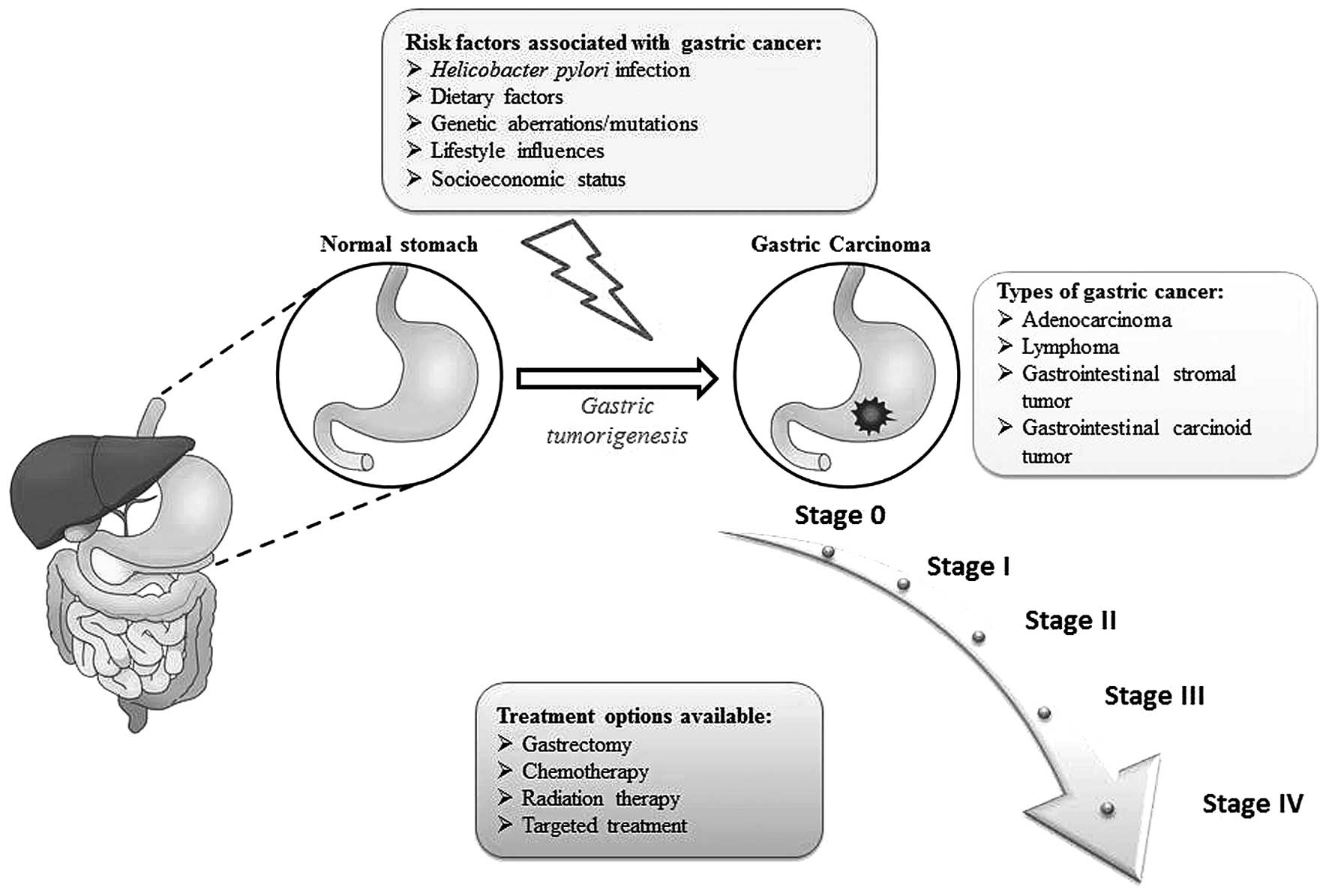
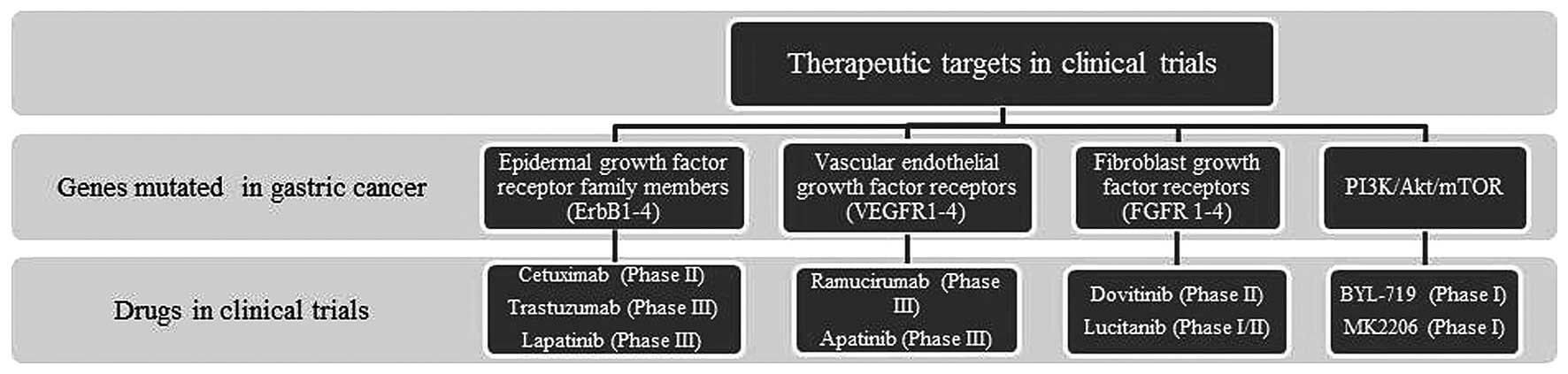
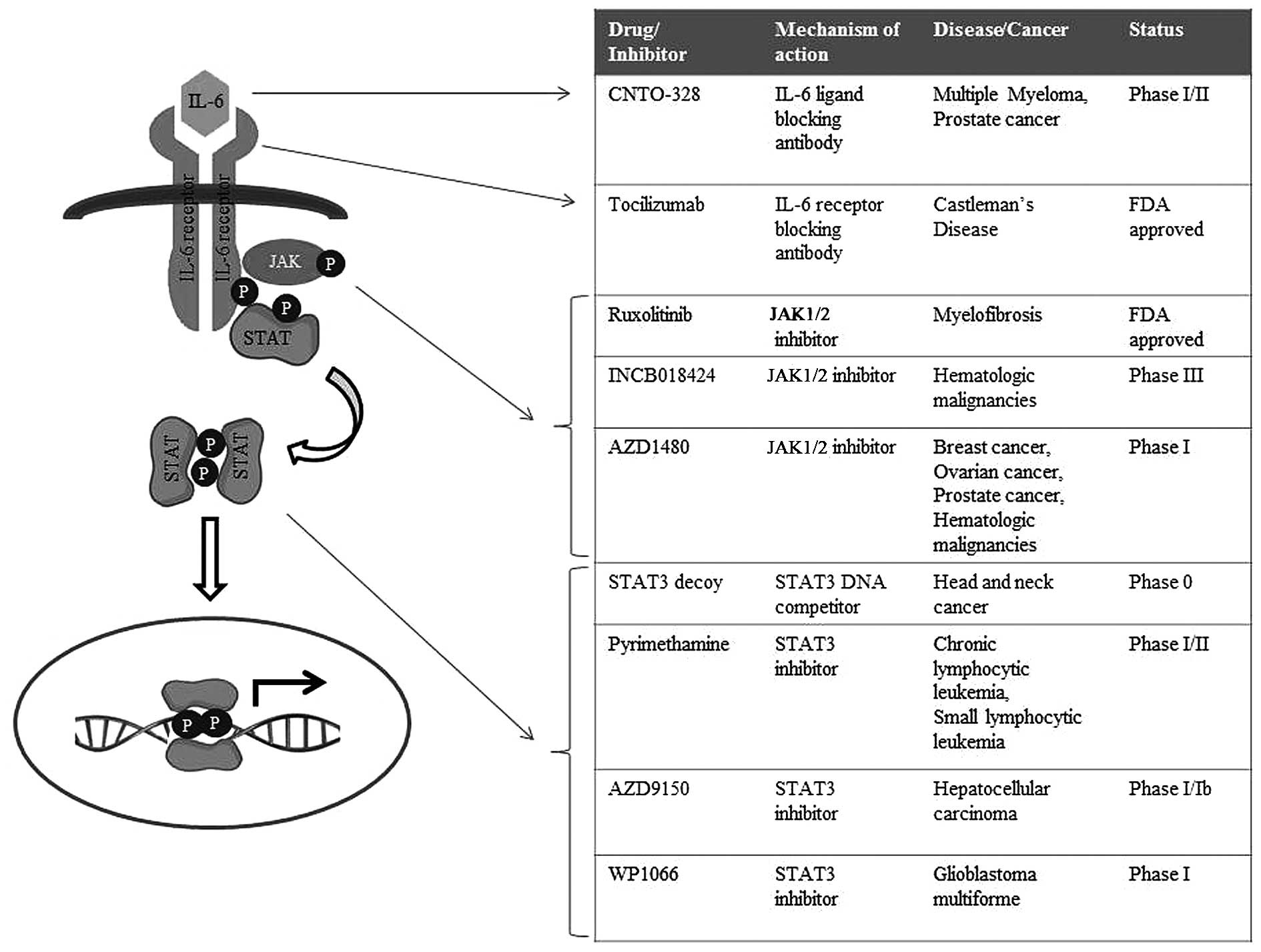
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Parkin DM: The global health burden of
infection-associated cancers in the year 2002. Int J Cancer.
