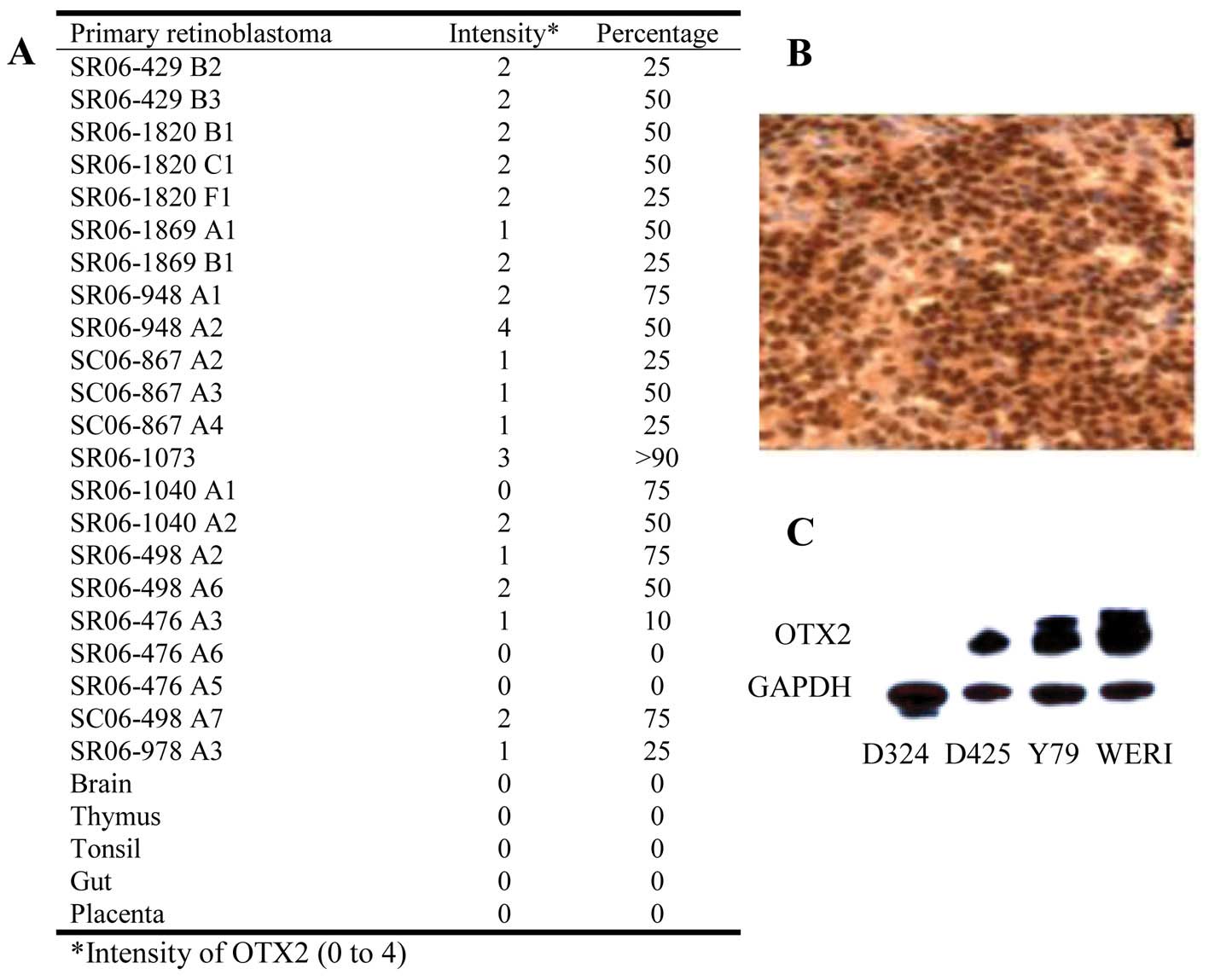
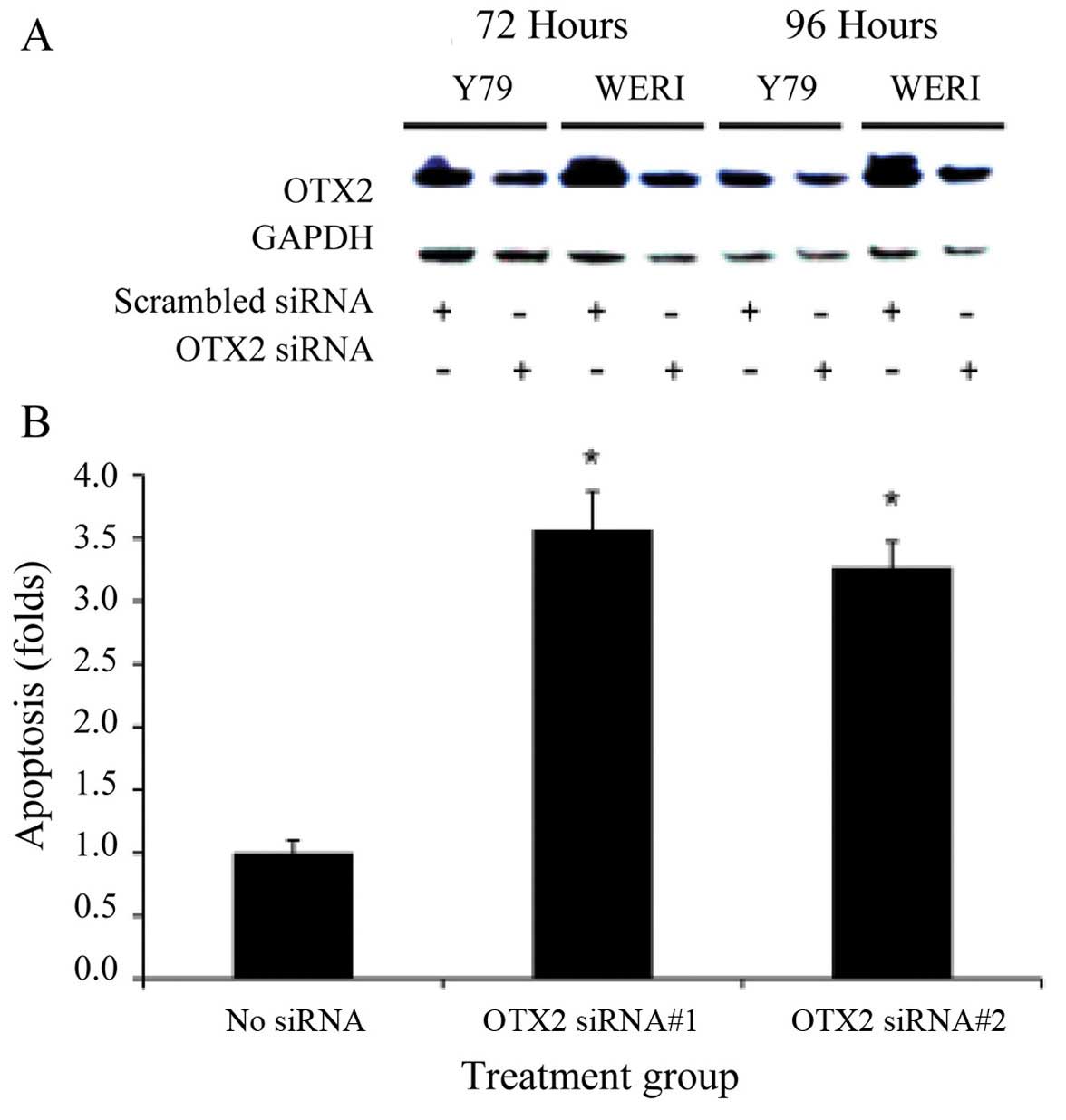
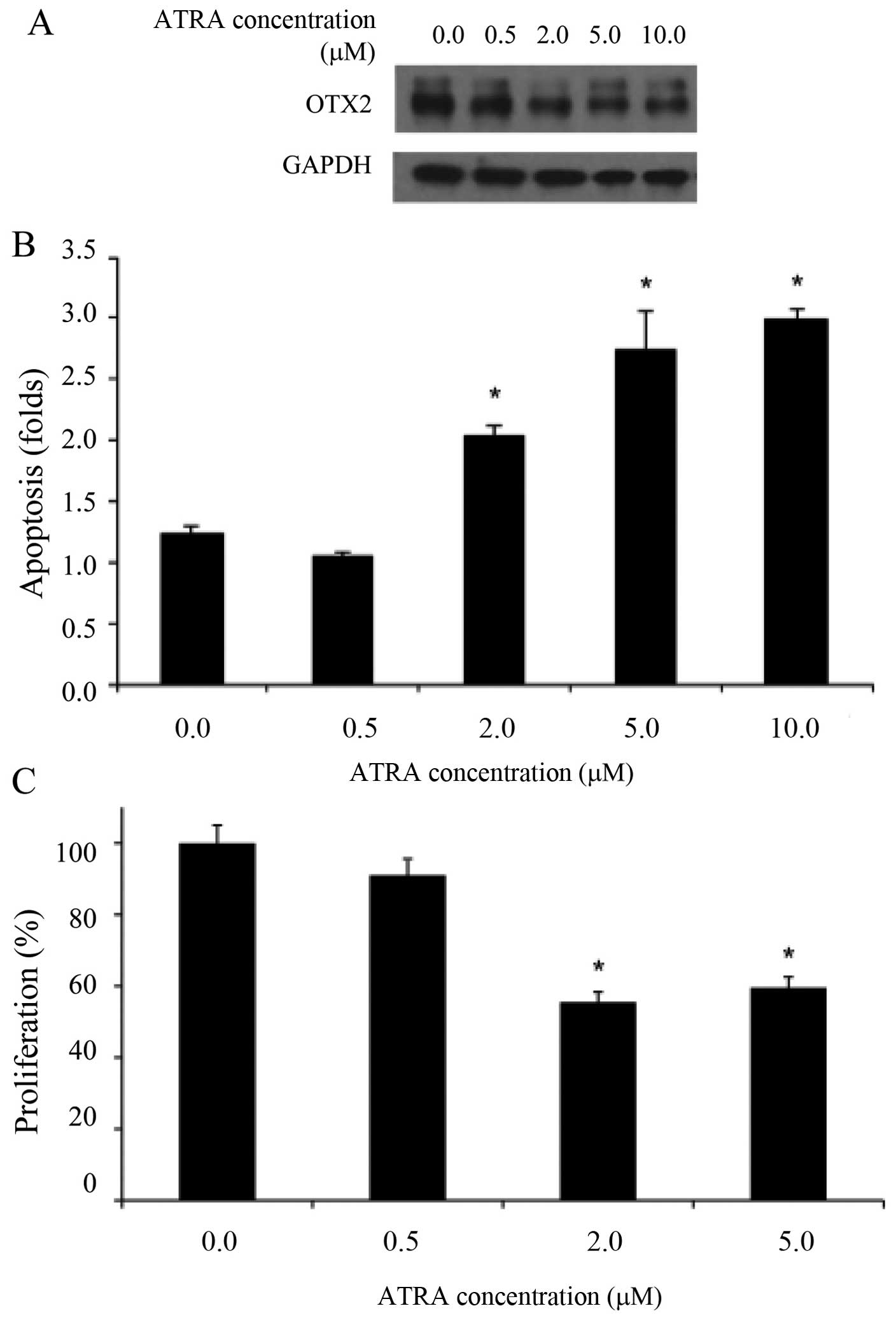
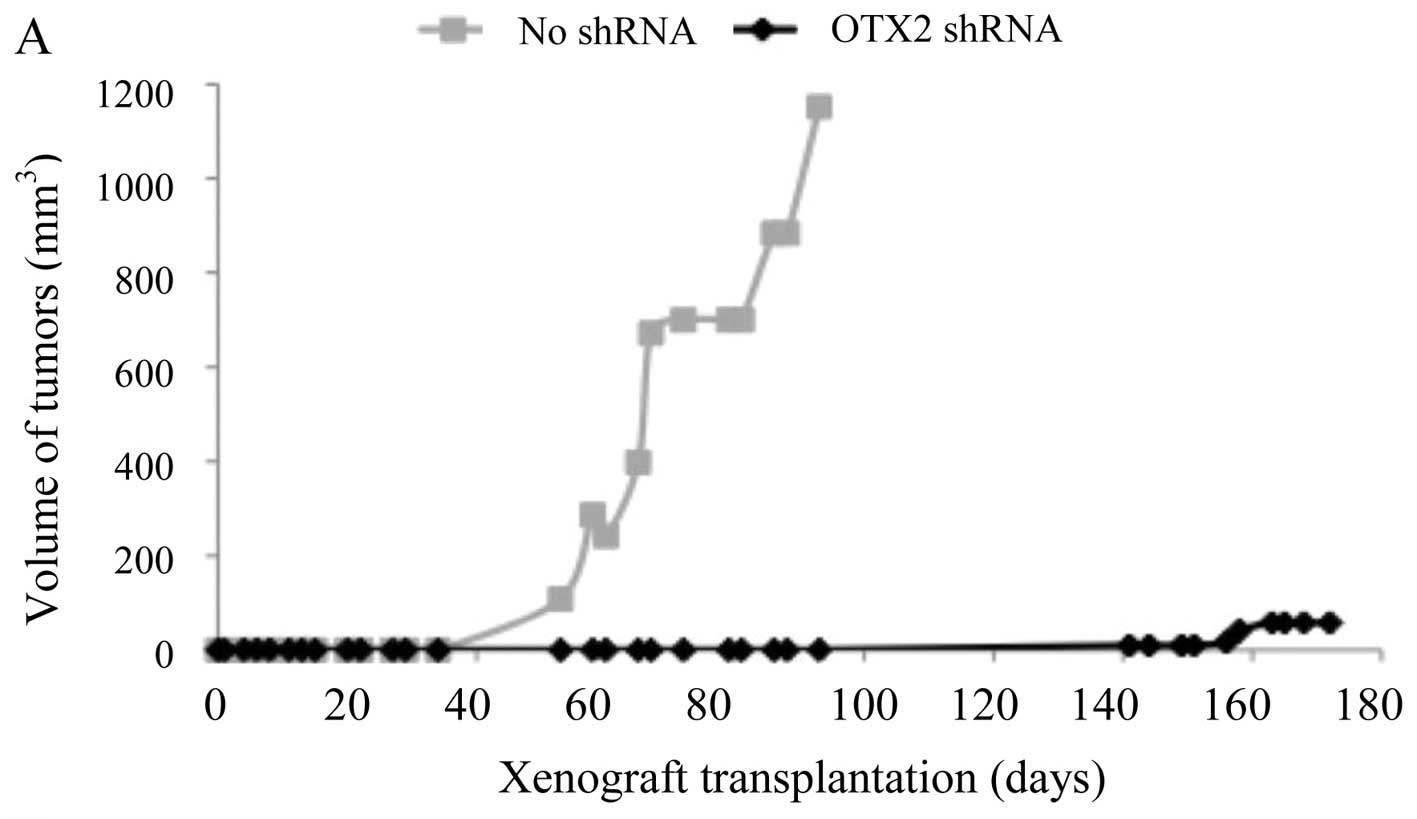
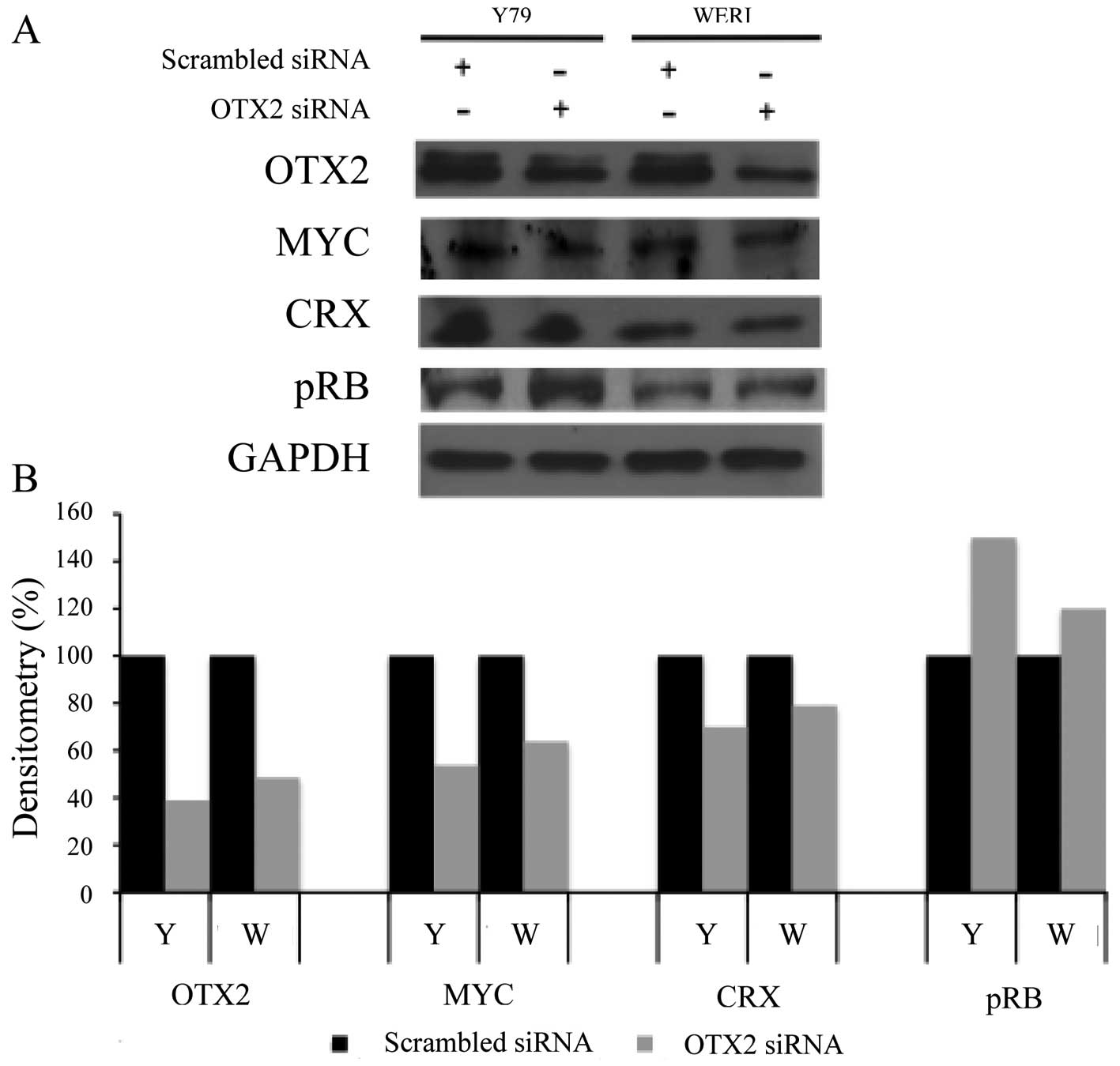
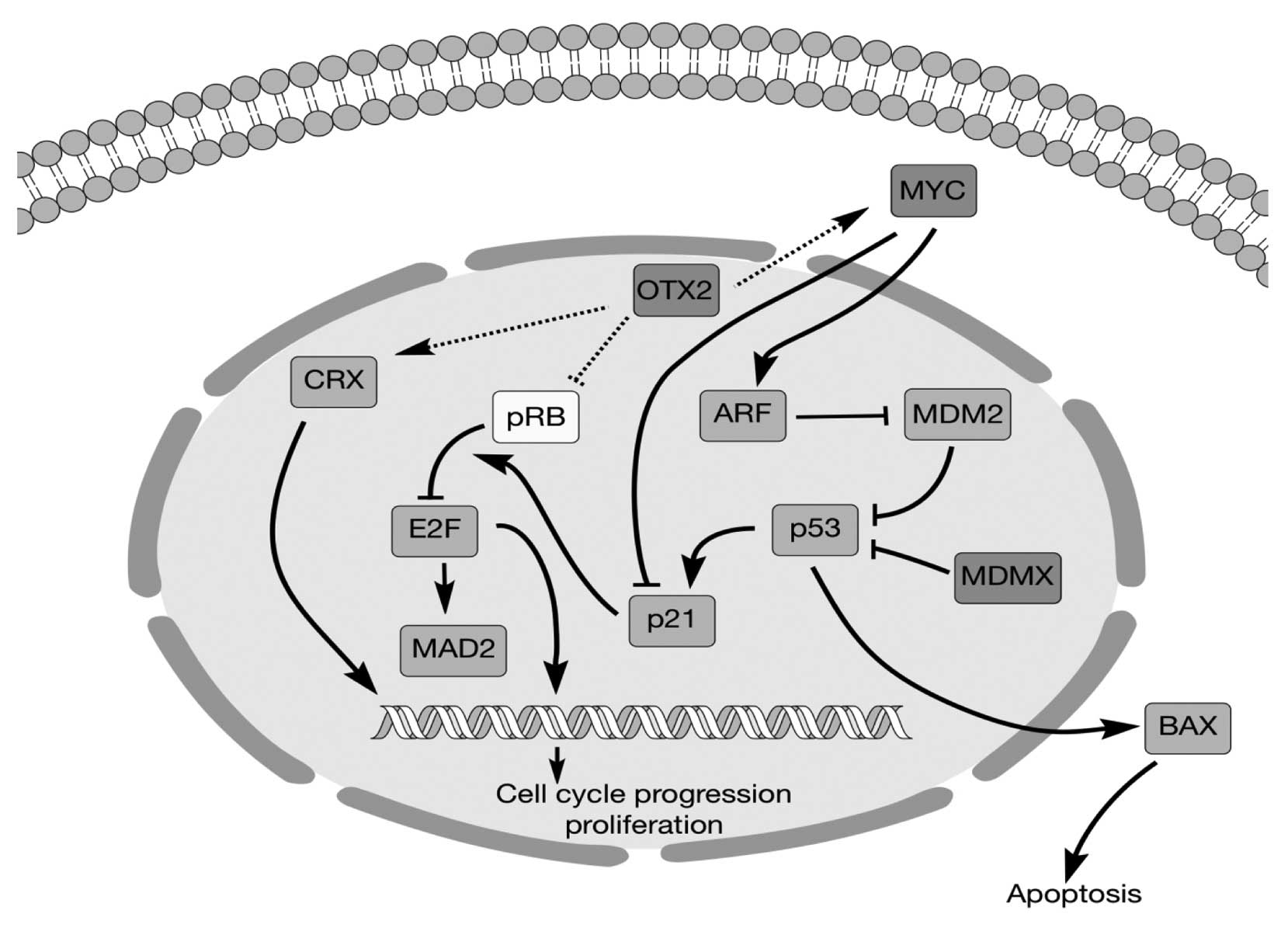
|
1
|
Wilson WG: Retinoblastoma. Pediatr Rev.
28:37–38. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Eldebawy E, Parker W, Abdel Rahman W and
Freeman CR: Dosimetric study of current treatment options for
radiotherapy in retinoblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
82:e501–e505. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhang J, Benavente CA, McEvoy J,
Flores-Otero J, Ding L, Chen X, Ulyanov A, Wu G, Wilson M, Wang J,
