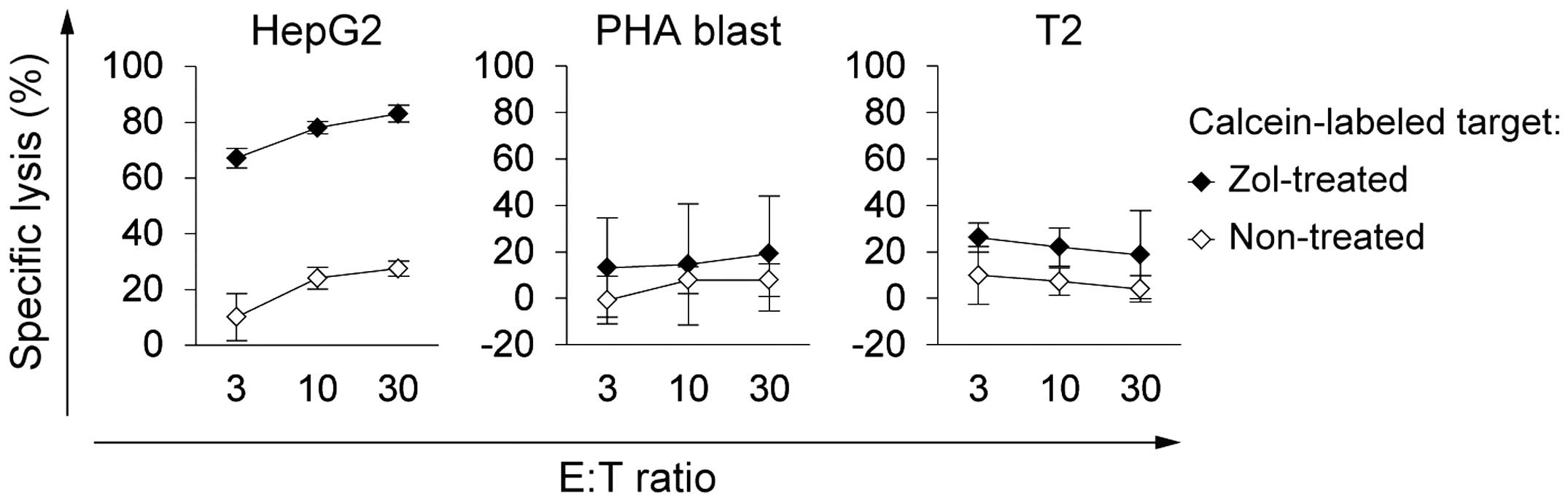
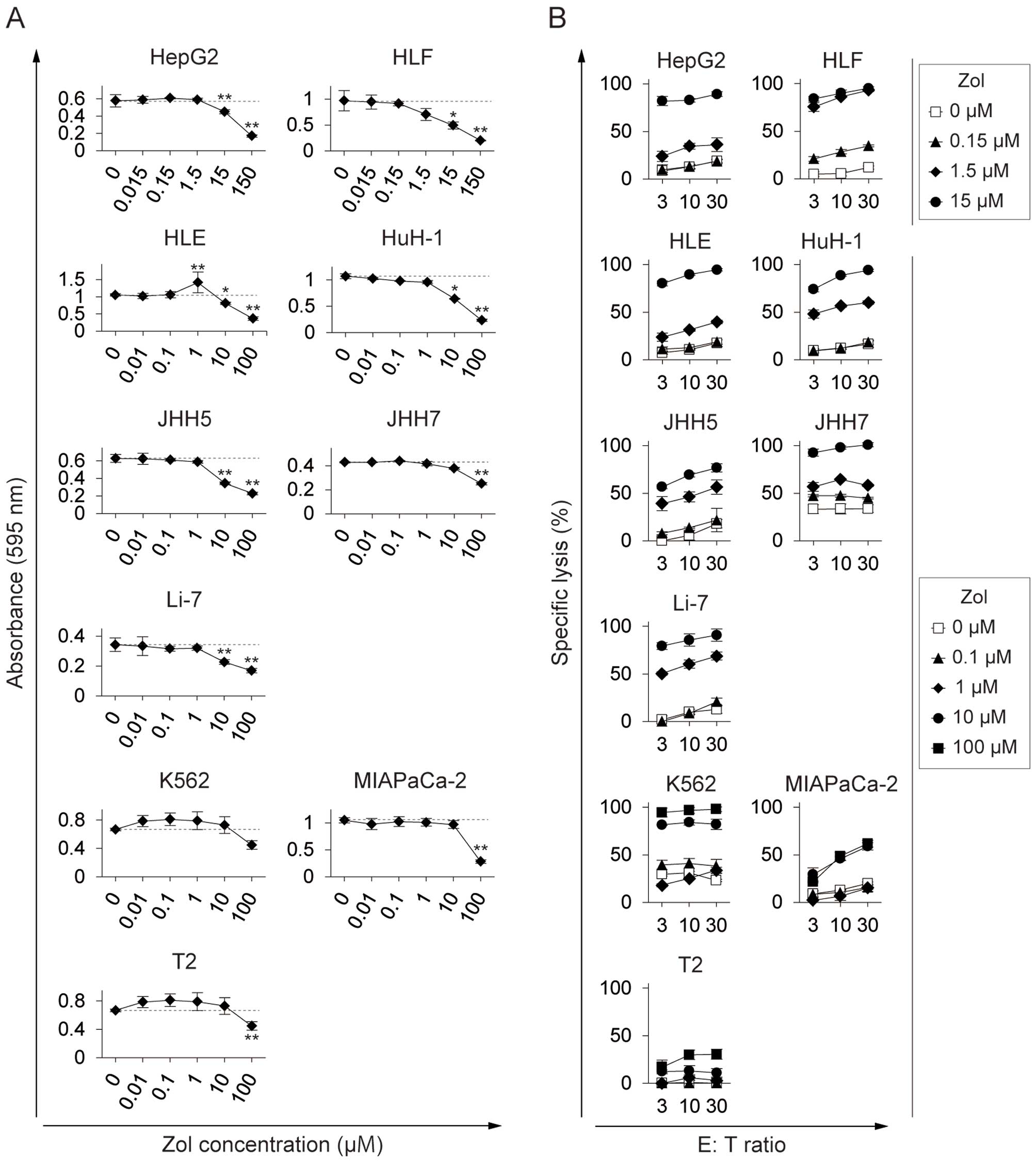
|
1
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S,
Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, et al: Efficacy and safety of
sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomised, double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 10:25–34. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kelley RK: Adjuvant sorafenib for liver
cancer: Wrong stage, wrong dose. Lancet Oncol. 16:1279–1281. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mahoney KM, Rennert PD and Freeman GJ:
Combination cancer immunotherapy and new immunomodulatory targets.
Nat Rev Drug Discov. 14:561–584. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rosenberg SA and Restifo NP: Adoptive cell
transfer as personalized immunotherapy for human cancer. Science.
348:62–68. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sharma P and Allison JP: The future of
immune checkpoint therapy. Science. 348:56–61. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hayashi E, Motomura Y, Shirakawa H,
Yoshikawa T, Oba N, Nishinakagawa S, Mizuguchi Y, Kojima T, Nomura
K and Nakatsura T: Detection of glypican-3-specific CTLs in chronic
hepatitis and liver cirrhosis. Oncol Rep. 22:149–154. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sawada Y, Yoshikawa T, Nobuoka D,
Shirakawa H, Kuronuma T, Motomura Y, Mizuno S, Ishii H, Nakachi K,
Konishi M, et al: Phase I trial of a glypican-3-derived peptide
vaccine for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Immunologic evidence
and potential for improving overall survival. Clin Cancer Res.
18:3686–3696. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yoshikawa T, Takahara M, Tomiyama M, Nieda
M, Maekawa R and Nakatsura T: Large-scale expansion of γδ T cells
and peptide-specific cytotoxic T cells using zoledronate for
adoptive immunotherapy. Int J Oncol. 45:1847–1856. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bonneville M, O'Brien RL and Born WK:
Gammadelta T cell effector functions: A blend of innate programming
and acquired plasticity. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:467–478. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Van Acker HH, Anguille S, Van Tendeloo VF
and Lion E: Empowering gamma delta T cells with antitumor immunity
by dendritic cell-based immunotherapy. OncoImmunology.