118:3030–3044. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fock KM: Review article: The epidemiology
and prevention of gastric cancer. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.
40:250–260. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Owen DA: Normal histology of the stomach.
Am J Surg Pathol. 10:48–61. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dicken BJ, Bigam DL, Cass C, Mackey JR,
Joy AA and Hamilton SM: Gastric adenocarcinoma: Review and
considerations for future directions. Ann Surg. 241:27–39.
2005.
|
|
7
|
Kelley JR and Duggan JM: Gastric cancer
epidemiology and risk factors. J Clin Epidemiol. 56:1–9. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Allum WH: Tumours of the stomach. Surgery.
29:575–580. 2011.
|
|
9
|
Gilligan CJ, Lawton GP, Tang LH, West AB
and Modlin IM: Gastric carcinoid tumors: The biology and therapy of
an enigmatic and controversial lesion. Am J Gastroenterol.
90:338–352. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lauren P: The two histological main types
of gastric carcinoma: Diffuse and so-called intestinal-type
carcinoma. An attempt at a histo-clinical classification. Acta
Pathol Microbiol Scand. 64:31–49. 1965.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Munoz N, Correa P, Cuello C and Duque E:
Histologic types of gastric carcinoma in high- and low-risk areas.
Int J Cancer. 3:809–818. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Crew KD and Neugut AI: Epidemiology of
gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 12:354–362. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Davessar K, Pezzullo JC, Kessimian N, Hale
JH and Jauregui HO: Gastric adenocarcinoma: Prognostic significance
of several pathologic parameters and histologic classifications.
Hum Pathol. 21:325–332. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ming SC: Gastric carcinoma. A
pathobiological classification. Cancer. 39:2475–2485. 1977.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rugge M, Capelle LG, Cappellesso R, Nitti
D and Kuipers EJ: Precancerous lesions in the stomach: From biology
to clinical patient management. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol.
27:205–223. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Forman D and Burley VJ: Gastric cancer:
Global pattern of the disease and an overview of environmental risk
factors. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 20:633–649. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pizzi M, Saraggi D, Fassan M, Megraud F,
Di Mario F and Rugge M: Secondary prevention of epidemic gastric
cancer in the model of Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis.
Dig Dis. 32:265–274. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Levi E, Sochacki P, Khoury N, Patel BB and
Majumdar AP: Cancer stem cells in Helicobacter pylori infection and
aging: Implications for gastric carcinogenesis. World J
Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 5:366–372. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Compare D, Rocco A and Nardone G: Risk
factors in gastric cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 14:302–308.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sheh A, Ge Z, Parry NM, Muthupalani S,
Rager JE, Raczynski AR, Mobley MW, McCabe AF, Fry RC, Wang TC, et
al: 17β-estradiol and tamoxifen prevent gastric cancer by
modulating leukocyte recruitment and oncogenic pathways in
Helicobacter pylori-infected INS-GAS male mice. Cancer Prev Res
(Phila). 4:1426–1435. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bertuccio P, Chatenoud L, Levi F, Praud D,
Ferlay J, Negri E, Malvezzi M and La Vecchia C: Recent patterns in
gastric cancer: a global overview. Int J Cancer. 125:666–673. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Curado M-P, Edwards B, Shin HR, et al:
Cancer incidence in five continents. IX. IARC Press, International
Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon: 2007
|
|
23
|
Howson CP, Hiyama T and Wynder EL: The
decline in gastric cancer: Epidemiology of an unplanned triumph.
Epidemiol Rev. 8:1–27. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
De Stefani E, Correa P, Boffetta P,
Deneo-Pellegrini H, Ronco AL and Mendilaharsu M: Dietary patterns
and risk of gastric cancer: a case-control study in Uruguay.
Gastric cancer. 7:211–220. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wadhwa R, Song S, Lee JS, Yao Y, Wei Q and
Ajani JA: Gastric cancer-molecular and clinical dimensions. Nat Rev
Clin Oncol. 10:643–655. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Deng N, Goh LK, Wang H, Das K, Tao J, Tan
IB, Zhang S, Lee M, Wu J, Lim KH, et al: A comprehensive survey of
genomic alterations in gastric cancer reveals systematic patterns
of molecular exclusivity and co-occurrence among distinct
therapeutic targets. Gut. 61:673–684. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang J, Chiodini R, Badr A and Zhang G:
The impact of next-generation sequencing on genomics. J Genet
Genomics. 38:95–109. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Grada A and Weinbrecht K: Next-generation
sequencing: Methodology and application. J Invest Dermatol.
