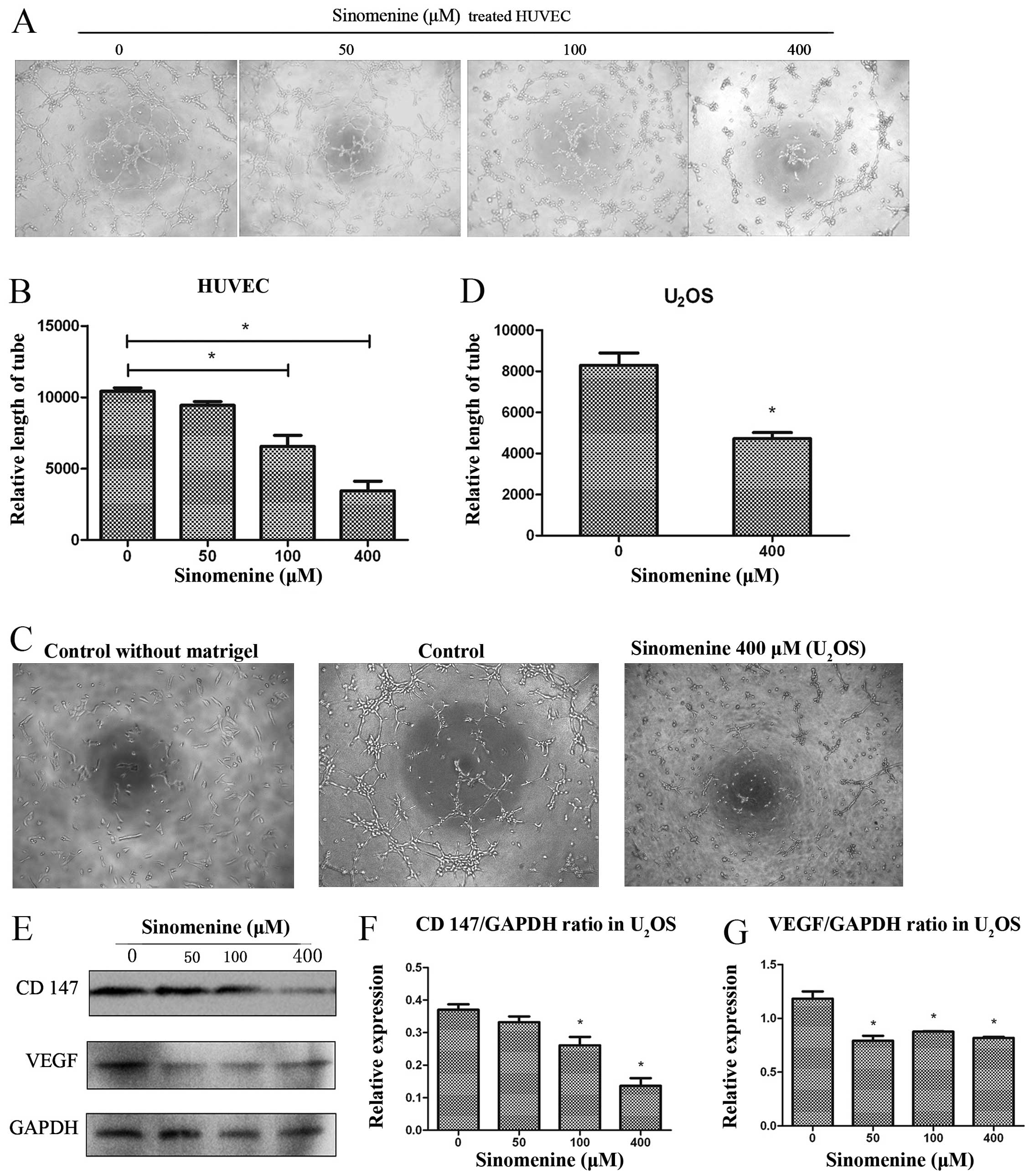
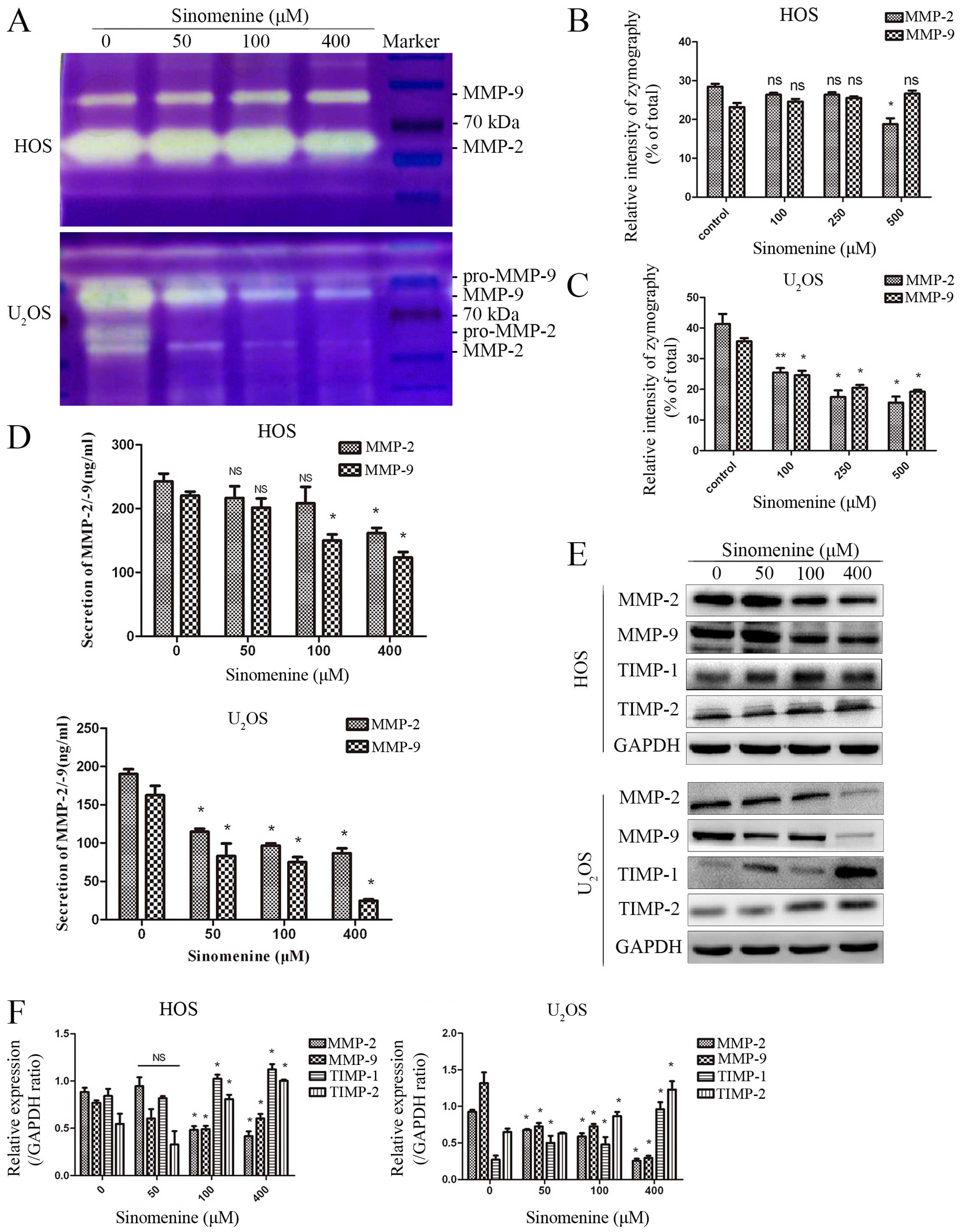
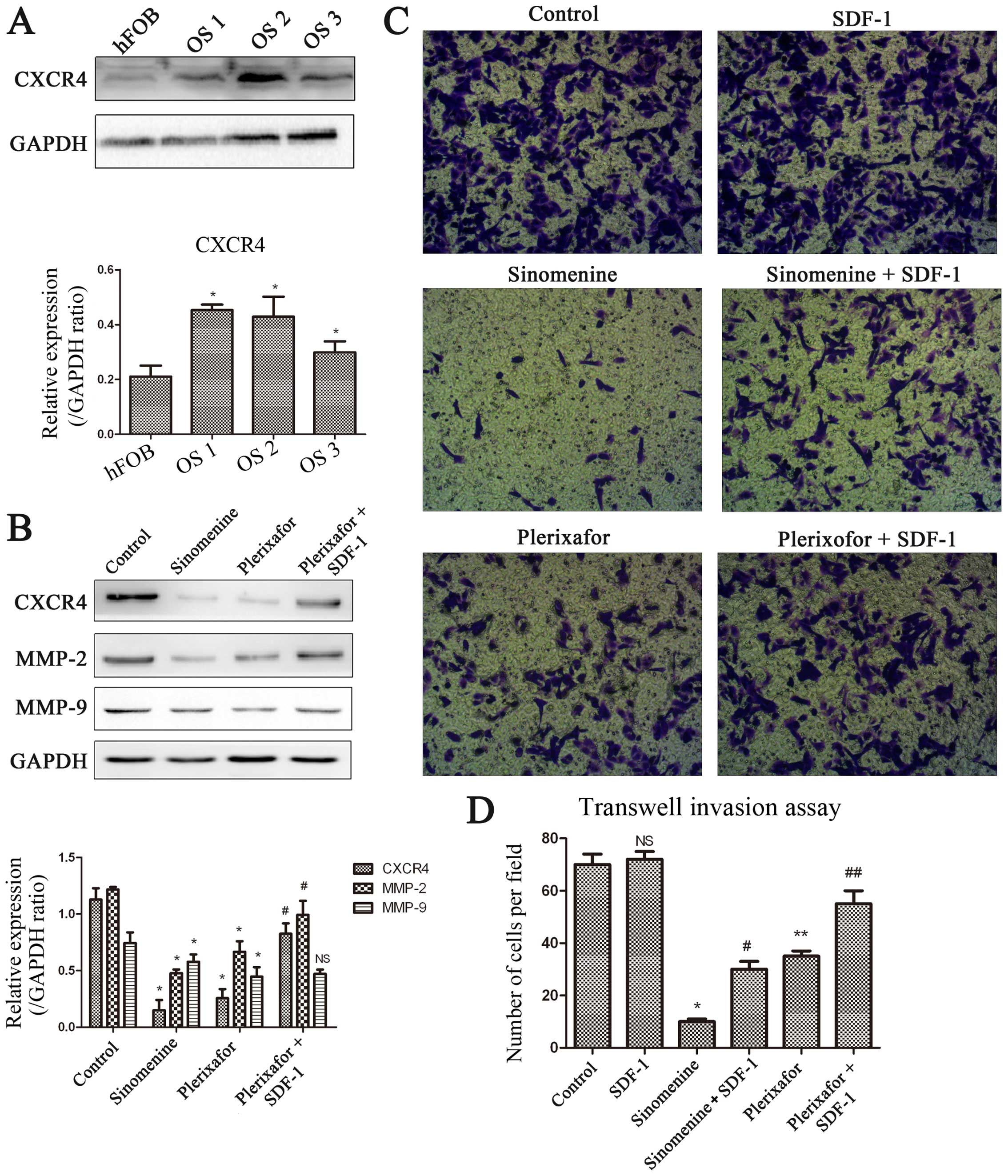
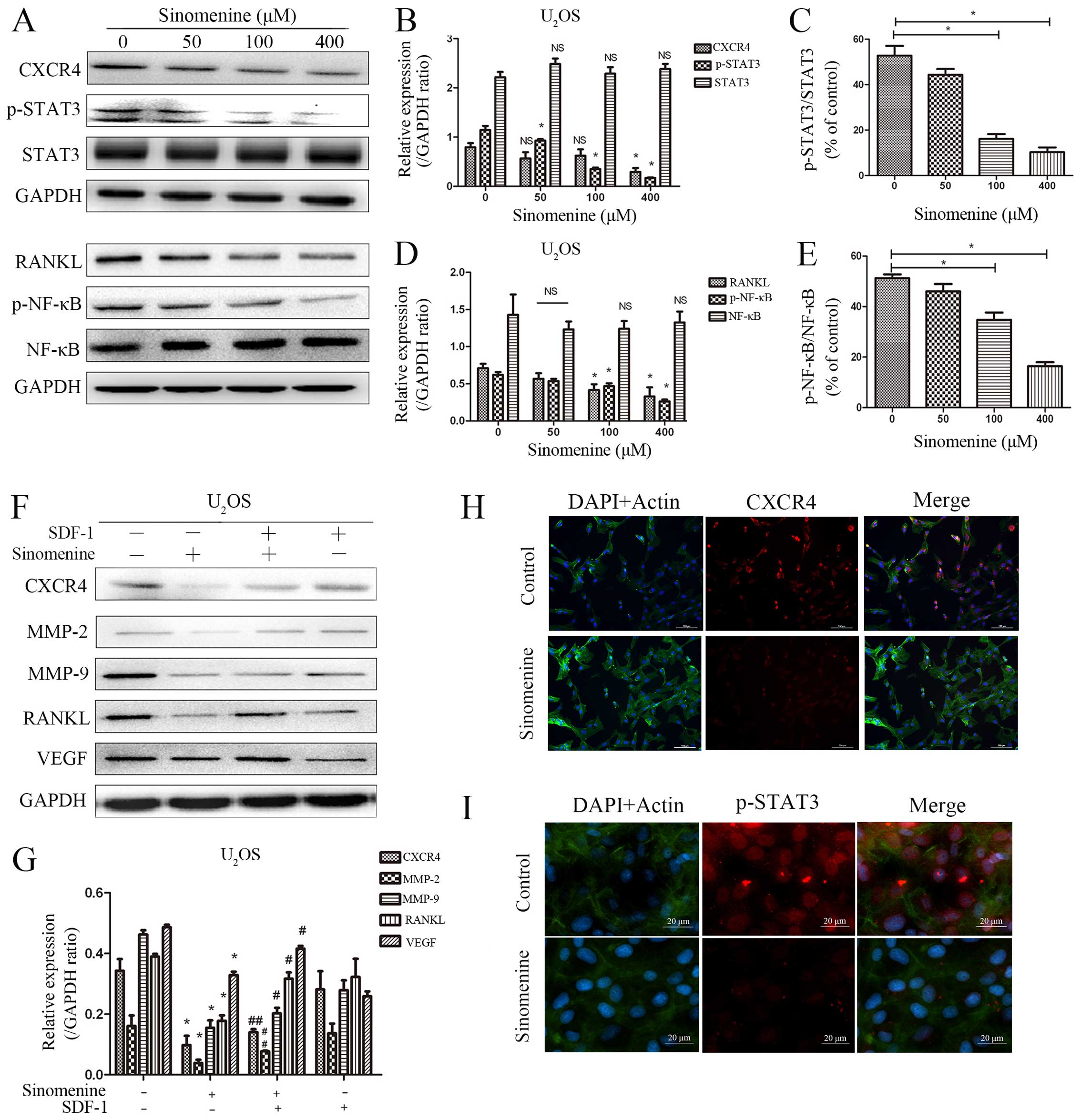
|
1
|
Quaye AA, Raskin KA, Ecker JL and Leffert
LR: Management of a parturient with high-grade osteosarcoma of the
proximal femur: A multidisciplinary approach. Int J Obstet Anesth.
19:340–342. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Raymond AK and Jaffe N: Osteosarcoma
multidisciplinary approach to the management from the pathologist's
perspective. Cancer Treat Res. 152:63–84. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Weiss A, Gill J, Goldberg J, Lagmay J,
