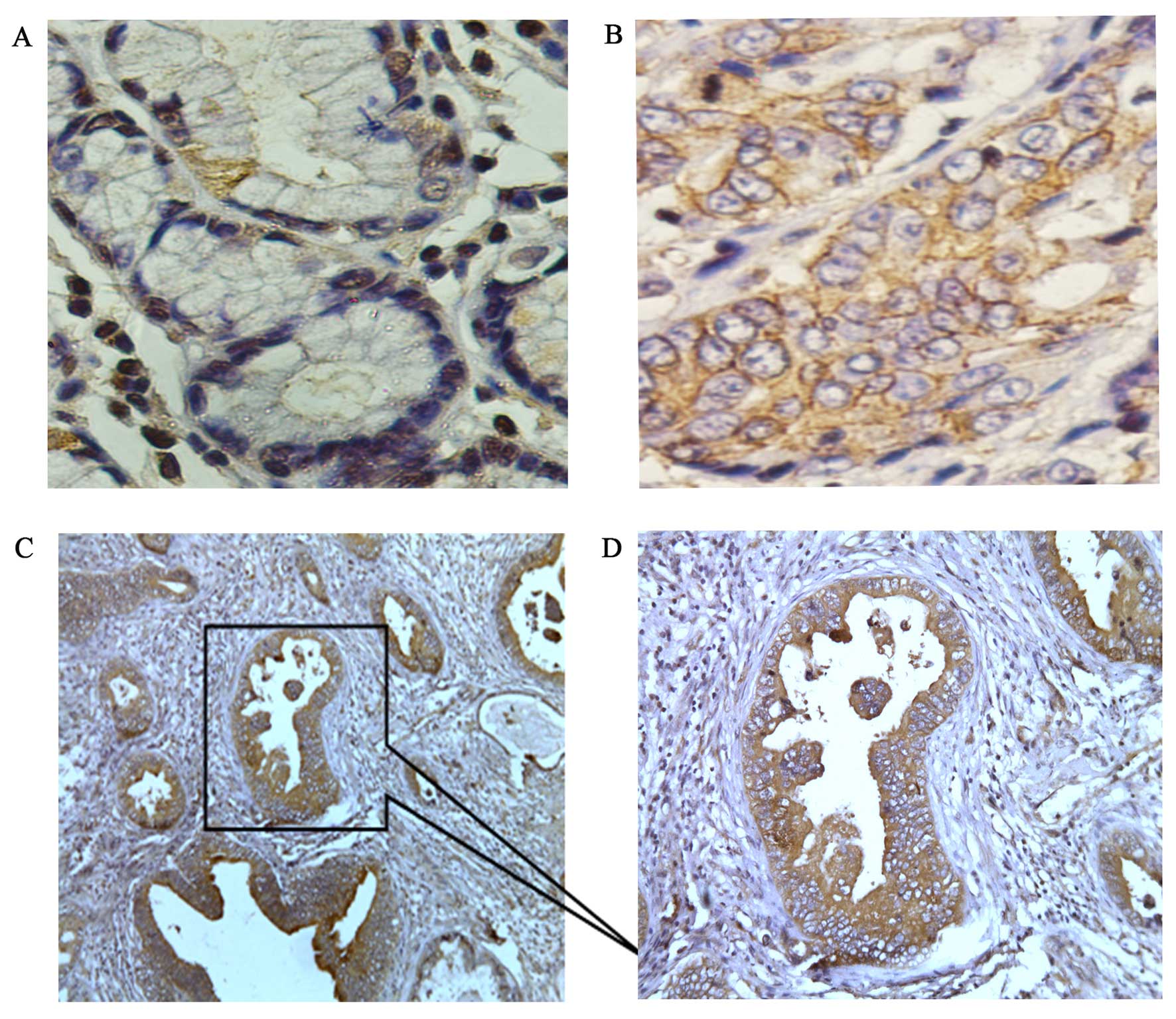
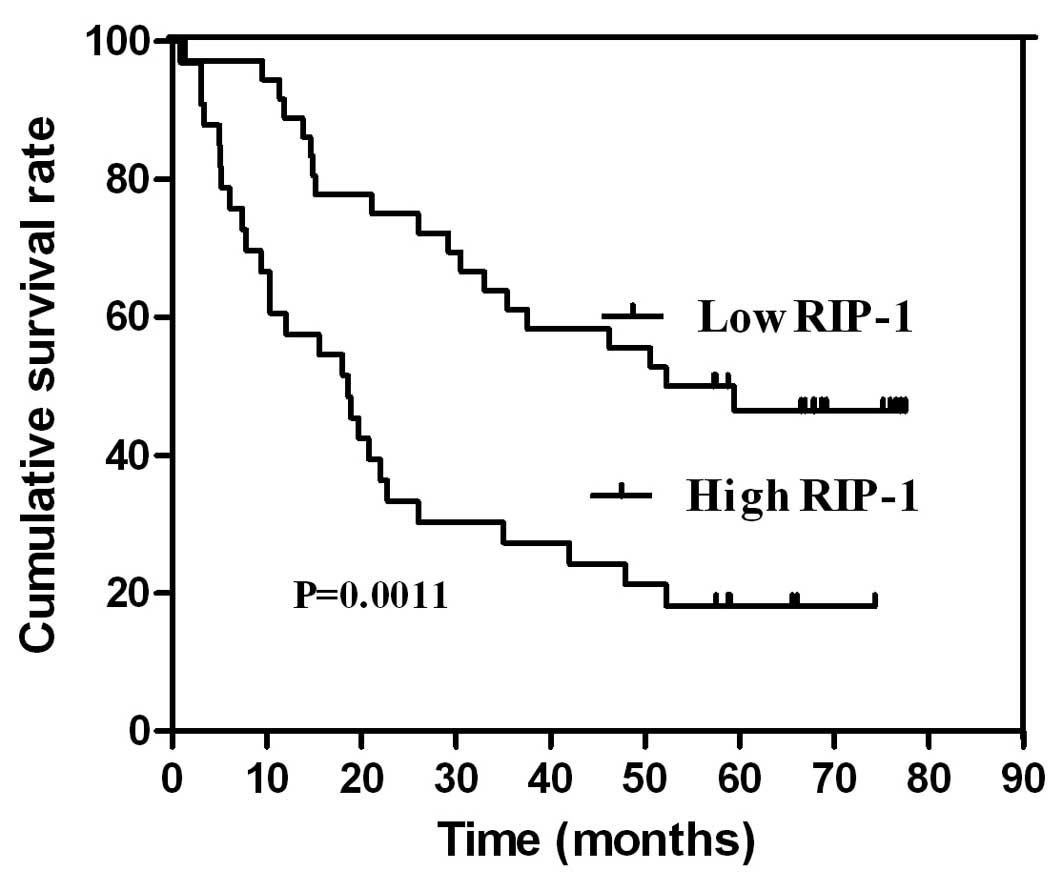
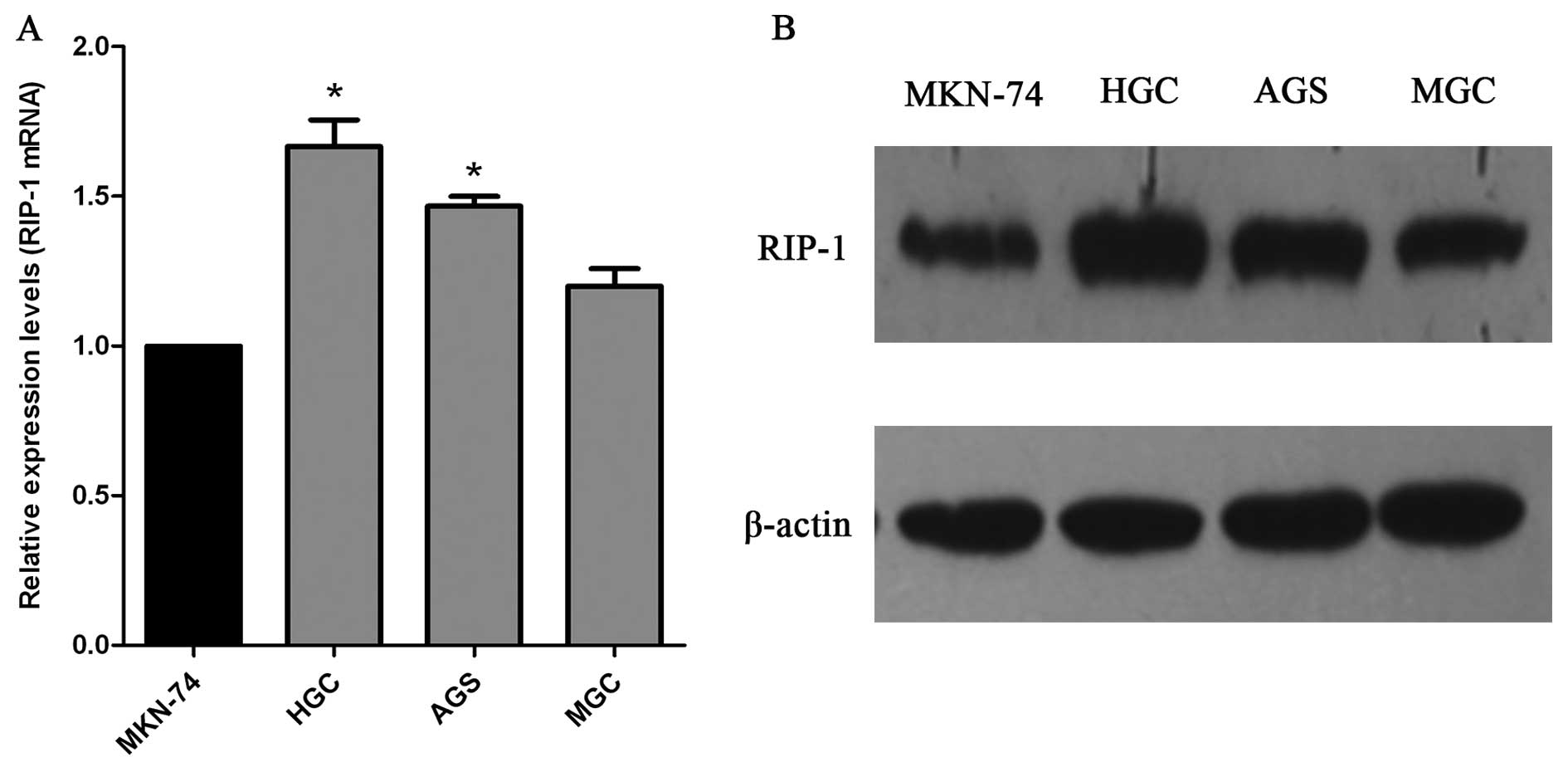
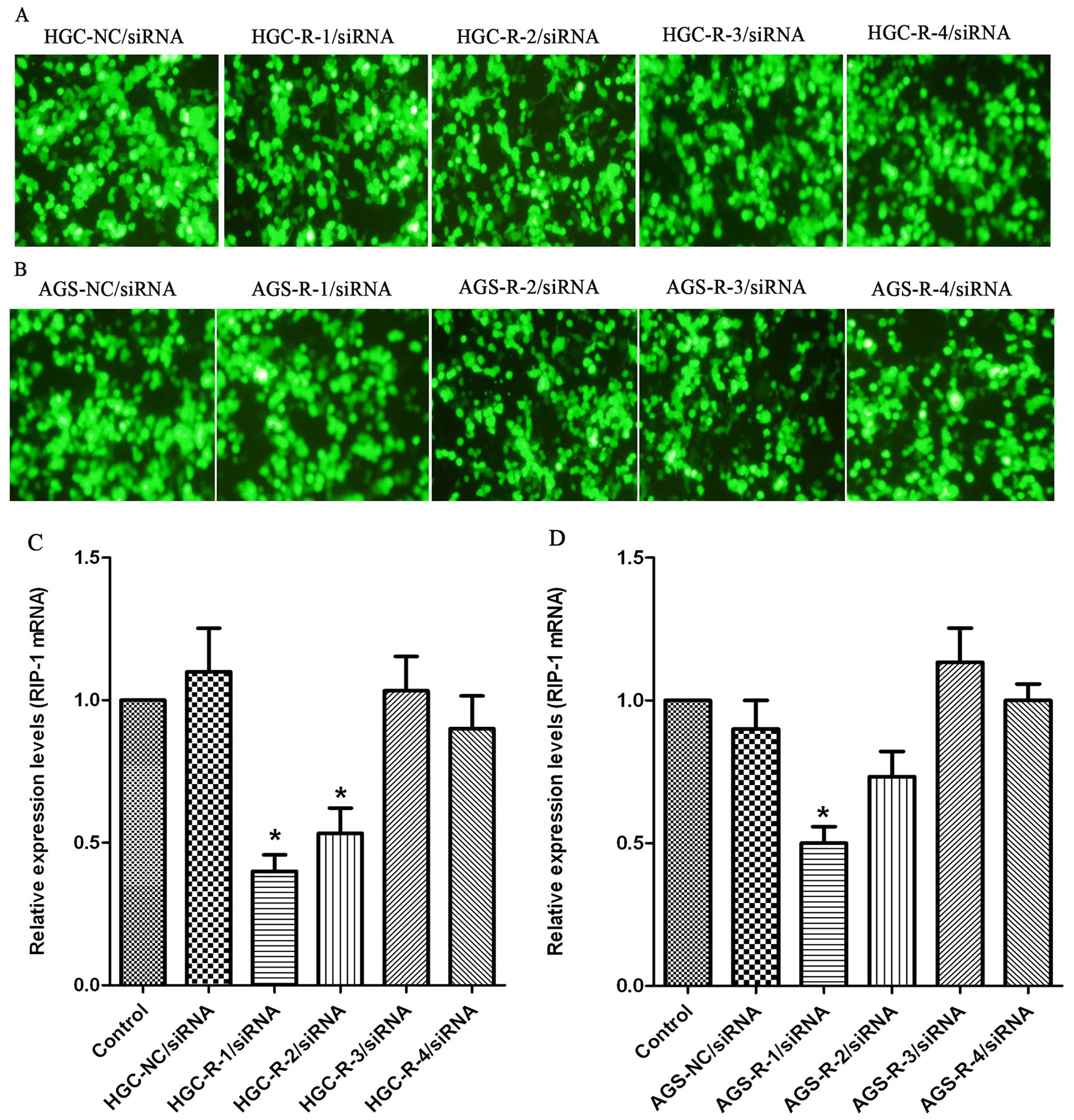
|
1
|
Ferlay JSI, Ervik M, et al: GLOBOCAN
2012v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide. IARC CancerBase
No. 11 (Internet). International Agency for Research on Cancer;
Lyon: 2013, http://globocan.iarc.fr.
Accessed Apr 25, 2014
|
|
2
|
Carneiro F: Stomach cancer. World Cancer
Report 2014. Steward B and Wild CP: International Agency for
Research on Cancer; Lyon: pp. 383–391. 2014
|
|
3
|
Waters JP, Pober JS and Bradley JR: Tumour
necrosis factor in infectious disease. J Pathol. 230:132–147. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
