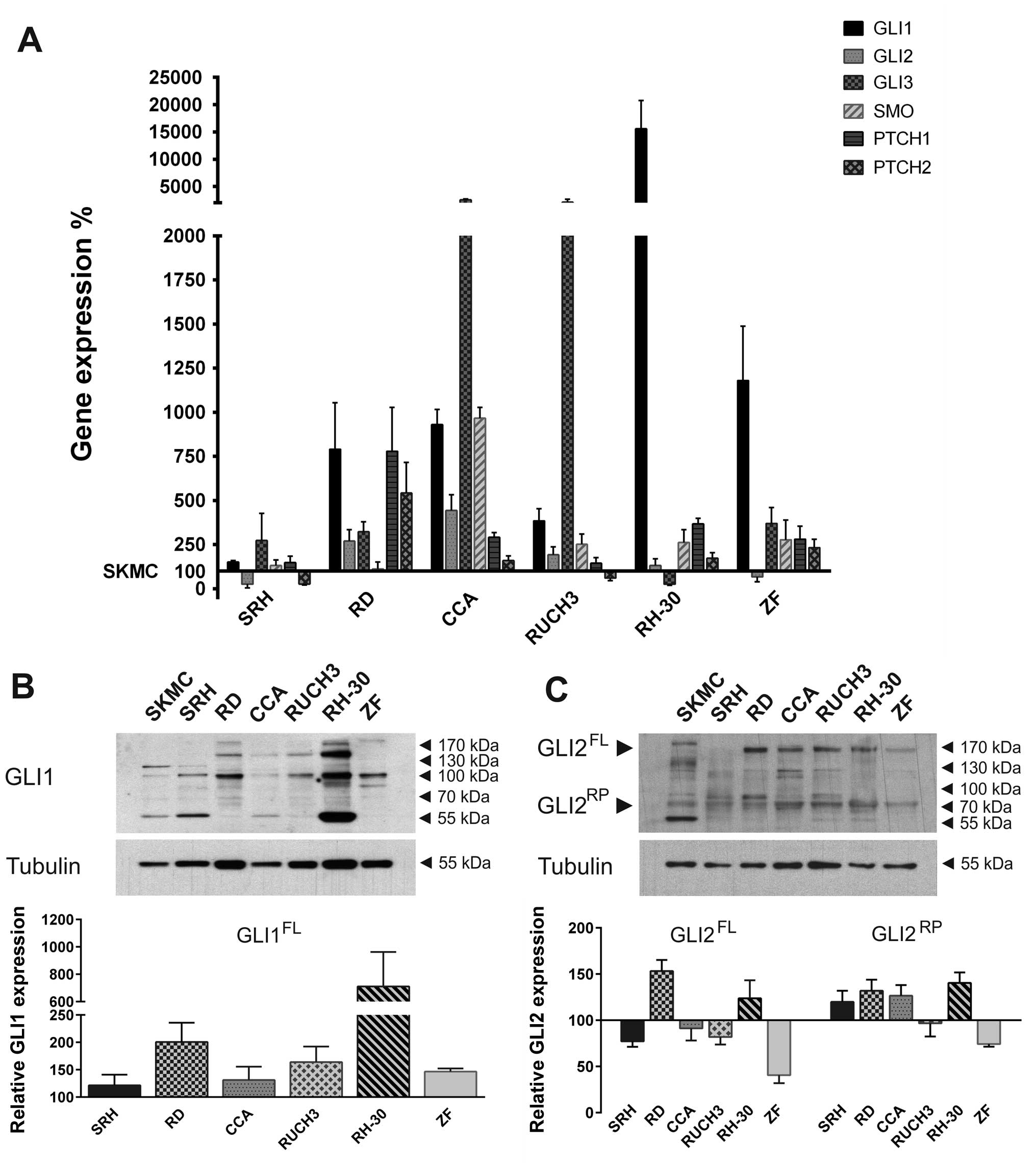
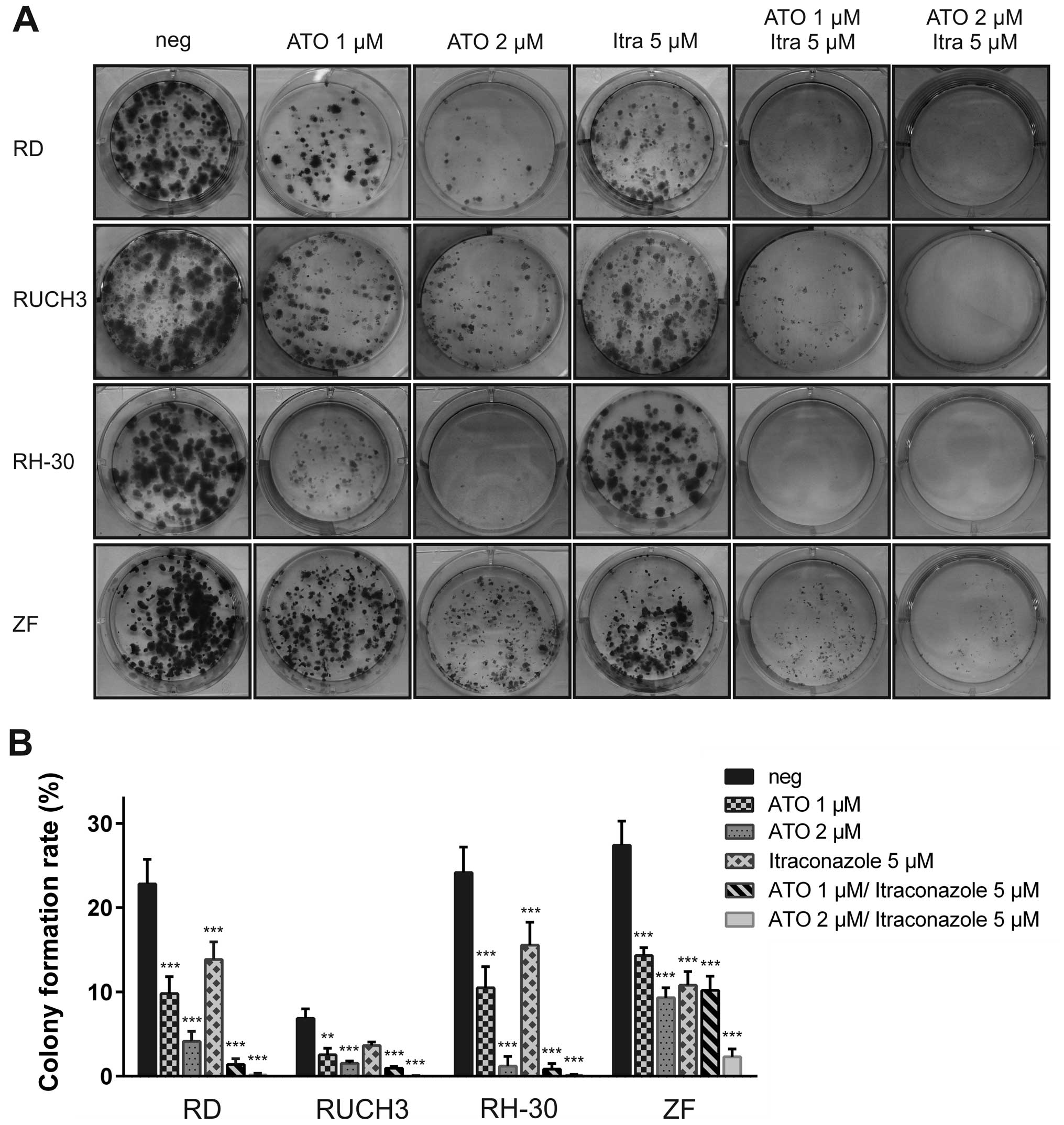
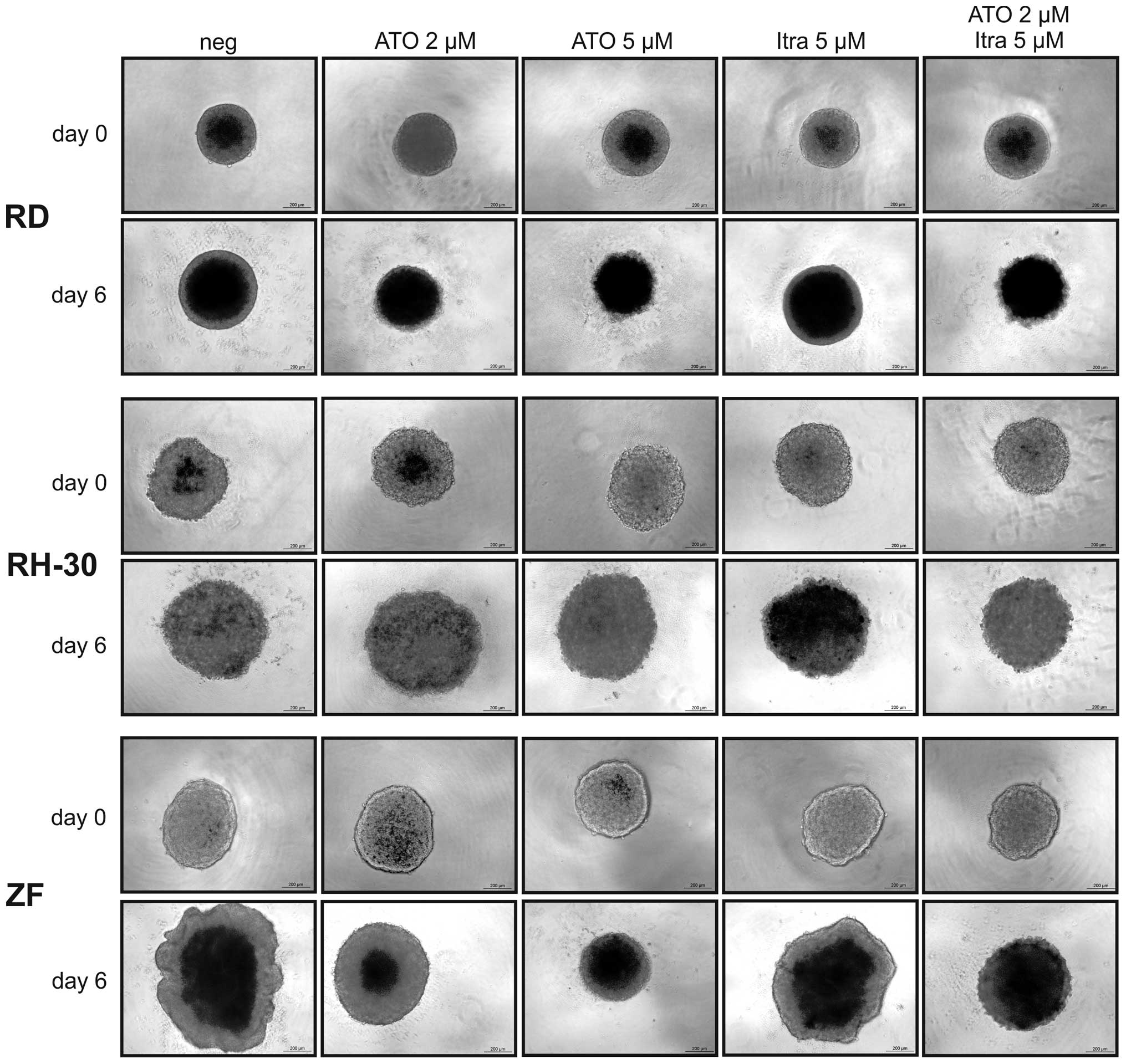
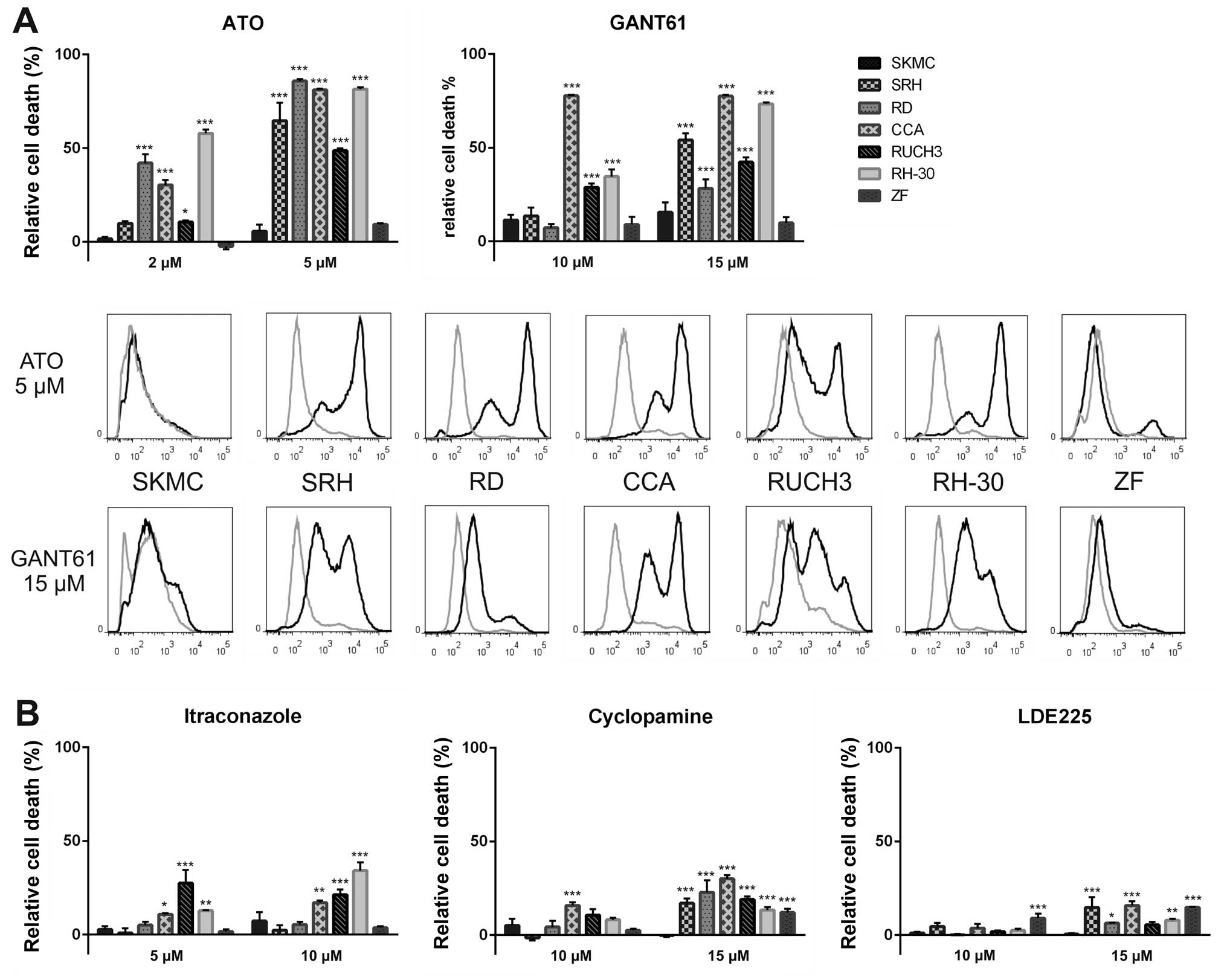
|
1
|
Tostar U, Toftgård R, Zaphiropoulos PG and
Shimokawa T: Reduction of human embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma tumor
growth by inhibition of the hedgehog signaling pathway. Genes
Cancer. 1:941–951. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Egas-Bejar D and Huh WW: Rhabdomyosarcoma
in adolescent and young adult patients: Current perspectives.
Adolesc Health Med Ther. 5:115–125. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ferrari A, Dileo P, Casanova M, Bertulli
R, Meazza C, Gandola L, Navarria P, Collini P, Gronchi A, Olmi P,
et al: Rhabdomyosarcoma in adults. A retrospective analysis of 171
patients treated at a single institution. Cancer. 98:571–580. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Agaram NP, Chen CL, Zhang L, LaQuaglia MP,
Wexler L and Antonescu CR: Recurrent MYOD1 mutations in pediatric
and adult sclerosing and spindle cell rhabdomyosarcomas: Evidence
for a common pathogenesis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 53:779–787.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nascimento AF and Fletcher CD: Spindle
cell rhabdomyosarcoma in adults. Am J Surg Pathol. 29:1106–1113.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hawkins DS, Gupta AA and Rudzinski ER:
What is new in the biology and treatment of pediatric
rhabdomyosarcoma? Curr Opin Pediatr. 26:50–56. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Eichenmüller M, Hemmerlein B, von
Schweinitz D and Kappler R: Betulinic acid induces apoptosis and
inhibits hedgehog signalling in rhabdomyosarcoma. Br J Cancer.
