-Sørensen M: Prognostic significance of circulating intact and
cleaved forms of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor in
inoperable chemotherapy treated cholangiocarcinoma patients. Clin
Biochem. 47:599–604. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Illemann M, Laerum OD, Hasselby JP,
Thurison T, Høyer-Hansen G, Nielsen HJ and Christensen IJ; Danish
Study Group on Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer. Urokinase-type
plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) on tumor-associated
macrophages is a marker of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer.
Cancer Med. 3:855–864. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Thurison T, Christensen IJ, Lund IK,
Nielsen HJ and Hoyer-Hansen G: Circulating intact and cleaved forms
of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor: biological
variation, reference intervals and clinical useful cut-points. Clin
Chim Acta. 439:84–90. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Nozaki S, Endo Y, Nakahara H, Yoshizawa K,
Hashiba Y, Kawashiri S, Tanaka A, Nakagawa K, Matsuoka Y, Kogo M,
et al: Inhibition of invasion and metastasis in oral cancer by
targeting urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor. Oral
Oncol. 41:971–977. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sager R, Sheng S, Pemberton P and Hendrix
MJ: Maspin. A tumor suppressing serpin. Adv Exp Med Biol.
425:77–88. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sager R, Sheng S, Pemberton P and Hendrix
MJ: Maspin: A tumor suppressing serpin. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol.
213:51–64. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chen EI and Yates JR III: Maspin and tumor
metastasis. IUBMB Life. 58:25–29. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Teoh SS, Vieusseux J, Prakash M, Berkowicz
S, Luu J, Bird CH, Law RH, Rosado C, Price JT, Whisstock JC, et al:
Maspin is not required for embryonic development or tumour
suppression. Nat Commun. 5:31642014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Nozaki S, Endo Y, Kawashiri S, Nakagawa K,
Yamamoto E, Yonemura Y and Sasaki T: Immunohistochemical
localization of a urokinase-type plasminogen activator system in
squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity: Association with mode
of invasion and lymph node metastasis. Oral Oncol. 34:58–62. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Shi Z, Liu Y, Johnson JJ and Stack MS:
Urinary-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) modulates oral
cancer cell behavior with alteration in p130cas. Mol Cell Biochem.
357:151–161. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Henneke I, Greschus S, Savai R, Korfei M,
Markart P, Mahavadi P, Schermuly RT, Wygrecka M, Stürzebecher J,
Seeger W, et al: Inhibition of urokinase activity reduces primary
tumor growth and metastasis formation in a murine lung carcinoma
model. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 181:611–619. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Schweinitz A, Steinmetzer T, Banke IJ,
Arlt MJ, Stürzebecher A, Schuster O, Geissler A, Giersiefen H,
Zeslawska E, Jacob U, et al: Design of novel and selective
inhibitors of urokinase-type plasminogen activator with improved
pharmacokinetic properties for use as antimetastatic agents. J Biol
Chem. 279:33613–33622. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Jankun J and Skrzypczak-Jankun E:
Molecular basis of specific inhibition of urokinase plasminogen
activator by amiloride. Cancer Biochem Biophys. 17:109–123.
1999.
|
|
61
|
Jankun J and Skrzypczak-Jankun E: Binding
site of amiloride to urokinase plasminogen activator depends on
species. Int J Mol Med. 8:365–371. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Swiercz R, Skrzypczak-Jankun E, Merrell
MM, Selman SH and Jankun J: Angiostatic activity of synthetic
inhibitors of urokinase type plasminogen activator. Oncol Rep.
6:523–526. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wendt MD, Rockway TW, Geyer A, McClellan
W, Weitzberg M, Zhao X, Mantei R, Nienaber VL, Stewart K,
Klinghofer V, et al: Identification of novel binding interactions
in the development of potent, selective 2-naphthamidine inhibitors
of urokinase. Synthesis, structural analysis, and SAR of N-phenyl
amide 6-substitution. J Med Chem. 47:303–324. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Jankun J, Keck RW and Selman SH:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate prevents tumor cell implantation/growth
in an experimental rat bladder tumor model. Int J Oncol.
44:147–152. 2014.
|
|
65
|
Jankun J, Selman SH, Swiercz R and
Skrzypczak-Jankun E: Why drinking green tea could prevent cancer.
