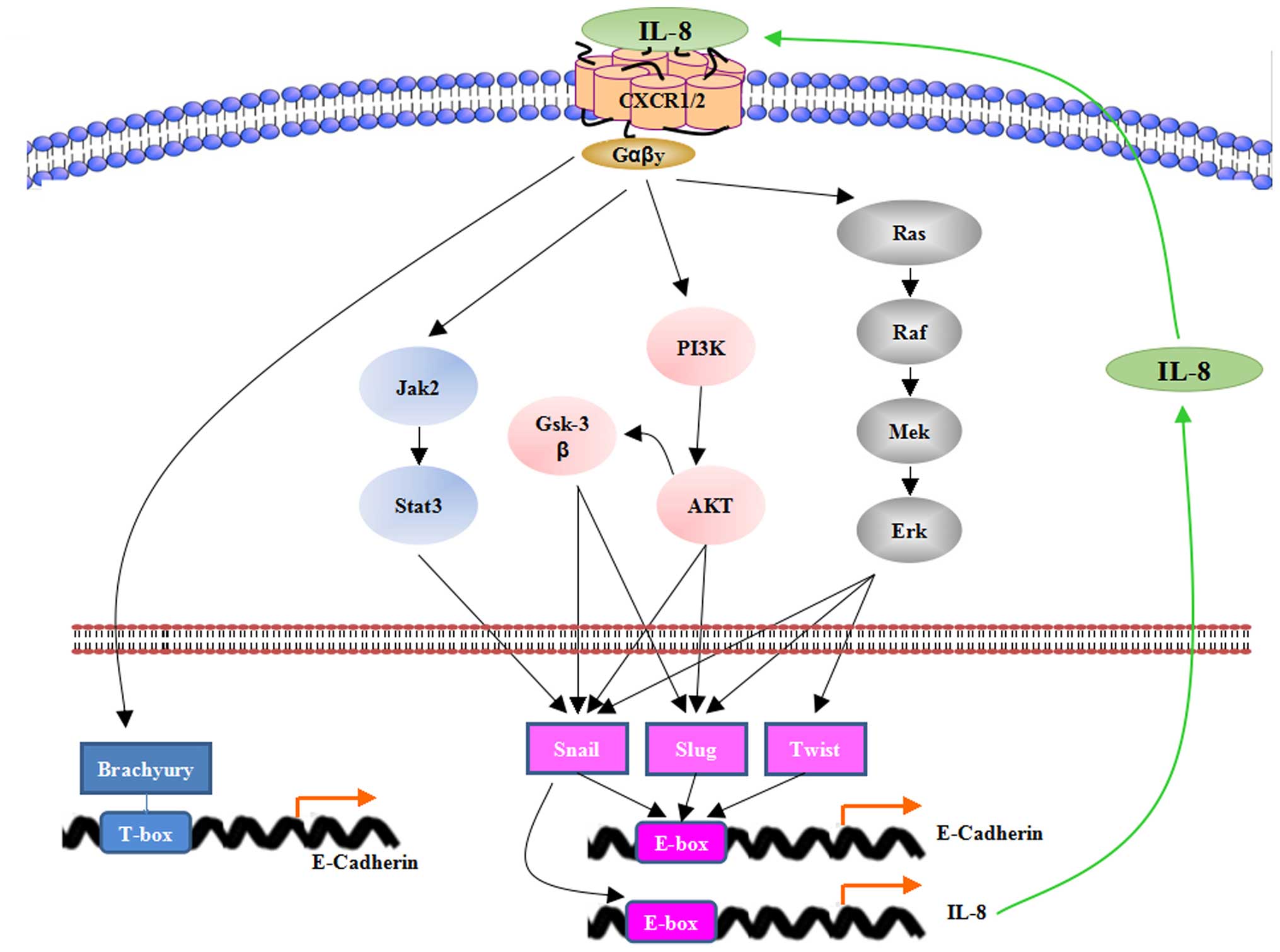
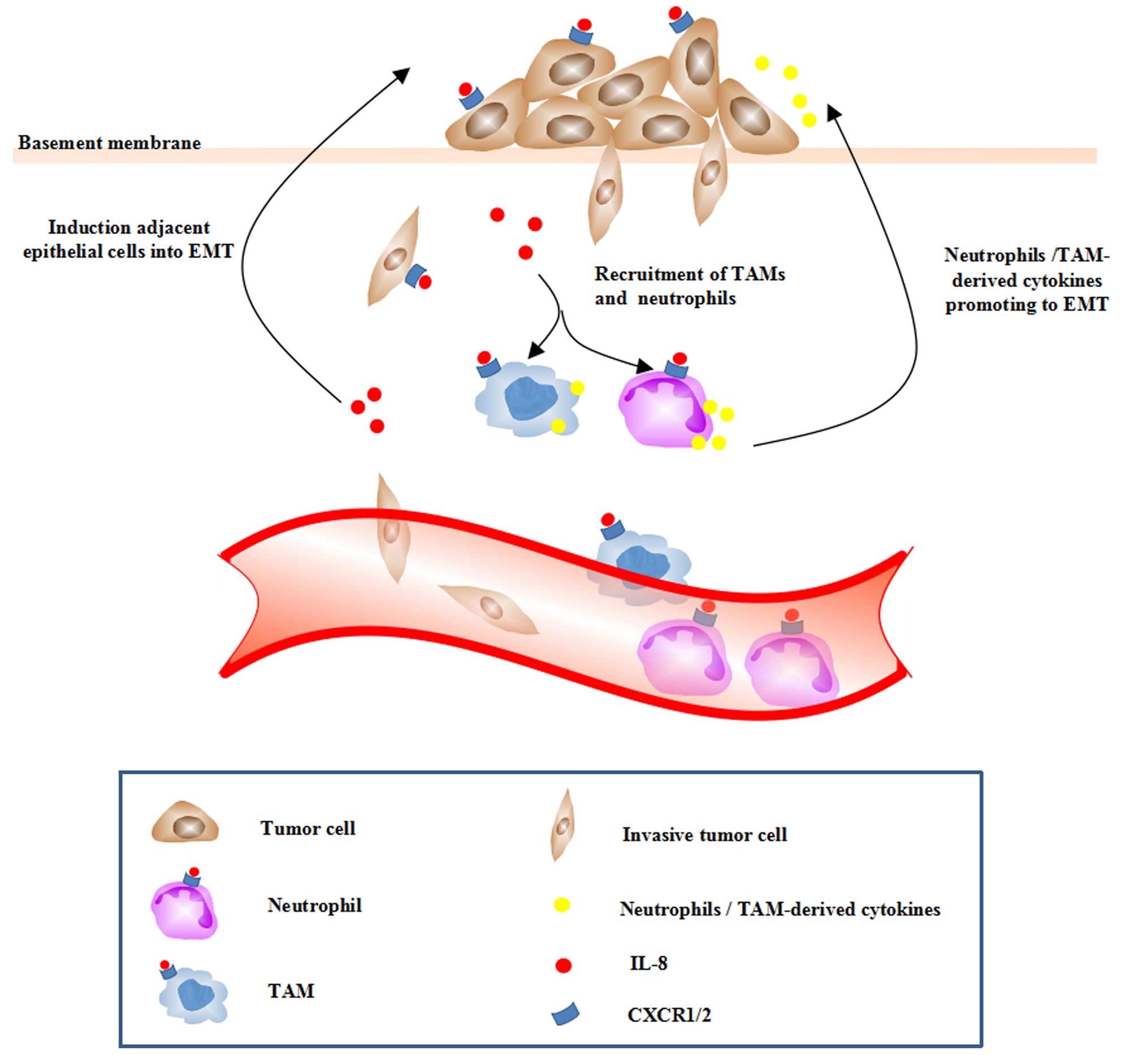
|
1
|
Catalano V, Turdo A, Di Franco S, Dieli F,
Todaro M and Stassi G: Tumor and its microenvironment: A
synergistic interplay. Semin Cancer Biol. 23B:522–532. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hsu M, Wu SY, Chang SS, Su IJ, Tsai CH,
Lai SJ, Shiau AL, Takada K and Chang Y: Epstein-Barr virus lytic
transactivator Zta enhances chemotactic activity through induction
of interleukin-8 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. J Virol.
