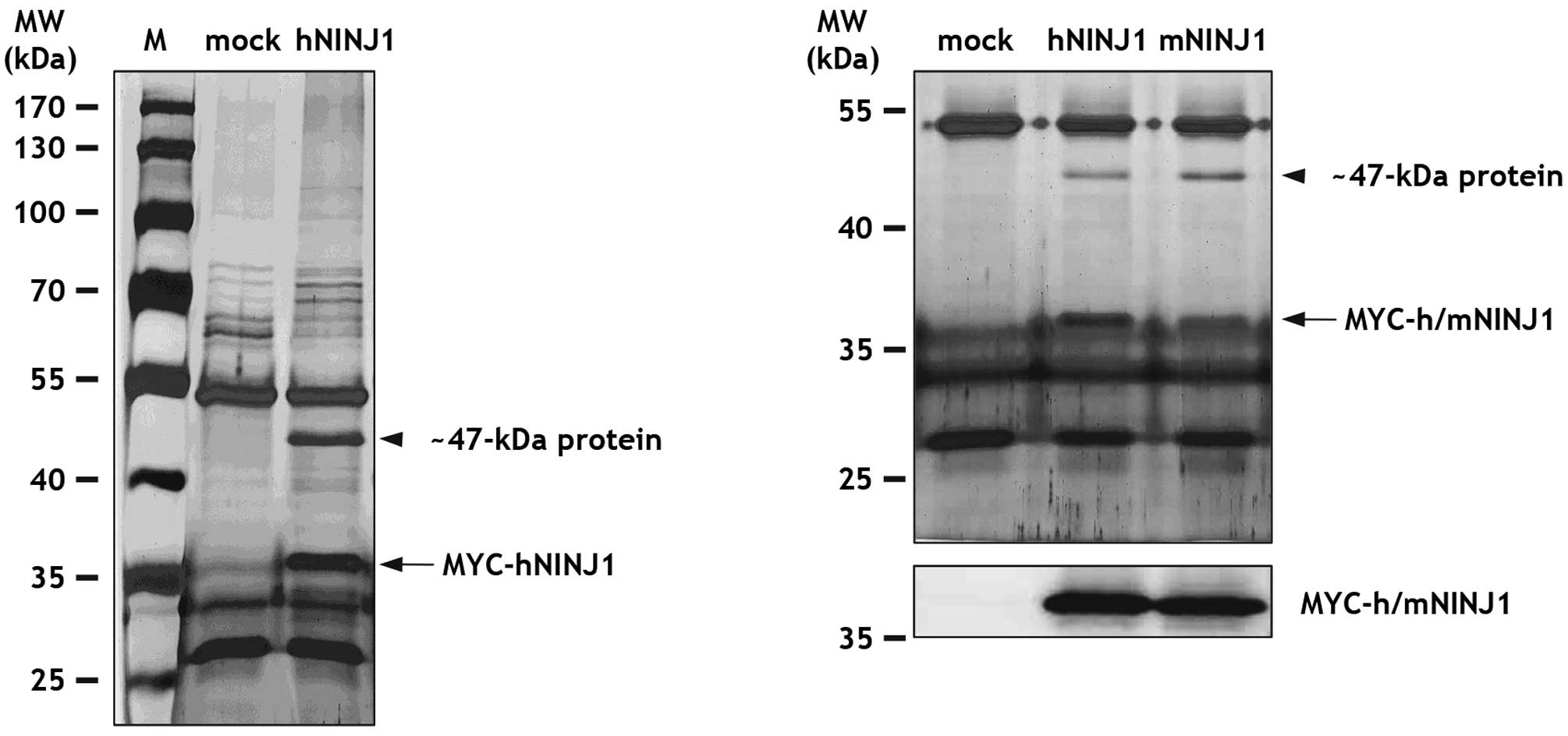
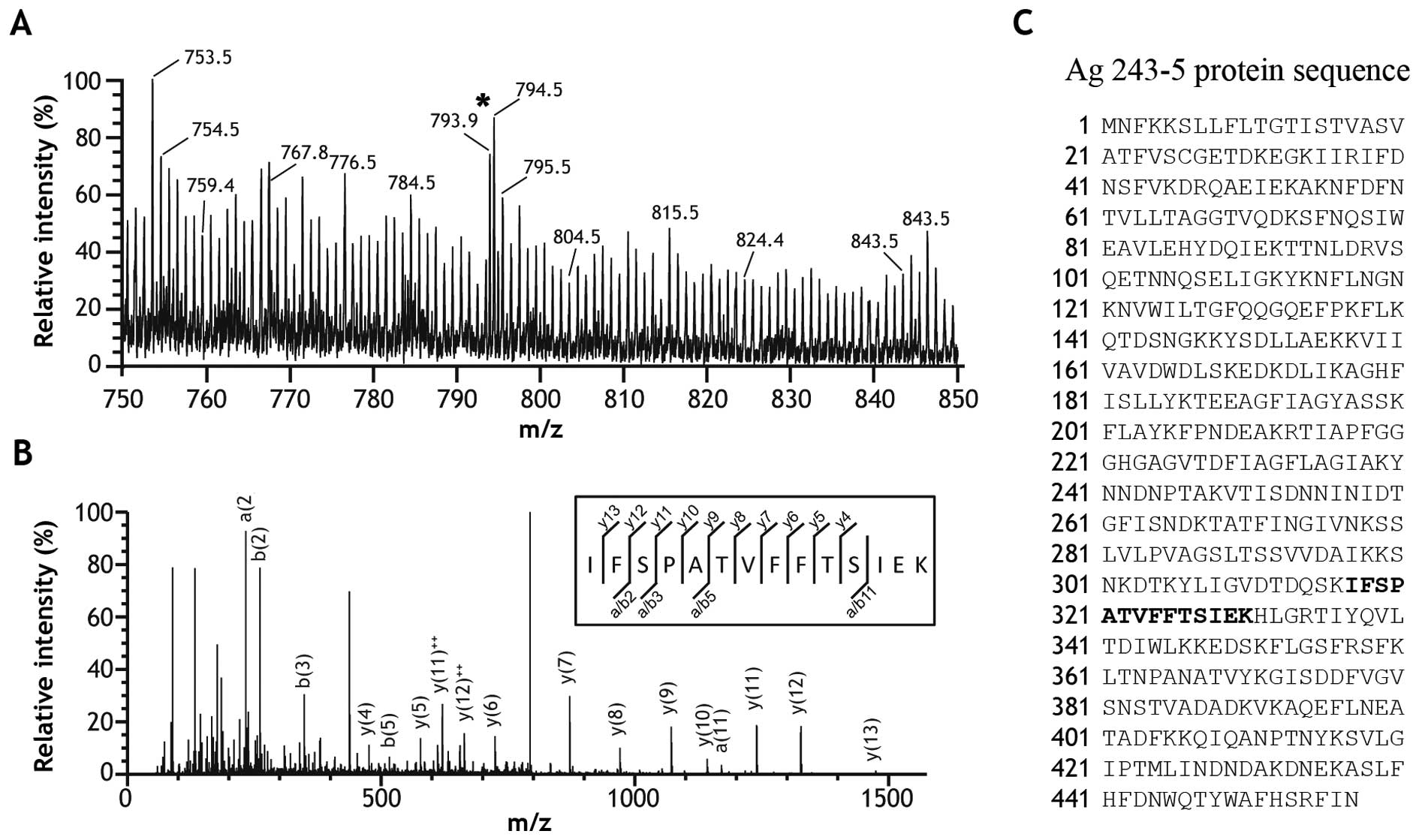
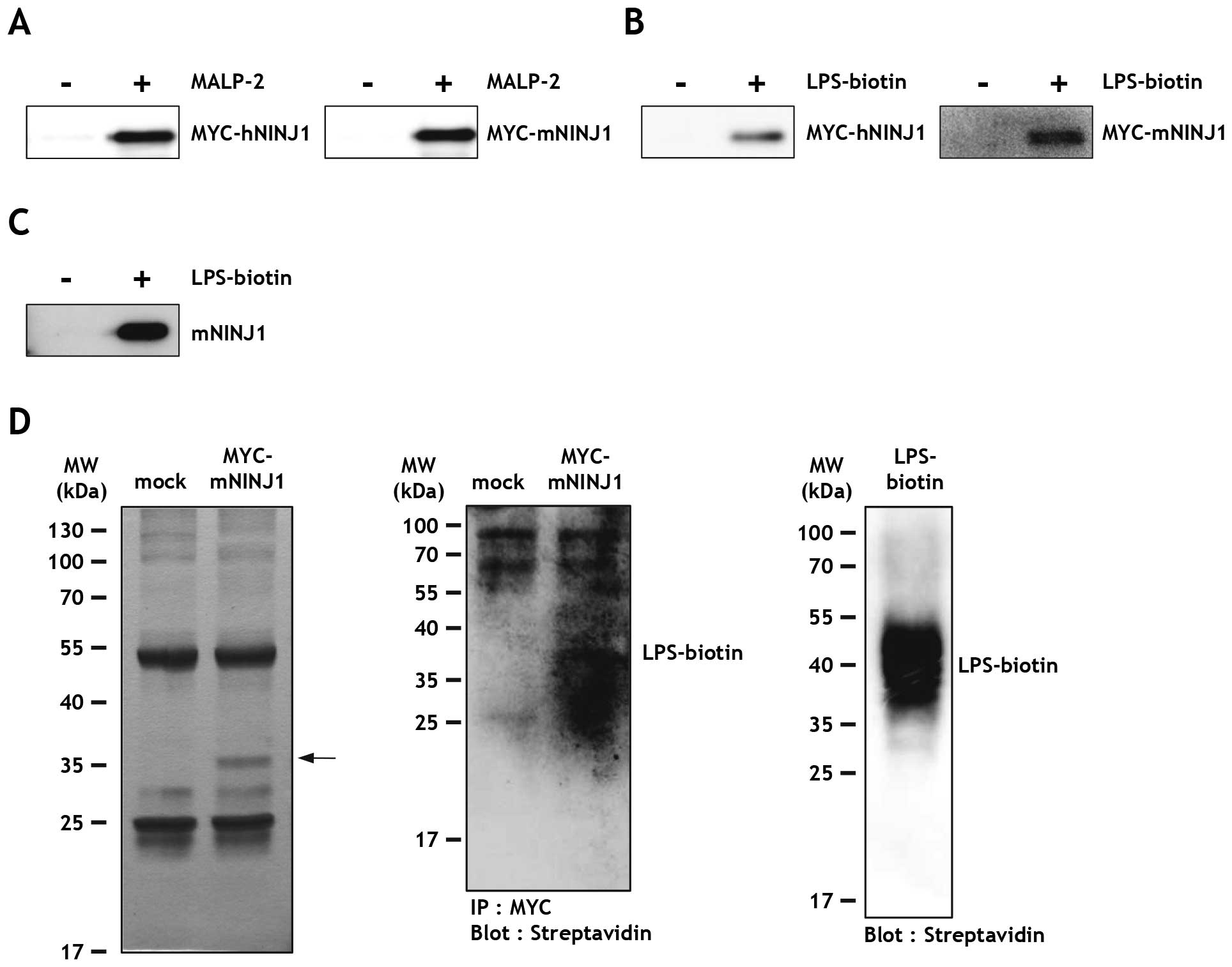
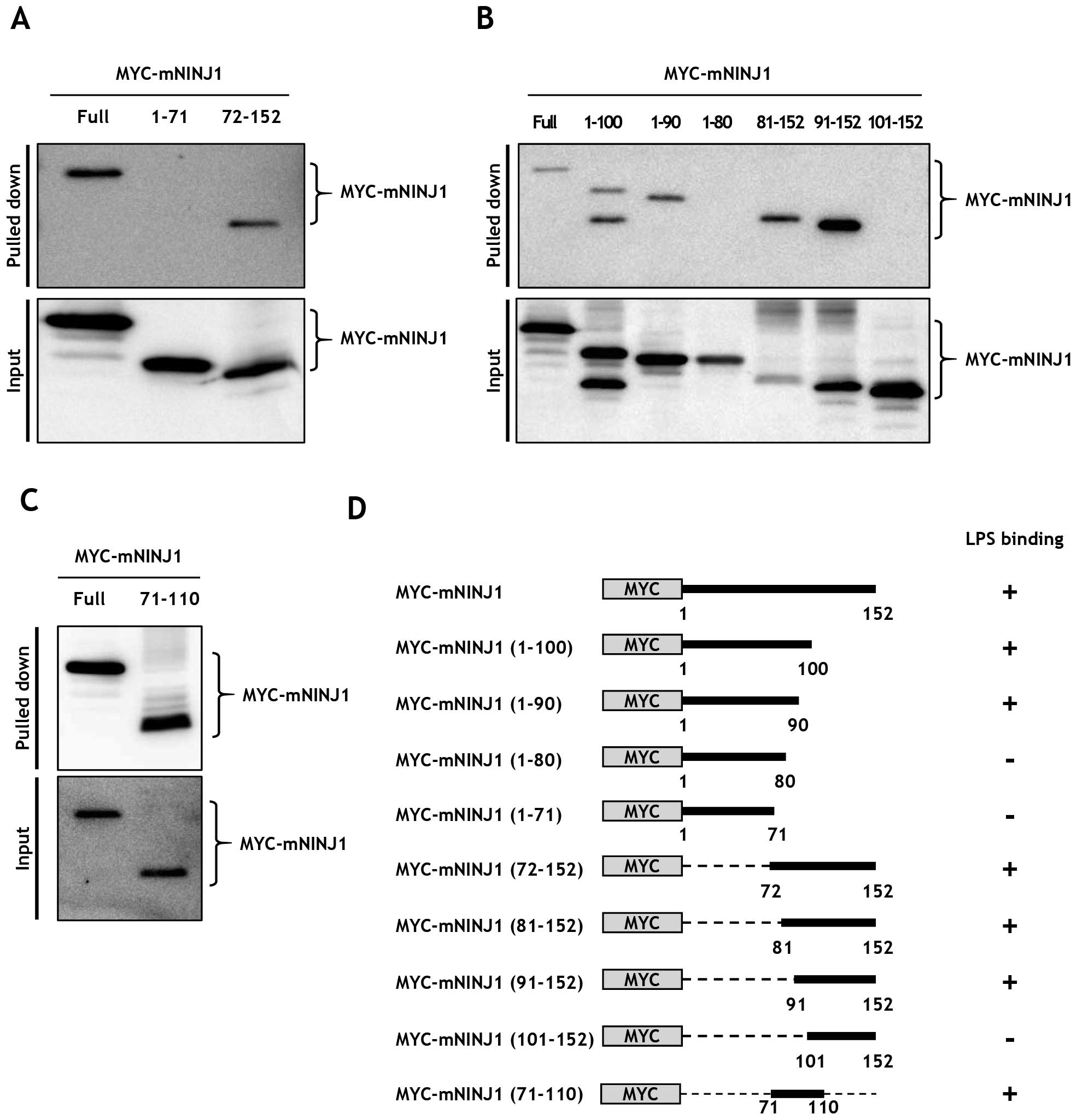
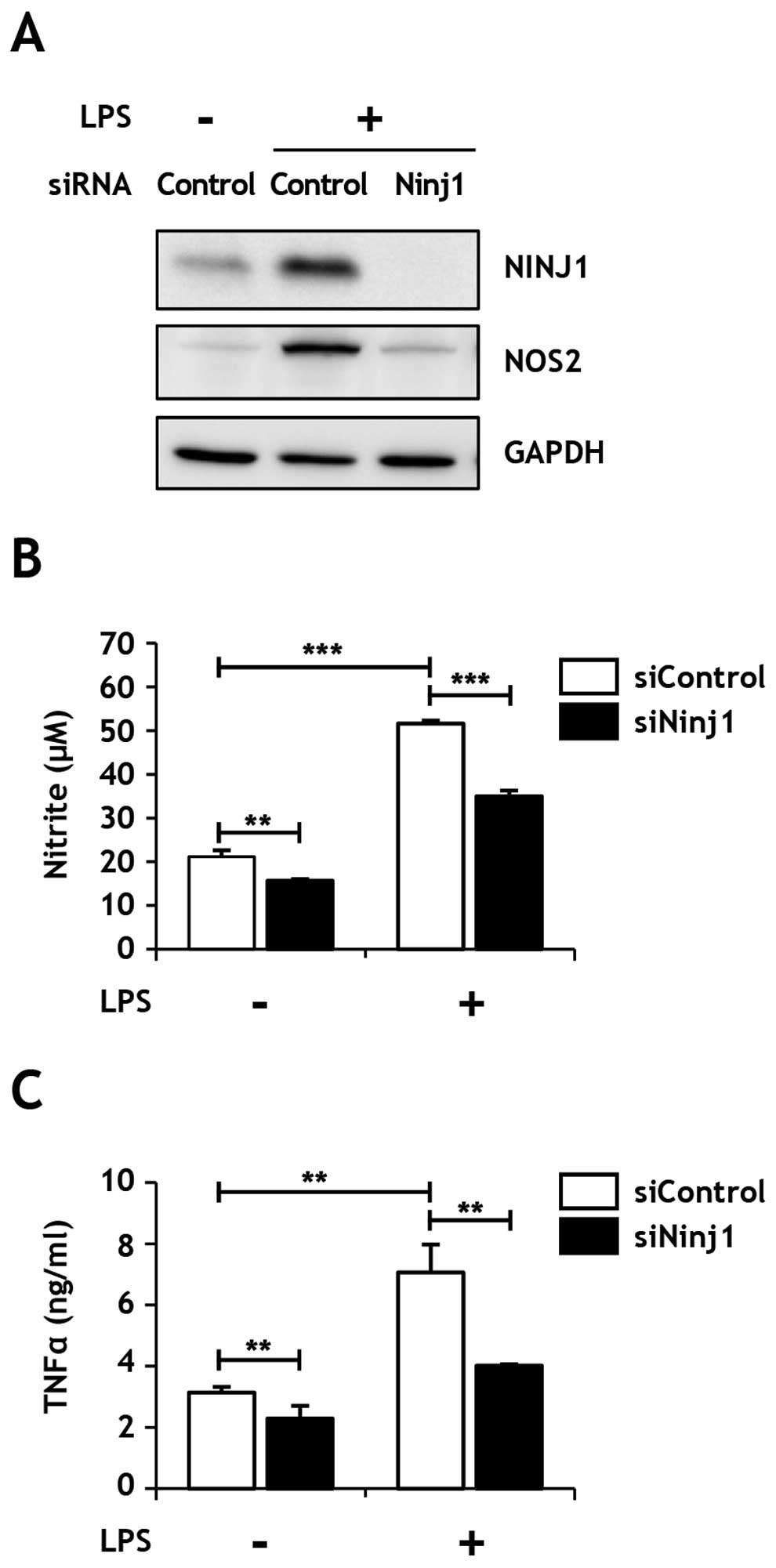
|
1
|
Medzhitov R: Inflammation 2010: New
adventures of an old flame. Cell. 140:771–776. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Urban JL, Shepard HM, Rothstein JL,
Sugarman BJ and Schreiber H: Tumor necrosis factor: A potent
effector molecule for tumor cell killing by activated macrophages.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 83:5233–5237. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR and Karin M:
Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 140:883–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gocheva V, Wang HW, Gadea BB, Shree T,