et al: A novel retinoblastoma therapy from genomic and epigenetic
analyses. Nature. 481:329–334. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Devesa SS: The incidence of
retinoblastoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 80:263–265. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bhagia P, Colanta AB, Abramson DH, Carlson
DL, Kleinerman RA, Kraus D and Dunkel IJ: Sinonasal adenocarcinoma:
a rare second malignancy in long term retinoblastoma survivors.
Pediatr Blood Cancer. 57:693–695. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Draf C, Schaberg MR, Anand VK, Nyquist G
and Hoda S: Radiation induced malignancy in retinoblastoma: new
pathology in a case report. Laryngoscope. 120(Suppl 4): S2382010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lohmann D: Retinoblastoma. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 685:220–227. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Abramson DH, Melson MR, Dunkel IJ and
Frank CM: Third (fourth and fifth) nonocular tumors in survivors of
retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology. 108:1868–1876. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Eng C, Li FP, Abramson DH, Ellsworth RM,
Wong FL, Goldman MB, Seddon J, Tarbell N and Boice JD Jr: Mortality
from second tumors among long-term survivors of retinoblastoma. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 85:1121–1128. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Di C, Liao S, Adamson DC, Parrett TJ,
Broderick DK, Shi Q, Lengauer C, Cummins JM, Velculescu VE, Fults
DW, et al: Identification of OTX2 as a medulloblastoma oncogene
whose product can be targeted by all-trans retinoic acid. Cancer
Res. 65:919–924. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Adamson DC, Shi Q, Wortham M, Northcott
PA, Di C, Duncan CG, Li J, McLendon RE, Bigner DD, Taylor MD, et
al: OTX2 is critical for the maintenance and progression of
Shh-independent medulloblastomas. Cancer Res. 70:181–191. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Mattox A, Li J, Di C and Adamson DC:
Medulloblastoma: role of OTX2 transcription factors. Tumors of the