82:3679–3688. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu Y, Deng J, Rychahou PG, Qiu S, Evers BM
and Zhou BP: Stabilization of snail by NF-kappaB is required for
inflammation-induced cell migration and invasion. Cancer Cell.
15:416–428. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, et al: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sabbah M, Emami S, Redeuilh G, Julien S,
Prévost G, Zimber A, Ouelaa R, Bracke M, De Wever O and Gespach C:
Molecular signature and therapeutic perspective of the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions in epithelial cancers. Drug
Resist Updat. 11:123–151. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Micalizzi DS, Farabaugh SM and Ford HL:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer: Parallels between
normal development and tumor progression. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 15:117–134. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guarino M, Rubino B and Ballabio G: The
role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer pathology.
Pathology. 39:305–318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gravdal K, Halvorsen OJ, Haukaas SA and
Akslen LA: A switch from E-cadherin to N-cadherin expression
indicates epithelial to mesenchymal transition and is of strong and
independent importance for the progress of prostate cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 13:7003–7011. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sawada K, Mitra AK, Radjabi AR, Bhaskar V,
Kistner EO, Tretiakova M, Jagadeeswaran S, Montag A, Becker A,
Kenny HA, et al: Loss of E-cadherin promotes ovarian cancer
metastasis via alpha 5-integrin, which is a therapeutic target.
Cancer Res. 68:2329–2339. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhao ZL, Ma SR, Wang WM, Huang CF, Yu GT,
Wu TF, Bu LL, Wang YF, Zhao YF, Zhang WF, et al: Notch signaling
induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition to promote invasion and
metastasis in adenoid cystic carcinoma. Am J Transl Res. 7:162–174.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sarrió D, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Hardisson
D, Cano A, Moreno-Bueno G and Palacios J: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in breast cancer relates to the basal-like phenotype.
Cancer Res. 68:989–997. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fan QM, Jing YY, Yu GF, Kou XR, Ye F, Gao
L, Li R, Zhao QD, Yang Y, Lu ZH, et al: Tumor-associated
macrophages promote cancer stem cell-like properties via
transforming growth factor-beta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 352:160–168.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Javle MM, Gibbs JF, Iwata KK, Pak Y,
Rutledge P, Yu J, Black JD, Tan D and Khoury T:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and activated extracellular
signal-regulated kinase (p-Erk) in surgically resected pancreatic
cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 14:3527–3533. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Horiguchi K, Sakamoto K, Koinuma D, Semba
K, Inoue A, Inoue S, Fujii H, Yamaguchi A, Miyazawa K, Miyazono K,
et al: TGF-β drives epithelial-mesenchymal transition through
δEF1-mediated downregulation of ESRP. Oncogene. 31:3190–3201. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Matsushima K, Baldwin ET and Mukaida N:
Interleukin-8 and MCAF: Novel leukocyte recruitment and activating
cytokines. Chem Immunol. 51:236–265. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Brat DJ, Bellail AC and Van Meir EG: The
role of interleukin-8 and its receptors in gliomagenesis and
tumoral angiogenesis. Neuro-oncol. 7:122–133. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xie K: Interleukin-8 and human cancer
biology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 12:375–391. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nasser MW, Raghuwanshi SK, Grant DJ, Jala
VR, Rajarathnam K and Richardson RM: Differential activation and
regulation of CXCR1 and CXCR2 by CXCL8 monomer and dimer. J
Immunol. 183:3425–3432. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stillie R, Farooq SM, Gordon JR and
Stadnyk AW: The functional significance behind expressing two IL-8
receptor types on PMN. J Leukoc Biol. 86:529–543. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Murphy PM: The molecular biology of
leukocyte chemoattractant receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 12:593–633.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Balkwill F: Cancer and the chemokine
network. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:540–550. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Végran F, Boidot R, Michiels C, Sonveaux P
and Feron O: Lactate influx through the endothelial cell
monocarboxylate transporter MCT1 supports an NF-κB/IL-8 pathway
that drives tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 71:2550–2560. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Araki S, Omori Y, Lyn D, Singh RK,
Meinbach DM, Sandman Y, Lokeshwar VB and Lokeshwar BL:
Interleukin-8 is a molecular determinant of androgen independence
and progression in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 67:6854–6862. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Millar HJ, Nemeth JA, McCabe FL, Pikounis
B and Wickstrom E: Circulating human interleukin-8 as an indicator
of cancer progression in a nude rat orthotopic human non-small cell
lung carcinoma model. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
17:2180–2187. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rofstad EK and Halsør EF: Vascular
endothelial growth factor, interleukin 8, platelet-derived
endothelial cell growth factor, and basic fibroblast growth factor
promote angiogenesis and metastasis in human melanoma xenografts.
