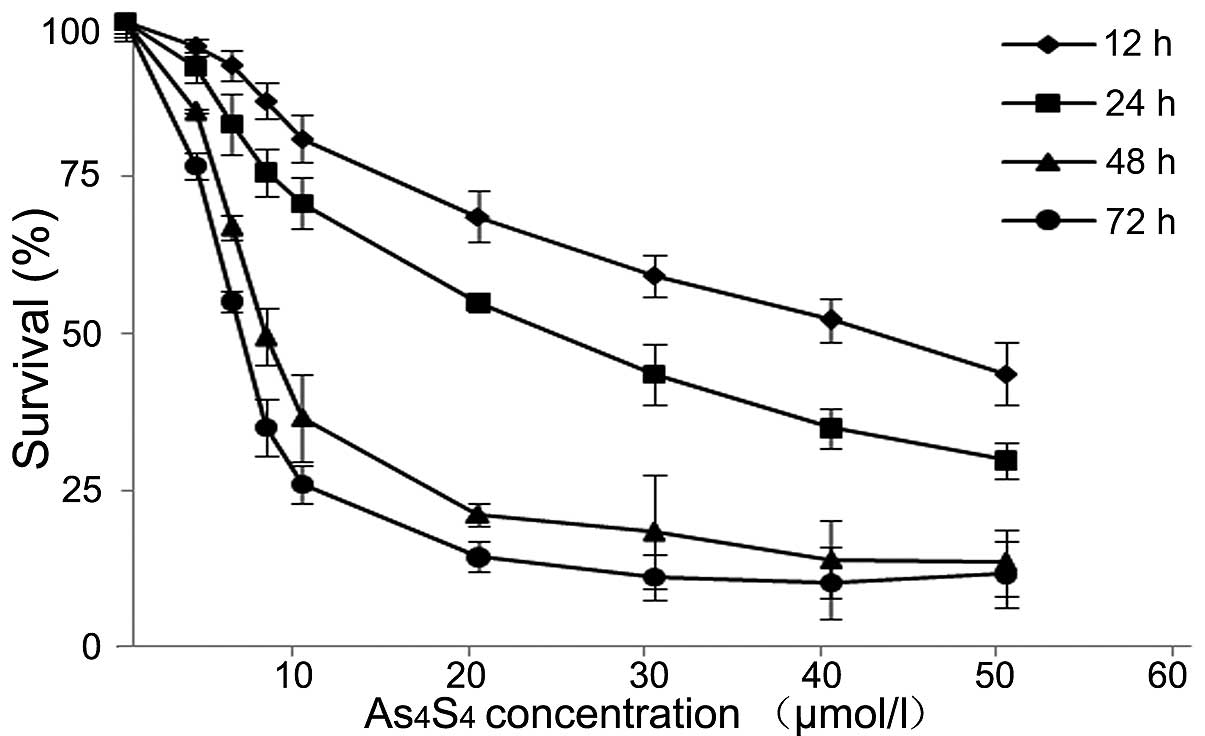
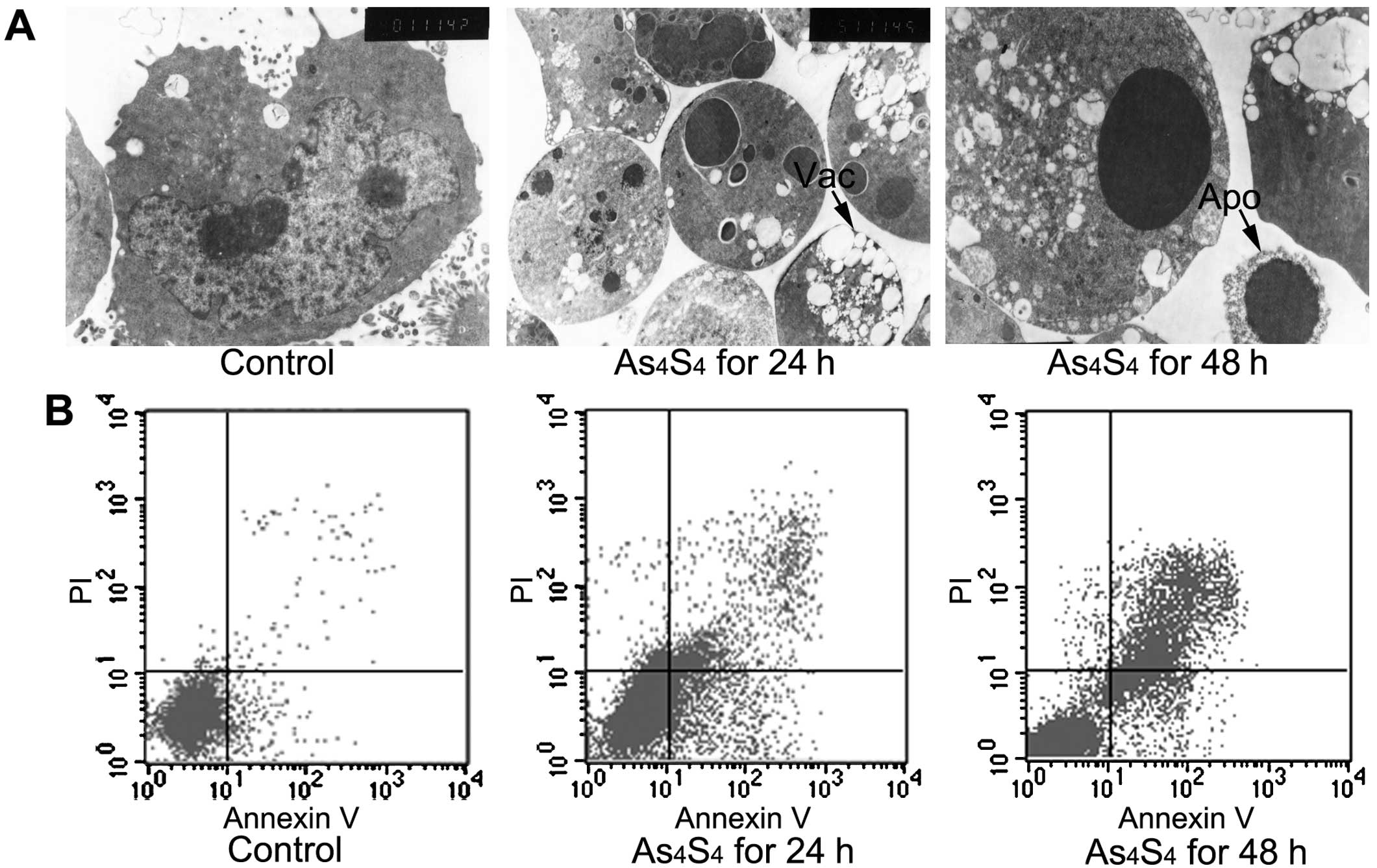
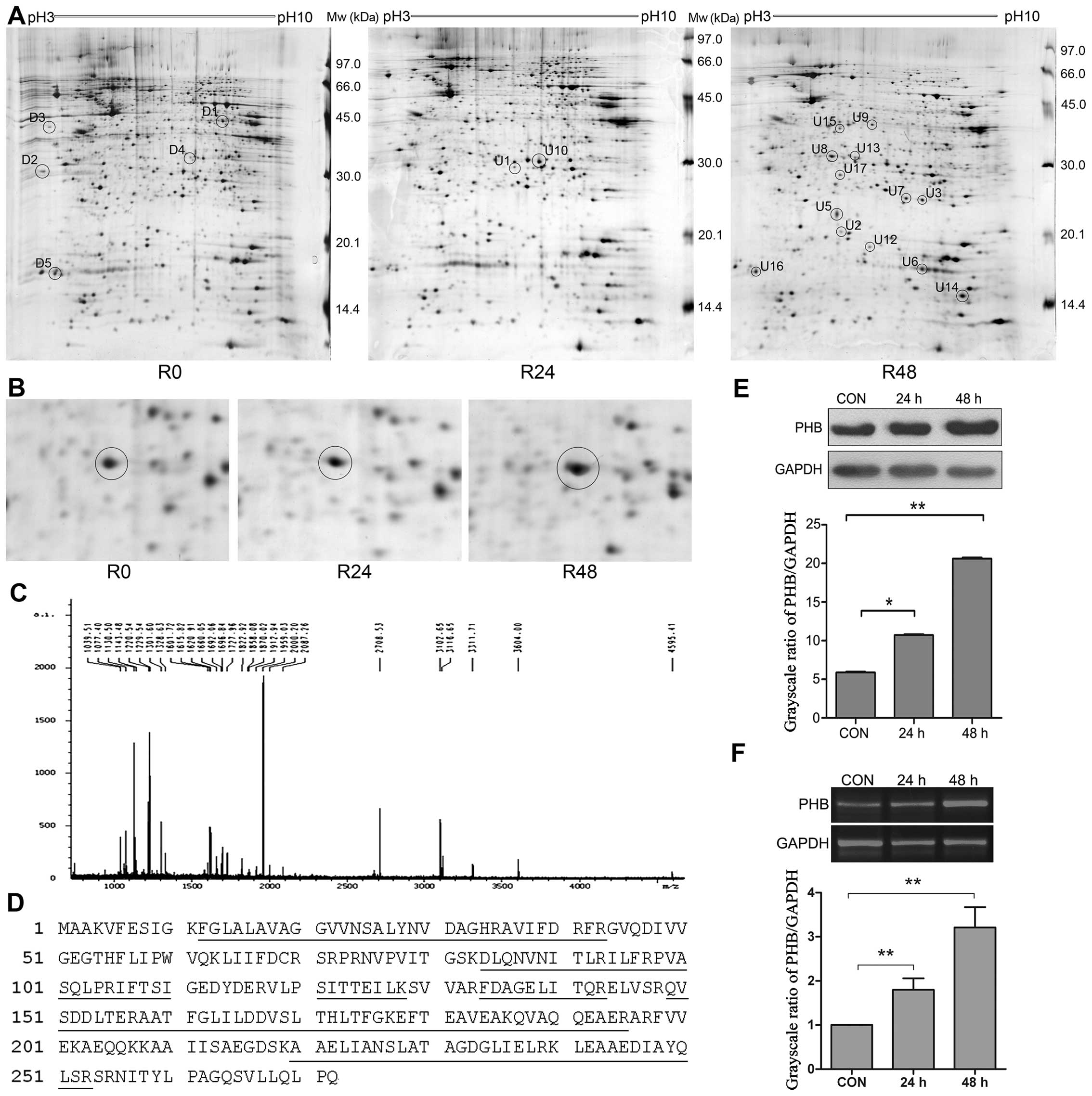
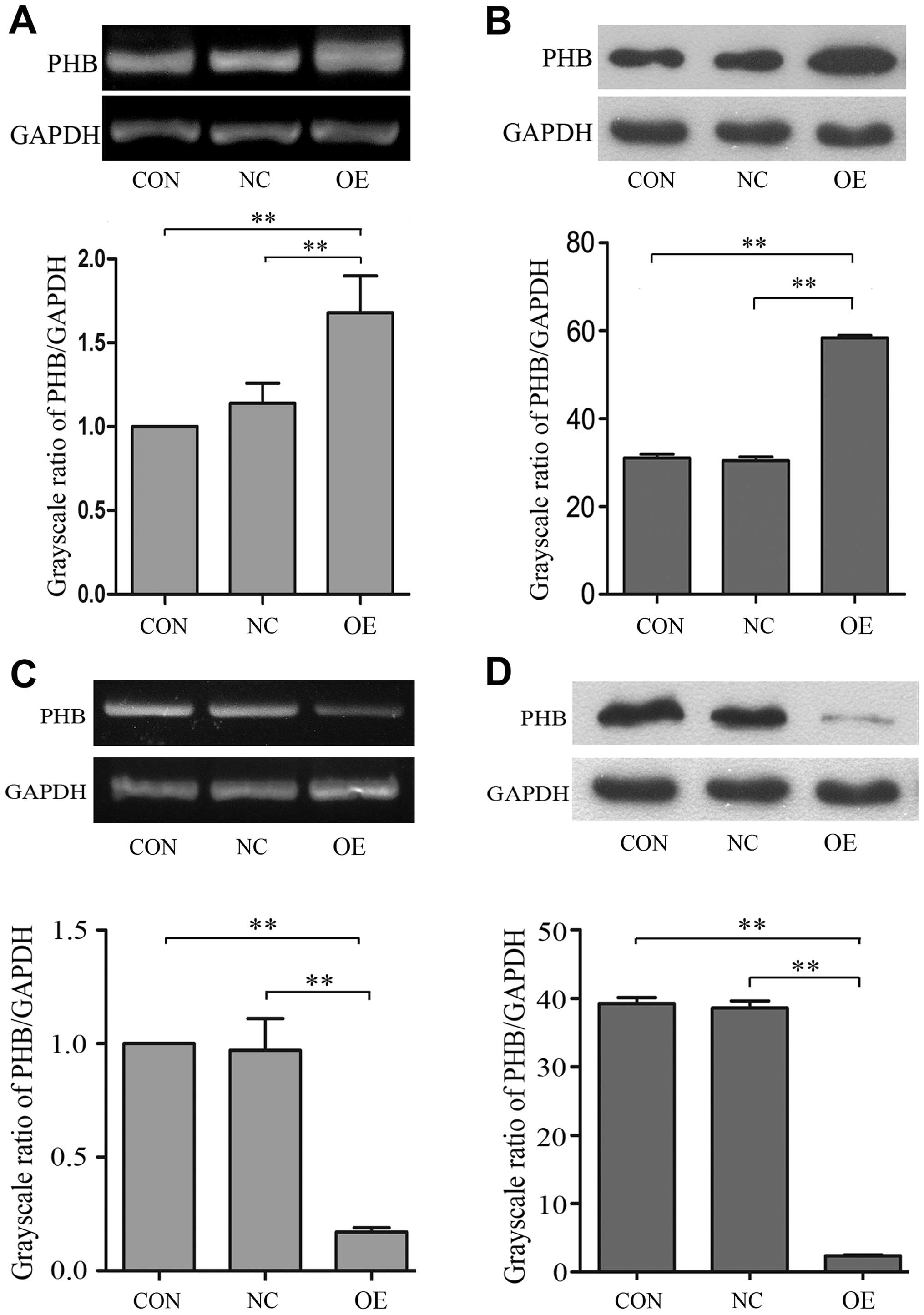
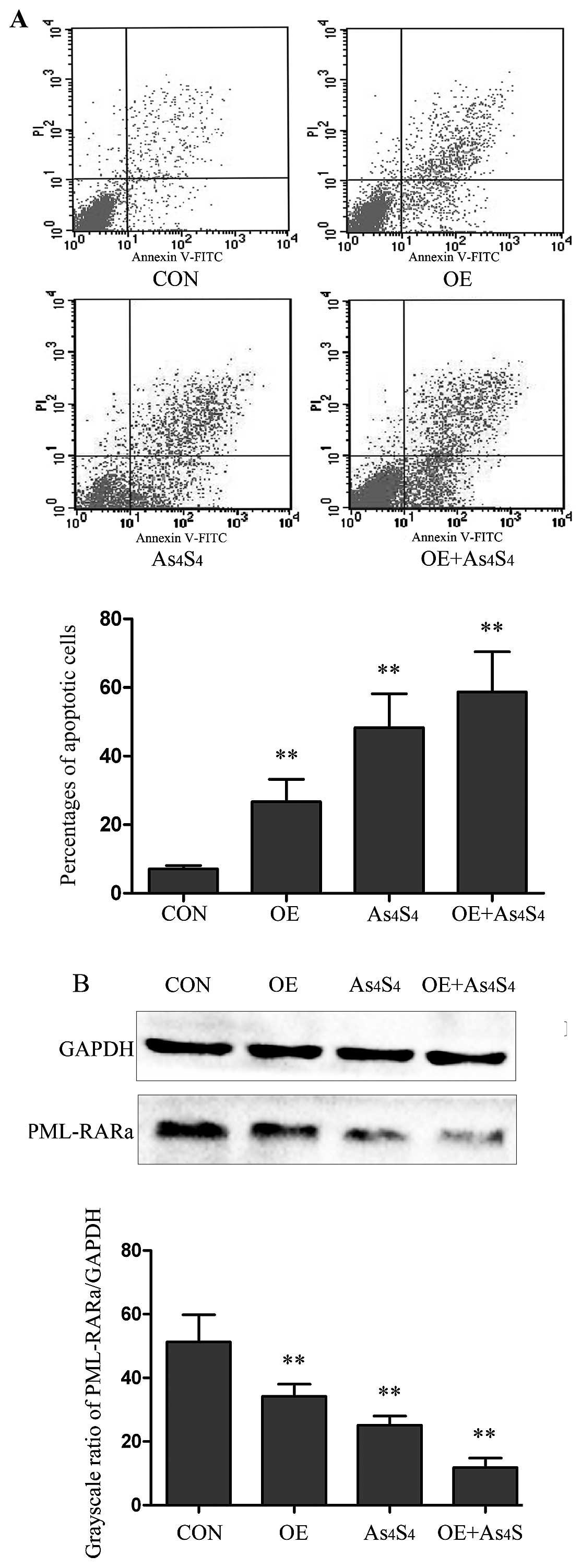
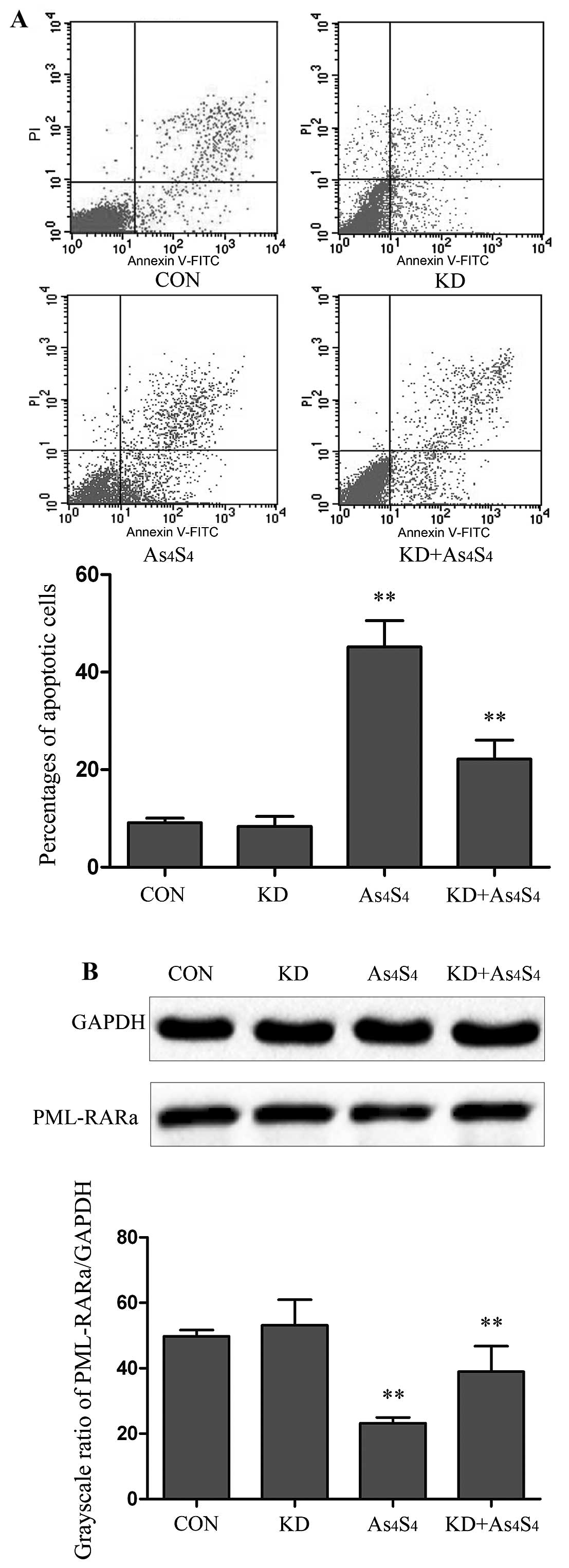
|
1
|
Sahin U, Lallemand-Breitenbach V and de
Thé H: PML nuclear bodies: Regulation, function and therapeutic
perspectives. J Pathol. 234:289–291. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rabellino A, Carter B, Konstantinidou G,
Wu SY, Rimessi A, Byers LA, Heymach JV, Girard L, Chiang CM,
Teruya-Feldstein J, et al: The SUMO E3-ligase PIAS1 regulates the
tumor suppressor PML and its oncogenic counterpart PML-RARA. Cancer
Res. 72:2275–2284. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Guo Y, Dolinko AV, Chinyengetere F,
Stanton B, Bomberger JM, Demidenko E, Zhou DC, Gallagher R, Ma T,
Galimberti F, et al: Blockade of the ubiquitin protease UBP43
destabilizes transcription factor PML/RARα and inhibits the growth
of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Cancer Res. 70:9875–9885. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
de Thé H and Chen Z: Acute promyelocytic
leukaemia: Novel insights into the mechanisms of cure. Nat Rev
Cancer. 10:775–783. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang ZY and Chen Z: Acute promyelocytic
leukemia: From highly fatal to highly curable. Blood.
