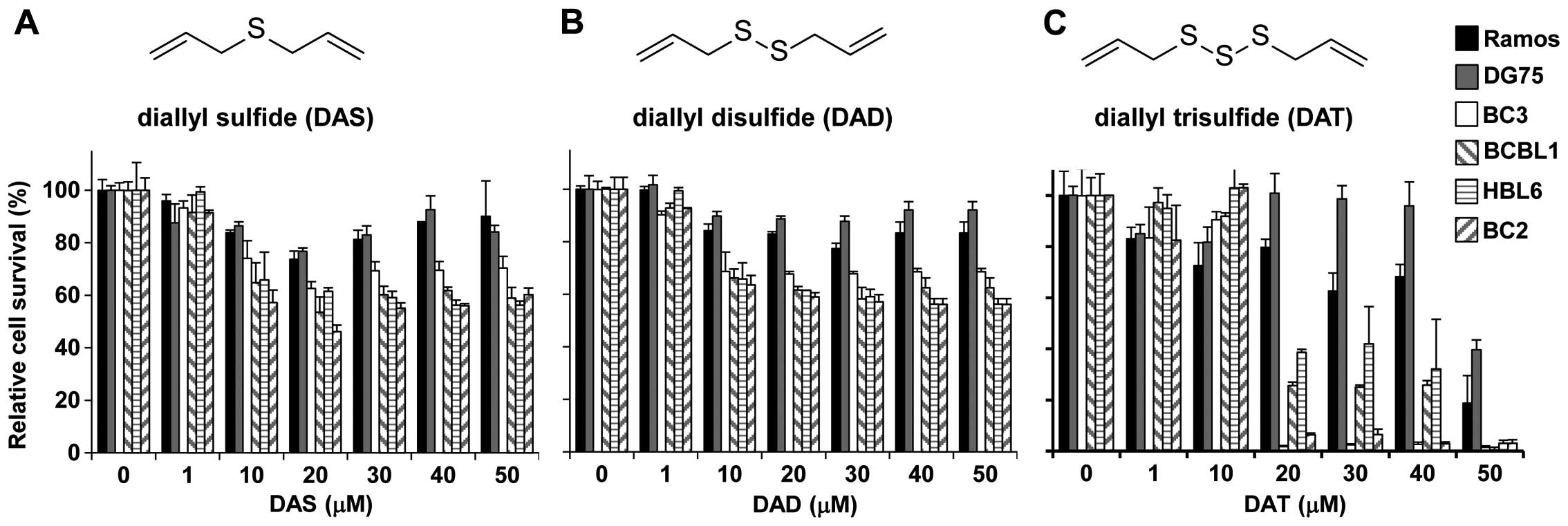
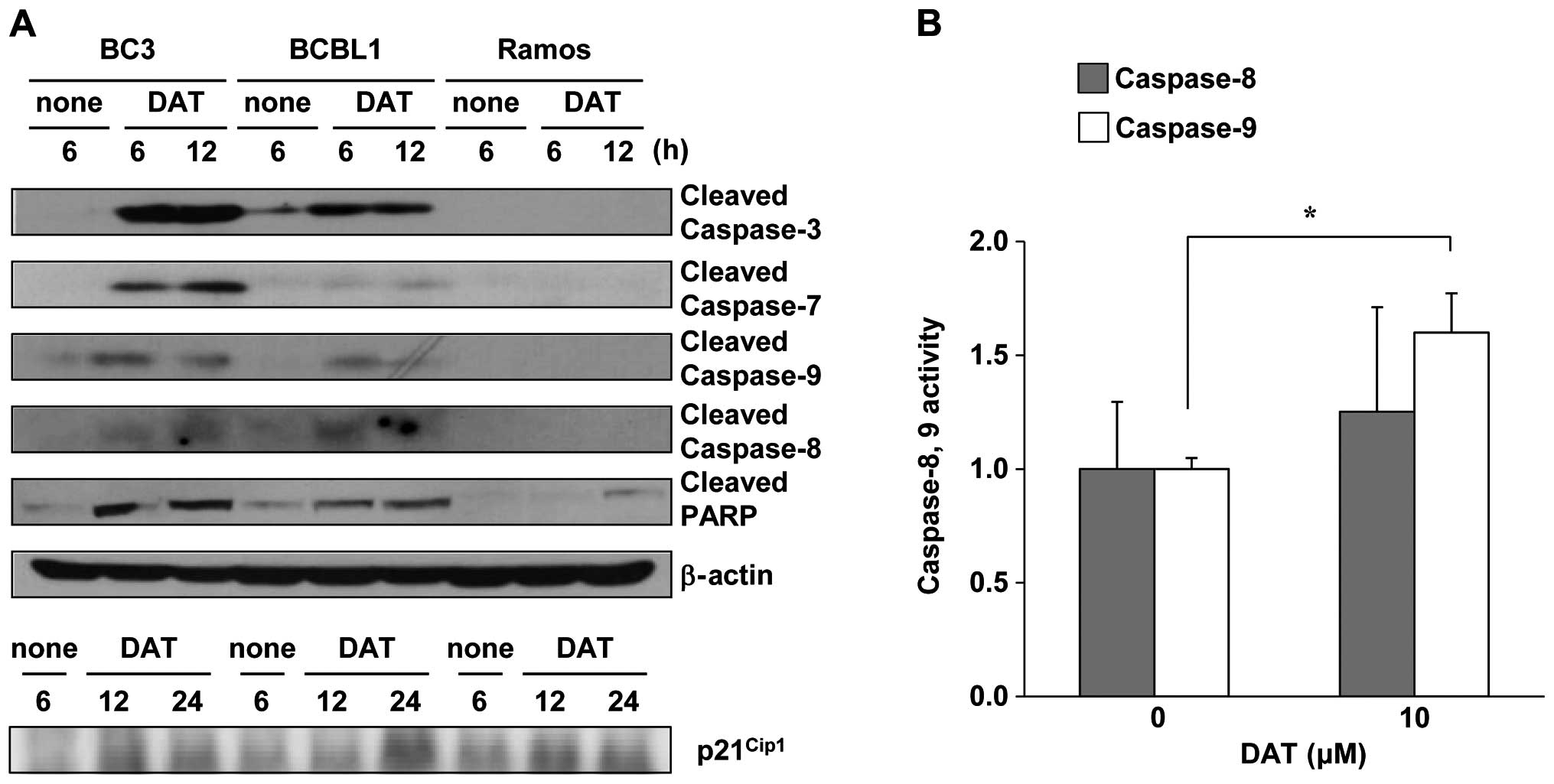
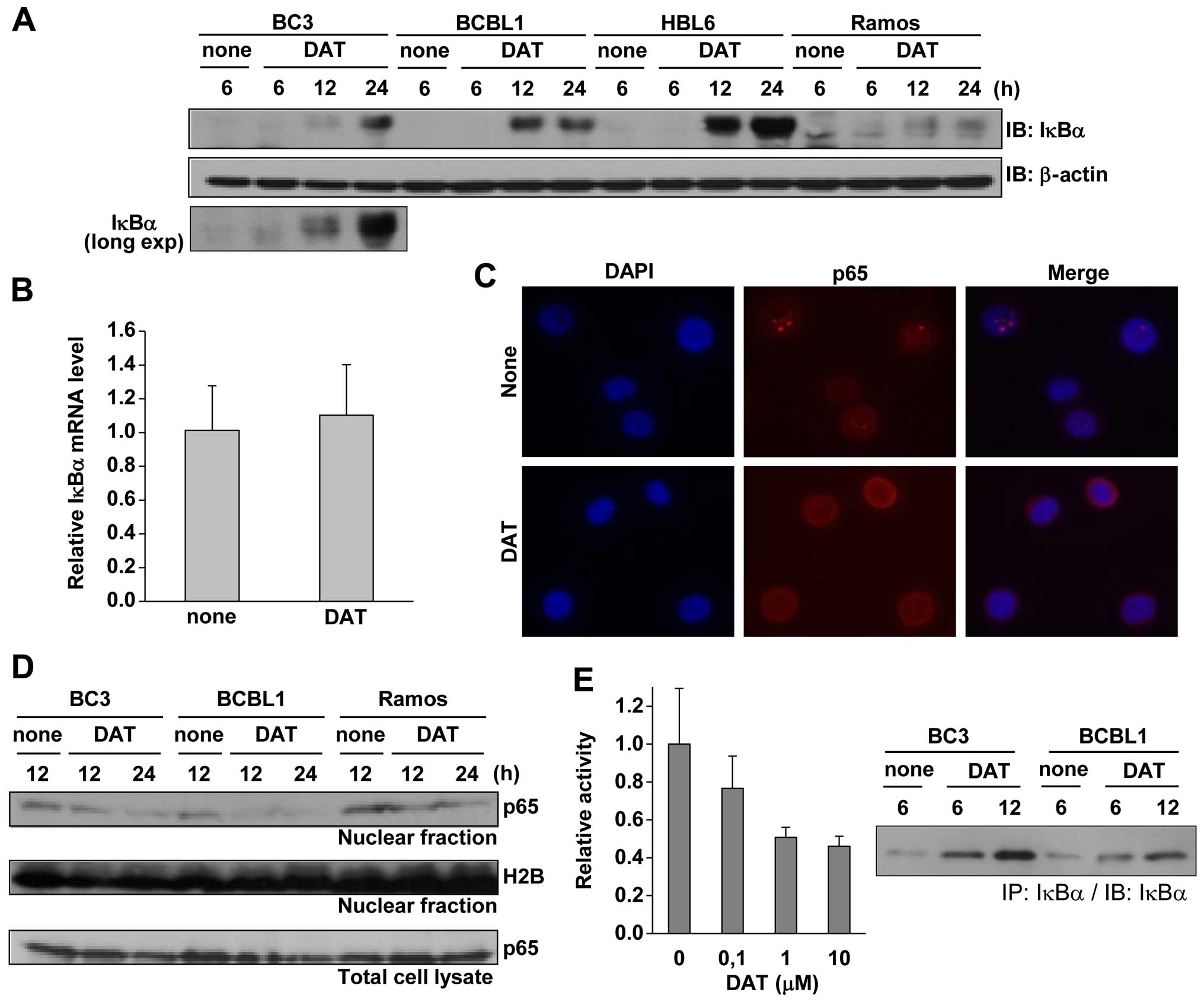
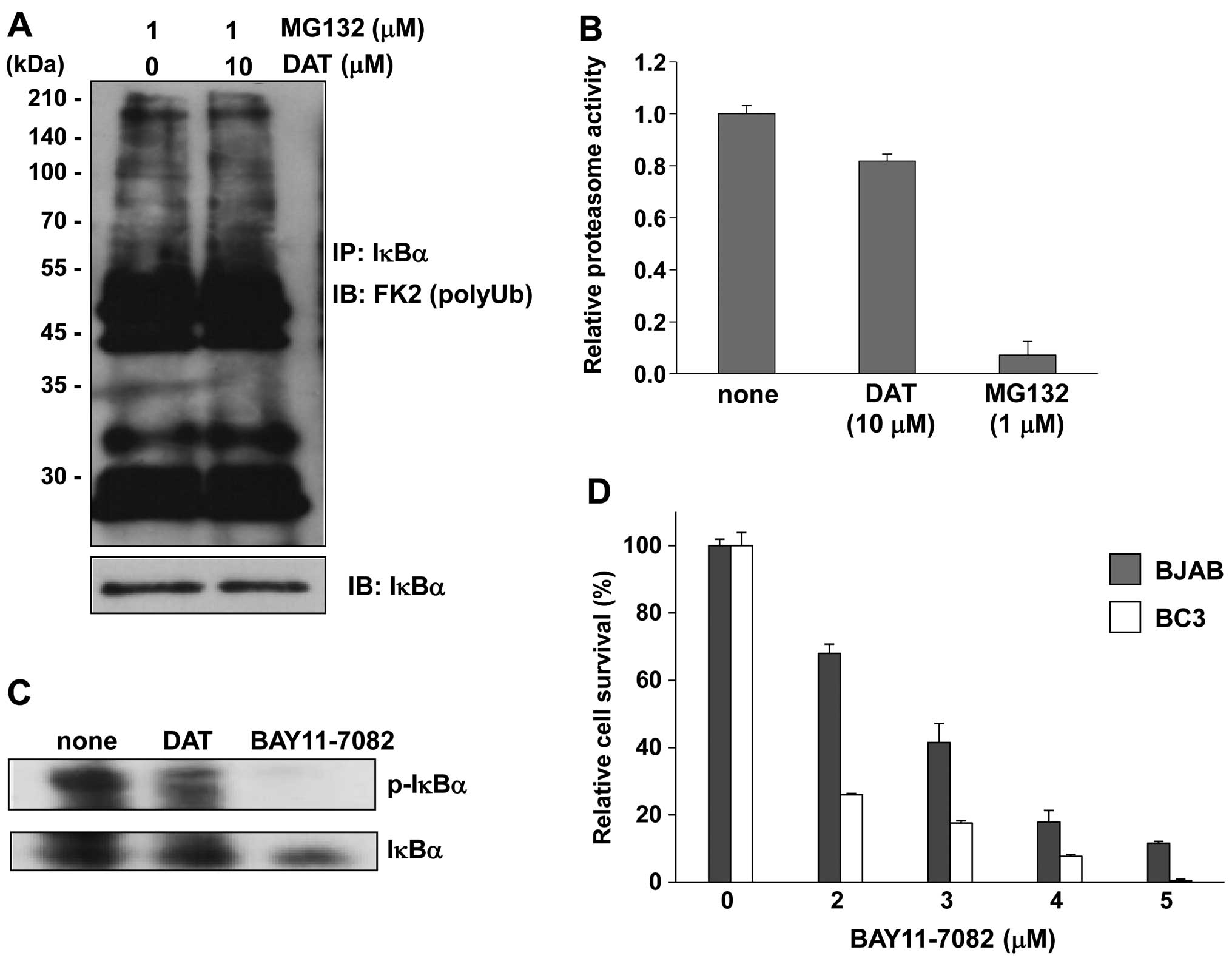
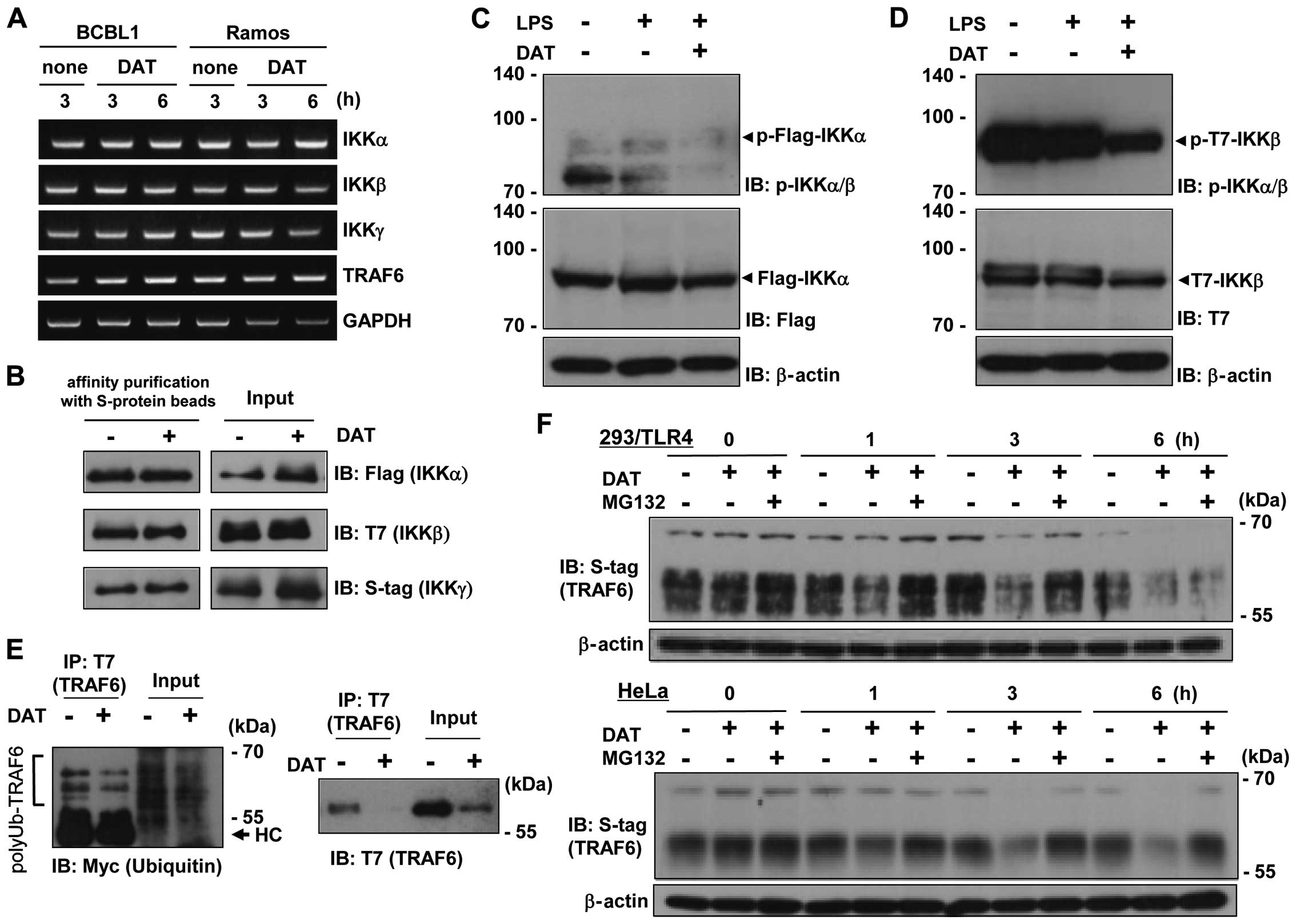
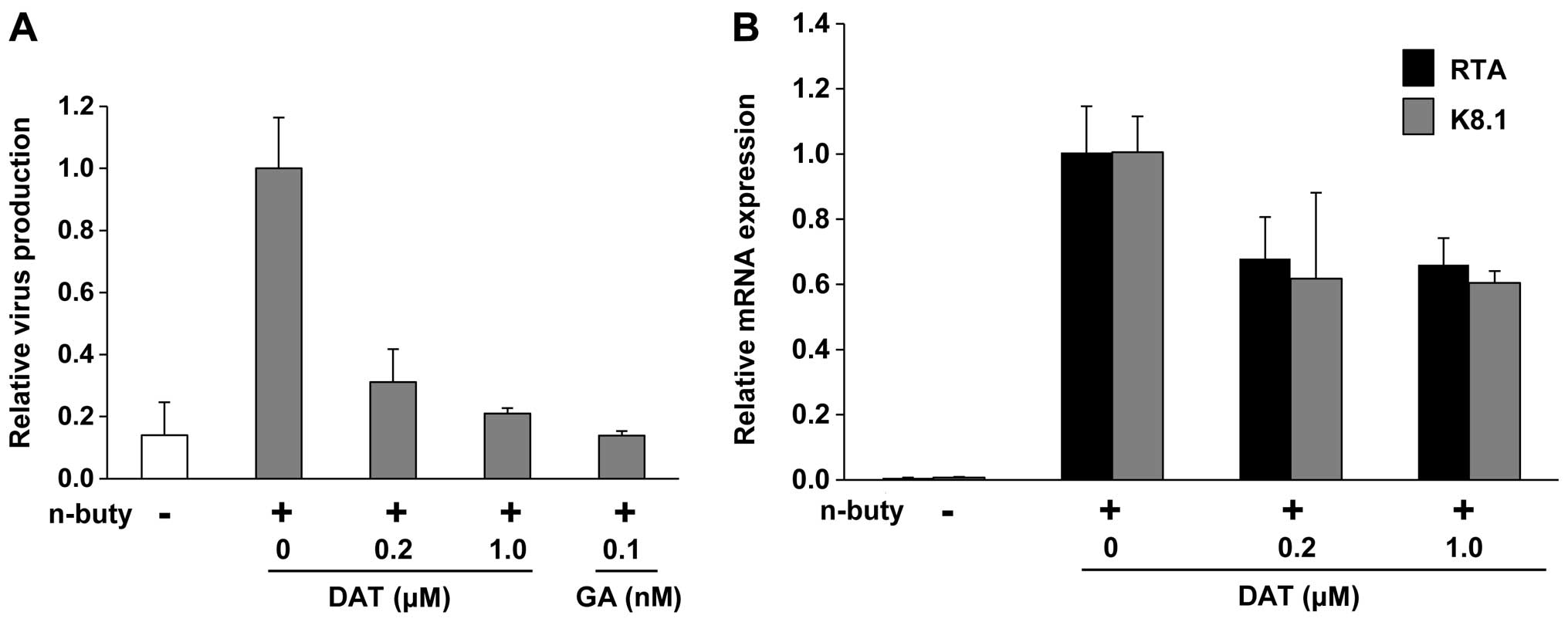
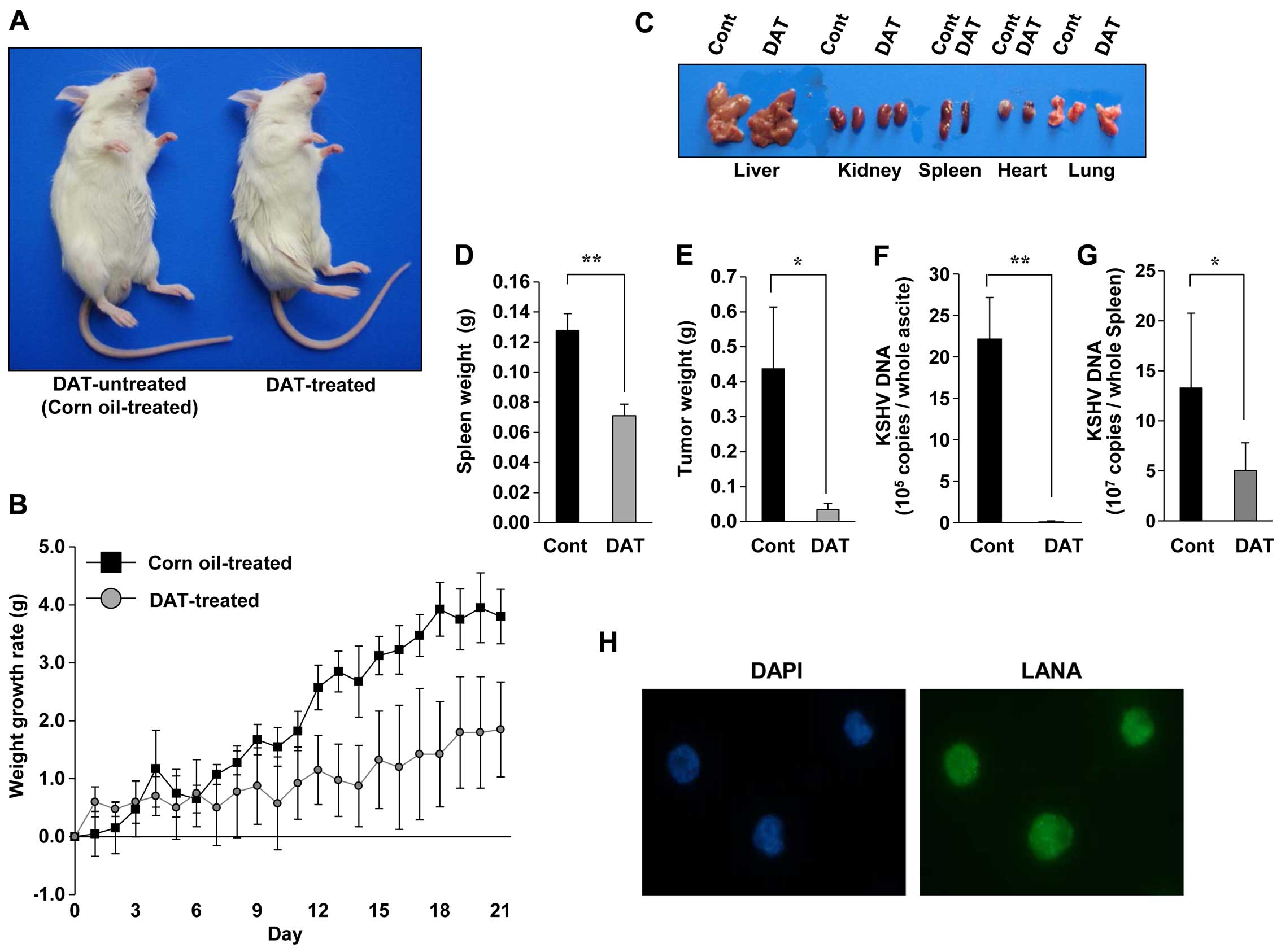
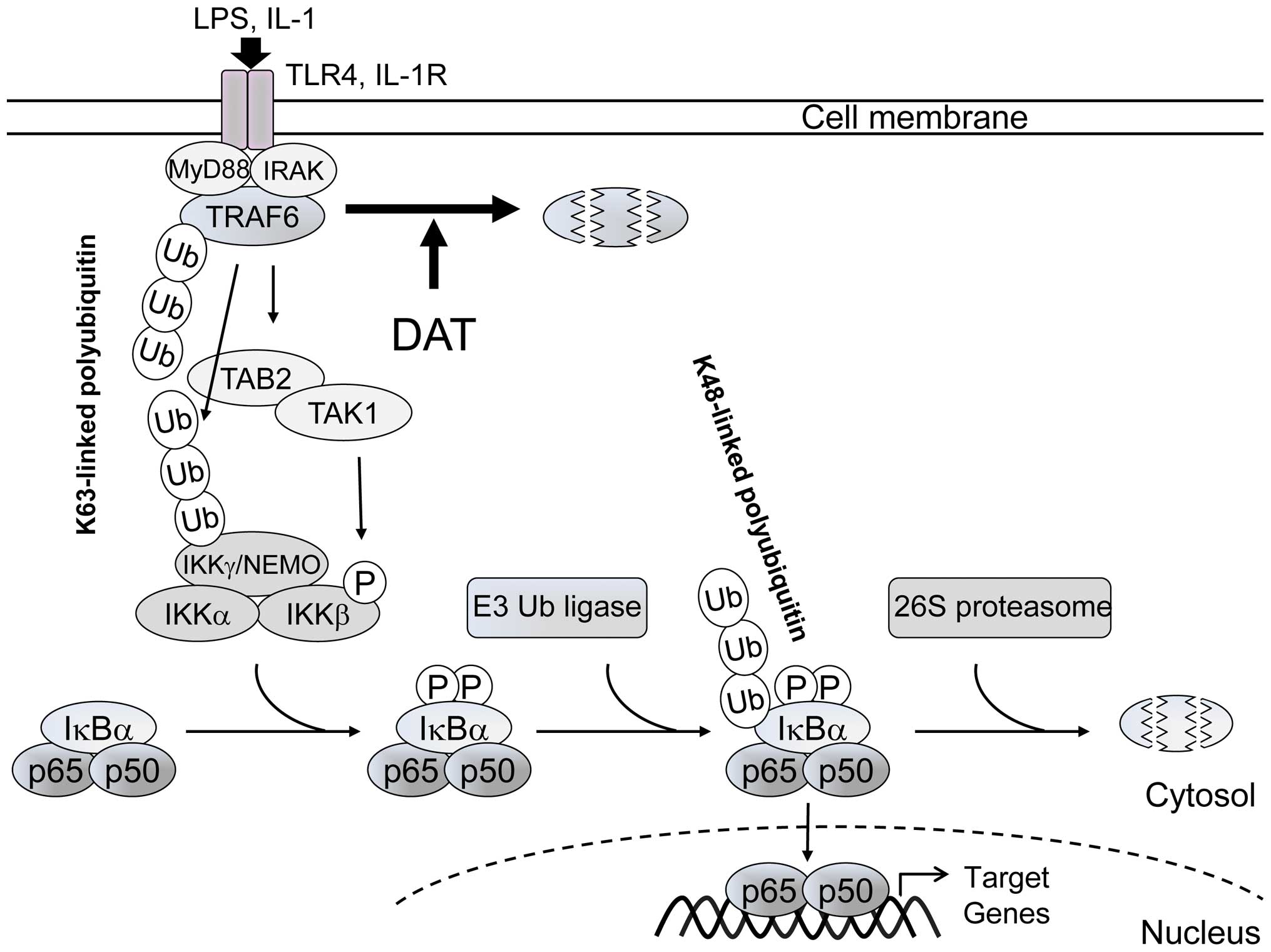
|
1
|
Russo JJ, Bohenzky RA, Chien MC, Chen J,
Yan M, Maddalena D, Parry JP, Peruzzi D, Edelman IS, Chang Y, et
al: Nucleotide sequence of the Kaposi sarcoma-associated
herpesvirus (HHV8). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:14862–14867. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nador RG, Cesarman E, Chadburn A, Dawson