133:e112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee J, van Hummelen P, Go C, Palescandolo
E, Jang J, Park HY, Kang SY, Park JO, Kang WK, MacConaill L, et al:
High-throughput mutation profiling identifies frequent somatic
mutations in advanced gastric adenocarcinoma. PLoS One.
7:e388922012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zang ZJ, Cutcutache I, Poon SL, Zhang SL,
McPherson JR, Tao J, Rajasegaran V, Heng HL, Deng N, Gan A, et al:
Exome sequencing of gastric adenocarcinoma identifies recurrent
somatic mutations in cell adhesion and chromatin remodeling genes.
Nat Genet. 44:570–574. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim MA, Lee HS, Lee HE, Jeon YK, Yang HK
and Kim WH: EGFR in gastric carcinomas: Prognostic significance of
protein overexpression and high gene copy number. Histopathology.
52:738–746. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Langer R, Von Rahden BH, Nahrig J, Von
Weyhern C, Reiter R, Feith M, Stein HJ, Siewert JR, Höfler H and
Sarbia M: Prognostic significance of expression patterns of
c-erbB-2, p53, p16INK4A, p27KIP1, cyclin D1
and epidermal growth factor receptor in oesophageal adenocarcinoma:
A tissue microarray study. J Clin Pathol. 59:631–634. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dulak AM, Schumacher SE, van Lieshout J,
Imamura Y, Fox C, Shim B, Ramos AH, Saksena G, Baca SC, Baselga J,
et al: Gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas of the esophagus, stomach,
and colon exhibit distinct patterns of genome instability and
oncogenesis. Cancer Res. 72:4383–4393. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Waddell T, Chau I, Cunningham D, Gonzalez
D, Okines AF, Okines C, Wotherspoon A, Saffery C, Middleton G,
Wadsley J, et al: Epirubicin, oxaliplatin, and capecitabine with or
without panitumumab for patients with previously untreated advanced
oesophagogastric cancer (REAL3): A randomised, open-label phase 3
trial. Lancet Oncol. 14:481–489. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gravalos C and Jimeno A: HER2 in gastric
cancer: a new prognostic factor and a novel therapeutic target. Ann
Oncol. 19:1523–1529. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yano T, Doi T, Ohtsu A, Boku N, Hashizume
K, Nakanishi M and Ochiai A: Comparison of HER2 gene amplification
assessed by fluorescence in situ hybridization and HER2 protein
expression assessed by immunohistochemistry in gastric cancer.
Oncol Rep. 15:65–71. 2006.
|
|
37
|
Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A,
Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, Lordick F, Ohtsu A, Omuro Y, Satoh T,
et al; ToGA Trial Investigators. Trastuzumab in combination with
chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of
HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction
cancer (ToGA): A phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial.
Lancet. 376:687–697. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hayashi M, Inokuchi M, Takagi Y, Yamada H,
Kojima K, Kumagai J, Kawano T and Sugihara K: High expression of
HER3 is associated with a decreased survival in gastric cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 14:7843–7849. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang XL, Yang YS, Xu DP, Qu JH, Guo MZ,
Gong Y and Huang J: Comparative study on overexpression of HER2/neu
and HER3 in gastric cancer. World J Surg. 33:2112–2118. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang W, Raufi A and Klempner SJ: Targeted
therapy for gastric cancer: Molecular pathways and ongoing
investigations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1846:232–237. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim SE, Shim KN, Jung SA, Yoo K and Lee
JH: The clinicopathological significance of tissue levels of
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and vascular endothelial growth
factor in gastric cancer. Gut Liver. 3:88–94. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Cabuk D, Basaran G, Celikel C, Dane F,
Yumuk PF, Iyikesici MS, Ekenel M and Turhal NS: Vascular
endothelial growth factor, hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha and
CD34 expressions in early-stage gastric tumors: Relationship with
pathological factors and prognostic impact on survival. Oncology.
