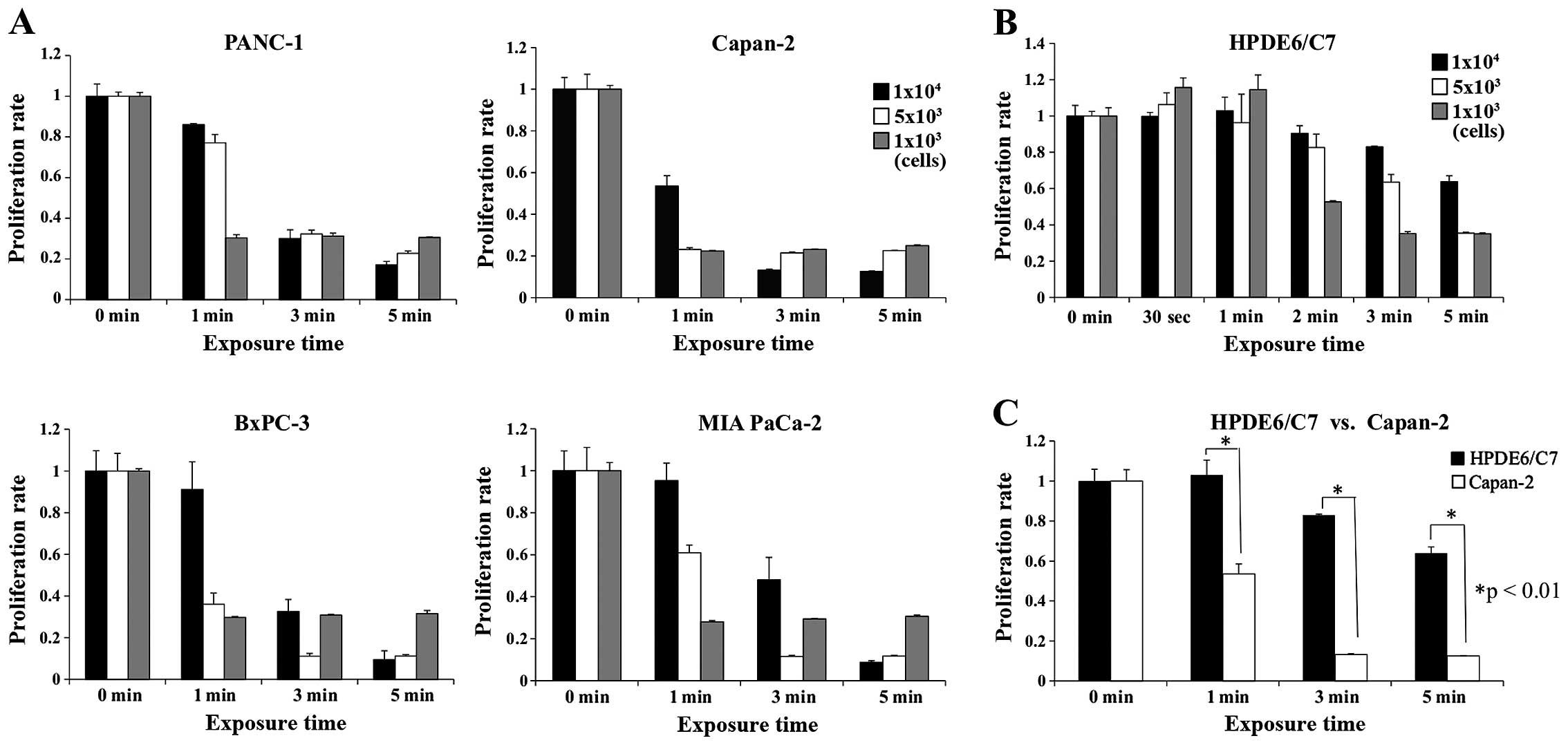
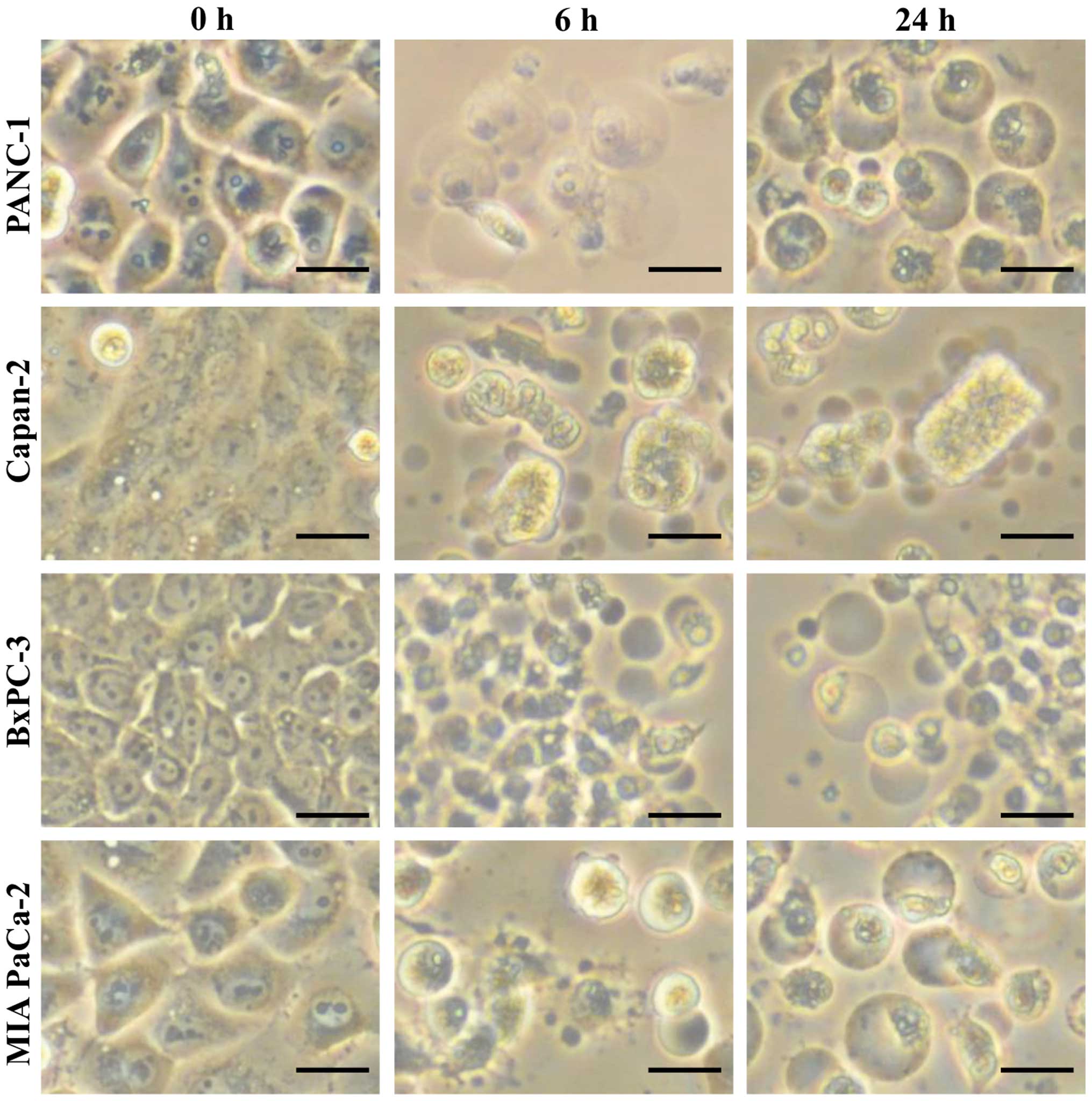
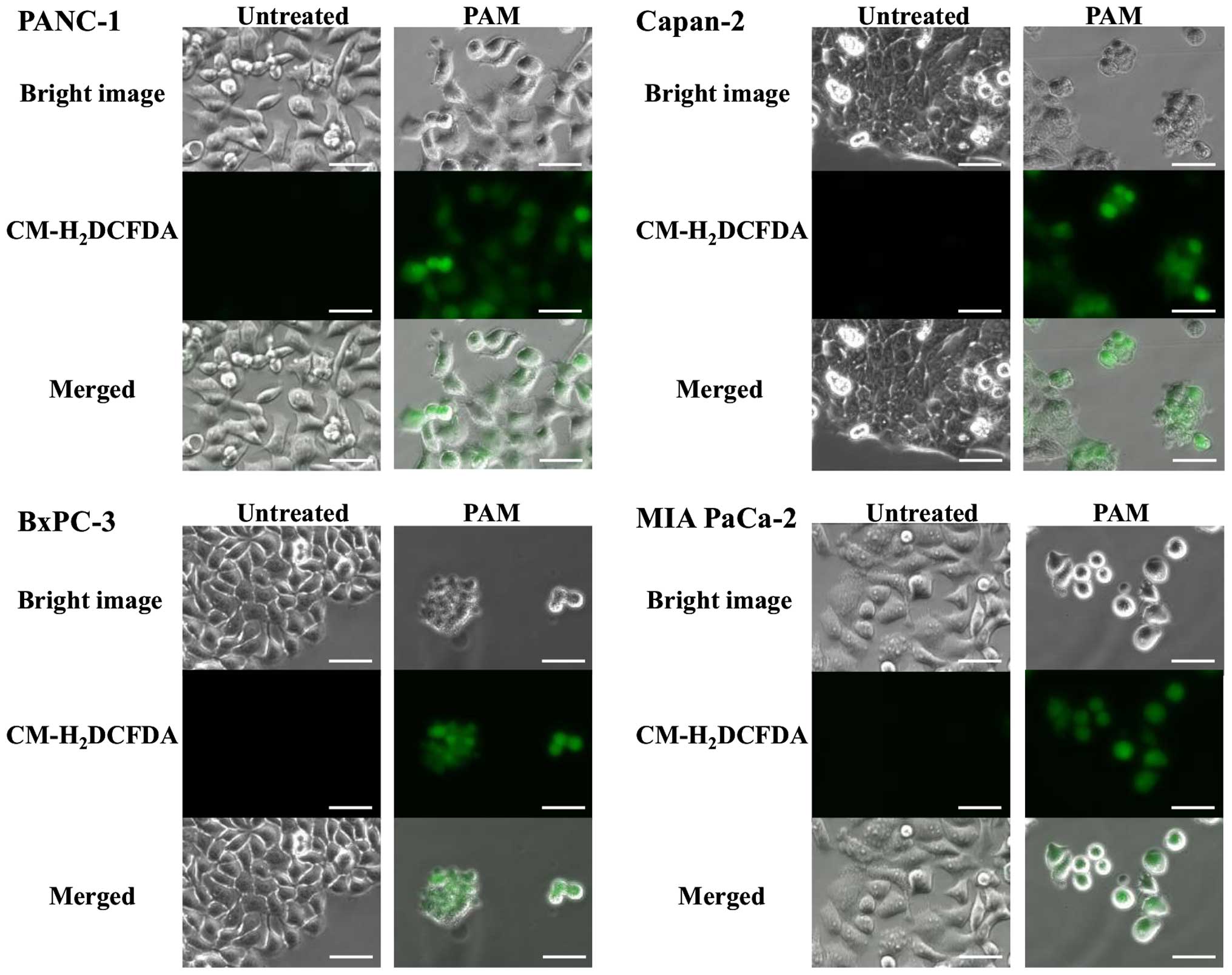
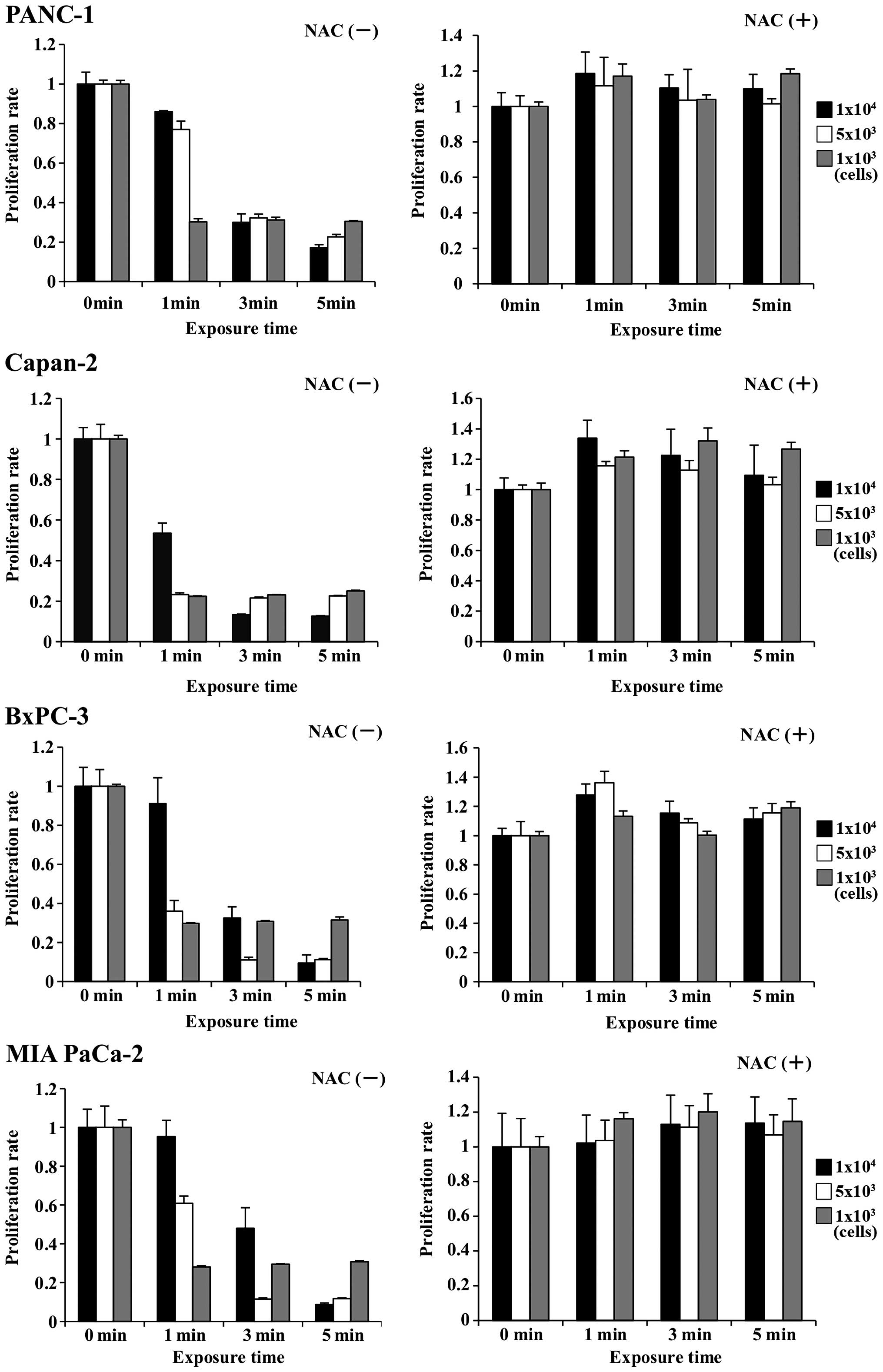
|
1
|
Malvezzi M, Bertuccio P, Levi F, La
Vecchia C and Negri E: European cancer mortality predictions for
the year 2012. Ann Oncol. 23:1044–1052. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Conlon KC, Klimstra DS and Brennan MF:
Long-term survival after curative resection for pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. Clinicopathologic analysis of 5-year survivors. Ann
Surg. 223:273–279. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schnelldorfer T, Ware AL, Sarr MG, Smyrk
TC, Zhang L, Qin R, Gullerud RE, Donohue JH, Nagorney DM and
Farnell MB: Long-term survival after pancreatoduodenectomy for
pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Is cure possible? Ann Surg. 247:456–462.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ferrone CR, Pieretti-Vanmarcke R, Bloom
JP, Zheng H, Szymonifka J, Wargo JA, Thayer SP, Lauwers GY,
Deshpande V, Mino-Kenudson M, et al: Pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma: Long-term survival does not equal cure. Surgery.