Cancer Res. 60:4932–4938. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shahzad MM, Arevalo JM, Armaiz-Pena GN, Lu
C, Stone RL, Moreno-Smith M, Nishimura M, Lee JW, Jennings NB,
Bottsford-Miller J, et al: Stress effects on FosB- and
interleukin-8 (IL8)-driven ovarian cancer growth and metastasis. J
Biol Chem. 285:35462–35470. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ahmed OI, Adel AM, Diab DR and Gobran NS:
Prognostic value of serum level of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8
in metastatic breast cancer patients. Egypt J Immunol. 13:61–68.
2006.
|
|
31
|
Shahzad A, Knapp M, Lang I and Köhler G:
Interleukin 8 (IL-8) - a universal biomarker? Int Arch Med.
3:112010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pine SR, Mechanic LE, Enewold L,
Chaturvedi AK, Katki HA, Zheng YL, Bowman ED, Engels EA, Caporaso
NE and Harris CC: Increased levels of circulating interleukin 6,
interleukin 8, C-reactive protein, and risk of lung cancer. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 103:1112–1122. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gabellini C, Trisciuoglio D, Desideri M,
Candiloro A, Ragazzoni Y, Orlandi A, Zupi G and Del Bufalo D:
Functional activity of CXCL8 receptors, CXCR1 and CXCR2, on human
malignant melanoma progression. Eur J Cancer. 45:2618–2627. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cullen BR: MicroRNAs as mediators of viral
evasion of the immune system. Nat Immunol. 14:205–210. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen L, Min L, Wang X, Zhao J, Chen H, Qin
J, Chen W, Shen Z, Tang Z, Gan Q, et al: Loss of RACK1 Promotes
Metastasis of Gastric Cancer by Inducing a miR-302c/IL8 Signaling
Loop. Cancer Res. 75:3832–3841. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Qu JQ, Yi HM, Ye X, Zhu JF, Yi H, Li LN,
Xiao T, Yuan L, Li JY, Wang YY, et al: MiRNA-203 reduces
nasopharyngeal carcinoma radioresistance by targeting IL-8/AKT
signaling. Mol Cancer Ther. Aug 24–2015.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Qu JQ, Yi HM, Ye X, Li LN, Zhu JF, Xiao T,
Yuan L, Li JY, Wang YY, Feng J, et al: MiR-23a sensitizes
nasopharyngeal carcinoma to irradiation by targeting IL-8/Stat3
pathway. Oncotarget. 6:28341–28356. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Van der Goten J, Vanhove W, Lemaire K, Van
Lommel L, Machiels K, Wollants WJ, De Preter V, De Hertogh G,
Ferrante M, Van Assche G, et al: Integrated miRNA and mRNA
expression profiling in inflamed colon of patients with ulcerative
colitis. PLoS One. 9:e1161172014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Oglesby IK, Vencken SF, Agrawal R, Gaughan
K, Molloy K, Higgins G, McNally P, McElvaney NG, Mall MA and Greene
CM: miR-17 overexpression in cystic fibrosis airway epithelial
cells decreases interleukin-8 production. Eur Respir J
ERJ-01634-2014. 2015.