72:111–117. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jüttner S, Wissmann C, Jöns T, Vieth M,
Hertel J, Gretschel S, Schlag PM, Kemmner W and Höcker M: Vascular
endothelial growth factor-D and its receptor VEGFR-3: Two novel
independent prognostic markers in gastric adenocarcinoma. J Clin
Oncol. 24:228–240. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Shah MA, Ramanathan RK, Ilson DH, Levnor
A, D'Adamo D, O'Reilly E, Tse A, Trocola R, Schwartz L, Capanu M,
et al: Multicenter phase II study of irinotecan, cisplatin, and
bevacizumab in patients with metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal
junction adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 24:5201–5206. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ohtsu A, Shah MA, Van Cutsem E, Rha SY,
Sawaki A, Park SR, Lim HY, Yamada Y, Wu J, Langer B, et al:
Bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy as first-line therapy
in advanced gastric cancer: A randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 29:3968–3976.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fuchs CS, Tomasek J, Yong CJ, Dumitru F,
Passalacqua R, Goswami C, Safran H, dos Santos LV, Aprile G, Ferry
DR, et al; REGARD Trial Investigators. Ramucirumab monotherapy for
previously treated advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction
adenocarcinoma (REGARD): An international, randomised, multicentre,
placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 383:31–39. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Su X, Zhan P, Gavine PR, Morgan S, Womack
C, Ni X, Shen D, Bang YJ, Im SA, Ho Kim W, et al: FGFR2
amplification has prognostic significance in gastric cancer:
Results from a large international multicentre study. Br J Cancer.
110:967–975. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xie L, Su X, Zhang L, Yin X, Tang L, Zhang
X, Xu Y, Gao Z, Liu K, Zhou M, et al: FGFR2 gene amplification in
gastric cancer predicts sensitivity to the selective FGFR inhibitor
AZD4547. Clin Cancer Res. 19:2572–2583. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liu JF, Zhou XK, Chen JH, Yi G, Chen HG,
Ba MC, Lin SQ and Qi YC: Up-regulation of PIK3CA promotes
metastasis in gastric carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol.
16:4986–4991. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Shi J, Yao D, Liu W, Wang N, Lv H, Zhang
G, Ji M, Xu L, He N, Shi B, et al: Highly frequent PIK3CA
amplification is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer.
BMC Cancer. 12:502012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Dong M, Phan AT and Yao JC: New strategies
for advanced neuroendocrine tumors in the era of targeted therapy.
Clin Cancer Res. 18:1830–1836. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ohtsu A, Ajani JA, Bai YX, Bang YJ, Chung
HC, Pan HM, Sahmoud T, Shen L, Yeh KH, Chin K, et al: Everolimus
for previously treated advanced gastric cancer: Results of the
randomized, double-blind, phase III GRANITE-1 study. J Clin Oncol.
31:3935–3943. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yang W, Raufi A and Klempner SJ: Targeted
therapy for gastric cancer: Molecular pathways and ongoing
investigations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1846:232–237. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Proserpio I, Rausei S, Barzaghi S,
Frattini F, Galli F, Iovino D, Rovera F, Boni L, Dionigi G and
Pinotti G: Multimodal treatment of gastric cancer. World J
Gastrointest Surg. 6:55–58. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Darnell JE Jr, Kerr IM and Stark GR:
Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to
IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science.
264:1415–1421. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Aaronson DS and Horvath CM: A road map for
those who don't know JAK-STAT. Science. 296:1653–1655. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Rawlings JS, Rosler KM and Harrison DA:
The JAK/STAT signaling pathway. J Cell Sci. 117:1281–1283. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Harrison DA: The Jak/STAT pathway. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 4:42012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Kiu H and Nicholson SE: Biology and
significance of the JAK/ STAT signalling pathways. Growth Factors.
30:88–106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Espert L, Dusanter-Fourt I and Chelbi-Alix
MK: Negative regulation of the JAK/STAT: Pathway implication in
tumorigenesis. Bull Cancer. 92:845–857. 2005.(In French).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Valentino L and Pierre J: JAK/STAT signal
transduction: Regulators and implication in hematological
malignancies. Biochem Pharmacol. 71:713–721. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kisseleva T, Bhattacharya S, Braunstein J
and Schindler CW: Signaling through the JAK/STAT pathway, recent
advances and future challenges. Gene. 285:1–24. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Li WX: Canonical and non-canonical
JAK-STAT signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 18:545–551. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Sansone P and Bromberg J: Targeting the
interleukin-6/Jak/stat pathway in human malignancies. J Clin Oncol.
30:1005–1014. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Scott LM: The JAK2 exon 12 mutations: A
comprehensive review. Am J Hematol. 86:668–676. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, Teo
SS, Tiedt R, Passweg JR, Tichelli A, Cazzola M and Skoda RC: A
gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders.
N Engl J Med. 352:1779–1790. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Rebouissou S, Amessou M, Couchy G, Poussin
K, Imbeaud S, Pilati C, Izard T, Balabaud C, Bioulac-Sage P and
Zucman-Rossi J: Frequent in-frame somatic deletions activate gp130
in inflammatory hepatocellular tumours. Nature. 457:200–204. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
69
|
Lee H, Deng J, Kujawski M, Yang C, Liu Y,
Herrmann A, Kortylewski M, Horne D, Somlo G, Forman S, et al:
STAT3-induced S1PR1 expression is crucial for persistent STAT3
activation in tumors. Nat Med. 16:1421–1428. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Oh ST, Simonds EF, Jones C, Hale MB,
Goltsev Y, Gibbs KD Jr, Merker JD, Zehnder JL, Nolan GP and Gotlib
J: Novel mutations in the inhibitory adaptor protein LNK drive
JAK-STAT signaling in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms.
