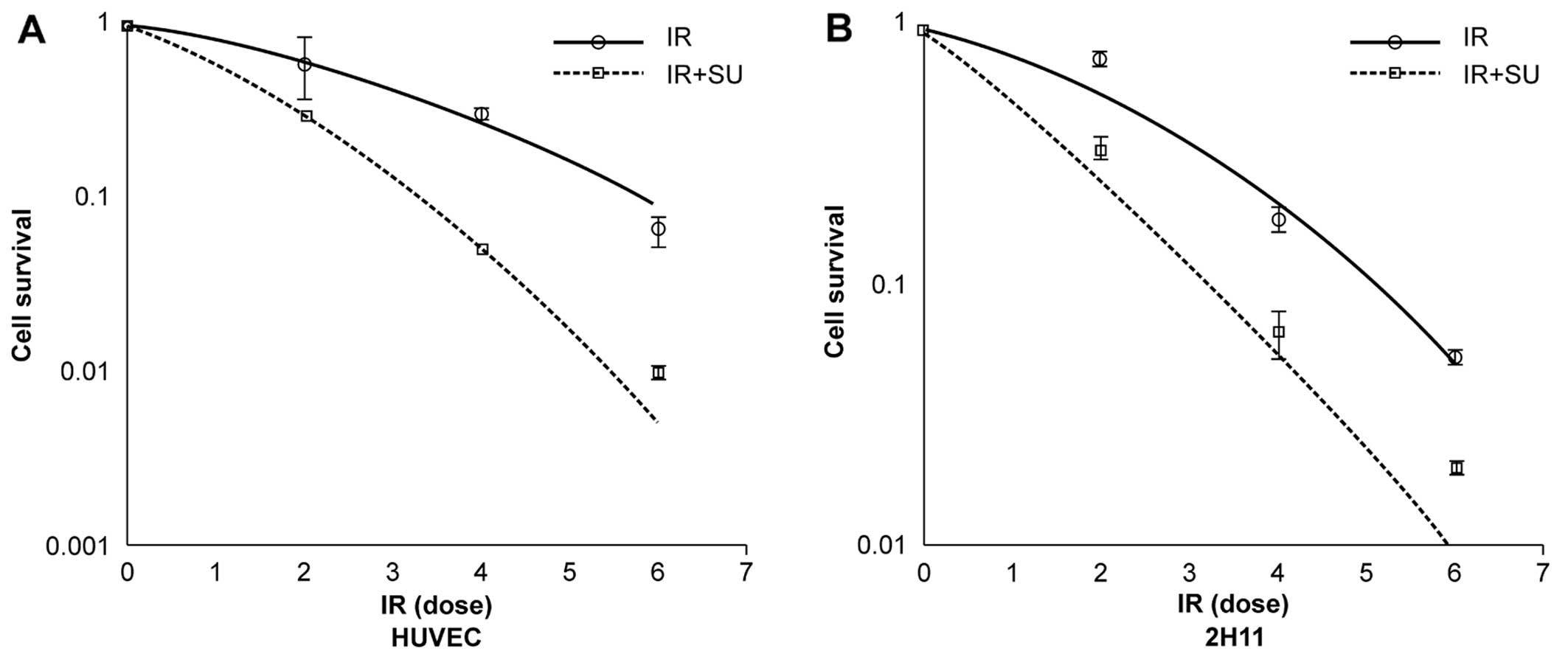
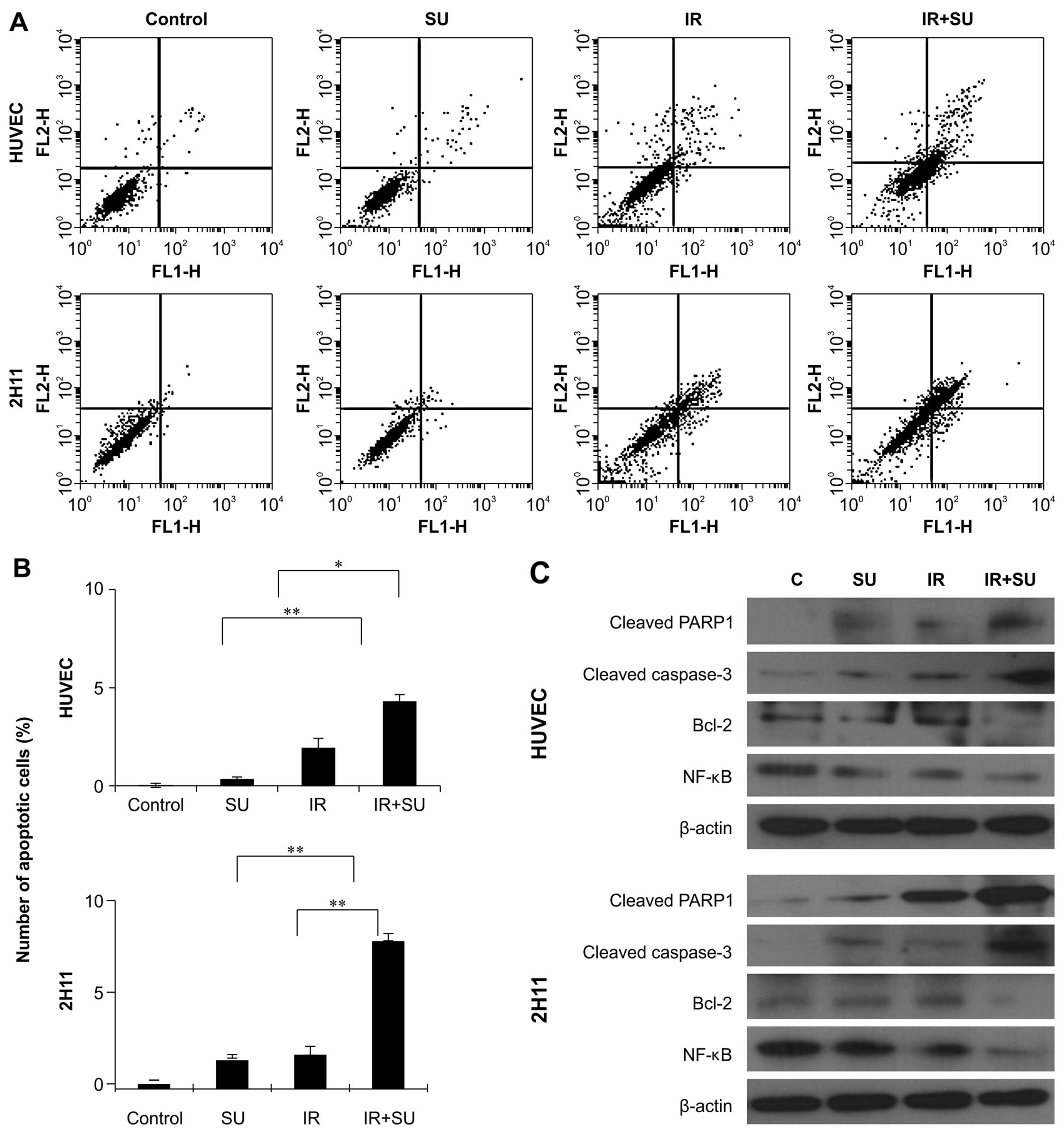
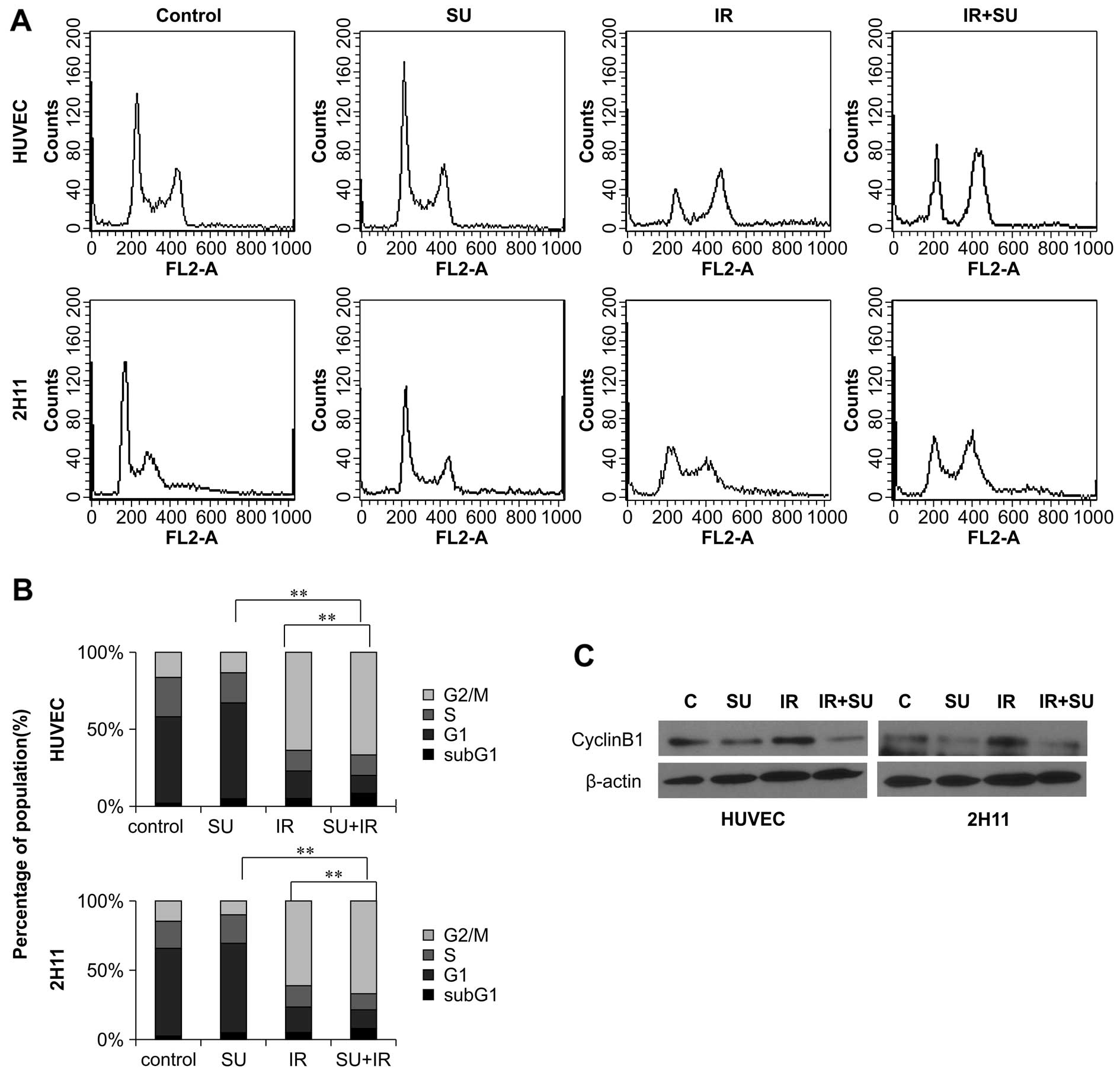
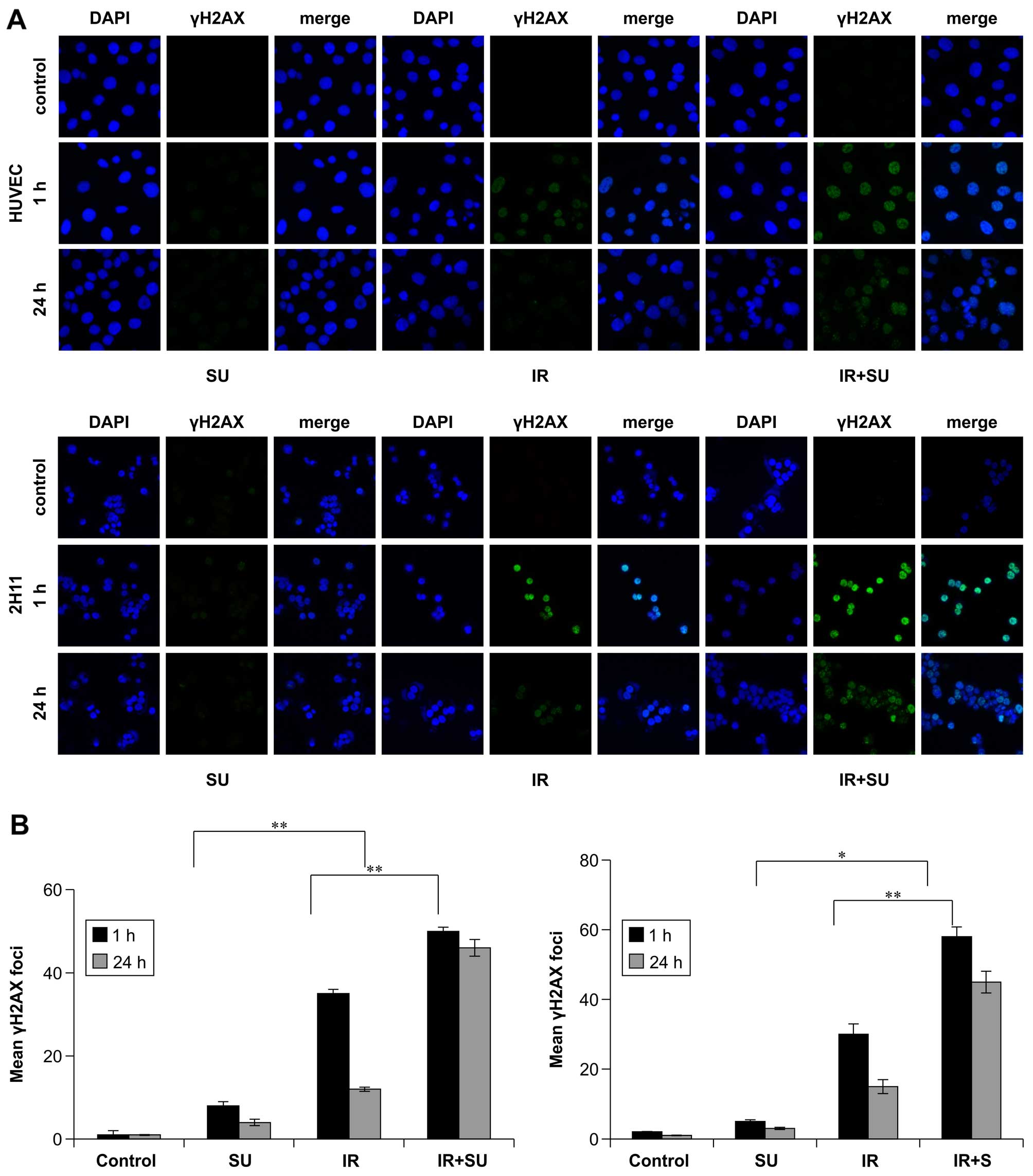
|
1
|
Jubb AM, Pham TQ, Hanby AM, Frantz GD,
Peale FV, Wu TD, Koeppen HW and Hillan KJ: Expression of vascular
endothelial growth factor, hypoxia inducible factor 1α, and
carbonic anhydrase IX in human tumours. J Clin Pathol. 57:504–512.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Garcia-Barros M, Paris F, Cordon-Cardo C,
Lyden D, Rafii S, Haimovitz-Friedman A, Fuks Z and Kolesnick R:
Tumor response to radiotherapy regulated by endothelial cell
apoptosis. Science. 300:1155–1159. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huber PE, Bischof M, Jenne J, Heiland S,
Peschke P, Saffrich R, Gröne HJ, Debus J, Lipson KE and Abdollahi
A: Trimodal cancer treatment: Beneficial effects of combined
antiangiogenesis, radiation, and chemotherapy. Cancer Res.
