Introduction
Gastric cancer is a heterogeneous disease that has
its basis in various genetic and epigenetic alterations. Based on
Lauren's classification, gastric cancer has been divided into two
histological subtypes, namely the intestinal type and diffuse type
(1). Recent advances in
high-throughput analysis have delivered new insights into the
heterogeneity underlying distinct molecular subtypes of gastric
cancer. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) network investigated exome
sequences, copy-number alterations, gene expression, DNA
methylation, and protein activities of gastric cancers and
classified gastric cancers into four subtypes: Epstein-Barr virus
(EBV)-positive, microsatellite instability (MSI), genomically
stable (GS), and chromosomal instability (CIN) (2). Nearly 9% of gastric cancer is
EBV-positive (3), for which
methylation of tumor suppressor genes is a key abnormality
(4). MSI is a common feature of
gastric cancers that occurs in 15–30% of cases (5). DNA mismatch repair deficiency such as
methylation of the MLH1 promoter increases the frequency of
mutations across the genome, creating MSI (5). Not only MLH1 but also many
other tumor suppressor genes are frequently hypermethylated in
MSI-positive gastric cancer (6).
The GS subtype is characterized by the enrichment of diffuse-type
gastric cancer, which is an aggressive, invasive, and stem-like
histological subtype (2). This
molecular classification has important biological and clinical
implications for basic research, diagnosis, and drug treatment of
gastric cancer.
SLIT proteins are highly conserved secreted
glycoproteins and the main ligands for roundabout receptors (ROBOs)
(7). The SLIT/ROBO pathway plays
an important part in cell-signaling pathways including axon
guidance, cell migration, cell motility, and angiogenesis. Recent
studies indicate that SLIT proteins have important roles in
tumorigenesis, cancer progression, and metastasis (8,9).
Three genes encoding SLITs (SLIT1, SLIT2 and SLIT3)
have been characterized in mammals. SLIT1 is located on
human chromosome 10q24.1, SLIT2 is on 4p15.31, and
SLIT3 is on 5q34-q35.1. SLIT2 regulates the β-catenin/TCF
and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways and enhances cell-cell adhesion in
breast cancer (10). Knockdown of
SLIT2 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration via
activation of AKT/β-catenin signaling (11). SLIT2 and SLIT3 are
frequently methylated and downregulated in various cancers such as
breast (12), colorectal (13), cervical (14), and lung (12), but their methylation status in
gastric cancer has not been unequivocally defined.
miR-218 is an intronic microRNA (miRNA) co-expressed
with its host genes, SLIT2 and SLIT3 (15). The mature form of miR-218 is
generated from two separate loci, miR-128-1 and
miR-218-2, which are located within the introns of
SLIT2 and SLIT3, respectively (16). miR-218 functions as a tumor
suppressor, inhibiting cell invasion and metastasis (17). In gastric cancer cells deficient in
miR-218 expression, ectopic expression of miR-218 suppresses both
ROBO1 expression and tumor cell invasiveness/metastasis (18).
The genome-wide DNA methylation profiling of gastric
cancer reported here shows that the CpG islands of SLIT1,
SLIT2 and SLIT3 are hypermethylated. We analyzed
expression and methylation of SLITs in gastric cancer cell
lines and primary gastric tumors. We also analyzed subtype-specific
methylation and expression of SLITs using TCGA data.
Furthermore, we examined the correlation between miR-218 expression
and CpG island methylation of SLIT2 or SLIT3 in
gastric cancer.
Materials and methods
Cell lines and tissue samples
Eleven gastric cancer cell lines were obtained from
the Korean Cell Line Bank and were cultured in RPMI-1640
supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1%
antibiotic-antimycotic solution (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA).
Ninety-six paired frozen gastric tumor tissues and normal adjacent
tissues were collected from the Tissue Bank at Chungnam National
University Hospital. All samples were obtained with informed
consent, and their use was approved by the institutional review
board (19).