Blood. 116:988–992. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Veeriah S, Brennan C, Meng S, Singh B,
Fagin JA, Solit DB, Paty PB, Rohle D, Vivanco I, Chmielecki J, et
al: The tyrosine phosphatase PTPRD is a tumor suppressor that is
frequently inactivated and mutated in glioblastoma and other human
cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:9435–9440. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G,
Zhao Y, Pestell RG, Albanese C and Darnell JE Jr: Stat3 as an
oncogene. Cell. 98:295–303. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Stephanou A, Brar BK, Knight RA and
Latchman DS: Opposing actions of STAT-1 and STAT-3 on the Bcl-2 and
Bcl-x promoters. Cell Death Differ. 7:329–330. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
O'Connor DS, Grossman D, Plescia J, Li F,
Zhang H, Villa A, Tognin S, Marchisio PC and Altieri DC: Regulation
of apoptosis at cell division by p34cdc2 phosphorylation of
survivin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:13103–13107. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Wendt MK, Balanis N, Carlin CR and
Schiemann WP: STAT3 and epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in
carcinomas. JAK-STAT. 3:e289752014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Teng Y, Ross JL and Cowell JK: The
involvement of JAK-STAT3 in cell motility, invasion, and
metastasis. JAK-STAT. 3:e280862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Wei D, Le X, Zheng L, Wang L, Frey JA, Gao
AC, Peng Z, Huang S, Xiong HQ, Abbruzzese JL, et al: Stat3
activation regulates the expression of vascular endothelial growth
factor and human pancreatic cancer angiogenesis and metastasis.
Oncogene. 22:319–329. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Kujawski M, Kortylewski M, Lee H, Herrmann
A, Kay H and Yu H: Stat3 mediates myeloid cell-dependent tumor
angiogenesis in mice. J Clin Invest. 118:3367–3377. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Gong W, Wang L, Yao JC, Ajani JA, Wei D,
Aldape KD, Xie K, Sawaya R and Huang S: Expression of activated
signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 predicts
expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in and angiogenic
phenotype of human gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 11:1386–1393.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Wang T, Niu G, Kortylewski M, Burdelya L,
Shain K, Zhang S, Bhattacharya R, Gabrilovich D, Heller R, Coppola
D, et al: Regulation of the innate and adaptive immune responses by
Stat-3 signaling in tumor cells. Nat Med. 10:48–54. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Wang F, Arun P, Friedman J, Chen Z and Van
Waes C: Current and potential inflammation targeted therapies in
head and neck cancer. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 9:389–395. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Niu G, Wright KL, Huang M, Song L, Haura
E, Turkson J, Zhang S, Wang T, Sinibaldi D, Coppola D, et al:
Constitutive Stat3 activity up-regulates VEGF expression and tumor
angiogenesis. Oncogene. 21:2000–2008. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Wang Z, Si X, Xu A, Meng X, Gao S, Qi Y,
Zhu L, Li T, Li W and Dong L: Activation of STAT3 in human gastric
cancer cells via interleukin (IL)-6-type cytokine signaling
correlates with clinical implications. PLoS One. 8:e757882013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Giraud AS, Menheniott TR and Judd LM:
Targeting STAT3 in gastric cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
16:889–901. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Kanda N, Seno H, Konda Y, Marusawa H,
Kanai M, Nakajima T, Kawashima T, Nanakin A, Sawabu T, Uenoyama Y,
et al: STAT3 is constitutively activated and supports cell survival
in association with survivin expression in gastric cancer cells.
Oncogene. 23:4921–4929. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Sekikawa A, Fukui H, Fujii S, Ichikawa K,
Tomita S, Imura J, Chiba T and Fujimori T: REG Ialpha protein
mediates an anti-apoptotic effect of STAT3 signaling in gastric
cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 29:76–83. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Jackson CB, Judd LM, Menheniott TR,
Kronborg I, Dow C, Yeomans ND, Boussioutas A, Robb L and Giraud AS:
Augmented gp130-mediated cytokine signalling accompanies human
gastric cancer progression. J Pathol. 213:140–151. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Kim DY, Cha ST, Ahn DH, Kang HY, Kwon CI,
Ko KH, Hwang SG, Park PW, Rim KS and Hong SP: STAT3 expression in
gastric cancer indicates a poor prognosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
24:646–651. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Deng JY, Sun D, Liu XY, Pan Y and Liang H:
STAT-3 correlates with lymph node metastasis and cell survival in
gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 16:5380–5387. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Deng J, Jiao X, Liu H, Wu L, Zhang R, Wang
B, Pan Y, Hao X and Liang H: Lymph node metastasis is mediated by
suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol.