103:43–51. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Petrova R and Joyner AL: Roles for
Hedgehog signaling in adult organ homeostasis and repair.
Development. 141:3445–3457. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Amakye D, Jagani Z and Dorsch M:
Unraveling the therapeutic potential of the Hedgehog pathway in
cancer. Nat Med. 19:1410–1422. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kelleher FC, Cain JE, Healy JM, Watkins DN
and Thomas DM: Prevailing importance of the hedgehog signaling
pathway and the potential for treatment advancement in sarcoma.
Pharmacol Ther. 136:153–168. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nakamura S, Nagano S, Nagao H, Ishidou Y,
Yokouchi M, Abematsu M, Yamamoto T, Komiya S and Setoguchi T:
Arsenic trioxide prevents osteosarcoma growth by inhibition of GLI
transcription via DNA damage accumulation. PLoS One. 8:e694662013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aberger F, Aberger F and Ruiz I Altaba A:
Context-dependent signal integration by the GLI code: The oncogenic
load, pathways, modifiers and implications for cancer therapy.
Semin Cell Dev Biol. 33:93–104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kasper M, Regl G, Frischauf AM and Aberger
F: GLI transcription factors: Mediators of oncogenic Hedgehog
signalling. Eur J Cancer. 42:437–445. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Roberts WM, Douglass EC, Peiper SC,
Houghton PJ and Look AT: Amplification of the gli gene in childhood
sarcomas. Cancer Res. 49:5407–5413. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lynn M, Shah N, Conroy J, Ennis S, Morris
T, Betts D and O'Sullivan M: A study of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma
copy number alterations by single nucleotide polymorphism analysis.
Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 22:213–221. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Matsumoto T, Tabata K and Suzuki T: The
GANT61, a GLI inhibitor, induces caspase-independent apoptosis of
SK-N-LO cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 37:633–641. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin TL and Matsui W: Hedgehog pathway as a
drug target: Smoothened inhibitors in development. Onco Targets
Ther. 5:47–58. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ruat M, Hoch L, Faure H and Rognan D:
Targeting of Smoothened for therapeutic gain. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
35:237–246. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pan S, Wu X, Jiang J, Gao W, Wan Y, Cheng
D, Han D, Liu J, Englund NP, Wang Y, et al: Discovery of
NVP-LDE225, a Potent and Selective Smoothened Antagonist. ACS Med
Chem Lett. 1:130–134. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim J, Tang JY, Gong R, Kim J, Lee JJ,
Clemons KV, Chong CR, Chang KS, Fereshteh M, Gardner D, et al:
Itraconazole, a commonly used antifungal that inhibits Hedgehog
pathway activity and cancer growth. Cancer Cell. 17:388–399. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Watts JM and Tallman MS: Acute
promyelocytic leukemia: What is the new standard of care? Blood
Rev. 28:205–212. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim J, Lee JJ, Kim J, Gardner D and Beachy
PA: Arsenic antagonizes the Hedgehog pathway by preventing ciliary
accumulation and reducing stability of the Gli2 transcriptional
effector. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:13432–13437. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lauth M, Bergström A, Shimokawa T and
Toftgård R: Inhibition of GLI-mediated transcription and tumor cell
growth by small-molecule antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:8455–8460. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Laurendeau I, Ferrer M, Garrido D, D'Haene
N, Ciavarelli P, Basso A, Vidaud M, Bieche I, Salmon I and Szijan
I: Gene expression profiling of the hedgehog signaling pathway in
human meningiomas. Mol Med. 16:262–270. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Forus A, Florenes VA, Maelandsmo GM,
Meltzer PS, Fodstad O and Myklebost O: Mapping of amplification
units in the q13–14 region of chromosome 12 in human sarcomas: some
amplica do not include MDM2. Cell Growth Differ. 4:1065–1070.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Prigent C and Dimitrov S: Phosphorylation
of serine 10 in histone H3, what for? J Cell Sci. 116:3677–3685.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gu Y, Rosenblatt J and Morgan DO: Cell
cycle regulation of CDK2 activity by phosphorylation of Thr160 and
Tyr15. EMBO J. 11:3995–4005. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Loughery J, Cox M, Smith LM and Meek DW:
Critical role for p53-serine 15 phosphorylation in stimulating
transactivation at p53-responsive promoters. Nucleic Acids Res.
