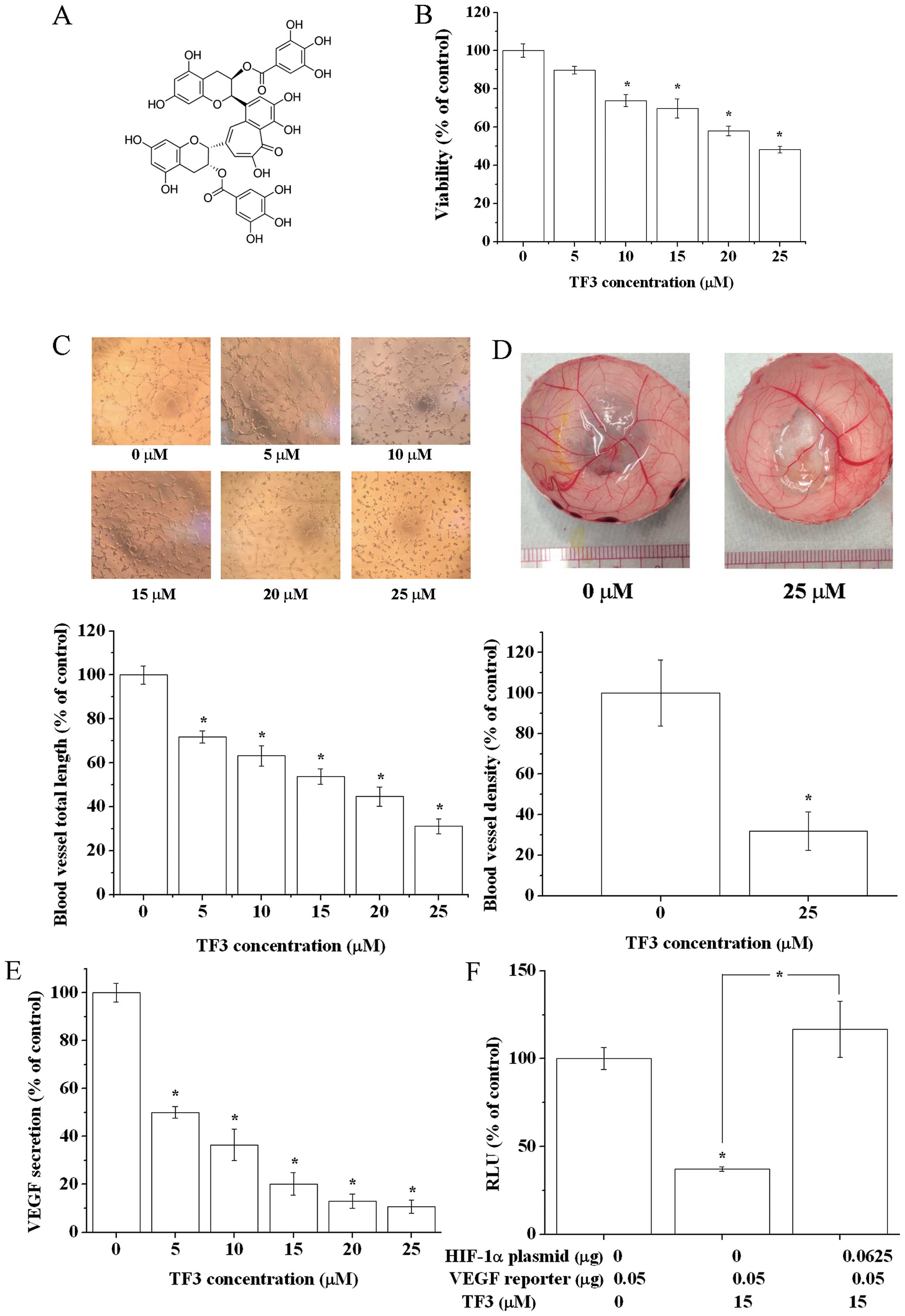
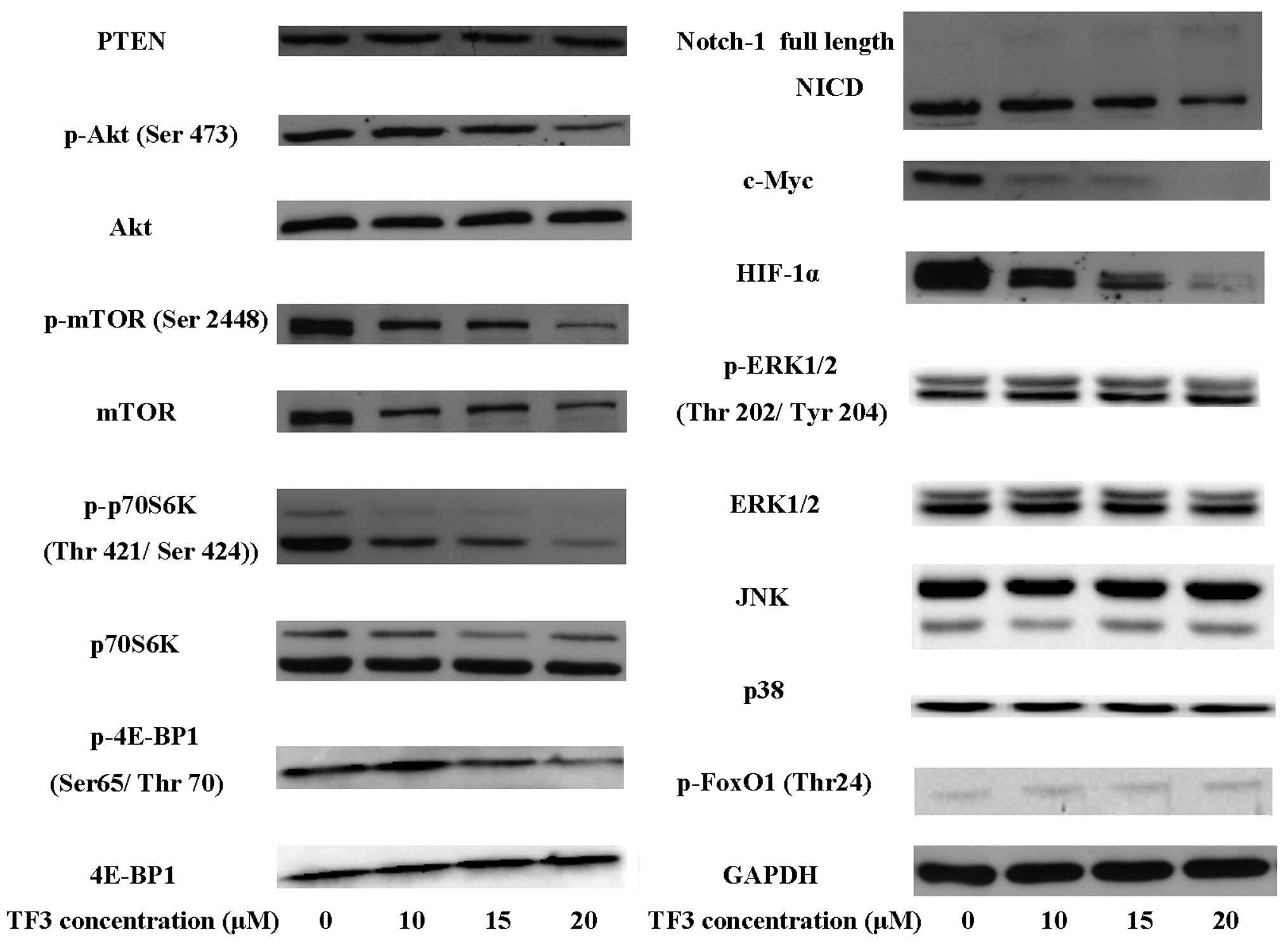
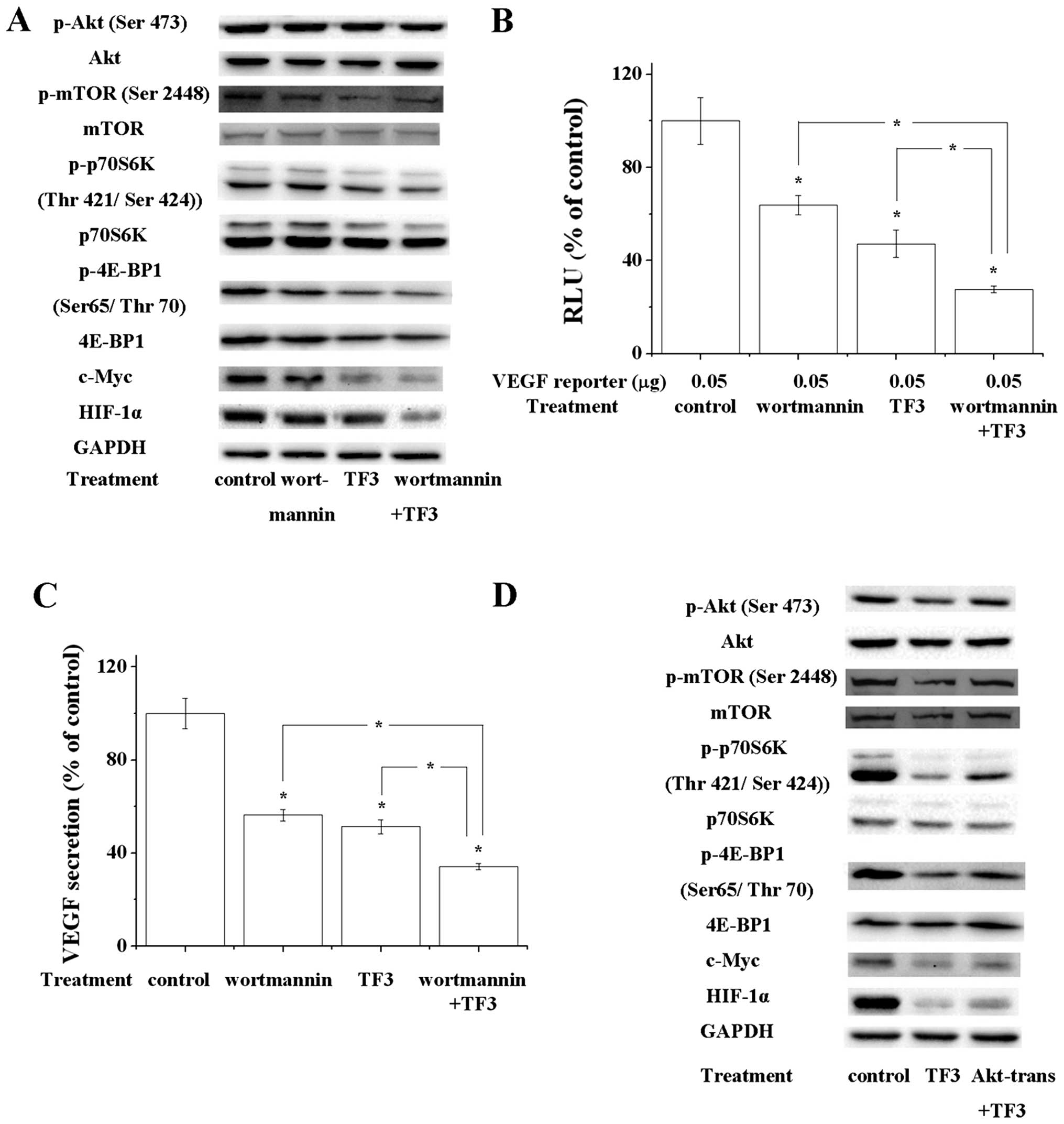