4:e10215382015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gertner-Dardenne J, Castellano R,
Mamessier E, Garbit S, Kochbati E, Etienne A, Charbonnier A,
Collette Y, Vey N and Olive D: Human Vγ9Vδ2 T cells specifically
recognize and kill acute myeloid leukemic blasts. J Immunol.
188:4701–4708. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gober HJ, Kistowska M, Angman L, Jenö P,
Mori L and De Libero G: Human T cell receptor gammadelta cells
recognize endogenous mevalonate metabolites in tumor cells. J Exp
Med. 197:163–168. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kong Y, Cao W, Xi X, Ma C, Cui L and He W:
The NKG2D ligand ULBP4 binds to TCRgamma9/delta2 and induces
cytotoxicity to tumor cells through both TCRgammadelta and NKG2D.
Blood. 114:310–317. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nedellec S, Sabourin C, Bonneville M and
Scotet E: NKG2D costimulates human V gamma 9V delta 2 T cell
antitumor cytotoxicity through protein kinase C theta-dependent
modulation of early TCR-induced calcium and transduction signals. J
Immunol. 185:55–63. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Benzaïd I, Mönkkönen H, Bonnelye E,
Mönkkönen J and Clézardin P: In vivo phosphoantigen levels in
bisphosphonate-treated human breast tumors trigger Vγ9Vδ2 T-cell
antitumor cytotoxicity through ICAM-1 engagement. Clin Cancer Res.
18:6249–6259. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Benzaïd I, Mönkkönen H, Stresing V,
Bonnelye E, Green J, Mönkkönen J, Touraine JL and Clézardin P: High
phosphoantigen levels in bisphosphonate-treated human breast tumors
promote Vgamma9Vdelta2 T-cell chemotaxis and cytotoxicity in vivo.
Cancer Res. 71:4562–4572. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rei M, Pennington DJ and Silva-Santos B:
The emerging Protumor role of γδ T lymphocytes: Implications for
cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 75:798–802. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fisher JP, Heuijerjans J, Yan M,
Gustafsson K and Anderson J: γδ T cells for cancer immunotherapy: A
systematic review of clinical trials. OncoImmunology. 3:e275722014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Corvaisier M, Moreau-Aubry A, Diez E,
Bennouna J, Mosnier JF, Scotet E, Bonneville M and Jotereau F: V
gamma 9V delta 2 T cell response to colon carcinoma cells. J
Immunol. 175:5481–5488. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Di Carlo E, Bocca P, Emionite L, Cilli M,
Cipollone G, Morandi F, Raffaghello L, Pistoia V and Prigione I:
Mechanisms of the antitumor activity of human Vγ9Vδ2 T cells in
combination with zoledronic acid in a preclinical model of
neuroblastoma. Mol Ther. 21:1034–1043. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Idrees AS, Sugie T, Inoue C, Murata-Hirai
K, Okamura H, Morita CT, Minato N, Toi M and Tanaka Y: Comparison
of γδ T cell responses and farnesyl diphosphate synthase inhibition
in tumor cells pretreated with zoledronic acid. Cancer Sci.
104:536–542. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sugie T, Murata-Hirai K, Iwasaki M, Morita
CT, Li W, Okamura H, Minato N, Toi M and Tanaka Y: Zoledronic
acid-induced expansion of γδ T cells from early-stage breast cancer
patients: Effect of IL-18 on helper NK cells. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 62:677–687. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Toutirais O, Cabillic F, Le Friec G, Salot
S, Loyer P, Le Gallo M, Desille M, de La Pintière CT, Daniel P,
Bouet F, et al: DNAX accessory molecule-1 (CD226) promotes human
hepatocellular carcinoma cell lysis by Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cells. Eur
J Immunol. 39:1361–1368. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deniger DC, Maiti SN, Mi T, Switzer KC,
Ramachandran V, Hurton LV, Ang S, Olivares S, Rabinovich BA, Huls
MH, et al: Activating and propagating polyclonal gamma delta T
cells with broad specificity for malignancies. Clin Cancer Res.