34:3627–3636. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Bollrath J, Phesse TJ, von Burstin VA,
Putoczki T, Bennecke M, Bateman T, Nebelsiek T, Lundgren-May T,
Canli O, Schwitalla S, et al: gp130-mediated Stat3 activation in
enterocytes regulates cell survival and cell-cycle progression
during colitis-associated tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 15:91–102.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Grivennikov S, Karin E, Terzic J, Mucida
D, Yu GY, Vallabhapurapu S, Scheller J, Rose-John S, Cheroutre H,
Eckmann L, et al: IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of
intestinal epithelial cells and development of colitis-associated
cancer. Cancer Cell. 15:103–113. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Rigby RJ, Simmons JG, Greenhalgh CJ,
Alexander WS and Lund PK: Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3
(SOCS3) limits damage-induced crypt hyper-proliferation and
inflammation-associated tumorigenesis in the colon. Oncogene.
26:4833–4841. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Ernst M and Putoczki TL: Stat3: Linking
inflammation to (gastrointestinal) tumourigenesis. Clin Exp
Pharmacol Physiol. 39:711–718. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Leonard WJ: Role of Jak kinases and STATs
in cytokine signal transduction. Int J Hematol. 73:271–277. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Ihle JN: The Stat family in cytokine
signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 13:211–217. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Carpenter RL and Lo HW: STAT3 target genes
relevant to human cancers. Cancers (Basel). 6:897–925. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Nishimoto N and Kishimoto T: Interleukin
6: From bench to bedside. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2:619–626.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Nakashima Y, Kondo M, Harada H, Horiuchi
T, Ishinishi T, Jojima H, Kuroda K, Miyahara H, Nagamine R,
Nakashima H, et al: Clinical evaluation of tocilizumab for patients
with active rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-TNF biologics:
tocilizumab in combination with methotrexate. Mod Rheumatol.
20:343–352. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Garnero P, Thompson E, Woodworth T and
Smolen JS: Rapid and sustained improvement in bone and cartilage
turnover markers with the anti-interleukin-6 receptor inhibitor
tocilizumab plus methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis patients with
an inadequate response to methotrexate: Results from a substudy of
the multi-center double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of
tocilizumab in inadequate responders to methotrexate alone.
Arthritis Rheum. 62:33–43. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Ando K, Takahashi F, Motojima S, Nakashima
K, Kaneko N, Hoshi K and Takahashi K: Possible role for
tocilizumab, an anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody, in treating
cancer cachexia. J Clin Oncol. 31:e69–e72. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Isobe A, Sawada K, Kinose Y, Ohyagi-Hara
C, Nakatsuka E, Makino H, Ogura T, Mizuno T, Suzuki N, Morii E, et
al: Interleukin 6 receptor is an independent prognostic factor and
a potential therapeutic target of ovarian cancer. PLoS One.
10:e01180802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Goumas FA, Holmer R, Egberts JH, et al:
Inhibition of IL-6 signaling significantly reduces primary tumor
growth and recurrencies in orthotopic xenograft models of
pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. Jan 21–2015.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Dijkgraaf EM, Welters MJ, Nortier JW, van
der Burg SH and Kroep JR: Interleukin-6/interleukin-6 receptor
pathway as a new therapy target in epithelial ovarian cancer. Curr
Pharm Des. 18:3816–3827. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Yao X, Huang J, Zhong H, Shen N, Faggioni
R, Fung M and Yao Y: Targeting interleukin-6 in inflammatory
autoimmune diseases and cancers. Pharmacol Ther. 141:125–139. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Wallner L, Dai J, Escara-Wilke J, Zhang J,
Yao Z, Lu Y, Trikha M, Nemeth JA, Zaki MH and Keller ET: Inhibition
of interleukin-6 with CNTO328, an anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal
antibody, inhibits conversion of androgen-dependent prostate cancer
to an androgen-independent phenotype in orchiectomized mice. Cancer
Res. 66:3087–3095. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Puchalski T, Prabhakar U, Jiao Q, Berns B
and Davis HM: Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling of an
anti-interleukin-6 chimeric monoclonal antibody (siltuximab) in
patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
16:1652–1661. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Dorff TB, Goldman B, Pinski JK, Mack PC,
Lara PN Jr, Van Veldhuizen PJ Jr, Quinn DI, Vogelzang NJ, Thompson
IM Jr and Hussain MH: Clinical and correlative results of SWOG
S0354: a phase II trial of CNTO328 (siltuximab), a monoclonal
antibody against interleukin-6, in chemotherapy-pretreated patients
with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
16:3028–3034. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Mascarenhas J and Hoffman R: Ruxolitinib:
the first FDA approved therapy for the treatment of myelofibrosis.