Methylated DNA-binding domain sequencing
(MBD-seq)
MBD-seq was performed as described (20). Briefly, methylated DNA was
precipitated from 1 μg of fragmented genomic DNA via binding to the
methyl-CpG-binding domain of human MBD2 protein using the
MethylMiner methylated DNA enrichment kit (Invitrogen). The
methylated DNA fragments were ligated to a pair of adaptors for
sequencing on the Illumina HiSeq 2500 sequencing system. The
ligation products were size fractioned to obtain 250–350-bp
fragments on a 2% agarose gel and subjected to 18 cycles of PCR
amplification. Cluster generation and 100 cycles of paired-read
sequencing were done. The sequences were mapped to the human genome
(UCSC hg19). The sequencing data have been deposited in the NCBI
Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) under accession no. GSE46595.
Quantitative reverse transcription
(qRT)-PCR
qRT-PCR was performed as described (21). RNA was isolated using the RNeasy
kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA) and treated with DNase I (Promega,
Madison, WI, USA). Total RNA (5 μg) was reverse-transcribed into
cDNA using SuperScript II (Invitrogen). qRT-PCR was done in a
Bio-Rad CFX96 real-time PCR detection system (Bio-Rad, Foster City,
CA, USA). cDNA (100 ng) was amplified in a 15-μl reaction
containing 2× SYBR Premix EX Taq (Takara, Shiga, Japan) using the
primer sets listed in Table I.
Samples were heated to 95°C for 30 sec, followed by 39 cycles of
95°C for 30 sec, 60°C for 30 sec, and 72°C for 30 sec. The gene
encoding β-actin was used as an internal control. Each expression
level was expressed as the cycle threshold (CT) value, and the
difference in CT values for the gene and β-actin was calculated.
Each mRNA level in tumors is presented relative to that of the
normal tissue counterpart. If the expression level in the tumor was
less than half that in paired normal tissue, it was considered a
‘loss of expression’.
 | Table IPrimers for RT-PCR, MSP, and
pyrosequencing. |
Table I
Primers for RT-PCR, MSP, and
pyrosequencing.
| Primers for
RT-PCR |
|---|
|
|---|
| Gene | Forward primer
(5′-3′) | Reverse primer
(5′-3′) | Annealing
temperature (°C) | Product size
(bp) |
|---|
| SLIT1 |
CTGGTTGCCTTTGACCAGAT |
TGTACAGGTTTCGGATGCAA | 60 | 205 |
| SLIT2 |
TCAAGGTCCTGTGGATGTCA |
GTGGCAAGTTCCTCCATGTT | 60 | 199 |
| SLIT3 |
CCTGCCCCTACAGCTACAAG |
TTGTTTTCGCAGTCGTTGTC | 60 | 199 |
|
| Primers for
MSP |
|
| Gene | Forward primer
(5′-3′) | Reverse primer
(5′-3′) | Annealing
temperature (°C) | Product size
(bp) |
|
| SLIT1 |
AATTAAGAATTGATATAGCGAGTCG |
ACACACACGACGAAAATACG | 57 | 197 |
| SLIT2 |
GTAGAGCGTCGTTAAGGACGT |
CGAAAACTAAAAAACGCGAA | 58 | 284 |
| SLIT3 |
AATGGAGAGAGCGAGCGTC |
AACCCGCGAACCGAATTA | 60 | 149 |
|
| Primers for
pyrosequencing |
|
| Gene | Forward primer
(5′-3′) | Reverse primer
(5′-3′) | Sequencing primer
(5′-3′) | Annealing
temperature (°C) | Product size
(bp) |
|
| SLIT1 |
TGGAGGAGTAAGGTGTTTTTTAG |
Biotin-ATCAACCCCATAATACCCTC |
GAGTAAGGTGTTTTTTAGTT | 60 | 170 |
| SLIT2 |
TAAGGAGGGAGTGTTGAGTAGAAA |
Biotin-ACTCCCAAACCCCTAACAAAT |
TGTTGAGTAGAAAGGGGA | 60 | 212 |
| SLIT3 |
GGGGGAGTTTAGTATTTGGGTAT |
Biotin-CCACCCCAAAACCATAATATA |
GGTTTAGTAGATGGAGTTG | 60 | 282 |
Methylation-specific PCR (MSP)
MSP was performed as described (22). Genomic DNA was modified by sodium
bisulfite using the Ez DNA Methylation kit (Zymo Research, Orange,
CA, USA). Bisulfite-modified DNA (50 ng) was amplified in a 20-μl
reaction with primers specific for methylated DNA (Table I) as follows: 94°C for 5 min, 35
cycles of 94°C for 30 sec, at the given annealing temperature for
30 sec, and 72°C for 60 sec, followed by 72°C for 10 min. The PCR
products were separated on a 3% agarose gel and visualized with
ethidium bromide staining.