Spraker-Perlman H, Venkatramani R and Reed D: Advances in therapy
for pediatric sarcomas. Curr Oncol Rep. 16:3952014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kudawara I, Aoki Y, Ueda T, Araki N, Naka
N, Nakanishi H, Matsumine A, Ieguchi M, Mori S, Myoui A, et al:
Neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy with high-dose ifosfamide,
doxorubicin, cisplatin and high-dose methotrexate in non-metastatic
osteosarcoma of the extremities: A phase II trial in Japan. J
Chemother. 25:41–48. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kager L, Zoubek A, Pötschger U, Kastner U,
Flege S, Kempf-Bielack B, Branscheid D, Kotz R, Salzer-Kuntschik M,
Winkelmann W, et al; Cooperative German-Austrian-Swiss Osteosarcoma
Study Group. Primary metastatic osteosarcoma: Presentation and
outcome of patients treated on neoadjuvant Cooperative Osteosarcoma
Study Group protocols. J Clin Oncol. 21:2011–2018. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kempf-Bielack B, Bielack SS, Jürgens H,
Branscheid D, Berdel WE, Exner GU, Göbel U, Helmke K, Jundt G,
Kabisch H, et al: Osteosarcoma relapse after combined modality
therapy: An analysis of unselected patients in the Cooperative
Osteosarcoma Study Group (COSS). J Clin Oncol. 23:559–568. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Birkedal-Hansen H, Moore WG, Bodden MK,
Windsor LJ, Birkedal-Hansen B, DeCarlo A and Engler JA: Matrix
metalloproteinases: A review. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 4:197–250.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nabeshima K, Iwasaki H, Koga K, Hojo H,
Suzumiya J and Kikuchi M: Emmprin (basigin/CD147): Matrix
metalloproteinase modulator and multifunctional cell recognition
molecule that plays a critical role in cancer progression. Pathol
Int. 56:359–367. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Clézardin P: The role of
RANK/RANKL/osteoprotegerin (OPG) triad in cancer-induced bone
diseases: Physiopathology and clinical implications. Bull Cancer.