111:2505–2515. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tomita A, Kiyoi H and Naoe T: Mechanisms
of action and resistance to all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and
arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in acute
promyelocytic leukemia. Int J Hematol. 97:717–725. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mathews V, George B, Lakshmi KM,
Viswabandya A, Bajel A, Balasubramanian P, Shaji RV, Srivastava VM,
Srivastava A and Chandy M: Single-agent arsenic trioxide in the
treatment of newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia: Durable
remissions with minimal toxicity. Blood. 107:2627–2632. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lengfelder E, Hofmann WK and Nowak D:
Impact of arsenic trioxide in the treatment of acute promyelocytic
leukemia. Leukemia. 26:433–442. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wu J, Shao Y, Liu J, Chen G and Ho PC: The
medicinal use of realgar (As4S4) and its
recent development as an anticancer agent. J Ethnopharmacol.
135:595–602. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lengfelder E, Hofmann WK and Nowak D:
Treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with arsenic trioxide:
Clinical results and open questions. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther.
13:1035–1043. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
van Meerloo J, Kaspers GJ and Cloos J:
Cell sensitivity assays: the MTT assay. Methods Mol Biol.
731:237–245. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Qian X, Dong H, Hu X, Tian H, Guo L, Shen
Q, Gao X and Yao W: Analysis of the interferences in quantitation
of a site-specifically PEGylated exendin-4 analog by the Bradford
method. Anal Biochem. 465:50–52. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rabilloud T and Lelong C: Two-dimensional
gel electrophoresis in proteomics: A tutorial. J Proteomics.
74:1829–1841. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dupont FM, Vensel WH, Tanaka CK, Hurkman
WJ and Altenbach SB: Deciphering the complexities of the wheat
flour proteome using quantitative two-dimensional electrophoresis,
three proteases and tandem mass spectrometry. Proteome Sci.
9:102011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lelong C, Chevallet M, Luche S and
Rabilloud T: Silver staining of proteins in 2DE gels. Methods Mol
Biol. 519:339–350. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Granvogl B, Plöscher M and Eichacker LA:
Sample preparation by in-gel digestion for mass spectrometry-based
proteomics. Anal Bioanal Chem. 389:991–1002. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu Y, He P, Zhang M and Wu D: Lentiviral
vector-mediated RNA interference targeted against prohibitin
inhibits apoptosis of the retinoic acid-resistant acute
promyelocytic leukemia cell line NB4-R1. Mol Med Rep. 6:1288–1292.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lu DP, Qiu JY, Jiang B, Wang Q, Liu KY,
Liu YR and Chen SS: Tetra-arsenic tetra-sulfide for the treatment
of acute promyelocytic leukemia: A pilot report. Blood.
99:3136–3143. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhu HH, Wu DP, Jin J, Li JY, Ma J, Wang
JX, Jiang H, Chen SJ and Huang XJ: Oral tetra-arsenic tetra-sulfide
formula versus intravenous arsenic trioxide as first-line treatment
of acute promyelocytic leukemia: A multicenter randomized
controlled trial. J Clin Oncol. 31:4215–4221. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu HH and Huang XJ: Oral arsenic and
retinoic acid for non-high-risk acute promyelocytic leukemia. N
Engl J Med. 371:2239–2241. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang L, Zhou GB, Liu P, Song JH, Liang Y,
Yan XJ, Xu F, Wang BS, Mao JH, Shen ZX, et al: Dissection of
mechanisms of Chinese medicinal formula Realgar-Indigo naturalis as
an effective treatment for promyelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 105:4826–4831. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen S, Fang Y, Ma L, Liu S and Li X:
Realgar-induced apoptosis and differentiation in all-trans retinoic
acid (ATRA)-sensitive NB4 and ATRA-resistant MR2 cells. Int J
Oncol. 40:1089–1096. 2012.
|
|
23
|
Zhou TB and Qin YH: Signaling pathways of
prohibitin and its role in diseases. J Recept Signal Transduct Res.