Pyrosequencing
Methylation was quantified by pyrose-quencing at
selected CpG sites in SLIT genes. For SLIT1, CpG sites at 99, 107,
110, 112, 114, 122, and 124 bases from the transcription start site
(TSS) were analyzed. For SLIT2, CpG sites at −1,489, −1,486,
−1,478, −1,472, −1,466, −1,460, −1,458, and −1,453 bases from the
TSS were analyzed. For SLIT3, CpG sites at 77, 80, 83, 86,
90, 95, and 100 bases from the TSS were analyzed. Pyrosequencing
was performed as described (19)
using primers listed in Table I.
Bisulfite-modified DNA (100 ng) was used in a 25-μl reaction
containing the primer set and 2× Premix EX Taq (Takara). All
samples were heated to 95°C for 5 min and then amplified for 50
cycles of 95°C for 30 sec, 60°C for 40 sec, and 72°C for 30 sec,
followed by a final extension step at 72°C for 5 min.
Pyrosequencing reactions were carried out using a sequencing primer
and the PSQ HS 96A System (Biotage, Uppsala, Sweden) according to
the specifications of Biotage.
5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine (5-Aza-dC)
treatment
The two gastric cancer cells SNU-601 and SNU-638
were seeded at a density of 1×106 cells/10-cm dish 1 day
before drug treatment. The cells were treated with 10 μM 5-Aza-dC
(Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) every 24 h for 3 days and then
harvested. Total RNA was prepared for each cell sample, and changes
in SLIT expression were measured by qRT-PCR as described
above.
Statistical analysis
The significance of differences in CpG region
hypermethylation between normal and tumor tissues was inferred
using the paired t-test. The correlation between downregulation of
SLITs and hypermethylation of SLIT CpG regions was
inferred from the Pearson's correlation test. A linear model was
used to understand the contribution of each clinical variable to
the observed differences in SLIT expression and promoter
hypermethylation. Six clinical parameters were used: tumor (tumor
vs. normal), tumor depth (early vs. advanced gastric cancer), age,
gender, TNM stage (IA, IB, II, IIIA, IIIB and IV), and Lauren's
classification (intestinal vs. diffuse). The model formula was
SLIT − tumor + histology + depth + age + gender + stage +
Lauren. The R statistical language (http://cran.r-project.org) was used for all
statistical tests. To compare characteristics of the different
groups of patients, the t-test and analysis of variance were used.