|
|
40
|
Mei Q, Xue G, Li X, Wu Z, Li X, Yan H, Guo
M, Sun S and Han W: Methylation-induced loss of miR-484 in
microsatellite-unstable colorectal cancer promotes both viability
and IL-8 production via CD137L. J Pathol. 236:165–174. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li L, Liu Y, Guo Y, Liu B, Zhao Y, Li P,
Song F, Zheng H, Yu J, Song T, et al: Regulatory miR-148a-ACVR1/BMP
circuit defines a cancer stem cell-like aggressive subtype of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 61:574–584. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ding XM: MicroRNAs: Regulators of cancer
metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Chin J
Cancer. 33:140–147. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
43
|
Sun Y, Guo F, Bagnoli M, Xue FX, Sun BC,
Shmulevich I, Mezzanzanica D, Chen KX, Sood AK, Yang D, et al: Key
nodes of a microRNA network associated with the integrated
mesenchymal subtype of high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Chin J
Cancer. 34:28–40. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Scheel C, Eaton EN, Li SH, Chaffer CL,
Reinhardt F, Kah KJ, Bell G, Guo W, Rubin J, Richardson AL, et al:
Paracrine and autocrine signals induce and maintain mesenchymal and
stem cell states in the breast. Cell. 145:926–940. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fernando RI, Litzinger M, Trono P,
Hamilton DH, Schlom J and Palena C: The T-box transcription factor
Brachyury promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human tumor
cells. J Clin Invest. 120:533–544. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hwang WL, Yang MH, Tsai ML, Lan HY, Su SH,
Chang SC, Teng HW, Yang SH, Lan YT, Chiou SH, et al: SNAIL
regulates interleukin-8 expression, stem cell-like activity, and
tumorigenicity of human colorectal carcinoma cells.
Gastroenterology. 141:279–291. 2912011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
MacManus CF, Pettigrew J, Seaton A, Wilson
C, Maxwell PJ, Berlingeri S, Purcell C, McGurk M, Johnston PG and
Waugh DJ: Interleukin-8 signaling promotes translational regulation
of cyclin D in androgen-independent prostate cancer cells. Mol
Cancer Res. 5:737–748. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li XJ, Peng LX, Shao JY, Lu WH, Zhang JX,
Chen S, Chen ZY, Xiang YQ, Bao YN, Zheng FJ, et al: As an
independent unfavorable prognostic factor, IL-8 promotes metastasis
of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through induction of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and activation of AKT signaling.
Carcinogenesis. 33:1302–1309. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Visciano C, Liotti F, Prevete N, Cali' G,
Franco R, Collina F, de Paulis A, Marone G, Santoro M and Melillo
RM: Mast cells induce epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stem
cell features in human thyroid cancer cells through an
IL-8-Akt-Slug pathway. Oncogene. 34:5175–5186. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mannoury la Cour C, Salles MJ, Pasteau V
and Millan MJ: Signaling pathways leading to phosphorylation of Akt
and GSK-3β by activation of cloned human and rat cerebral
D2 and D3 receptors. Mol Pharmacol.
79:91–105. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Kim JY, Kim YM, Yang CH, Cho SK, Lee JW
and Cho M: Functional regulation of Slug/Snail2 is dependent on
GSK-3β-mediated phosphorylation. FEBS J. 279:2929–2939. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Knall C, Young S, Nick JA, Buhl AM,
Worthen GS and Johnson GL: Interleukin-8 regulation of the
Ras/Raf/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in human
neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 271:2832–2838. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Nagarajan D, Melo T, Deng Z, Almeida C and
Zhao W: ERK/GSK3β/Snail signaling mediates radiation-induced
alveolar epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Free Radic Biol Med.
52:983–992. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
54
|
Weiss MB, Abel EV, Mayberry MM, Basile KJ,
Berger AC and Aplin AE: TWIST1 is an ERK1/2 effector that promotes
invasion and regulates MMP-1 expression in human melanoma cells.
Cancer Res. 72:6382–6392. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Fu XT, Dai Z, Song K, Zhang ZJ, Zhou ZJ,
Zhou SL, Zhao YM, Xiao YS, Sun QM, Ding ZB, et al:
Macrophage-secreted IL-8 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activating the
JAK2/STAT3/Snail pathway. Int J Oncol. 46:587–596. 2015.
|
|
56
|
Fernando RI, Castillo MD, Litzinger M,
Hamilton DH and Palena C: IL-8 signaling plays a critical role in
the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human carcinoma cells.