O'Donnell MA and Ting AT: RIP1 comes back
to life as a cell death regulator in TNFR1 signaling. FEBS J.
278:877–887. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stanger BZ, Leder P, Lee TH, Kim E and
Seed B: RIP: A novel protein containing a death domain that
interacts with Fas/APO-1 (CD95) in yeast and causes cell death.
Cell. 81:513–523. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hur GM, Lewis J, Yang Q, Lin Y, Nakano H,
Nedospasov S and Liu ZG: The death domain kinase RIP has an
essential role in DNA damage-induced NF-kappa B activation. Genes
Dev. 17:873–882. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Devin A, Lin Y and Liu ZG: The role of the
death-domain kinase RIP in tumour-necrosis-factor-induced
activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases. EMBO Rep.
4:623–627. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bradley JR and Pober JS: Tumor necrosis
factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFs). Oncogene. 20:6482–6491.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ting AT, Pimentel-Muiños FX and Seed B:
RIP mediates tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 activation of
NF-kappaB but not Fas/APO-1-initiated apoptosis. EMBO J.
15:6189–6196. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Park S, Hatanpaa KJ, Xie Y, Mickey BE,
Madden CJ, Raisanen JM, Ramnarain DB, Xiao G, Saha D, Boothman DA,
et al: The receptor interacting protein 1 inhibits p53 induction
through NF-kappaB activation and confers a worse prognosis in
glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 69:2809–2816. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Han W, Xie J, Fang Y, Wang Z and Pan H:
Nec-1 enhances shikonin-induced apoptosis in leukemia cells by
inhibition of RIP-1 and ERK1/2. Int J Mol Sci. 13:7212–7225. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu XY, Lai F, Yan XG, Jiang CC, Guo ST,
Wang CY, Croft A, Tseng HY, Wilmott JS, Scolyer RA, et al: RIP1
kinase is an oncogenic driver in melanoma. Cancer Res.