A p-value <0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Methylation of CpG islands in SLIT1,
SLIT2 and SLIT3 in gastric cancer
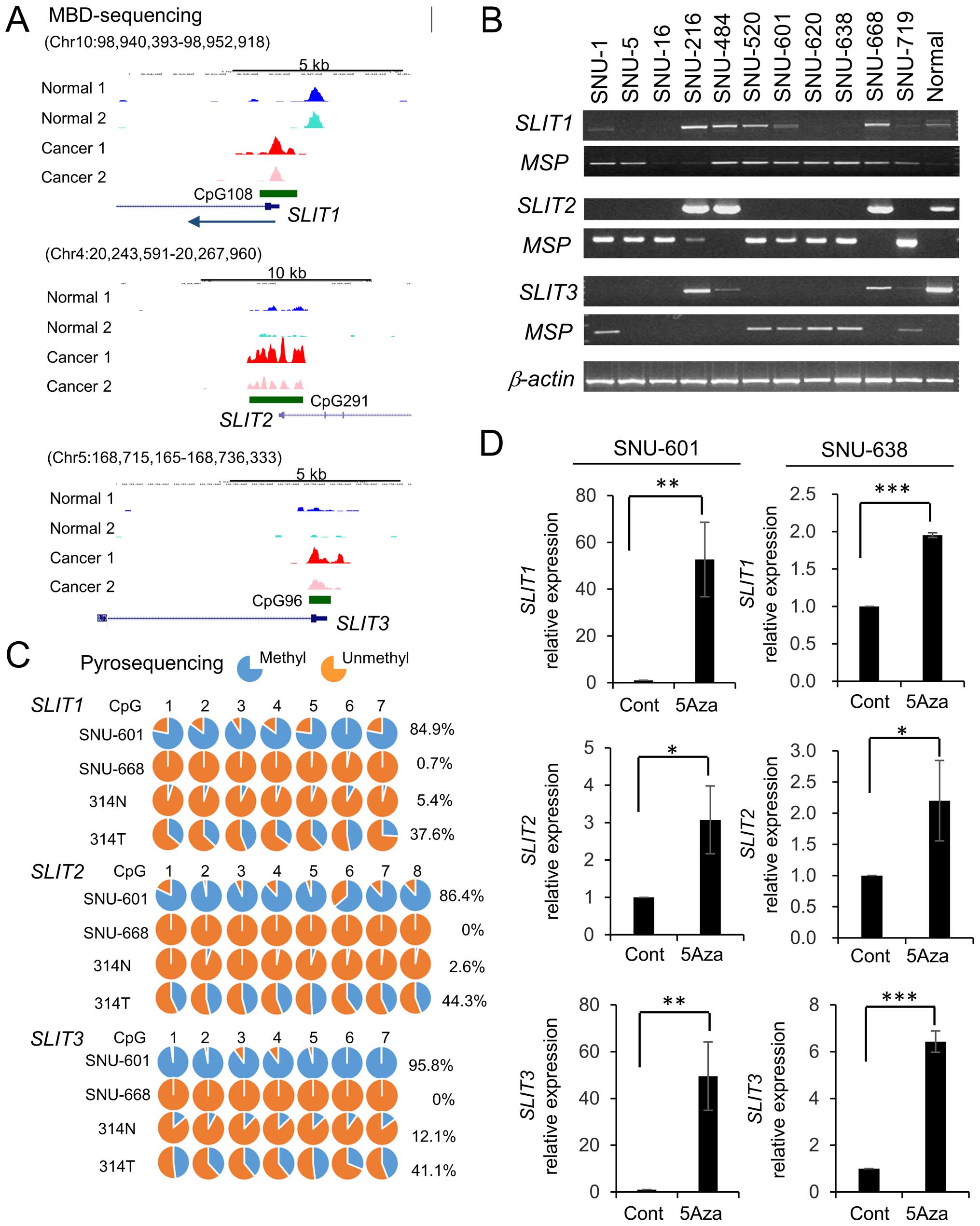
To identify differentially methylated genes in
gastric cancer, we performed MBD-seq, a high-throughput sequencing
of methylated DNA fragments captured by methyl-CpG-binding domain
protein 2, of patient-derived gastric cancer cells and adjacent
normal gastric mucosa cells. Among the differentially methylated
regions, we found that CpG islands in SLITs were hypermethylated in
gastric cancer (Fig. 1A). To
examine the relationship between expression and methylation of
SLITs in gastric cancer, we analyzed the expression of
SLITs in gastric cancer cell lines using RT-PCR and
methylation status using MSP. SLIT1 was repressed in 55% (6
of 11) of gastric cancer lines, SLIT2 was repressed in 73% (8 of
11), and SLIT3 was repressed in 82% (9 of 11) (Fig. 1B). The inactivation of SLITs
correlated with CpG island methylation as revealed by MSP (Fig. 1B). To assess DNA methylation at
single-base resolution, we also performed pyrosequencing (Fig. 1C). The gastric cancer cell line
SNU-601 had heavily methylated CpG sites of SLITs, but
SNU-668 cells showed hypomethylation. In addition, these CpG sites
were hypomethylated in normal tissues and moderately methylated in
tumors (Fig. 1C). We next treated
SNU-601 and SNU-638 cells with the DNA methylation inhibitor
5-Aza-dC (23) to examine whether
the silencing of SLITs in gastric cancer cells could be
reversed. Treatment with 5-Aza-dC induced the expression of SLITs
(Fig. 1D), suggesting that DNA
methylation plays a causal role in SLIT silencing in gastric
cancer cells.