33:28–36. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rossi L, Bonuccelli L, Iacopetti P,
Evangelista M, Ghezzani C, Tana L and Salvetti A: Prohibitin 2
regulates cell proliferation and mitochondrial cristae
morphogenesis in planarian stem cells. Stem Cell Rev. 10:871–887.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu YH, Peck K and Lin JY: Involvement of
prohibitin upregulation in abrin-triggered apoptosis. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2012:6051542012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Puppin C, Passon N, Franzoni A, Russo D
and Damante G: Histone deacetylase inhibitors control the
transcription and alternative splicing of prohibitin in thyroid
tumor cells. Oncol Rep. 25:393–397. 2011.
|
|
27
|
Joshi B, Ko D, Ordonez-Ercan D and
Chellappan SP: A putative coiled-coil domain of prohibitin is
sufficient to repress E2F1-mediated transcription and induce
apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 312:459–466. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chander H, Halpern M, Resnick-Silverman L,
Manfredi JJ and Germain D: Skp2B attenuates p53 function by
inhibiting prohibitin. EMBO Rep. 11:220–225. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Joshi B, Rastogi S, Morris M, Carastro LM,
DeCook C, Seto E and Chellappan SP: Differential regulation of
human YY1 and caspase 7 promoters by prohibitin through E2F1 and
p53 binding sites. Biochem J. 401:155–166. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Wang S, Fusaro G, Padmanabhan J and
Chellappan SP: Prohibitin co-localizes with Rb in the nucleus and
recruits N-CoR and HDAC1 for transcriptional repression. Oncogene.
21:8388–8396. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rajalingam K, Wunder C, Brinkmann V,
Churin Y, Hekman M, Sievers C, Rapp UR and Rudel T: Prohibitin is
required for Ras-induced Raf-MEK-ERK activation and epithelial cell
migration. Nat Cell Biol. 7:837–843. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang S and Faller DV: Roles of prohibitin
in growth control and tumor suppression in human cancers. Transl
Oncogenomics. 3:23–37. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dart DA, Spencer-Dene B, Gamble SC, Waxman
J and Bevan CL: Manipulating prohibitin levels provides evidence
for an in vivo role in androgen regulation of prostate tumours.
Endocr Relat Cancer. 16:1157–1169. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang Y, Chen Y, Qu C, Zhou M, Ni Q and Xu
L: siRNA targeting prohibitins inhibits proliferation and promotes
apoptosis of gastric carcinoma cell line SGC7901 in vitro and in
vivo. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 60:26–32. 2014.
|
|
35
|
Jia L, Ren JM, Wang YY, Zheng Y, Zhang H,
Zhang Q, Kong BH and Zheng WX: Inhibitory role of prohibitin in
human ovarian epithelial cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:2247–2255. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Theiss AL and Sitaraman SV: The role and
therapeutic potential of prohibitin in disease. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1813:1137–1143. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rajalingam K and Rudel T: Ras-Raf
signaling needs prohibitin. Cell Cycle. 4:1503–1505. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chowdhury I, Thompson WE and Thomas K:
Prohibitins role in cellular survival through Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK
pathway. J Cell Physiol. 229:998–1004. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Song W, Tian L, Li SS, Shen DY and Chen
QX: The aberrant expression and localization of prohibitin during
apoptosis of human cholangiocarcinoma Mz-ChA-1 cells. FEBS Lett.
588:422–428. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhou GB, Zhang J, Wang ZY, Chen SJ and
Chen Z: Treatment of acute promyelocytic leukaemia with all-trans
retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide: A paradigm of synergistic
molecular targeting therapy. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci.
362:959–971. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shinagawa K: All-trans retinoic acid and
arsenic trioxide: Their molecular mechanisms of action and updated
clinical progress in APL therapy. Rinsho Ketsueki. 52:469–483.
2011.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|