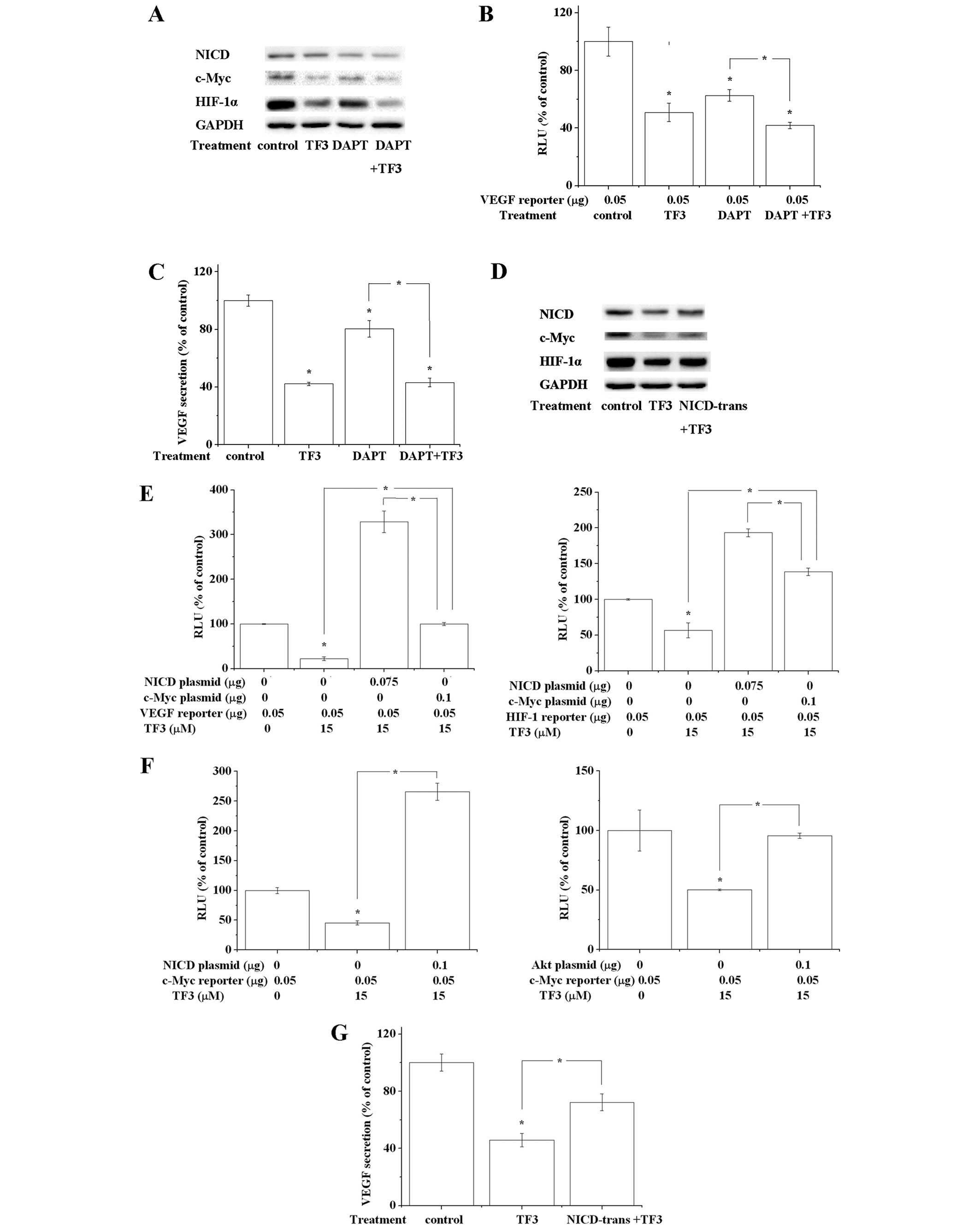
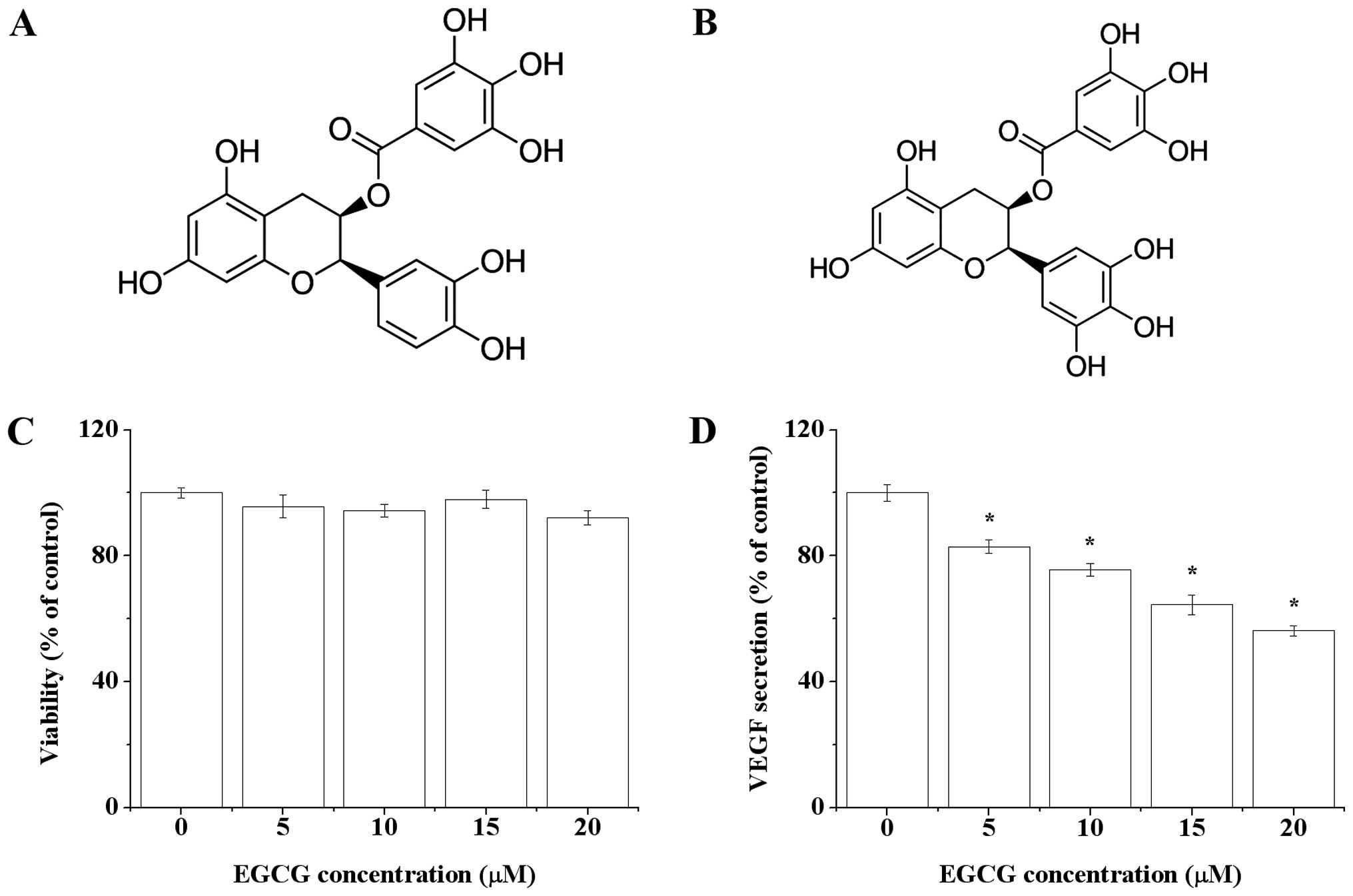