Central Nervous System. 8. Hayat MA: Springer Science; 2012
|
|
13
|
Martinez-Morales JR, Dolez V, Rodrigo I,
Zaccarini R, Leconte L, Bovolenta P and Saule S: OTX2 activates the
molecular network underlying retina pigment epithelium
differentiation. J Biol Chem. 278:21721–21731. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nishida A, Furukawa A, Koike C, Tano Y,
Aizawa S, Matsuo I and Furukawa T: Otx2 homeobox gene controls
retinal photoreceptor cell fate and pineal gland development. Nat
Neurosci. 6:1255–1263. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sato S, Inoue T, Terada K, Matsuo I,
Aizawa S, Tano Y, Fujikado T and Furukawa T: Dkk3-Cre BAC
transgenic mouse line: a tool for highly efficient gene deletion in
retinal progenitor cells. Genesis. 45:502–507. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Elias WJ, Lopes MBS, Golden WL, Jane JA
and Gonzalez-Fernandez F: Trilateral retinoblastoma variant
indicative of the relevance of the retinoblastoma tumor-suppressor
pathway to medulloblastomas in humans. J Neurosurg. 95:871–878.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jurkiewicz E, Pakuła-Kościesza I,
Rutynowska O and Nowak K: Trilateral retinoblastoma: an
institutional experience and review of the literature. Child's
Nervous System. 26:129–132. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Mouratova T: Trilateral retinoblastoma: a
literature review, 1971–2004. Bull Soc Belge Ophtalmol. 297:25–35.