Cancer Res. 71:5296–5306. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Techasen A, Loilome W, Namwat N, Dokduang
H, Jongthawin J and Yongvanit P: Cytokines released from activated
human macrophages induce epithelial mesenchymal transition markers
of cholangiocarcinoma cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13(Suppl):
S115–S118. 2012.
|
|
58
|
Katsuno Y, Lamouille S and Derynck R:
TGF-β signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer
progression. Curr Opin Oncol. 25:76–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Zhang H, Liu L, Wang Y, Zhao G, Xie R, Liu
C, Xiao X, Wu K, Nie Y, Zhang H, et al: KLF8 involves in
TGF-beta-induced EMT and promotes invasion and migration in gastric
cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 139:1033–1042. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wendt MK, Allington TM and Schiemann WP:
Mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by TGF-beta.
Future Oncol. 5:1145–1168. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Peinado H, Olmeda D and Cano A: Snail, Zeb
and bHLH factors in tumour progression: An alliance against the
epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 7:415–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Bonde AK, Tischler V, Kumar S, Soltermann
A and Schwendener RA: Intratumoral macrophages contribute to
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in solid tumors. BMC Cancer.
12:352012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Yu Y, Xiao CH, Tan LD, Wang QS, Li XQ and
Feng YM: Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells through
paracrine TGF-β signalling. Br J Cancer. 110:724–732. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
64
|
Henson ES and Gibson SB: Surviving cell
death through epidermal growth factor (EGF) signal transduction
pathways: Implications for cancer therapy. Cell Signal.
18:2089–2097. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Barr S, Thomson S, Buck E, Russo S, Petti
F, Sujka-Kwok I, Eyzaguirre A, Rosenfeld-Franklin M, Gibson NW,
Miglarese M, et al: Bypassing cellular EGF receptor dependence
through epithelial-to-mesenchymal-like transitions. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 25:685–693. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Clapéron A, Mergey M, Nguyen Ho-Bouldoires
TH, Vignjevic D, Wendum D, Chrétien Y, Merabtene F, Frazao A,
Paradis V, Housset C, et al: EGF/EGFR axis contributes to the
progression of cholangiocarcinoma through the induction of an
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Hepatol. 61:325–332. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Sullivan NJ, Sasser AK, Axel AE, Vesuna F,
Raman V, Ramirez N, Oberyszyn TM and Hall BM: Interleukin-6 induces
an epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in human breast
cancer cells. Oncogene. 28:2940–2947. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Rojas A, Liu G, Coleman I, Nelson PS,
Zhang M, Dash R, Fisher PB, Plymate SR and Wu JD: IL-6 promotes
prostate tumorigenesis and progression through autocrine
cross-activation of IGF-IR. Oncogene. 30:2345–2355. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Xiong H, Hong J, Du W, Lin YW, Ren LL,
Wang YC, Su WY, Wang JL, Cui Y, Wang ZH, et al: Roles of STAT3 and
ZEB1 proteins in E-cadherin down-regulation and human colorectal
cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem.
287:5819–5832. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
70
|
Liu RY, Zeng Y, Lei Z, Wang L, Yang H, Liu
Z, Zhao J and Zhang HT: JAK/STAT3 signaling is required for
TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer
cells. Int J Oncol. 44:1643–1651. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Shih JY and Yang PC: The EMT regulator
slug and lung carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 32:1299–1304. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Dohadwala M, Wang G, Heinrich E, Luo J,
Lau O, Shih H, Munaim Q, Lee G, Hong L and Lai C: The role of ZEB1
in the inflammation-induced promotion of EMT in HNSCC. Otolaryngol
Head Neck Surg. 142:753–759. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
St John MA, Dohadwala M, Luo J, Wang G,
Lee G, Shih H, Heinrich E, Krysan K, Walser T, Hazra S, et al:
Proinflammatory mediators upregulate snail in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:6018–6027. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Petrella BL, Armstrong DA and Vincenti MP:
Interleukin-1 beta and transforming growth factor-beta 3 cooperate
to activate matrix metalloproteinase expression and invasiveness in
A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 325:220–226. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Balkwill F: Tumour necrosis factor and
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:361–371. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Wu ST, Sun GH, Hsu CY, Huang CS, Wu YH,
Wang HH and Sun KH: Tumor necrosis factor-α induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal cell carcinoma cells via
a nuclear factor kappa B-independent mechanism. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 236:1022–1029. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Schraufstatter IU, Zhao M, Khaldoyanidi SK
and Discipio RG: The chemokine CCL18 causes maturation of cultured
monocytes to macrophages in the M2 spectrum. Immunology.