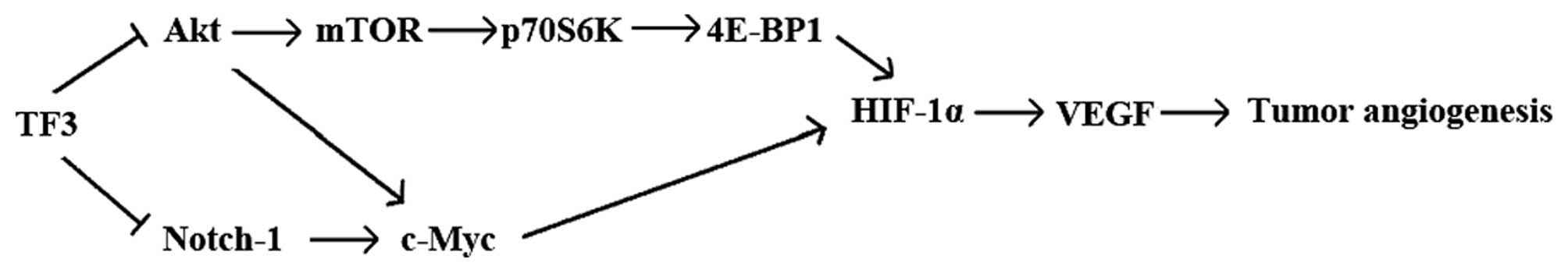
|
1
|
Mizuno T, Suzuki N, Makino H, Furui T,
Morii E, Aoki H, Kunisada T, Yano M, Kuji S, Hirashima Y, et al:
Cancer stem-like cells of ovarian clear cell carcinoma are enriched
in the ALDH-high population associated with an accelerated
scavenging system in reactive oxygen species. Gynecol Oncol.