DB, Ansari MQ, Sald J and Knowles DM: Primary effusion lymphoma: A
distinct clinicopathologic entity associated with the Kaposi's
sarcoma-associated herpes virus. Blood. 88:645–656. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chang Y, Cesarman E, Pessin MS, Lee F,
Culpepper J, Knowles DM and Moore PS: Identification of
herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma.
Science. 266:1865–1869. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Järviluoma A and Ojala PM: Cell signaling
pathways engaged by KSHV. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1766:140–158.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fujimuro M, Wu FY, ApRhys C, Kajumbula H,
Young DB, Hayward GS and Hayward SD: A novel viral mechanism for
dysregulation of beta-catenin in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated
herpesvirus latency. Nat Med. 9:300–306. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ashizawa A, Higashi C, Masuda K, Ohga R,
Taira T and Fujimuro M: The ubiquitin system and Kaposi's
sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Front Microbiol. 3:662012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chaudhary PM, Jasmin A, Eby MT and Hood L:
Modulation of the NF-κB pathway by virally encoded death effector
domains-containing proteins. Oncogene. 18:5738–5746. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Keller SA, Schattner EJ and Cesarman E:
Inhibition of NF-kappaB induces apoptosis of KSHV-infected primary
effusion lymphoma cells. Blood. 96:2537–2542. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Keller SA, Hernandez-Hopkins D, Vider J,
Ponomarev V, Hyjek E, Schattner EJ and Cesarman E: NF-kappaB is
essential for the progression of KSHV- and EBV-infected lymphomas
in vivo. Blood. 107:3295–3302. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Saji C, Higashi C, Niinaka Y, Yamada K,
Noguchi K and Fujimuro M: Proteasome inhibitors induce apoptosis