2005.
|
|
19
|
Jaffey PB, To GT, Xu HJ, Hu SX, Benedict
WF, Donoso LA and Campbell GA: Retinoblastoma-like phenotype
expressed in medulloblastomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
54:664–672. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Santagata S, Maire CL, Idbaih A, Geffers
L, Correll M, Holton K, Quackenbush J and Ligon KL: CRX is a
diagnostic marker of retinal and pineal lineage tumors. PLoS One.
4:e79322009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stephan H, Zakrzewski JL, Bölöni R,
Grasemann C, Lohmann DR and Eggert A: Neurotrophin receptor
expression in human primary retinoblastomas and retinoblastoma cell
lines. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 50:218–222. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Omori Y, Katoh K, Sato S, Muranishi Y,
Chaya T, Onishi A, Minami T, Fujikado T and Furukawa T: Analysis of
transcriptional regulatory pathways of photoreceptor genes by
expression profiling of the Otx2-deficient retina. PLoS One.
6:e196852011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bunt J, De Haas TG, Hasselt NE,
Zwijnenburg DA, Koster J, Versteeg R and Kool M: Regulation of cell
cycle genes and induction of senescence by overexpression of OTX2
in medulloblastoma cell lines. Mol Cancer Res. 8:1344–1357. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wong FL, Boice JD Jr, Abramson DH, Tarone
RE, Kleinerman RA, Stovall M, Goldman MB, Seddon JM, Tarbell N,
Fraumeni JF Jr, et al: Cancer incidence after retinoblastoma.
Radiation dose and sarcoma risk. JAMA. 278:1262–1267. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mohney BG, Robertson DM, Schomberg PJ and
Hodge DO: Second nonocular tumors in survivors of heritable
retinoblastoma and prior radiation therapy. Am J Ophthalmol.
126:269–277. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Smith LM, Donaldson SS, Egbert PR, Link MP
and Bagshaw MA: Aggressive management of second primary tumors in
survivors of hereditary retinoblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 17:499–505. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shields CL and Shields JA: Retinoblastoma
management: advances in enucleation, intravenous chemoreduction,
and intra-arterial chemotherapy. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 21:203–212.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mol BM, Massink MP, van der Hout AH,
Dommering CJ, Zaman JM, Bosscha MI, Kors WA, Meijers-Heijboer HE,
Kaspers GJ, Riele Ht, et al: High resolution SNP array profiling
identifies variability in retinoblastoma genome stability. Genes
Chromosomes Cancer. 53:1–14. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Glubrecht DD, Kim JH, Russell L, Bamforth
JS and Godbout R: Differential CRX and OTX2 expression in human
retina and retinoblastoma. J Neurochem. 111:250–263. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Furukawa T, Morrow EM and Cepko CL: Crx, a
novel otx-like homeobox gene, shows photoreceptor-specific
expression and regulates photoreceptor differentiation. Cell.
91:531–541. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nilsson JA and Cleveland JL: Myc pathways
provoking cell suicide and cancer. Oncogene. 22:9007–9021. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wiman K: The retinoblastoma gene: role in
cell cycle control and cell differentiation. FASEB J. 7:841–845.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Khanna H, Akimoto M, Siffroi-Fernandez S,
Friedman JS, Hicks D and Swaroop A: Retinoic acid regulates the
expression of photoreceptor transcription factor NRL. J Biol Chem.
281:27327–27334. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|