65:3643–3655. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Poggi MM, Coleman CN and Mitchell JB:
Sensitizers and protectors of radiation and chemotherapy. Curr
Probl Cancer. 25:334–411. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chan LW and Camphausen K: Angiogenic tumor
markers, anti-angiogenic agents and radiation therapy. Expert Rev
Anticancer Ther. 3:357–366. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wachsberger P, Burd R and Dicker AP: Tumor
response to ionizing radiation combined with antiangiogenesis or
vascular targeting agents: Exploring mechanisms of interaction.
Clin Cancer Res. 9:1957–1971. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gorski DH, Beckett MA, Jaskowiak NT,
Calvin DP, Mauceri HJ, Salloum RM, Seetharam S, Koons A, Hari DM,
Kufe DW, et al: Blockage of the vascular endothelial growth factor
stress response increases the antitumor effects of ionizing
radiation. Cancer Res. 59:3374–3378. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee CG, Heijn M, di Tomaso E,
Griffon-Etienne G, Ancukiewicz M, Koike C, Park KR, Ferrara N, Jain
RK, Suit HD, et al: Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor
treatment augments tumor radiation response under normoxic or
hypoxic conditions. Cancer Res. 60:5565–5570. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Geng L, Donnelly E, McMahon G, Lin PC,
Sierra-Rivera E, Oshinka H and Hallahan DE: Inhibition of vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor signaling leads to reversal of
tumor resistance to radiotherapy. Cancer Res. 61:2413–2419.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fong TA, Shawver LK, Sun L, Tang C, App H,
Powell TJ, Kim YH, Schreck R, Wang X, Risau W, et al: SU5416 is a
potent and selective inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth
factor receptor (Flk-1/KDR) that inhibits tyrosine kinase
catalysis, tumor vascularization, and growth of multiple tumor
types. Cancer Res. 59:99–106. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mendel DB, Laird AD, Smolich BD, Blake RA,
Liang C, Hannah AL, Shaheen RM, Ellis LM, Weitman S, Shawver LK, et
al: Development of SU5416, a selective small molecule inhibitor of
VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase activity, as an anti-angiogenesis
agent. Anticancer Drug Des. 15:29–41. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Peterson AC, Swiger S, Stadler WM, Medved
M, Karczmar G and Gajewski TF: Phase II study of the Flk-1 tyrosine
kinase inhibitor SU5416 in advanced melanoma. Clin Cancer Res.
10:4048–4054. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bäckman U, Svensson A and Christofferson
R: Importance of vascular endothelial growth factor A in the
progression of experimental neuroblastoma. Angiogenesis. 5:267–274.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Timke C, Zieher H, Roth A, Hauser K,
Lipson KE, Weber KJ, Debus J, Abdollahi A and Huber PE: Combination
of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor/platelet-derived
growth factor receptor inhibition markedly improves radiation tumor
therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2210–2219. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Abdollahi A, Lipson KE, Han X, Krempien R,
Trinh T, Weber KJ, Hahnfeldt P, Hlatky L, Debus J, Howlett AR, et
al: SU5416 and SU6668 attenuate the angiogenic effects of
radiation-induced tumor cell growth factor production and amplify
the direct anti-endothelial action of radiation in vitro. Cancer
Res. 63:3755–3763. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wachsberger PR, Burd R, Marero N,
Daskalakis C, Ryan A, McCue P and Dicker AP: Effect of the tumor
vascular-damaging agent, ZD6126, on the radioresponse of U87
glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 11:835–842. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ning S, Laird D, Cherrington JM and Knox
SJ: The antiangiogenic agents SU5416 and SU6668 increase the
antitumor effects of fractionated irradiation. Radiat Res.
