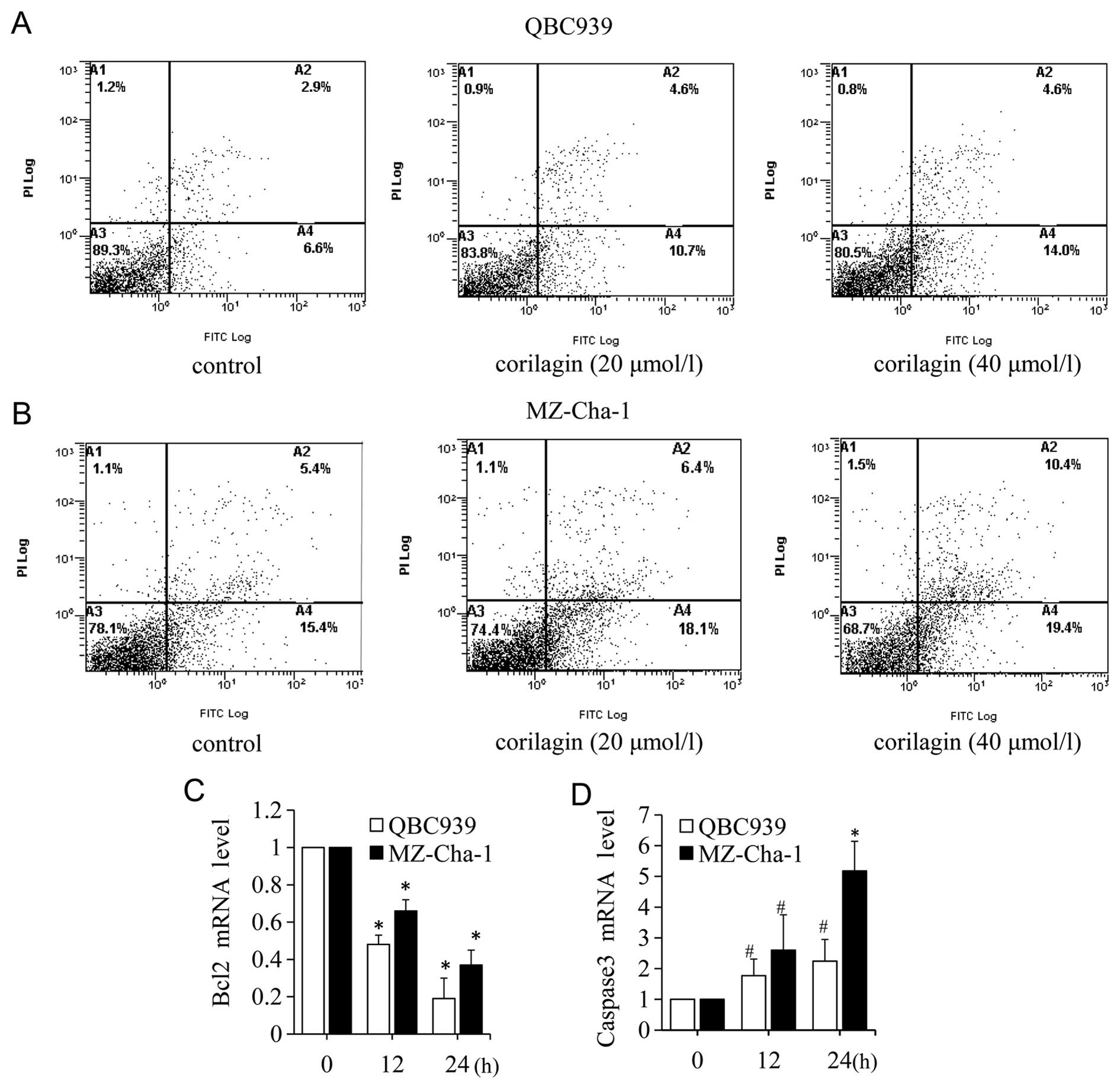
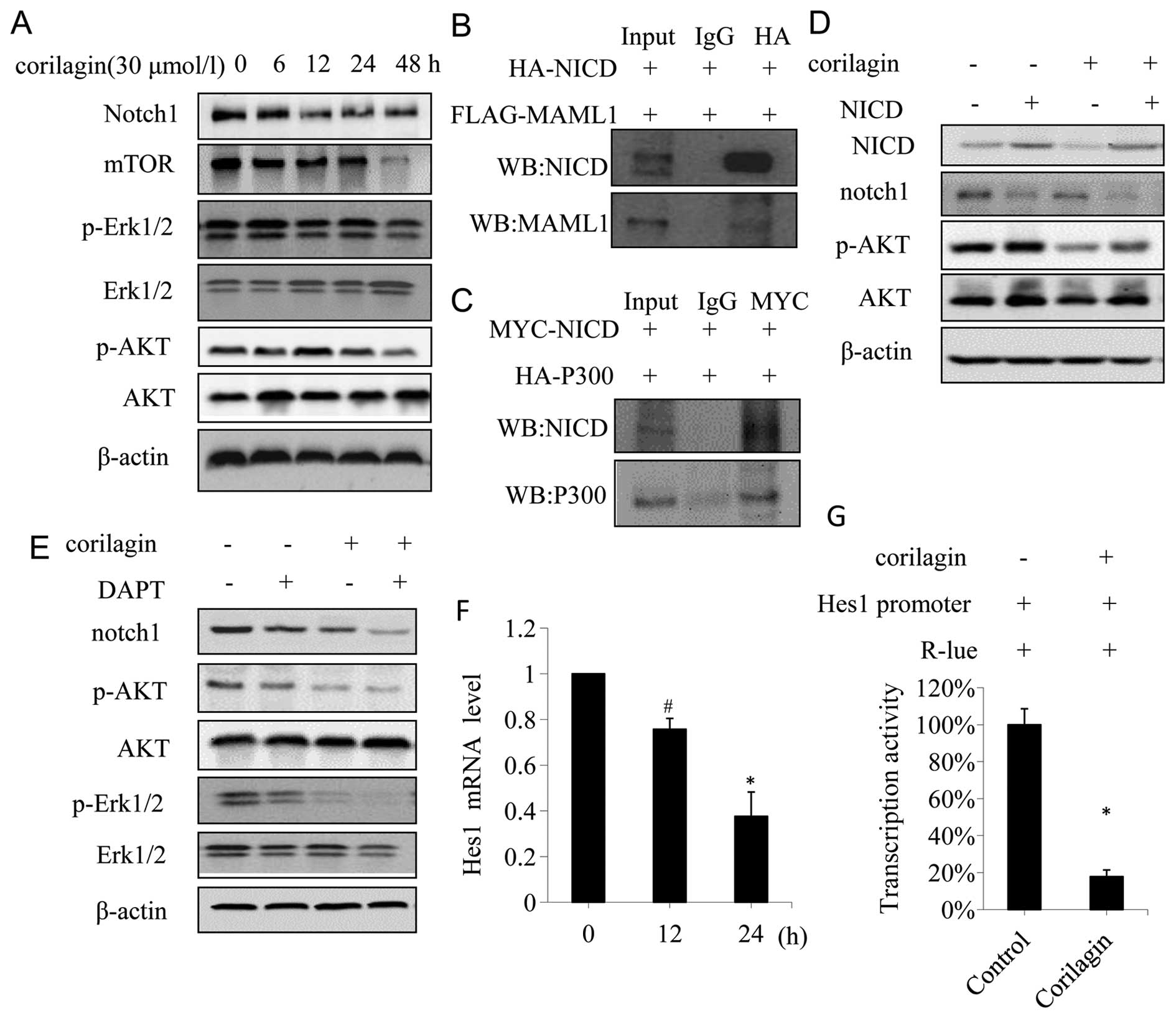
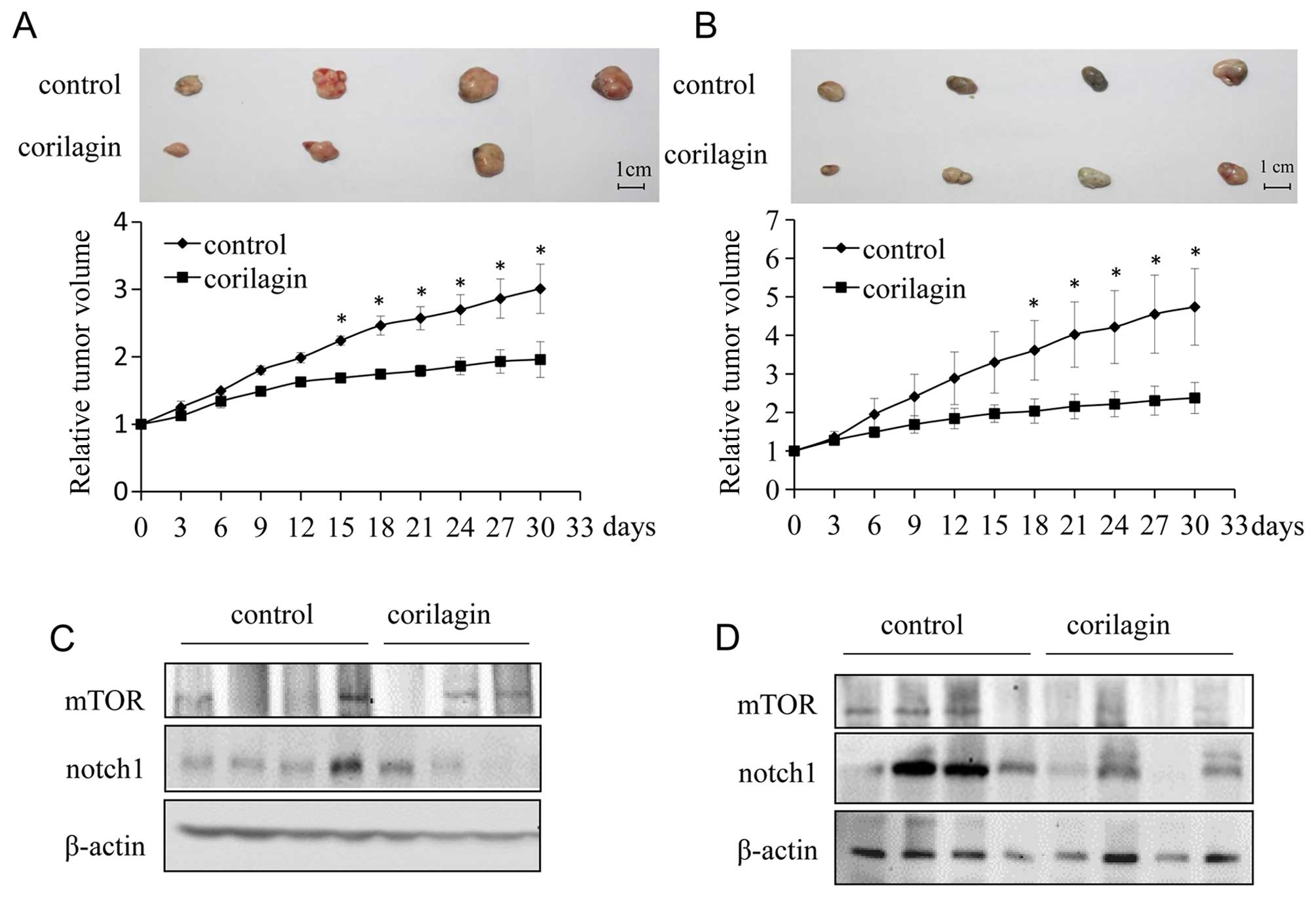
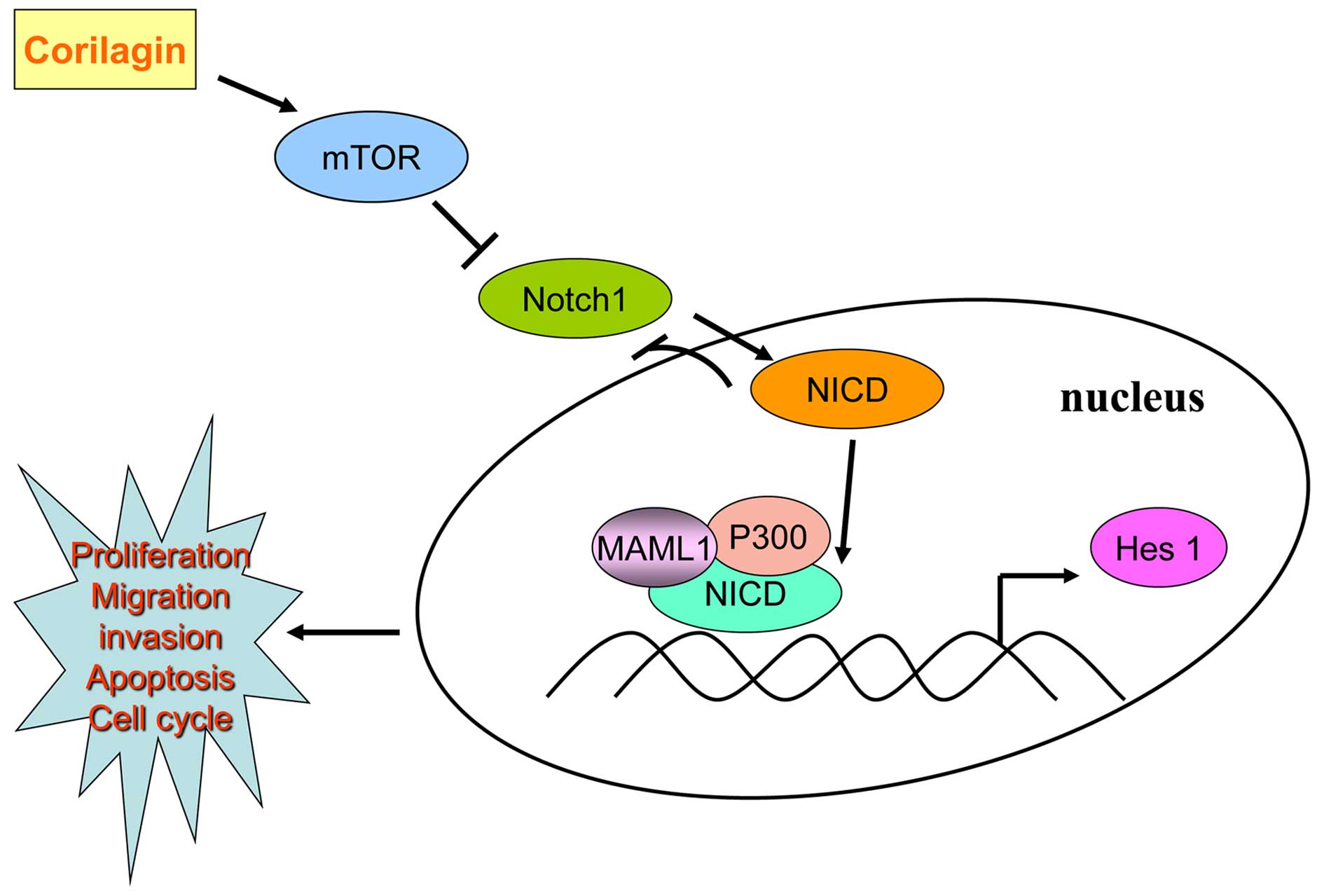
|
1
|
Singal AK, Vauthey JN, Grady JJ and
Stroehlein JR: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma - frequency and
demographic patterns: Thirty-year data from the M.D. Anderson
Cancer Center. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 137:1071–1078. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
McGlynn KA, Tarone RE and El-Serag HB: A
comparison of trends in the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma
and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 15:1198–1203. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Al-Bahrani R, Abuetabh Y, Zeitouni N and
Sergi C: Cholangiocarcinoma: Risk factors, environmental influences
and oncogenesis. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 43:195–210. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tepsiri N, Chaturat L, Sripa B, Namwat W,
Wongkham S, Bhudhisawasdi V and Tassaneeyakul W: Drug sensitivity
and drug resistance profiles of human intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma cell lines. World J Gastroenterol. 11:2748–2753.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shaib Y and El-Serag HB: The epidemiology
of cholangiocarcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 24:115–125. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Poggi G, Quaretti P, Minoia C, Palumbo I,
Villani L, Amatu A, Teragni C, Scelsi M, Zappoli F and Bernardo G:
Oxaliplatin-eluting microspheres for the treatment of intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma: A case report. Anticancer Res. 28:2987–2990.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shitara K, Ikami I, Munakata M, Muto O and
Sakata Y: Hepatic arterial infusion of mitomycin C with degradable
starch microspheres for unresectable intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 20:241–246. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yeo SG, Song JH, Hong EH, Lee BR, Kwon YS,
Chang SY, Kim SH, Lee SW, Park JH and Ko HJ: Antiviral effects of
Phyllanthus urinaria containing corilagin against human enterovirus
71 and Coxsackievirus A16 in vitro. Arch Pharm Res. 38:193–202.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Rangkadilok N, Sitthimonchai S,
Worasuttayangkurn L, Mahidol C, Ruchirawat M and Satayavivad J:
Evaluation of free radical scavenging and antityrosinase activities
of standardized longan fruit extract. Food Chem Toxicol.