137:299–305. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Barakat RR, Markman M and Randall M:
Principles and Practice of Gynecologic Oncology. Wolters Kluwer
Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA:
2009
|
|
3
|
Jayson GC, Kohn EC, Kitchener HC and
Ledermann JA: Ovarian cancer. Lancet. 384:1376–1388. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Folkman J, Watson K, Ingber D and Hanahan
D: Induction of angiogenesis during the transition from hyperplasia
to neoplasia. Nature. 339:58–61. 1989. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Giri S, Karakoti A, Graham RP, Maguire JL,
Reilly CM, Seal S, Rattan R and Shridhar V: Nanoceria: A rare-earth
nanoparticle as a novel anti-angiogenic therapeutic agent in
ovarian cancer. PLoS One. 8:e545782013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Burger RA: Overview of anti-angiogenic
agents in development for ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
121:230–238. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E, Lim M,
Hilton DA, Zagzag D, Buechler P, Isaacs WB, Semenza GL and Simons
JW: Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in common
human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res. 59:5830–5835.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liang YC, Chen YC, Lin YL, Lin-Shiau SY,
Ho CT and Lin JK: Suppression of extracellular signals and cell
proliferation by the black tea polyphenol,
theaflavin-3,3′-digallate. Carcinogenesis. 20:733–736. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sajilata MG, Bajaj PR and Singhai RS: Tea
polyphenols as nutraceuticals. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf.
7:229–254. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tu YY, Tang AB and Watanabe N: The
theaflavin monomers inhibit the cancer cells growth in vitro. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 36:508–512. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Schuck AG, Ausubel MB, Zuckerbraun HL and
Babich H: Theaflavin-3,3′-digallate, a component of black tea: an
inducer of oxidative stress and apoptosis. Toxicol In Vitro.
22:598–609. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gao Y, Li W, Jia L, Li B, Chen YC and Tu
Y: Enhancement of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and
theaflavin-3-3′-digallate induced apoptosis by ascorbic acid in
human lung adenocarcinoma SPC-A-1 cells and esophageal carcinoma
Eca-109 cells via MAPK pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
438:370–374. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kobayashi S, Iwai S, Tsujiyama K,
Kurahashi C, Udaka Y, Sanbe T, Suzaki H and Oguchi K:
Theaflavin-3,3′-digallate inhibits tube formation in cocultured
endothelial cells with fibroblasts. Showa Univ J Med Sci. 19:59–72.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Siddiqui IA, Zaman N, Aziz MH, Reagan-Shaw
SR, Sarfaraz S, Adhami VM, Ahmad N, Raisuddin S and Mukhtar H:
Inhibition of CWR22Rnu1 tumor growth and PSA secretion in athymic
nude mice by green and black teas. Carcinogenesis. 27:833–839.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu Y, Jin YX, Wu YY and Tu YY: Isolation
and purification of four individual theaflavins using
semi-preparative high performance liquid chromatography. J Liquid
Chromatogr Relat Technol. 33:1791–1801. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Fang J, Xia C, Cao Z, Zheng JZ, Reed E and
Jiang BH: Apigenin inhibits VEGF and HIF-1 expression via
PI3K/AKT/p70S6K1 and HDM2/p53 pathways. FASEB J. 19:342–353. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
García-Maceira P and Mateo J: Silibinin
inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and mTOR/p70S6K/4E-BP1
signalling pathway in human cervical and hepatoma cancer cells:
Implications for anticancer therapy. Oncogene. 28:313–324. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chen C, Cai S, Wang G, Cao X, Yang X, Luo
X, Feng Y and Hu J: c-Myc enhances colon cancer cell-mediated
angiogenesis through the regulation of HIF-1α. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 430:505–511. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Asano T, Yao Y, Zhu J, Li D, Abbruzzese JL
and Reddy SA: The PI 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway is activated
due to aberrant Pten expression and targets transcription factors
NF-kappaB and c-Myc in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene.
23:8571–8580. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Weng AP, Millholland JM, Yashiro-Ohtani Y,
Arcangeli ML, Lau A, Wai C, Del Bianco C, Rodriguez CG, Sai H,
Tobias J, et al: c-Myc is an important direct target of Notch1 in
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. Genes Dev.
20:2096–2109. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang D, Ding Y, Luo WM, Bender S, Qian
CN, Kort E, Zhang ZF, VandenBeldt K, Duesbery NS, Resau JH, et al:
Inhibition of MAPK kinase signaling pathways suppressed renal cell
carcinoma growth and angiogenesis in vivo. Cancer Res. 68:81–88.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Baker JA, Boakye K, McCann SE, Beehler GP,
Rodabaugh KJ, Villella JA and Moysich KB: Consumption of black tea
or coffee and risk of ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer.