157:45–51. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Griffin RJ, Williams BW, Wild R,
Cherrington JM, Park H and Song CW: Simultaneous inhibition of the
receptor kinase activity of vascular endothelial, fibroblast, and
platelet-derived growth factors suppresses tumor growth and
enhances tumor radiation response. Cancer Res. 62:1702–1706.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lu B, Geng L, Musiek A, Tan J, Cao C,
Donnelly E, McMahon G, Choy H and Hallahan DE: Broad spectrum
receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, SU6668, sensitizes radiation
via targeting survival pathway of vascular endothelium. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 58:844–850. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zips D, Eicheler W, Geyer P, Hessel F,
Dörfler A, Thames HD, Haberey M and Baumann M: Enhanced
susceptibility of irradiated tumor vessels to vascular endothelial
growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition. Cancer Res.
65:5374–5379. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Edwards E, Geng L, Tan J, Onishko H,
Donnelly E and Hallahan DE: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt
signaling in the response of vascular endothelium to ionizing
radiation. Cancer Res. 62:4671–4677. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schueneman AJ, Himmelfarb E, Geng L, Tan
J, Donnelly E, Mendel D, McMahon G and Hallahan DE: SU11248
maintenance therapy prevents tumor regrowth after fractionated
irradiation of murine tumor models. Cancer Res. 63:4009–4016.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Krystal GW, Honsawek S, Kiewlich D, Liang
C, Vasile S, Sun L, McMahon G and Lipson KE: Indolinone tyrosine
kinase inhibitors block Kit activation and growth of small cell
lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 61:3660–3668. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kumar P, Benedict R, Urzua F, Fischbach C,
Mooney D and Polverini P: Combination treatment significantly
enhances the efficacy of antitumor therapy by preferentially
targeting angiogenesis. Lab Invest. 85:756–767. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lea DE: Actions of Radiations on Living
Cells. 2nd edition. Cambridge University Press; New York, NY:
1955
|
|
26
|
Tang D, Wu D, Hirao A, Lahti JM, Liu L,
Mazza B, Kidd VJ, Mak TW and Ingram AJ: ERK activation mediates
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis after DNA damage independently of
p53. J Biol Chem. 277:12710–12717. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang J, Yu Y and Duerksen-Hughes PJ:
Protein kinases and their involvement in the cellular responses to
genotoxic stress. Mutat Res. 543:31–58. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kabakov AE, Makarova YM and Malyutina YV:
Radio-sensitization of human vascular endothelial cells through
HSP90 inhibition with 17-N-allilamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin. Int
J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 71:858–865. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tan J and Hallahan DE: Growth
factor-independent activation of protein kinase B contributes to
the inherent resistance of vascular endothelium to
radiation-induced apoptotic response. Cancer Res. 63:7663–7667.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cherrington JM, Strawn LM and Shawver LK:
New paradigms for the treatment of cancer: The role of
anti-angiogenesis agents. Adv Cancer Res. 79:1–38. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fontanini G, De Laurentiis M, Vignati S,
Chinè S, Lucchi M, Silvestri V, Mussi A, De Placido S, Tortora G,
Bianco AR, et al: Evaluation of epidermal growth factor-related
growth factors and receptors and of neoangiogenesis in completely
resected stage I–IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer: Amphiregulin and
microvessel count are independent prognostic indicators of
survival. Clin Cancer Res. 4:241–249. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kawaguchi T, Yamamoto S, Kudoh S, Goto K,
Wakasa K and Sakurai M: Tumor angiogenesis as a major prognostic
factor in stage I lung adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Res.
17:3743–3746. 1997.
|
|
33
|
Toi M, Hoshina S, Takayanagi T and
Tominaga T: Association of vascular endothelial growth factor
expression with tumor angiogenesis and with early relapse in
primary breast cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res. 85:1045–1049. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gasparini G and Harris AL: Clinical
importance of the determination of tumor angiogenesis in breast
carcinoma: Much more than a new prognostic tool. J Clin Oncol.
13:765–782. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dickinson AJ, Fox SB, Persad RA, Hollyer
J, Sibley GN and Harris AL: Quantification of angiogenesis as an
independent predictor of prognosis in invasive bladder carcinomas.