Downregulation of SLITs in primary
gastric tumors by CpG island methylation
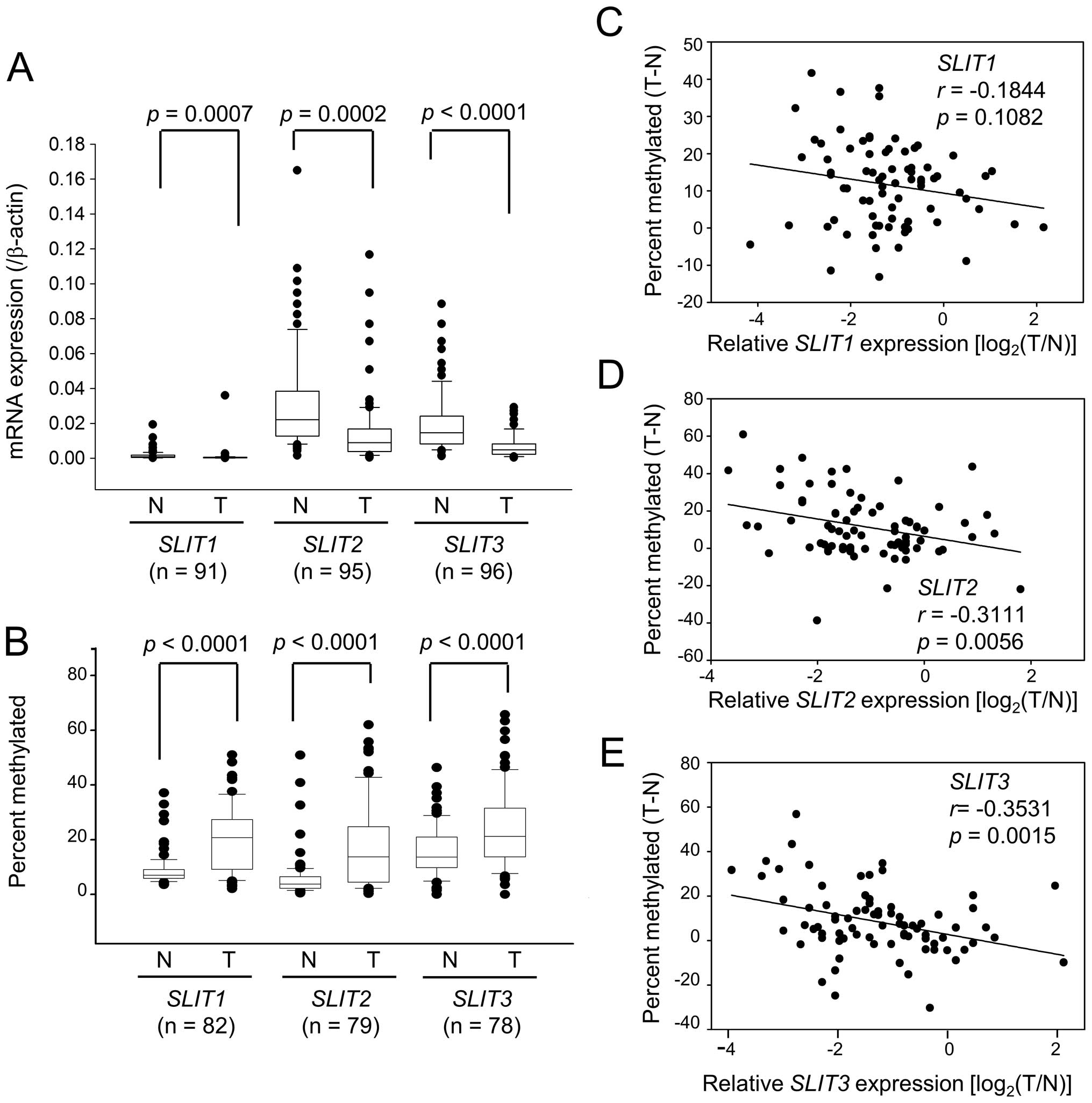
We next used qRT-PCR to assess SLIT expression in 96
paired normal and gastric tumor tissues. Data could not be obtained
for five tissue pairs for SLIT1 and one tissue pair for
SLIT3, so they were omitted from this analysis. Expression of
SLIT1, SLIT2 and SLIT3 was significantly reduced in
tumors (Fig. 2A). Loss of
expression, defined as tumor-specific expression >2-fold lower
compared with normal tissue, was observed in 76.9% (70 of 91),
63.2% (60 of 95), and 72.9% (70 of 96) of tumors for SLIT1,
SLIT2 and SLIT3, respectively. We also measured the
methylation levels of SLITs in paired normal and tumor DNAs
by pyrosequencing. Among 96 paired normal and tumor tissues used in
qRT-PCR, 83 paired DNAs were available for this analysis. One