75:1736–1748. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Azijli K, Yuvaraj S, Peppelenbosch MP,
Würdinger T, Dekker H, Joore J, van Dijk E, Quax WJ, Peters GJ, de
Jong S, et al: Kinome profiling of non-canonical TRAIL signaling
reveals RIP1-Src-STAT3-dependent invasion in resistant non-small
cell lung cancer cells. J Cell Sci. 125:4651–4661. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu G, Du Q, Wang X, Tang N, She F and
Chen Y: TNF-α promotes gallbladder cancer cell growth and invasion
through autocrine mechanisms. Int J Mol Med. 33:1431–1440.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nikolaou VA, Stratigos AJ, Flaherty KT and
Tsao H: Melanoma: New insights and new therapies. J Invest
Dermatol. 132:854–863. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu ZG, Hsu H, Goeddel DV and Karin M:
Dissection of TNF receptor 1 effector functions: JNK activation is
not linked to apoptosis while NF-kappaB activation prevents cell
death. Cell. 87:565–576. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Karin M, Cao Y, Greten FR and Li ZW:
NF-kappaB in cancer: From innocent bystander to major culprit. Nat
Rev Cancer. 2:301–310. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pacifico F and Leonardi A: NF-kappaB in
solid tumors. Biochem Pharmacol. 72:1142–1152. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang CY, Cusack JC Jr, Liu R and Baldwin
AS Jr: Control of inducible chemoresistance: Enhanced anti-tumor
therapy through increased apoptosis by inhibition of NF-kappaB. Nat
Med. 5:412–417. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Festjens N, Vanden Berghe T, Cornelis S
and Vandenabeele P: RIP1, a kinase on the crossroads of a cell's
decision to live or die. Cell Death Differ. 14:400–410. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bertrand MJ, Milutinovic S, Dickson KM, Ho
WC, Boudreault A, Durkin J, Gillard JW, Jaquith JB, Morris SJ and
Barker PA: cIAP1 and cIAP2 facilitate cancer cell survival by
functioning as E3 ligases that promote RIP1 ubiquitination. Mol
Cell. 30:689–700. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Imre G, Larisch S and Rajalingam K:
Ripoptosome: A novel IAP-regulated cell death-signalling platform.
J Mol Cell Biol. 3:324–326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Niu J, Shi Y, Iwai K and Wu ZH: LUBAC
regulates NF-κB activation upon genotoxic stress by promoting
linear ubiquitination of NEMO. EMBO J. 30:3741–3753. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Blackwell K, Zhang L, Workman LM, Ting AT,
Iwai K and Habelhah H: Two coordinated mechanisms underlie tumor
necrosis factor alpha-induced immediate and delayed IκB kinase
activation. Mol Cell Biol. 33:1901–1915. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhu G, Chen X, Wang X, Li X, Du Q, Hong H,
Tang N, She F and Chen Y: Expression of the RIP-1 gene and its role
in growth and invasion of human gallbladder carcinoma. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 34:1152–1165. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee TH, Shank J, Cusson N and Kelliher MA:
The kinase activity of Rip1 is not required for tumor necrosis
factor-alpha-induced IkappaB kinase or p38 MAP kinase activation or
for the ubiquitination of Rip1 by Traf2. J Biol Chem.
279:33185–33191. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jüttner S, Wissmann C, Jöns T, Vieth M,
Hertel J, Gretschel S, Schlag PM, Kemmner W and Höcker M: Vascular
endothelial growth factor-D and its receptor VEGFR-3: Two novel
independent prognostic markers in gastric adenocarcinoma. J Clin
Oncol. 24:228–240. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Choi JH, Oh YH, Park YW, Baik HK, Lee YY
and Kim IS: Correlation of vascular endothelial growth factor-D
expression and VEGFR-3-positive vessel density with lymph node
metastasis in gastric carcinoma. J Korean Med Sci. 23:592–597.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen Y, Jiang L, She F, Tang N, Wang X, Li
X, Han S and Zhu J: Vascular endothelial growth factor-C promotes
the growth and invasion of gallbladder cancer via an autocrine
mechanism. Mol Cell Biochem. 345:77–89. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bantounas I, Phylactou LA and Uney JB: RNA
interference and the use of small interfering RNA to study gene
function in mammalian systems. J Mol Endocrinol. 33:545–557. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kawasaki H and Taira K: Short hairpin type
of dsRNAs that are controlled by tRNA (Val) promoter significantly
induce RNAi-mediated gene silencing in the cytoplasm of human
cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:700–707. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Caplen NJ and Mousses S: Short interfering
RNA (siRNA)-mediated RNA interference (RNAi) in human cells. Ann NY
Acad Sci. 1002:56–62. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yang B, Tuo S, Tuo CW, Zhang N and Liu QZ:
Establishment of a nude mouse model of highly metastatic gastric
lymphoma constructed with orthotopic transplantation of surgical
specimen. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 13:436–439.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|