45:328–336. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Li N, Luo M, Fu YJ, Zu YG, Wang W, Zhang
L, Yao LP, Zhao CJ and Sun Y: Effect of corilagin on membrane
permeability of Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Candida
albicans. Phytother Res. 27:1517–1523. 2013.
|
|
11
|
Chen Y and Chen C: Corilagin prevents
tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced oxidative stress injury in
cultured N9 murine microglia cells. Neurochem Int. 59:290–296.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gambari R, Borgatti M, Lampronti I, Fabbri
E, Brognara E, Bianchi N, Piccagli L, Yuen MC, Kan CW, Hau DK, et
al: Corilagin is a potent inhibitor of NF-kappaB activity and
downregulates TNF-alpha induced expression of IL-8 gene in cystic
fibrosis IB3-1 cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 13:308–315. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Prasad KN, Yang B, Shi J, Yu C, Zhao M,
Xue S and Jiang Y: Enhanced antioxidant and antityrosinase
activities of longan fruit pericarp by ultra-high-pressure-assisted
extraction. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 51:471–477. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wang B: Corilagin nanoparticle-induced
apoptosis in human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells via the
mitochondrial pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 34:14. 2013.
|
|
15
|
Ming Y, Zheng Z, Chen L, Zheng G, Liu S,
Yu Y and Tong Q: Corilagin inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell
proliferation by inducing G2/M phase arrest. Cell Biol Int.
37:1046–1054. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ranganathan P, Weaver KL and Capobianco
AJ: Notch signalling in solid tumours: A little bit of everything
but not all the time. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:338–351. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Takebe N, Harris PJ, Warren RQ and Ivy SP:
Targeting cancer stem cells by inhibiting Wnt, Notch, and Hedgehog
pathways. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 8:97–106. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Miele L, Golde T and Osborne B: Notch
signaling in cancer. Curr Mol Med. 6:905–918. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Miele L, Miao H and Nickoloff BJ: NOTCH
signaling as a novel cancer therapeutic target. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 6:313–323. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou W, Wang G and Guo S: Regulation of
angiogenesis via Notch signaling in breast cancer and cancer stem
cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1836.304–320. 2013.
|
|
21
|
Borggrefe T and Oswald F: The Notch
signaling pathway: Transcriptional regulation at Notch target
genes. Cell Mol Life Sci. 66:1631–1646. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Z, Guo QY, Zhang XJ, Li X, Li WT, Ma
XT and Ma LJ: Corilagin attenuates aerosol bleomycin-induced
experimental lung injury. Int J Mol Sci. 15:9762–9779. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kimpton WG, McKenzie GA, Muller HK, Ruby
JC and Poskitt DC: Lymphocyte migration during the development of
regional lymph node anergy in experimental tumor growth. Cell
Immunol. 75:13–21. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Takahashi S, Hasebe T, Oda T, Sasaki S,
Kinoshita T, Konishi M, Ueda T, Ochiai T and Ochiai A: Extra-tumor
perineural invasion predicts postoperative development of
peritoneal dissemination in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Anticancer Res. 21:1407–1412. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
El-Habr EA, Levidou G, Trigka EA,
Sakalidou J, Piperi C, Chatziandreou I, Spyropoulou A, Soldatos R,
Tomara G, Petraki K, et al: Complex interactions between the
components of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, and with components of
MAPK, JAK/STAT and Notch-1 pathways, indicate their involvement in
meningioma development. Virchows Arch. 465:473–485. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Takebe N, Nguyen D and Yang SX: Targeting
notch signaling pathway in cancer: Clinical development advances
and challenges. Pharmacol Ther. 141:140–149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Oswald F, Täuber B, Dobner T, Bourteele S,
Kostezka U, Adler G, Liptay S and Schmid RM: p300 acts as a
transcriptional coactivator for mammalian Notch-1. Mol Cell Biol.
21:7761–7774. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stella MC, Trusolino L, Pennacchietti S
and Comoglio PM: Negative feedback regulation of Met-dependent
invasive growth by Notch. Mol Cell Biol. 25:3982–3996. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao L, Ma Y, Gu F and Fu L: Inhibition of
Notch1 increases paclitaxel sensitivity to human breast cancer.
Chin Med J (Engl). 127:442–447. 2014.
|
|
30
|
Kuang SQ, Fang Z, Zweidler-McKay PA, Yang
H, Wei Y, Gonzalez-Cervantes EA, Boumber Y and Garcia-Manero G:
Epigenetic inactivation of Notch-Hes pathway in human B-cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. PLoS One. 8:e618072013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huppert SS, Jacobsen TL and Muskavitch MA:
Feedback regulation is central to Delta-Notch signalling required
for Drosophila wing vein morphogenesis. Development. 124:3283–3291.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Trédan O, Lacroix-Triki M, Guiu S,
Mouret-Reynier MA, Barrière J, Bidard FC, Braccini AL, Mir O,
Villanueva C and Barthélémy P: Angiogenesis and tumor
microenvironment: Bevacizumab in the breast cancer model. Target
Oncol. 10:189–198. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Shen B: A new gloden age of natural
products drug discovery. Cell. 163:1297–1300. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|