17:50–54. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Banerjee P, Banerjee S and Mazumder S:
Effect of theaflavin, A black tea extract on ovarian cancer cell
line. Bombay Hosp J. 53:341–348. 2011.
|
|
24
|
Maity S, Ukil A, Vedasiromoni JR and Das
PK: Biodistribution and pharmacokinetics of
theaflavin-3,3′-digallate, the major antioxidant of black tea, in
mice. Int J Pharmacol. 2:240–246. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Huang H, Chen AY, Rojanasakul Y, Ye X,
Rankin GO and Chen YC: Dietary compounds galangin and myricetin
suppress ovarian cancer cell angiogenesis. J Funct Foods.
15:464–475. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen J, Chen AY, Huang H, Ye X, Rollyson
WD, Perry HE, Brown KC, Rojanasakul Y, Rankin GO, Dasgupta P, et
al: The flavonoid nobiletin inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis
of ovarian cancers via the Akt pathway. Int J Oncol. 46:2629–2638.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schoell WM, Pieber D, Reich O, Lahousen M,
Janicek M, Guecer F and Winter R: Tumor angiogenesis as a
prognostic factor in ovarian carcinoma: Quantification of
endothelial immunoreactivity by image analysis. Cancer.
80:2257–2262. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ciardiello F, Caputo R, Bianco R, Damiano
V, Fontanini G, Cuccato S, De Placido S, Bianco AR and Tortora G:
Inhibition of growth factor production and angiogenesis in human
cancer cells by ZD1839 (Iressa), a selective epidermal growth
factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res.
7:1459–1465. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hoeben A, Landuyt B, Highley MS, Wildiers
H, Van Oosterom AT and De Bruijn EA: Vascular endothelial growth
factor and angiogenesis. Pharmacol Rev. 56:549–580. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhu LQ, Liu J and Ma CJ: Effect of
theaflavin diagallate on anti-tumor proliferation and VEGF gene
expression in lung adenocancer A549 cells. Cent S Pharm. 9:23–26.
2011.
|
|
31
|
Jung YD and Ellis LM: Inhibition of tumour
invasion and angiogenesis by epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a
major component of green tea. Int J Exp Pathol. 82:309–316. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Su YL, Leung LK, Huang Y and Chen ZY:
Stability of tea theaflavins and catechins. Food Chem. 83:189–195.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yang ZY, Tu YY, Xia HL, Jie GL, Chen XM
and He PM: Suppression of free-radicals and protection against
H2O2-induced oxidative damage in HPF-1 cell
by oxidized phenolic compounds present in black tea. Food Chem.
105:1349–1356. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Gu JW, Makey KL, Tucker KB, Chinchar E,
Mao X, Pei I, Thomas EY and Miele L: EGCG, a major green tea
catechin suppresses breast tumor angiogenesis and growth via
inhibiting the activation of HIF-1α and NFκB, and VEGF expression.
Vasc Cell. 5:92013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang Q, Tang X, Lu Q, Zhang Z, Rao J and
Le AD: Green tea extract and (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibit
hypoxia- and serum-induced HIF-1alpha protein accumulation and VEGF
expression in human cervical carcinoma and hepatoma cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 5:1227–1238. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li W, Tan D, Zhang Z, Liang JJ and Brown
RE: Activation of Akt-mTOR-p70S6K pathway in angiogenesis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 20:713–719. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li G, Shan C, Liu L, Zhou T, Zhou J, Hu X,
Chen Y, Cui H and Gao N: Tanshinone IIA inhibits HIF-1α and VEGF
expression in breast cancer cells via mTOR/p70S6K/RPS6/4E-BP1
signaling pathway. PLoS One. 10:e01174402015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xu Q, Liu LZ, Qian X, Chen Q, Jiang Y, Li
D, Lai L and Jiang BH: MiR-145 directly targets p70S6K1 in cancer
cells to inhibit tumor growth and angiogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res.
40:761–774. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Pratheeshkumar P, Budhraja A, Son YO, Wang
X, Zhang Z, Ding S, Wang L, Hitron A, Lee JC, Xu M, et al:
Quercetin inhibits angiogenesis mediated human prostate tumor
growth by targeting VEGFR-2 regulated AKT/mTOR/P70S6K signaling
pathways. PLoS One. 7:e475162012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Baudino TA, McKay C, Pendeville-Samain H,
Nilsson JA, Maclean KH, White EL, Davis AC, Ihle JN and Cleveland
JL: c-Myc is essential for vasculogenesis and angiogenesis during
development and tumor progression. Genes Dev. 16:2530–2543. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee JG and Wu R: Erlotinib-cisplatin
combination inhibits growth and angiogenesis through c-MYC and
HIF-1α in EGFR-mutated lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. Neoplasia.