Br J Urol. 74:762–766. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Takahashi Y, Kitadai Y, Bucana CD, Cleary
KR and Ellis LM: Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor
and its receptor, KDR, correlates with vascularity, metastasis, and
proliferation of human colon cancer. Cancer Res. 55:3964–3968.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Williams JK, Carlson GW, Cohen C, Derose
PB, Hunter S and Jurkiewicz MJ: Tumor angiogenesis as a prognostic
factor in oral cavity tumors. Am J Surg. 168:373–380. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ferrara N: Molecular and biological
properties of vascular endothelial growth factor. J Mol Med Berl.
77:527–543. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Boehm-Viswanathan T: Is angiogenesis
inhibition the Holy Grail of cancer therapy? Curr Opin Oncol.
12:89–94. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Brieger J, Kattwinkel J, Berres M,
Gosepath J and Mann WJ: Impact of vascular endothelial growth
factor release on radiation resistance. Oncol Rep. 18:1597–1601.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jain RK, Duda DG, Clark JW and Loeffler
JS: Lessons from phase III clinical trials on anti-VEGF therapy for
cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 3:24–40. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chapman JD and Gillespie CJ:
Radiation-induced events and their time-scale in mammalian cells.
Adv Radiat Biol. 9:143–198. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Rogakou EP, Pilch DR, Orr AH, Ivanova VS
and Bonner WM: DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX
phosphorylation on serine 139. J Biol Chem. 273:5858–5868. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bonner WM, Redon CE, Dickey JS, Nakamura
AJ, Sedelnikova OA, Solier S and Pommier Y: GammaH2AX and cancer.
Nat Rev Cancer. 8:957–967. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bourton EC, Plowman PN, Smith D, Arlett CF
and Parris CN: Prolonged expression of the γ-H2AX DNA repair
biomarker correlates with excess acute and chronic toxicity from
radio-therapy treatment. Int J Cancer. 129:2928–2934. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Itokawa T, Nokihara H, Nishioka Y, Sone S,
Iwamoto Y, Yamada Y, Cherrington J, McMahon G, Shibuya M, Kuwano M,
et al: Antiangiogenic effect by SU5416 is partly attributable to
inhibition of Flt-1 receptor signaling. Mol Cancer Ther. 1:295–302.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Peña LA, Fuks Z and Kolesnick RN:
Radiation-induced apoptosis of endothelial cells in the murine
central nervous system: Protection by fibroblast growth factor and
sphingomyelinase deficiency. Cancer Res. 60:321–327.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kumar P, Miller AI and Polverini PJ: p38
MAPK mediates gamma-irradiation-induced endothelial cell apoptosis,
and vascular endothelial growth factor protects endothelial cells
through the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Akt-Bcl-2 pathway. J Biol
Chem. 279:43352–43360. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Datta SR, Brunet A and Greenberg ME:
Cellular survival: A play in three Akts. Genes Dev. 13:2905–2927.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Dangi S, Cha H and Shapiro P: Requirement
for phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase activity during progression
through S-phase and entry into mitosis. Cell Signal. 15:667–675.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kandel ES, Skeen J, Majewski N, Di
Cristofano A, Pandolfi PP, Feliciano CS, Gartel A and Hay N:
Activation of Akt/protein kinase B overcomes a G(2)/m cell cycle
checkpoint induced by DNA damage. Mol Cell Biol. 22:7831–7841.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Davies SP, Reddy H, Caivano M and Cohen P:
Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein
kinase inhibitors. Biochem J. 351:95–105. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D,
McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, Zhang X, Vincent P, McHugh M, et al:
BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and
targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases
involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res.
64:7099–7109. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Roberts PJ and Der CJ: Targeting the
Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the
treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 26:3291–3310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Figueroa C, Tarras S, Taylor J and Vojtek
AB: Akt2 negatively regulates assembly of the POSH-MLK-JNK
signaling complex. J Biol Chem. 278:47922–47927. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Shonai T, Adachi M, Sakata K, Takekawa M,
Endo T, Imai K and Hareyama M: MEK/ERK pathway protects ionizing
radiation-induced loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and cell
death in lymphocytic leukemia cells. Cell Death Differ. 9:963–971.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|