Nature. 387:5611997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Jankun J, Yang J, Zheng H, Han FQ,
Al-Senaidy A and Skrzypczak-Jankun E: Remarkable extension of PAI-1
half-life surprisingly brings no changes to its structure. Int J
Mol Med. 29:61–64. 2012.
|
|
67
|
Li X, Zheng T, Sang S and Lv L: Quercetin
inhibits advanced glycation end product formation by trapping
methylglyoxal and glyoxal. J Agric Food Chem. 62:12152–12158. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Liu P, Zou D, Yi L, Chen M, Gao Y, Zhou R,
Zhang Q, Zhou Y, Zhu J, Chen K, et al: Quercetin ameliorates
hypobaric hypoxia-induced memory impairment through mitochondrial
and neuron function adaptation via the PGC-1α pathway. Restor
Neurol Neurosci. 33:143–157. 2015.
|
|
69
|
Lai WW, Hsu SC, Chueh FS, Chen YY, Yang
JS, Lin JP, Lien JC, Tsai CH and Chung JG: Quercetin inhibits
migration and invasion of SAS human oral cancer cells through
inhibition of NF-κB and matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 signaling
pathways. Anticancer Res. 33:1941–1950. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Manolova Y, Deneva V, Antonov L, Drakalska
E, Momekova D and Lambov N: The effect of the water on the curcumin
tautomerism: A quantitative approach. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol
Spectrosc. 132:815–820. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Strimpakos AS and Sharma RA: Curcumin:
preventive and therapeutic properties in laboratory studies and
clinical trials. Antioxid Redox Signal. 10:511–545. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Hatcher H, Planalp R, Cho J, Torti FM and
Torti SV: Curcumin: From ancient medicine to current clinical
trials. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:1631–1652. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhen L, Fan D, Yi X, Cao X, Chen D and
Wang L: Curcumin inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma
proliferation and invasion via EGFR signaling pathways. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 7:6438–6446. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Li MJ, Yin YC, Wang J and Jiang YF: Green
tea compounds in breast cancer prevention and treatment. World J
Clin Oncol. 5:520–528. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Yang CS, Chen G and Wu Q: Recent
scientific studies of a traditional chinese medicine, tea, on
prevention of chronic diseases. J Tradit Complement Med. 4:17–23.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Yiannakopoulou EC: Green tea catechins:
Proposed mechanisms of action in breast cancer focusing on the
interplay between survival and apoptosis. Anticancer Agents Med
Chem. 14:290–295. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Ho YC, Yang SF, Peng CY, Chou MY and Chang
YC: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits the invasion of human oral
cancer cells and decreases the productions of matrix
metalloproteinases and urokinase-plasminogen activator. J Oral
Pathol Med. 36:588–593. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Miocinovic R, McCabe NP, Keck RW, Jankun
J, Hampton JA and Selman SH: In vivo and in vitro effect of
baicalein on human prostate cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 26:241–246.
2005.
|
|
79
|
Yan X, Rui X and Zhang K: Baicalein
inhibits the invasion of gastric cancer cells by suppressing the
activity of the p38 signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 33:737–743.
2015.
|
|
80
|
Zheng YH, Yin LH, Grahn TH, Ye AF, Zhao YR
and Zhang QY: Anticancer effects of baicalein on hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Phytother Res. 28:1342–1348. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Shukla S and Gupta S: Apigenin: A
promising molecule for cancer prevention. Pharm Res. 27:962–978.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Yang SF, Yang WE, Kuo WH, Chang HR, Chu SC
and Hsieh YS: Antimetastatic potentials of flavones on oral cancer
cell via an inhibition of matrix-degrading proteases. Arch Oral
Biol. 53:287–294. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Brown NJ: Therapeutic potential of
plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 inhibitors. Ther Adv Cardiovasc
Dis. 4:315–324. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Rouch A, Vanucci-Bacqué C, Bedos-Belval F
and Baltas M: Small molecules inhibitors of plasminogen activator
inhibitor-1: an overview. Eur J Med Chem. 92:619–636. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Gorlatova NV, Cale JM, Elokdah H, Li D,
Fan K, Warnock M, Crandall DL and Lawrence DA: Mechanism of
inactivation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 by a small
molecule inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 282:9288–9296. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Jankun J, Al-Senaidy A and
Skrzypczak-Jankun E: Can inactivators of plasminogen activator
inhibitor alleviate the burden of obesity and diabetes? (Review).
Int J Mol Med. 29:3–11. 2012.
|
|
87
|
Naessens D, Gils A, Compernolle G and
Declerck PJ: Elucidation of a novel epitope of a substrate-inducing
monoclonal antibody against the serpin PAI-1. J Thromb Haemost.