152(Suppl 1): S43–S49. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Winter JM, Brennan MF, Tang LH, D'Angelica
MI, Dematteo RP, Fong Y, Klimstra DS, Jarnagin WR and Allen PJ:
Survival after resection of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Results from
a single institution over three decades. Ann Surg Oncol.
19:169–175. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Vandamme M, Robert E, Pesnel S, Barbosa E,
Dozias S, Sobilo J, Lerondel S, Le Pape A and Pouvesle J-M:
Antitumor effect of plasma treatment on U87 glioma xnografts:
Preliminary results. Plasma Process Polym. 7:264–273. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yamazaki H, Ohshima T, Tsubota Y,
Yamaguchi H, Jayawardena JA and Nishimura Y: Microbicidal
activities of low frequency atmospheric pressure plasma jets on
oral pathogens. Dent Mater J. 30:384–391. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stoffels E, Kieft IE and Sladek REJ:
Superficial treatment of mammalian cells using plasma needle. J
Phys D Appl Phys. 36:29082003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Fridman G, Shereshevsky A, Jost MM, Brooks
AD, Fridman A, Gutsol A, Vasilets V and Friedman G: Floating
electrode dielectric barrier discharge plasma in air promoting
apoptotic behavior in melanoma skin cancer cell lines. Plasma Chem
Plasma Process. 27:163–176. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kim CH, Bahn JH, Lee SH, Kim GY, Jun SI,
Lee K and Baek SJ: Induction of cell growth arrest by atmospheric
non-thermal plasma in colorectal cancer cells. J Biotechnol.
150:530–538. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Iseki S, Nakamura K, Hayashi M, Tanaka H,
Kondo H, Kajiyama H, Kano H, Kikkawa F and Hori M: Selective
killing of ovarian cancer cells through induction of apoptosis by
nonequilibrium atmospheric pressure plasma. Appl Phys Lett.
100:1137022012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Georgescu N and Lupu AR: Tumoral and
normal cells treatment with high-voltage pulsed cold atmospheric
plasma jets. Plasma Science IEEE Trans. 38:1949–1955. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Keidar M, Walk R, Shashurin A, Srinivasan
P, Sandler A, Dasgupta S, Ravi R, Guerrero-Preston R and Trink B:
Cold plasma selectivity and the possibility of a paradigm shift in
cancer therapy. Br J Cancer. 105:1295–1301. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brullé L, Vandamme M, Riès D, Martel E,
Robert E, Lerondel S, Trichet V, Richard S, Pouvesle JM and Le Pape
A: Effects of a non thermal plasma treatment alone or in
combination with gemcitabine in a MIA PaCa2-luc orthotopic
pancreatic carcinoma model. PLoS One. 7:e526532012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tanaka H, Mizuno M, Ishikawa K, Nakamura
K, Kajiyama H, Kano H, Kikkawa F and Hori M: Plasma-activated
medium selectively kills glioblastoma brain tumor cells by
down-regulating a survival signaling molecule, AKT kinase. Plasma
Med. 1:265–277. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Utsumi F, Kajiyama H, Nakamura K, Tanaka
H, Mizuno M, Ishikawa K, Kondo H, Kano H, Hori M and Kikkawa F:
Effect of indirect nonequilibrium atmospheric pressure plasma on
anti-proliferative activity against chronic chemo-resistant ovarian
cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 8:e815762013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Torii K, Yamada S, Nakamura K, Tanaka H,
Kajiyama H, Tanahashi K, Iwata N, Kanda M, Kobayashi D, Tanaka C,
et al: Effectiveness of plasma treatment on gastric cancer cells.