42:7666–7680. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Soussi T and Béroud C: Significance of
TP53 mutations in human cancer: A critical analysis of mutations at
CpG dinucleotides. Hum Mutat. 21:192–200. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Burlacu A: Regulation of apoptosis by
Bcl-2 family proteins. J Cell Mol Med. 7:249–257. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hyman JM, Firestone AJ, Heine VM, Zhao Y,
Ocasio CA, Han K, Sun M, Rack PG, Sinha S, Wu JJ, et al:
Small-molecule inhibitors reveal multiple strategies for Hedgehog
pathway blockade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:14132–14137. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ragazzini P, Gamberi G, Pazzaglia L, Serra
M, Magagnoli G, Ponticelli F, Ferrari C, Ghinelli C, Alberghini M,
Bertoni F, et al: Amplification of CDK4, MDM2, SAS and GLI genes in
leiomyosarcoma, alveolar and embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Histol
Histopathol. 19:401–411. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Graab U, Hahn H and Fulda S:
Identification of a novel synthetic lethality of combined
inhibition of hedgehog and PI3K signaling in rhabdomyosarcoma.
Oncotarget. 6:8722–8735. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Raju GP: Arsenic: A potentially useful
poison for Hedgehog-driven cancers. J Clin Invest. 121:14–16. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Kim J, Aftab BT, Tang JY, Kim D, Lee AH,
Rezaee M, Kim J, Chen B, King EM, Borodovsky A, et al: Itraconazole
and arsenic trioxide inhibit Hedgehog pathway activation and tumor
growth associated with acquired resistance to smoothened
antagonists. Cancer Cell. 23:23–34. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Au WY, Tam S, Fong BM and Kwong YL:
Determinants of cerebrospinal fluid arsenic concentration in
patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia on oral arsenic trioxide
therapy. Blood. 112:3587–3590. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu Q, Hilsenbeck S and Gazitt Y: Arsenic
trioxide-induced apoptosis in myeloma cells: p53-dependent G1 or
G2/M cell cycle arrest, activation of caspase-8 or caspase-9, and
synergy with APO2/TRAIL. Blood. 101:4078–4087. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lunghi P, Tabilio A, Lo-Coco F, Pelicci PG
and Bonati A: Arsenic trioxide (ATO) and MEK1 inhibition synergize
to induce apoptosis in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells.
Leukemia. 19:234–244. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Downward J: How BAD phosphorylation is
good for survival. Nat Cell Biol. 1:E33–E35. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zha J, Harada H, Yang E, Jockel J and
Korsmeyer SJ: Serine phosphorylation of death agonist BAD in
response to survival factor results in binding to 14-3-3 not
BCL-X(L). Cell. 87:619–628. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Han YH, Kim SZ, Kim SH and Park WH:
Arsenic trioxide inhibits the growth of Calu-6 cells via inducing a
G2 arrest of the cell cycle and apoptosis accompanied with the
depletion of GSH. Cancer Lett. 270:40–55. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jiang L, Wang L, Chen L, Cai GH, Ren QY,
Chen JZ, Shi HJ and Xie YH: As2O3 induces
apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells through a
ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway and activation of caspases. Int
J Clin Exp Med. 8:2190–2196. 2015.
|
|
43
|
Lu TH, Su CC, Chen YW, Yang CY, Wu CC,
Hung DZ, Chen CH, Cheng PW, Liu SH and Huang CF: Arsenic induces
pancreatic β-cell apoptosis via the oxidative stress-regulated
mitochondria-dependent and endoplasmic reticulum stress-triggered
signaling pathways. Toxicol Lett. 201:15–26. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wu X, Shi J, Wu Y, Tao Y, Hou J, Meng X,
Hu X, Han Y, Jiang W, Tang S, et al: Arsenic trioxide-mediated
growth inhibition of myeloma cells is associated with an extrinsic
or intrinsic signaling pathway through activation of TRAIL or TRAIL
receptor 2. Cancer Biol Ther. 10:1201–1214. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|