and reduce viral replication in primary effusion lymphoma cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 415:573–578. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Higashi C, Saji C, Yamada K, Kagawa H,
Ohga R, Taira T and Fujimuro M: The effects of heat shock protein
90 inhibitors on apoptosis and viral replication in primary
effusion lymphoma cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 35:725–730. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang G, Gao Y, Li L, Jin G, Cai Z, Chao JI
and Lin HK: K63-linked ubiquitination in kinase activation and
cancer. Front Oncol. 2:52012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen ZJ: Ubiquitination in signaling to
and activation of IKK. Immunol Rev. 246:95–106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Skaug B, Jiang X and Chen ZJ: The role of
ubiquitin in NF-kappaB regulatory pathways. Annu Rev Biochem.
78:769–796. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Calvo-Gómez O, Morales-López J and López
MG: Solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatographic-mass
spectrometric analysis of garlic oil obtained by hydrodistillation.
J Chromatogr A. 1036:91–93. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lawson LD, Wang ZJ and Hughes BG:
Identification and HPLC quantitation of the sulfides and
dialk(en)yl thiosulfinates in commercial garlic products. Planta
Med. 57:363–370. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yi L and Su Q: Molecular mechanisms for
the anti-cancer effects of diallyl disulfide. Food Chem Toxicol.
57:362–370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang HC, Pao J, Lin SY and Sheen LY:
Molecular mechanisms of garlic-derived allyl sulfides in the
inhibition of skin cancer progression. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1271:44–52. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
You S, Nakanishi E, Kuwata H, Chen J,
Nakasone Y, He X, He J, Liu X, Zhang S, Zhang B, et al: Inhibitory
effects and molecular mechanisms of garlic organosulfur compounds
on the production of inflammatory mediators. Mol Nutr Food Res.