Gastric Cancer. 18:635–643. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Iwasaki M, Inui H, Matsudaira Y, Kano H,
Yoshida N, Ito M and Hori M: Nonequilibrium atmospheric pressure
plasma with ultrahigh electron density and high performance for
glass surface cleaning. Appl Phys Lett. 92:p0815032008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Jia F, Sumi N, Ishikawa K, Kano H, Inui H,
Kularatne J, Takeda K, Kondo H, Sekine M, Kono A, et al: Laser
scattering diagnosis of a 60-Hz non-equilibrium atmospheric
pressure plasma jet. Appl Phys Express. 4:0261012011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wray CJ, Ahmad SA, Matthews JB and Lowy
AM: Surgery for pancreatic cancer: Recent controversies and current
practice. Gastroenterology. 128:1626–1641. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Furuse J, Ishii H and Okusaka T: The
Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Oncology (HBPO) Group of the Japan
Clinical Oncology Group (JCOG): History and future direction. Jpn J
Clin Oncol. 43:2–7. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ishigami H, Kitayama J, Kaisaki S,
Hidemura A, Kato M, Otani K, Kamei T, Soma D, Miyato H, Yamashita
H, et al: Phase II study of weekly intravenous and intraperitoneal
paclitaxel combined with S-1 for advanced gastric cancer with
peritoneal metastasis. Ann Oncol. 21:67–70. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Takahara N, Isayama H, Nakai Y, Sasaki T,
Ishigami H, Yamashita H, Yamaguchi H, Hamada T, Uchino R, Mizuno S,
et al: Intravenous and intraperitoneal paclitaxel with S-1 for
refractory pancreatic cancer with malignant ascites: An interim
analysis. J Gastrointest Cancer. 45:307–311. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim G, Kim W, Kim K and Lee J: DNA damage
and mitochondria dysfunction in cell apoptosis induced by
nonthermal air plasma. Appl Phys Lett. 96:0215022010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ma Y, Ha CS, Hwang SW, Lee HJ, Kim GC, Lee
KW and Song K: Non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma
preferentially induces apoptosis in p53-mutated cancer cells by
activating ROS stress-response pathways. PLoS One. 9:e919472014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kalghatgi S, Kelly CM, Cerchar E, Torabi
B, Alekseev O, Fridman A, Friedman G and Azizkhan-Clifford J:
Effects of non-thermal plasma on mammalian cells. PLoS One.
6:e162702011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sensenig R, Kalghatgi S, Cerchar E,
Fridman G, Shereshevsky A, Torabi B, Arjunan KP, Podolsky E,
Fridman A, Friedman G, et al: Non-thermal plasma induces apoptosis
in melanoma cells via production of intracellular reactive oxygen
species. Ann Biomed Eng. 39:674–687. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Aruoma O: Free radicals, oxidative stress,
and antioxidants in human health and disease. J Am Oil Chem Soc.
75:199–212. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ninomiya K, Ishijima T, Imamura M,
Yamahara T, Enomoto H, Takahashi K, Tanaka Y, Uesugi Y and Shimizu
N: Evaluation of extra- and intracellular OH radical generation,
cancer cell injury, and apoptosis induced by a non-thermal
atmospheric-pressure plasma jet. J Phys D Appl Phys. 46:4254012013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Nicco C, Laurent A, Chereau C, Weill B and
Batteux F: Differential modulation of normal and tumor cell
proliferation by reactive oxygen species. Biomed Pharmacother.
59:169–174. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nishikawa M: Reactive oxygen species in
tumor metastasis. Cancer Lett. 266:53–59. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Arjunan KP, Friedman G, Fridman A and
Clyne AM: Non-thermal dielectric barrier discharge plasma induces
angiogenesis through reactive oxygen species. J R Soc Interface.
9:147–157. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kalghatgi S, Friedman G, Fridman A and
Clyne AM: Endothelial cell proliferation is enhanced by low dose
non-thermal plasma through fibroblast growth factor-2 release. Ann
Biomed Eng. 38:748–757. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Barrera G: Oxidative stress and lipid
peroxidation products in cancer progression and therapy. ISRN
Oncol. 2012:1372892012.PubMed/NCBI
|