Hunter KE, Garfall AL, Berman T and Joyce JA: IL-4 induces
cathepsin protease activity in tumor-associated macrophages to
promote cancer growth and invasion. Genes Dev. 24:241–255. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Akira S: Pathogen recognition by innate
immunity and its signaling. Proc Jpn Acad, Ser B, Phys Biol Sci.
85:143–156. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chambaud I, Wróblewski H and Blanchard A:
Interactions between mycoplasma lipoproteins and the host immune
system. Trends Microbiol. 7:493–499. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Beutler B and Rietschel ET: Innate immune
sensing and its roots: The story of endotoxin. Nat Rev Immunol.
3:169–176. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Calcutt MJ, Kim MF, Karpas AB, Mühlradt PF
and Wise KS: Differential posttranslational processing confers
intraspecies variation of a major surface lipoprotein and a
macrophage-activating lipopeptide of Mycoplasma fermentans. Infect
Immun. 67:760–771. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ushio S, Iwaki K, Taniai M, Ohta T, Fukuda
S, Sugimura K and Kurimoto M: Metastasis-promoting activity of a
novel molecule, Ag 243–5, derived from mycoplasma, and the complete
nucleotide sequence. Microbiol Immunol. 39:393–400. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Rosati S, Pozzi S, Robino P, Montinaro B,