20:5708–5719. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Viey E, Fromont G, Escudier B, Morel Y, Da
Rocha S, Chouaib S and Caignard A: Phosphostim-activated gamma
delta T cells kill autologous metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J
Immunol. 174:1338–1347. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Honda Y, Takahashi S, Zhang Y, Ono A,
Murakami E, Shi N, Kawaoka T, Miki D, Tsuge M, Hiraga N, et al:
Effects of bisphosphonate zoledronic acid in hepatocellular
carcinoma, depending on mevalonate pathway. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 30:619–627. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Bouet-Toussaint F, Cabillic F, Toutirais
O, Le Gallo M, Thomas de la Pintière C, Daniel P, Genetet N,
Meunier B, Dupont-Bierre E, Boudjema K, et al: Vgamma9Vdelta2 T
cell-mediated recognition of human solid tumors. Potential for
immunotherapy of hepatocellular and colorectal carcinomas. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 57:531–539. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Cabillic F, Toutirais O, Lavoué V, de La
Pintière CT, Daniel P, Rioux-Leclerc N, Turlin B, Mönkkönen H,
Mönkkönen J, Boudjema K, et al: Aminobisphosphonate-pretreated
dendritic cells trigger successful Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cell
amplification for immunotherapy in advanced cancer patients. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 59:1611–1619. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yi Y, He HW, Wang JX, Cai XY, Li YW, Zhou
J, Cheng YF, Jin JJ, Fan J and Qiu SJ: The functional impairment of
HCC-infiltrating γδ T cells, partially mediated by regulatory T
cells in a TGFβ- and IL-10-dependent manner. J Hepatol. 58:977–983.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li J, Herold MJ, Kimmel B, Müller I,
Rincon-Orozco B, Kunzmann V and Herrmann T: Reduced expression of
the mevalonate pathway enzyme farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase
unveils recognition of tumor cells by Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cells. J
Immunol. 182:8118–8124. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Thompson K, Rogers MJ, Coxon FP and
Crockett JC: Cytosolic entry of bisphosphonate drugs requires
acidification of vesicles after fluid-phase endocytosis. Mol
Pharmacol. 69:1624–1632. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ribot JC, Ribeiro ST, Correia DV, Sousa AE
and Silva-Santos B: Human γδ thymocytes are functionally immature
and differentiate into cytotoxic type 1 effector T cells upon
IL-2/IL-15 signaling. J Immunol. 192:2237–2243. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wu P, Wu D, Ni C, Ye J, Chen W, Hu G, Wang
Z, Wang C, Zhang Z, Xia W, et al: γδT17 cells promote the
accumulation and expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in
human colorectal cancer. Immunity. 40:785–800. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Caccamo N, La Mendola C, Orlando V,
Meraviglia S, Todaro M, Stassi G, Sireci G, Fournié JJ and Dieli F:
Differentiation, phenotype, and function of
interleukin-17-producing human Vγ9Vδ2 T cells. Blood. 118:129–138.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Johnston RJ, Comps-Agrar L, Hackney J, Yu
X, Huseni M, Yang Y, Park S, Javinal V, Chiu H, Irving B, et al:
The immunoreceptor TIGIT regulates antitumor and antiviral CD8(+) T
cell effector function. Cancer Cell. 26:923–937. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chauvin JM, Pagliano O, Fourcade J, Sun Z,
Wang H, Sander C, Kirkwood JM, Chen TH, Maurer M, Korman AJ, et al:
TIGIT and PD-1 impair tumor antigen-specific CD8+ T
cells in melanoma patients. J Clin Invest. 125:2046–2058. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schumacher TN and Schreiber RD:
Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy. Science. 348:69–74. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Brandes M, Willimann K and Moser B:
Professional antigen-presentation function by human gammadelta T
Cells. Science. 309:264–268. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Moser B and Eberl M: γδ T-APCs: A novel
tool for immunotherapy? Cell Mol Life Sci. 68:2443–2452. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|