17:190–200. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Meng RD, Shelton CC, Li YM, Qin LX,
Notterman D, Paty PB and Schwartz GK: gamma-Secretase inhibitors
abrogate oxaliplatin-induced activation of the Notch-1 signaling
pathway in colon cancer cells resulting in enhanced
chemosensitivity. Cancer Res. 69:573–582. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Garcia A and Kandel JJ: Notch: A key
regulator of tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Histol Histopathol.
27:151–156. 2012.
|
|
44
|
Guo D, Li C, Teng Q, Sun Z, Li Y and Zhang
C: Notch1 over-expression promotes cell growth and tumor
angiogenesis in myeloma. Neoplasma. 60:33–40. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Proia T, Jiang F, Bell A, Nicoletti R,
Kong L, Kreuter K, Poling L, Winston WM, Flaherty M, Weiler S, et
al: 23814, an inhibitory antibody of ligand-mediated Notch1
activation, modulates angiogenesis and inhibits tumor growth
without gastrointestinal toxicity. Mol Cancer Ther. 14:1858–1867.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yan B, Zhou Y, Feng S, et al:
beta-elemene-attenuated tumor angiogenesis by targeting Notch-1 in
gastric cancer stem-like cells. J Evid Based Complementary Altern
Med. 2013:2684682013.
|
|
47
|
Rose SL, Kunnimalaiyaan M, Drenzek J and
Seiler N: Notch 1 signaling is active in ovarian cancer. Gynecol
Oncol. 117:130–133. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shankar S, Chen Q and Srivastava RK:
Inhibition of PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK pathways act synergistically to
enhance anti-angiogenic effects of EGCG through activation of FOXO
transcription factor. J Mol Signal. 3:72008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Potente M, Urbich C, Sasaki K, Hofmann WK,
Heeschen C, Aicher A, Kollipara R, DePinho RA, Zeiher AM and
Dimmeler S: Involvement of Foxo transcription factors in
angiogenesis and postnatal neovascularization. J Clin Invest.
115:2382–2392. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Asada S, Daitoku H, Matsuzaki H, Saito T,
Sudo T, Mukai H, Iwashita S, Kako K, Kishi T, Kasuya Y, et al:
Mitogen-activated protein kinases, Erk and p38, phosphorylate and
regulate Foxo1. Cell Signal. 19:519–527. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Lam EW, Francis RE and Petkovic M: FOXO
transcription factors: Key regulators of cell fate. Biochem Soc
Trans. 34:722–726. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jung YD, Kim MS, Shin BA, Chay KO, Ahn BW,
Liu W, Bucana CD, Gallick GE and Ellis LM: EGCG, a major component
of green tea, inhibits tumour growth by inhibiting VEGF induction
in human colon carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer. 84:844–850. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Shankar S, Marsh L and Srivastava RK: EGCG
inhibits growth of human pancreatic tumors orthotopically implanted
in Balb C nude mice through modulation of FKHRL1/FOXO3a and
neuropilin. Mol Cell Biochem. 372:83–94. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Wang F, Chang Z, Fan Q and Wang L:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits the proliferation and migration
of human ovarian carcinoma cells by modulating p38 kinase and
matrix metal-loproteinase-2. Mol Med Rep. 9:1085–1089.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Jhoo JW, Lo CY, Li S, Sang S, Ang CY,
Heinze TM and Ho CT: Stability of black tea polyphenol, theaflavin,
and identification of theanaphthoquinone as its major radical
reaction product. J Agric Food Chem. 53:6146–6150. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Sang S, Lambert JD, Tian S, Hong J, Hou Z,
Ryu JH, Stark RE, Rosen RT, Huang MT, Yang CS, et al: Enzymatic
synthesis of tea theaflavin derivatives and their anti-inflammatory
and cytotoxic activities. Bioorg Med Chem. 12:459–467. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Park HY, Kunitake Y and Matsui T:
Benzotropolone moiety in theaflavins is responsible for inhibiting
peptide-transport and activating AMP-activated protein kinase in
Caco-2 cells. Funct Foods Health Dis. 3:111–121. 2013.
|