57:2049–2060. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Das A, Banik NL and Ray SK: Garlic
compounds generate reactive oxygen species leading to activation of
stress kinases and cysteine proteases for apoptosis in human
glioblastoma T98G and U87MG cells. Cancer. 110:1083–1095. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chandra-Kuntal K, Lee J and Singh SV:
Critical role for reactive oxygen species in apoptosis induction
and cell migration inhibition by diallyl trisulfide, a cancer
chemopreventive component of garlic. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
138:69–79. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang HC, Hsieh SC, Yang JH, Lin SY and
Sheen LY: Diallyl trisulfide induces apoptosis of human basal cell
carcinoma cells via endoplasmic reticulum stress and the
mitochondrial pathway. Nutr Cancer. 64:770–780. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Filomeni G, Rotilio G and Ciriolo MR:
Molecular transduction mechanisms of the redox network underlying
the antiproliferative effects of allyl compounds from garlic. J
Nutr. 138:2053–2057. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee HJ, Lee HG, Choi KS, Surh YJ and Na
HK: Diallyl trisulfide suppresses dextran sodium sulfate-induced
mouse colitis: NF-κB and STAT3 as potential targets. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 437:267–273. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shin DY, Kim GY, Hwang HJ, Kim WJ and Choi
YH: Diallyl trisulfide-induced apoptosis of bladder cancer cells is
caspase-dependent and regulated by PI3K/Akt and JNK pathways.
Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 37:74–83. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Okada S, Goto H and Yotsumoto M: Current
status of treatment for primary effusion lymphoma. Intractable Rare
Dis Res. 3:65–74. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wakao K, Watanabe T, Takadama T, Ui S,
Shigemi Z, Kagawa H, Higashi C, Ohga R, Taira T and Fujimuro M:
Sangivamycin induces apoptosis by suppressing Erk signaling in
primary effusion lymphoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
444:135–140. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fujimuro M, Liu J, Zhu J, Yokosawa H and
Hayward SD: Regulation of the interaction between glycogen synthase
kinase 3 and the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus
latency-associated nuclear antigen. J Virol. 79:10429–10441. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fujimuro M, Sawada H and Yokosawa H:
Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific
to multi-ubiquitin chains of polyubiquitinated proteins. FEBS Lett.
349:173–180. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen C and Okayama H: High-efficiency
transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol.
7:2745–2752. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Milner JA: A historical perspective on
garlic and cancer. J Nutr. 131(Suppl 3): 1027S–1031S.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xiao D, Choi S, Johnson DE, Vogel VG,
Johnson CS, Trump DL, Lee YJ and Singh SV: Diallyl
trisulfide-induced apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells
involves c-Jun N-terminal kinase and extracellular-signal regulated
kinase-mediated phosphorylation of Bcl-2. Oncogene. 23:5594–5606.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Antosiewicz J, Herman-Antosiewicz A,
Marynowski SW and Singh SV: c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase signaling
axis regulates diallyl trisulfide-induced generation of reactive
oxygen species and cell cycle arrest in human prostate cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 66:5379–5386. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Murai M, Inoue T, Suzuki-Karasaki M,
Ochiai T, Ra C, Nishida S and Suzuki-Karasaki Y: Diallyl trisulfide
sensitizes human melanoma cells to TRAIL-induced cell death by
promoting endoplasmic reticulum-mediated apoptosis. Int J Oncol.
41:2029–2037. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu KL, Chen HW, Wang RY, Lei YP, Sheen LY
and Lii CK: DATS reduces LPS-induced iNOS expression, NO
production, oxidative stress, and NF-kappaB activation in RAW 264.7
macrophages. J Agric Food Chem. 54:3472–3478. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kuo WW, Wang WJ, Tsai CY, Way CL, Hsu HH
and Chen LM: Diallyl trisufide (DATS) suppresses high
glucose-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by inhibiting JNK/NFκB
signaling via attenuating ROS generation. Int J Cardiol.
168:270–280. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wang Z, Xia Q, Cui J, Diao Y and Li J:
Reversion of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance by
diallyl trisulfide in a human osteosarcoma cell line. Oncol Rep.
31:2720–2726. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nakayama KI and Nakayama K: Ubiquitin
ligases: Cell-cycle control and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:369–381.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hershko A and Ciechanover A: The ubiquitin
system for protein degradation. Annu Rev Biochem. 61:761–807. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Choi YB and Harhaj EW: HTLV-1 tax
stabilizes MCL-1 via TRAF6-dependent K63-linked polyubiquitination
to promote cell survival and transformation. PLoS Pathog.
10:e10044582014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang WL, Wang J, Chan CH, Lee SW, Campos
AD, Lamothe B, Hur L, Grabiner BC, Lin X, Darnay BG, et al: The E3
ligase TRAF6 regulates Akt ubiquitination and activation. Science.
325:1134–1138. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|