tissue pair for SLIT1, four tissue pairs for SLIT2,
and five tissue pairs for SLIT3 were omitted from the
analysis because of poor data generation. Tumor DNAs showed a
significant methylation increase of 2.3-fold for SLIT1,
2.9-fold for SLIT2, and 1.5-fold for SLIT3 compared
with normal tissues (Fig. 2B,
p<0.0001). Regression analysis showed that decreased SLIT
expression correlated with increased CpG methylation (Fig. 2C–E). The correlation was highly
significant for SLIT2 (r=−0.3111, p=0.0056) and SLIT3
(r=−0.3531, p=0.0015) but not significant for SLIT1
(r=−0.1844, p=0.1082).
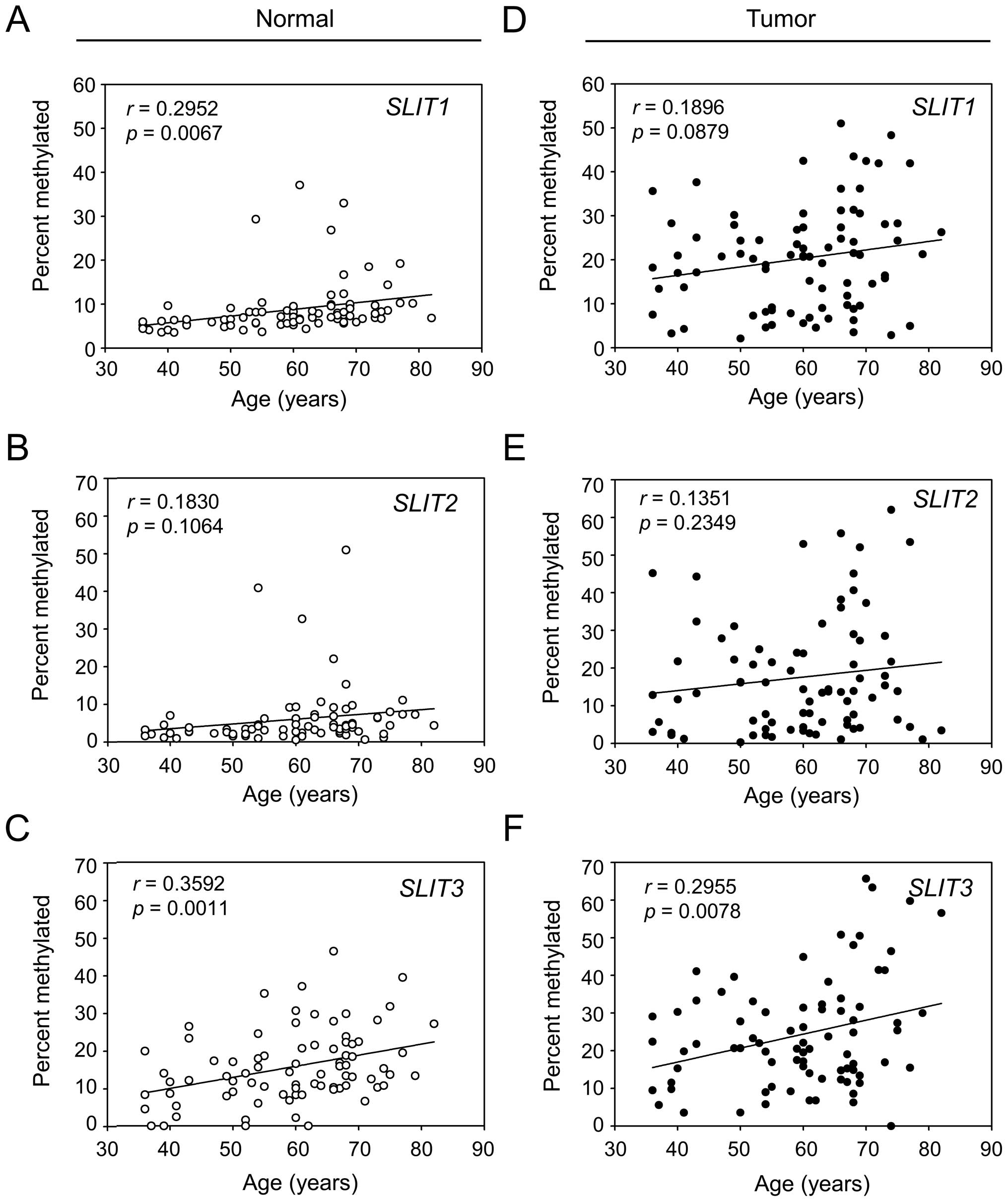
Methylation status of SLITs during
gastric carcinogenesis and aging
Inactivation of SLITs occurred in early-stage as
well as in advanced-stage tumors and in both intestinal type and
diffuse type (Fig. 3). As
expected, based SLIT expression patterns, methylation of
SLITs occurred in early-stage and advanced-stage tumors, and
both intestinal-type and diffuse-type tumors showed high levels of
methylation (Fig. 3). Although no
clinical parameter was significantly related to SLIT
methylation, we observed a positive correlation of a gradual
increase of methylation status with increasing patient age
(Fig. 4). Regression analysis
revealed a significant correlation for SLIT1 (Fig. 4A, p=0.0067) and SLIT3
(Fig. 4C, p=0.0011) but not for
SLIT2 (Fig. 4B, p=0.1064)
in normal tissues. The positive correlation was also observed in
tumor tissues, but the significance was maintained only for
SLIT3 (Fig. 4F, p=0.0078).
These data suggested that SLIT3 is methylated in both an
age- and cancer-related manner, but SLIT2 is methylated only
in a cancer-related manner.