1:1028–1033. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Verhamme I, Kvassman JO, Day D, Debrock S,
Vleugels N, Declerck PJ and Shore JD: Accelerated conversion of
human plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 to its latent form by
antibody binding. J Biol Chem. 274:17511–17517. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Egelund R, Einholm AP, Pedersen KE,
Nielsen RW, Christensen A, Deinum J and Andreasen PA: A regulatory
hydrophobic area in the flexible joint region of plasminogen
activator inhibitor-1, defined with fluorescent
activity-neutralizing ligands. Ligand-induced serpin
polymerization. J Biol Chem. 276:13077–13086. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Crandall DL, Elokdah H, Di L, Hennan JK,
Gorlatova NV and Lawrence DA: Characterization and comparative
evaluation of a structurally unique PAI-1 inhibitor exhibiting oral
in-vivo efficacy. J Thromb Haemost. 2:1422–1428. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Gardell SJ, Krueger JA, Antrilli TA,
Elokdah H, Mayer S, Orcutt SJ, Crandall DL and Vlasuk GP:
Neutralization of plasminogen activator inhibitor I (PAI-1) by the
synthetic antagonist PAI-749 via a dual mechanism of action. Mol
Pharmacol. 72:897–906. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Jankun J, Skotnicka M, Łysiak-Szydłowska
W, Al-Senaidy A and Skrzypczak-Jankun E: Diverse inhibition of
plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 by theaflavins of black tea.
Int J Mol Med. 27:525–529. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhang YF, Xu Q, Lu J, Wang P, Zhang HW,
Zhou L, Ma XQ and Zhou YH: Tea consumption and the incidence of
cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective
observational studies. Eur J Cancer Prev. Nov 3–2014.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Lee MJ, Lambert JD, Prabhu S, Meng X, Lu
H, Maliakal P, Ho CT and Yang CS: Delivery of tea polyphenols to
the oral cavity by green tea leaves and black tea extract. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 13:132–137. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Yang CS, Maliakal P and Meng X: Inhibition
of carcinogenesis by tea. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 42:25–54.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Ghosh S, Johnson JJ, Sen R, Mukhopadhyay
S, Liu Y, Zhang F, Wei Y, Chapman HA and Stack MS: Functional
relevance of urinary-type plasminogen activator
receptor-alpha3beta1 integrin association in proteinase regulatory
pathways. J Biol Chem. 281:13021–13029. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Lee EJ, Whang JH, Jeon NK and Kim J: The
epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839
(Iressa) suppresses proliferation and invasion of human oral
squamous carcinoma cells via p53 independent and MMP, uPAR
dependent mechanism. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1095:113–128. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Liang X, Yang X, Tang Y, Zhou H, Liu X,
Xiao L, Gao J and Mao Z: RNAi-mediated downregulation of urokinase
plasminogen activator receptor inhibits proliferation, adhesion,
migration and invasion in oral cancer cells. Oral Oncol.
44:1172–1180. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Pasini FS, Brentani MM, Kowalski LP and
Federico MH: Transforming growth factor beta1, urokinase-type
plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 mRNA
expression in head and neck squamous carcinoma and normal adjacent
mucosa. Head Neck. 23:725–732. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Vairaktaris E, Serefoglou Z, Avgoustidis
D, Yapijakis C, Critselis E, Vylliotis A, Spyridonidou S, Derka S,
Vassiliou S, Nkenke E, et al: Gene polymorphisms related to
angiogenesis, inflammation and thrombosis that influence risk for
oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 45:247–253. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Hercberg S, Kesse-Guyot E, Druesne-Pecollo
N, Touvier M, Favier A, Latino-Martel P, Briançon S and Galan P:
Incidence of cancers, ischemic cardiovascular diseases and
mortality during 5-year follow-up after stopping antioxidant
vitamins and minerals supplements: a postintervention follow-up in
the SU.VI.MAX Study. Int J Cancer. 127:1875–1881. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Press OA, Zhang W, Gordon MA, Yang D,
Lurje G, Iqbal S, El-Khoueiry A and Lenz HJ: Gender-related
survival differences associated with EGFR polymorphisms in
metastatic colon cancer. Cancer Res. 68:3037–3042. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Nainani P, Paliwal A, Nagpal N and Agrawal
M: Sex hormones in gender-specific risk for head and neck cancer: A
review. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 4(Suppl 1): S1–S4. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Wang YJ, Pan MH, Cheng AL, Lin LI, Ho YS,
Hsieh CY and Lin JK: Stability of curcumin in buffer solutions and
characterization of its degradation products. J Pharm Biomed Anal.
15:1867–1876. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Stout TJ, Graham H, Buckley DI and
Matthews DJ: Structures of active and latent PAI-1: A possible
stabilizing role for chloride ions. Biochemistry. 39:8460–8469.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Zeslawska E, Jacob U, Schweinitz A, Coombs
G, Bode W and Madison E: Crystals of urokinase type plasminogen
activator complexes reveal the binding mode of peptidomimetic
inhibitors. J Mol Biol. 328:109–118. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Li SH, Reinke AA, Sanders KL, Emal CD,
Whisstock JC, Stuckey JA and Lawrence DA: Mechanistic
characterization and crystal structure of a small molecule
inactivator bound to plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 110:E4941–E4949. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Shen L and Ji HF: Contribution of
degradation products to the anticancer activity of curcumin. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:7108author reply 7108–7109. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|