135:287–298. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
78
|
Chen P, Li K, Liang Y, Li L and Zhu X:
High NUAK1 expression correlates with poor prognosis and involved
in NSCLC cells migration and invasion. Exp Lung Res. 39:9–17. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Zhang B, Yin C, Li H, Shi L, Liu N, Sun Y,
Lu S, Liu Y, Sun L, Li X, et al: Nir1 promotes invasion of breast
cancer cells by binding to chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 18 through
the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β/Snail signalling pathway. Eur J Cancer.
49:3900–3913. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Grosse-Steffen T, Giese T, Giese N,
Longerich T, Schirmacher P, Hänsch GM and Gaida MM:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma and pancreatic tumor cell lines: The role of
neutrophils and neutrophil–derived elastase. Clin Dev Immunol.
2012:7207682012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Inoue K, Slaton JW, Eve BY, Kim SJ,
Perrotte P, Balbay MD, Yano S, Bar-Eli M, Radinsky R, Pettaway CA,
et al: Interleukin 8 expression regulates tumorigenicity and
metastases in androgen-independent prostate cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 6:2104–2119. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Kitadai Y, Haruma K, Mukaida N, Ohmoto Y,
Matsutani N, Yasui W, Yamamoto S, Sumii K, Kajiyama G, Fidler IJ,
et al: Regulation of disease-progression genes in human gastric
carcinoma cells by interleukin 8. Clin Cancer Res. 6:2735–2740.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Jamieson T, Clarke M, Steele CW, Samuel
MS, Neumann J, Jung A, Huels D, Olson MF, Das S, Nibbs RJ, et al:
Inhibition of CXCR2 profoundly suppresses inflammation-driven and
spontaneous tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest. 122:3127–3144. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Lee YS, Choi I, Ning Y, Kim NY,
Khatchadourian V, Yang D, Chung HK, Choi D, LaBonte MJ, Ladner RD,
et al: Interleukin-8 and its receptor CXCR2 in the tumour
microenvironment promote colon cancer growth, progression and
metastasis. Br J Cancer. 106:1833–1841. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Yang G, Rosen DG, Liu G, Yang F, Guo X,
Xiao X, Xue F, Mercado-Uribe I, Huang J, Lin SH, et al: CXCR2
promotes ovarian cancer growth through dysregulated cell cycle,
diminished apoptosis, and enhanced angiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res.
16:3875–3886. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Tazzyman S, Barry ST, Ashton S, Wood P,
Blakey D, Lewis CE and Murdoch C: Inhibition of neutrophil
infiltration into A549 lung tumors in vitro and in vivo using a
CXCR2-specific antagonist is associated with reduced tumor growth.
Int J Cancer. 129:847–858. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Singh JK, Farnie G, Bundred NJ, Simões BM,
Shergill A, Landberg G, Howell SJ and Clarke RB: Targeting CXCR1/2
significantly reduces breast cancer stem cell activity and
increases the efficacy of inhibiting HER2 via HER2-dependent and
-independent mechanisms. Clin Cancer Res. 19:643–656. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Grund EM, Kagan D, Tran CA, Zeitvogel A,
Starzinski-Powitz A, Nataraja S and Palmer SS: Tumor necrosis
factor-alpha regulates inflammatory and mesenchymal responses via
mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, p38, and nuclear factor
kappaB in human endometriotic epithelial cells. Mol Pharmacol.
73:1394–1404. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|