Conti A, Fadda M and Pittau M: P48 major surface antigen of
Mycoplasma agalactiae is homologous to a malp product of Mycoplasma
fermentans and belongs to a selected family of bacterial
lipoproteins. Infect Immun. 67:6213–6216. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hailman E, Lichenstein HS, Wurfel MM,
Miller DS, Johnson DA, Kelley M, Busse LA, Zukowski MM and Wright
SD: Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein accelerates the
binding of LPS to CD14. J Exp Med. 179:269–277. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wright SD, Ramos RA, Tobias PS, Ulevitch
RJ and Mathison JC: CD14, a receptor for complexes of
lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science.
249:1431–1433. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jerala R: Structural biology of the LPS
recognition. Int J Med Microbiol. 297:353–363. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Miyake K: Innate recognition of
lipopolysaccharide by Toll-like receptor 4-MD-2. Trends Microbiol.
12:186–192. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Youn JH, Oh YJ, Kim ES, Choi JE and Shin
JS: High mobility group box 1 protein binding to lipopolysaccharide
facilitates transfer of lipopolysaccharide to CD14 and enhances
lipopolysaccharide-mediated TNF-alpha production in human
monocytes. J Immunol. 180:5067–5074. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Triantafilou K, Triantafilou M and Dedrick
RL: A CD14-independent LPS receptor cluster. Nat Immunol.