98:837–846. 2011.In French.
|
|
10
|
Yamasaki H: Pharmacology of sinomenine, an
anti-rheumatic alkaloid from Sinomenium acutum. Acta Med Okayama.
30:1–20. 1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou L, Luan H, Liu Q, Jiang T, Liang H,
Dong X and Shang H: Activation of PI3K/Akt and ERK signaling
pathways antagonized sinomenine-induced lung cancer cell apoptosis.
Mol Med Rep. 5:1256–1260. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li XJ, Yue PY, Ha WY, Wong DY, Tin MM,
Wang PX, Wong RN and Liu L: Effect of sinomenine on gene expression
of the IL-1 beta-activated human synovial sarcoma. Life Sci.
79:665–673. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lu XL, Zeng J, Chen YL, He PM, Wen MX, Ren
MD, Hu YN, Lu GF and He S: Sinomenine hydrochloride inhibits human
hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth in vitro and in vivo:
Involvement of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction. Int J
Oncol. 42:229–238. 2013.
|
|
14
|
Lv Y, Li C, Li S and Hao Z: Sinomenine
inhibits proliferation of SGC-7901 gastric adenocarcinoma cells via
suppression of cyclooxygenase-2 expression. Oncol Lett. 2:741–745.
2011.
|
|
15
|
Li X, Wang K, Ren Y, Zhang L, Tang XJ,
Zhang HM, Zhao CQ, Liu PJ, Zhang JM and He JJ: MAPK signaling
mediates sinomenine hydrochloride-induced human breast cancer cell
death via both reactive oxygen species-dependent and -independent
pathways: An in vitro and in vivo study. Cell Death Dis.
5:e13562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ou YQ, Chen LH, Li XJ, Lin ZB and Li WD:
Sinomenine influences capacity for invasion and migration in
activated human monocytic THP-1 cells by inhibiting the expression
of MMP-2, MMP-9, and CD147. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 30:435–441. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Song L, Liu D, Zhao Y, He J, Kang H, Dai
Z, Wang X, Zhang S and Zan Y: Sinomenine inhibits breast cancer
cell invasion and migration by suppressing NF-κB activation
mediated by IL-4/ miR-324-5p/CUEDC2 axis. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 464:705–710. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou Q, Zhu Y, Deng Z, Long H, Zhang S and
Chen X: VEGF and EMMPRIN expression correlates with survival of
patients with osteosarcoma. Surg Oncol. 20:13–19. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Benayoun Y, Petellat F, Leclerc O, et al:
Current treatments for corneal neovascularization. J Fr Ophtalmol.
38:996–1008. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yan L, Zucker S and Toole BP: Roles of the
multifunctional glycoprotein, emmprin (basigin; CD147), in tumour
progression. Thromb Haemost. 93:199–204. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Meyers PA, Schwartz CL, Krailo M,
Kleinerman ES, Betcher D, Bernstein ML, Conrad E, Ferguson W,
Gebhardt M, Goorin AM, et al: Osteosarcoma: A randomized,
prospective trial of the addition of ifosfamide and/or muramyl
tripeptide to cisplatin, doxorubicin, and high-dose methotrexate. J
Clin Oncol. 23:2004–2011. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen DP, Wong CK, Leung PC, Fung KP, Lau
CB, Lau CP, Li EK, Tam LS and Lam CW: Anti-inflammatory activities
of Chinese herbal medicine sinomenine and Liang Miao San on tumor
necrosis factor-α-activated human fibroblast-like synoviocytes in
rheumatoid arthritis. J Ethnopharmacol. 137:457–468. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Qian L, Xu Z, Zhang W, Wilson B, Hong JS
and Flood PM: Sinomenine, a natural dextrorotatory morphinan
analog, is anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective through inhibition
of microglial NADPH oxidase. J Neuroinflammation. 4:232007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tang Q, Luo J, Zhu Q, Li Y and Yin S:
Synthesis and anti-inflammatory activities investigation of
sinomenine derivatives on ring C. Nat Prod Res. 20:1015–1023. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu Z, Duan ZJ, Chang JY, Zhang ZF, Chu R,
Li YL, Dai KH, Mo GQ and Chang QY: Sinomenine sensitizes
multidrug-resistant colon cancer cells (Caco-2) to doxorubicin by
downregulation of MDR-1 expression. PLoS One. 9:e985602014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liao F, Yang Z, Lu X, Guo X and Dong W:
Sinomenine sensitizes gastric cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil in
vitro and in vivo. Oncol Lett. 6:1604–1610. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen Y, Zhang L, Lu X, Wu K, Zeng J, Gao
Y, Shi Q, Wang X, Chang LS and He D: Sinomenine reverses multidrug
resistance in bladder cancer cells via P-glycoprotein-dependent and
independent manners. Pharmazie. 69:48–54. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang JX, Yang ZR, Wu DD, Song J, Guo XF,
Wang J and Dong WG: Suppressive effect of sinomenine combined with
5-fluorouracil on colon carcinoma cell growth. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 15:6737–6743. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang H, Ren Y, Tang X, Wang K, Liu Y,
Zhang L, Li X, Liu P, Zhao C and He J: Vascular normalization
induced by sinomenine hydrochloride results in suppressed mammary
tumor growth and metastasis. Sci Rep. 5:88882015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li X, He L, Hu Y, Duan H, Li X, Tan S, Zou
M, Gu C, Zeng X, Yu L, et al: Sinomenine suppresses osteoclast
formation and Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Ra-induced bone loss by
modulating RANKL signaling pathways. PLoS One. 8:e742742013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ruffini PA, Morandi P, Cabioglu N,
Altundag K and Cristofanilli M: Manipulating the
chemokine-chemokine receptor network to treat cancer. Cancer.
109:2392–2404. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Micucci C, Matacchione G, Valli D, Orciari
S and Catalano A: HIF2α is involved in the expansion of
CXCR4-positive cancer stem-like cells in renal cell carcinoma. Br J
Cancer. 113:1178–1185. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gu JY, Shi HF, Gao XL, Ma QQ and Zhang B:
Effect of CXCR4 pretreated with ultrasound-exposed microbubbles on
accelerating homing of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to
ischemic myocardium in AMI rats. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 8:766–771.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sand LG, Scotlandi K, Berghuis D,
Snaar-Jagalska BE, Picci P, Schmidt T, Szuhai K and Hogendoorn PC:
CXCL14, CXCR7 expression and CXCR4 splice variant ratio associate
with survival and metastases in Ewing sarcoma patients. Eur J
Cancer. 51:2624–2633. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Han AR, Lee JY, Kim HJ, Min WS, Park G and
Kim SH: A CXCR4 antagonist leads to tumor suppression by activation
of immune cells in a leukemia-induced microenvironment. Oncol Rep.
34:2880–2888. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu X, Xiao Q, Bai X, Yu Z, Sun M, Zhao H,
Mi X, Wang E, Yao W, Jin F, et al: Activation of STAT3 is involved
in malignancy mediated by CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling in human breast
cancer. Oncol Rep. 32:2760–2768. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shen HB, Gu ZQ, Jian K and Qi J:
CXCR4-mediated Stat3 activation is essential for CXCL12-induced
cell invasion in bladder cancer. Tumour Biol. 34:1839–1845. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hanada R, Hanada T, Sigl V, Schramek D and
Penninger JM: RANKL/RANK - beyond bones. J Mol Med (Berl).
89:647–656. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Li C, Shi X, Zhou G, Liu X, Wu S and Zhao
J: The canonical Wnt-beta-catenin pathway in development and
chemotherapy of osteosarcoma. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed).
18:1384–1391. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Moore AS, Dernell WS, Ogilvie GK, Kristal
O, Elmslie R, Kitchell B, Susaneck S, Rosenthal R, Klein MK,
Obradovich J, et al: Doxorubicin and BAY 12-9566 for the treatment
of osteosarcoma in dogs: A randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled study. J Vet Intern Med. 21:783–790. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Durnali A, Alkis N, Cangur S, Yukruk FA,
Inal A, Tokluoglu S, Seker MM, Bal O, Akman T, Inanc M, et al:
Prognostic factors for teenage and adult patients with high-grade
osteosarcoma: An analysis of 240 patients. Med Oncol. 30:6242013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|