Clin Cancer Res. 18:3008–3014. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Ganetsky A: Ruxolitinib: A new treatment
option for myelofibrosis. Pharmacotherapy. 33:84–92. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Meydan N, Grunberger T, Dadi H, Shahar M,
Arpaia E, Lapidot Z, Leeder JS, Freedman M, Cohen A, Gazit A, et
al: Inhibition of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia by a Jak-2
inhibitor. Nature. 379:645–648. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Quintás-Cardama A, Vaddi K, Liu P,
Manshouri T, Li J, Scherle PA, Caulder E, Wen X, Li Y, Waeltz P, et
al: Preclinical characterization of the selective JAK1/2 inhibitor
INCB018424: Therapeutic implications for the treatment of
myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood. 115:3109–3117. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Hedvat M, Huszar D, Herrmann A, Gozgit JM,
Schroeder A, Sheehy A, Buettner R, Proia D, Kowolik CM, Xin H, et
al: The JAK2 inhibitor AZD1480 potently blocks Stat3 signaling and
oncogenesis in solid tumors. Cancer Cell. 16:487–497. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Munoz J, Dhillon N, Janku F, Watowich SS
and Hong DS: STAT3 inhibitors: Finding a home in lymphoma and
leukemia. Oncologist. 19:536–544. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Bar-Natan M, Nelson EA, Xiang M and Frank
DA: STAT signaling in the pathogenesis and treatment of myeloid
malignancies. JAK-STAT. 1:55–64. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Frank DA: STAT signaling in the
pathogenesis and treatment of cancer. Mol Med. 5:432–456.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Sen M, Tosca PJ, Zwayer C, Ryan MJ,
Johnson JD, Knostman KA, Giclas PC, Peggins JO, Tomaszewski JE,
McMurray TP, et al: Lack of toxicity of a STAT3 decoy
oligonucleotide. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 63:983–995. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Leong PL, Andrews GA, Johnson DE, Dyer KF,
Xi S, Mai JC, Robbins PD, Gadiparthi S, Burke NA, Watkins SF, et
al: Targeted inhibition of Stat3 with a decoy oligonucleotide
abrogates head and neck cancer cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:4138–4143. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Xi S, Gooding WE and Grandis JR: In vivo
antitumor efficacy of STAT3 blockade using a transcription factor
decoy approach: Implications for cancer therapy. Oncogene.
24:970–979. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Zhao W, Jaganathan S and Turkson J: A
cell-permeable Stat3 SH2 domain mimetic inhibits Stat3 activation
and induces antitumor cell effects in vitro. J Biol Chem.
285:35855–35865. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Redell MS, Ruiz MJ, Alonzo TA, Gerbing RB
and Tweardy DJ: Stat3 signaling in acute myeloid leukemia:
Ligand-dependent and -independent activation and induction of
apoptosis by a novel small-molecule Stat3 inhibitor. Blood.
117:5701–5709. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Zhang X, Yue P, Fletcher S, Zhao W,
Gunning PT and Turkson J: A novel small-molecule disrupts Stat3 SH2
domain-phosphotyrosine interactions and Stat3-dependent tumor
processes. Biochem Pharmacol. 79:1398–1409. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Nelson EA, Walker SR, Kepich A, Gashin LB,
Hideshima T, Ikeda H, Chauhan D, Anderson KC and Frank DA:
Nifuroxazide inhibits survival of multiple myeloma cells by
directly inhibiting STAT3. Blood. 112:5095–5102. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Nelson EA, Sharma SV, Settleman J and
Frank DA: A chemical biology approach to developing STAT
inhibitors: Molecular strategies for accelerating clinical
translation. Oncotarget. 2:518–524. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Jackson CB and Giraud AS: STAT3 as a
prognostic marker in human gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
24:505–507. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
To KF, Chan MW, Leung WK, Ng EK, Yu J, Bai
AH, Lo AW, Chu SH, Tong JH, Lo KW, et al: Constitutional activation
of IL-6-mediated JAK/STAT pathway through hypermethylation of
SOCS-1 in human gastric cancer cell line. Br J Cancer.
91:1335–1341. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Tye H, Kennedy CL, Najdovska M, McLeod L,
McCormack W, Hughes N, Dev A, Sievert W, Ooi CH, Ishikawa TO, et
al: STAT3-driven upregulation of TLR2 promotes gastric
tumorigenesis independent of tumor inflammation. Cancer Cell.
22:466–478. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Deng J, Liang H, Zhang R, Sun D, Pan Y,
Liu Y, Zhang L and Hao X: STAT3 is associated with lymph node
metastasis in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 34:2791–2800. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|