2:338–345. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Agar C, de Groot PG, Mörgelin M, Monk SD,
van Os G, Levels JH, de Laat B, Urbanus RT, Herwald H, van der Poll
T, et al: β(2)-glycoprotein I: A novel component of innate
immunity. Blood. 117:6939–6947. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Araki T and Milbrandt J: Ninjurin, a novel
adhesion molecule, is induced by nerve injury and promotes axonal
growth. Neuron. 17:353–361. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ahn BJ, Le H, Shin MW, Bae SJ, Lee EJ, Wee
HJ, Cha JH, Lee HJ, Lee HS, Kim JH, et al: Ninjurin1 deficiency
attenuates susceptibility of experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis in mice. J Biol Chem. 289:3328–3338. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Lee HJ, Ahn BJ, Shin MW, Jeong JW, Kim JH
and Kim KW: Ninjurin1 mediates macrophage-induced programmed cell
death during early ocular development. Cell Death Differ.
16:1395–1407. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jennewein C, Sowa R, Faber AC, Dildey M,
von Knethen A, Meybohm P, Scheller B, Dröse S and Zacharowski K:
Contribution of ninjurin1 to toll-like receptor 4 signaling and
systemic inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 53:656–663. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ahn BJ, Le H, Shin MW, Bae SJ, Lee EJ, Wee
HJ, Cha JH, Park JH, Lee HS, Lee HJ, et al: The N-terminal
ectodomain of Ninjurin1 liberated by MMP9 has chemotactic activity.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 428:438–444. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ifergan I, Kebir H, Terouz S, Alvarez JI,
Lécuyer MA, Gendron S, Bourbonnière L, Dunay IR, Bouthillier A,
Moumdjian R, et al: Role of Ninjurin-1 in the migration of myeloid
cells to central nervous system inflammatory lesions. Ann Neurol.
70:751–763. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Araki T, Zimonjic DB, Popescu NC and
Milbrandt J: Mechanism of homophilic binding mediated by ninjurin,
a novel widely expressed adhesion molecule. J Biol Chem.
272:21373–21380. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee HJ, Ahn BJ, Shin MW, Choi JH and Kim
KW: Ninjurin1: A potential adhesion molecule and its role in
inflammation and tissue remodeling. Mol Cells. 29:223–227. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Youn JH, Kwak MS, Wu J, Kim ES, Ji Y, Min
HJ, Yoo JH, Choi JE, Cho HS and Shin JS: Identification of
lipopolysaccharide-binding peptide regions within HMGB1 and their
effects on subclinical endotoxemia in a mouse model. Eur J Immunol.
41:2753–2762. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Matsuki M, Kabara M, Saito Y, Shimamura K,
Minoshima A, Nishimura M, Aonuma T, Takehara N, Hasebe N and Kawabe
J: Ninjurin1 is a novel factor to regulate angiogenesis through the
function of pericytes. Circ J. 79:1363–1371. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cho SJ, Rossi A, Jung YS, Yan W, Liu G,
Zhang J, Zhang M and Chen X: Ninjurin1, a target of p53, regulates
p53 expression and p53-dependent cell survival, senescence, and
radiation-induced mortality. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:9362–9367.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mhawech-Fauceglia P, Ali L, Cheney RT,
Groth J and Herrmann FR: Prognostic significance of
neuron-associated protein expression in non-muscle-invasive
urothelial bladder cancer. J Clin Pathol. 62:710–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim JW, Moon AR, Kim JH, Yoon SY, Oh GT,
Choe YK and Choe IS: Up-regulation of ninjurin expression in human
hepatocellular carcinoma associated with cirrhosis and chronic
viral hepatitis. Mol Cells. 11:151–157. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Strieter RM, Kunkel SL, Showell HJ, Remick
DG, Phan SH, Ward PA and Marks RM: Endothelial cell gene expression
of a neutrophil chemotactic factor by TNF-alpha, LPS, and IL-1
beta. Science. 243:1467–1469. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Luo JL, Maeda S, Hsu LC, Yagita H and
Karin M: Inhibition of NF-kappaB in cancer cells converts
inflammation- induced tumor growth mediated by TNFalpha to
TRAIL-mediated tumor regression. Cancer Cell. 6:297–305. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|