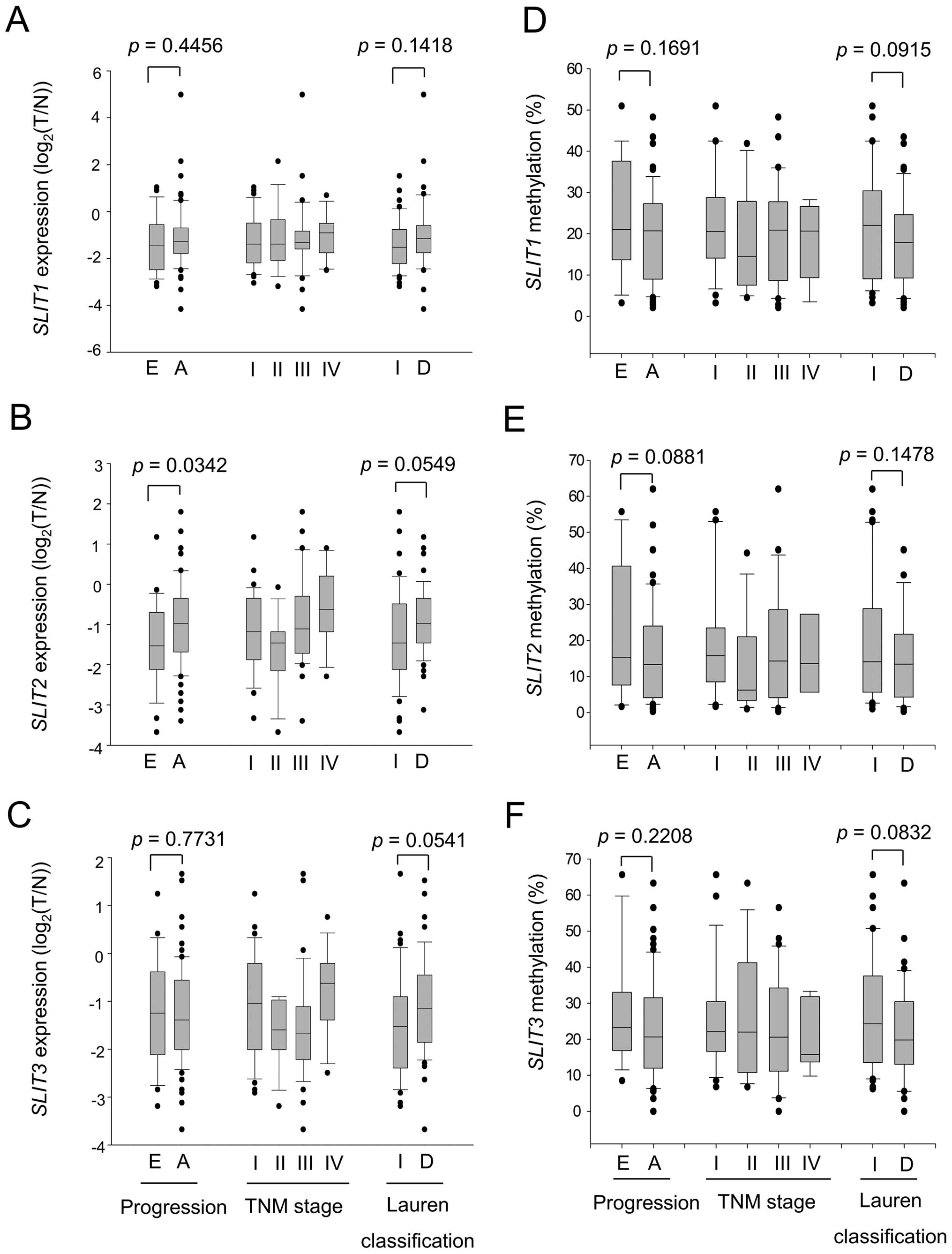 | Figure 3Expression and methylation of
SLIT genes in gastric tumors. The expression of SLIT1
(A), SLIT2 (B), and SLIT3 (C) in 96 pairs of normal
and tumor tissues was measured by qRT-PCR and is expressed as the
log2 ratio of tumor over normal. β-actin was used as a
control. Expression status was stratified by tumor progression (E,
early; A, advanced), TNM stage (I, II, III, and IV), and Lauren
classification (I, intestinal; D, diffuse). The methylation of
promoter regions of SLIT1 (D), SLIT2 (E), and
SLIT3 (F) in 83 pairs of normal and tumor tissues was
measured by pyrosequencing. Methylation status was stratified by
tumor progression, TNM stage, and Lauren classification. Each box
plot shows the median and 25th and 75th percentiles, and the dots
represent outliers. |
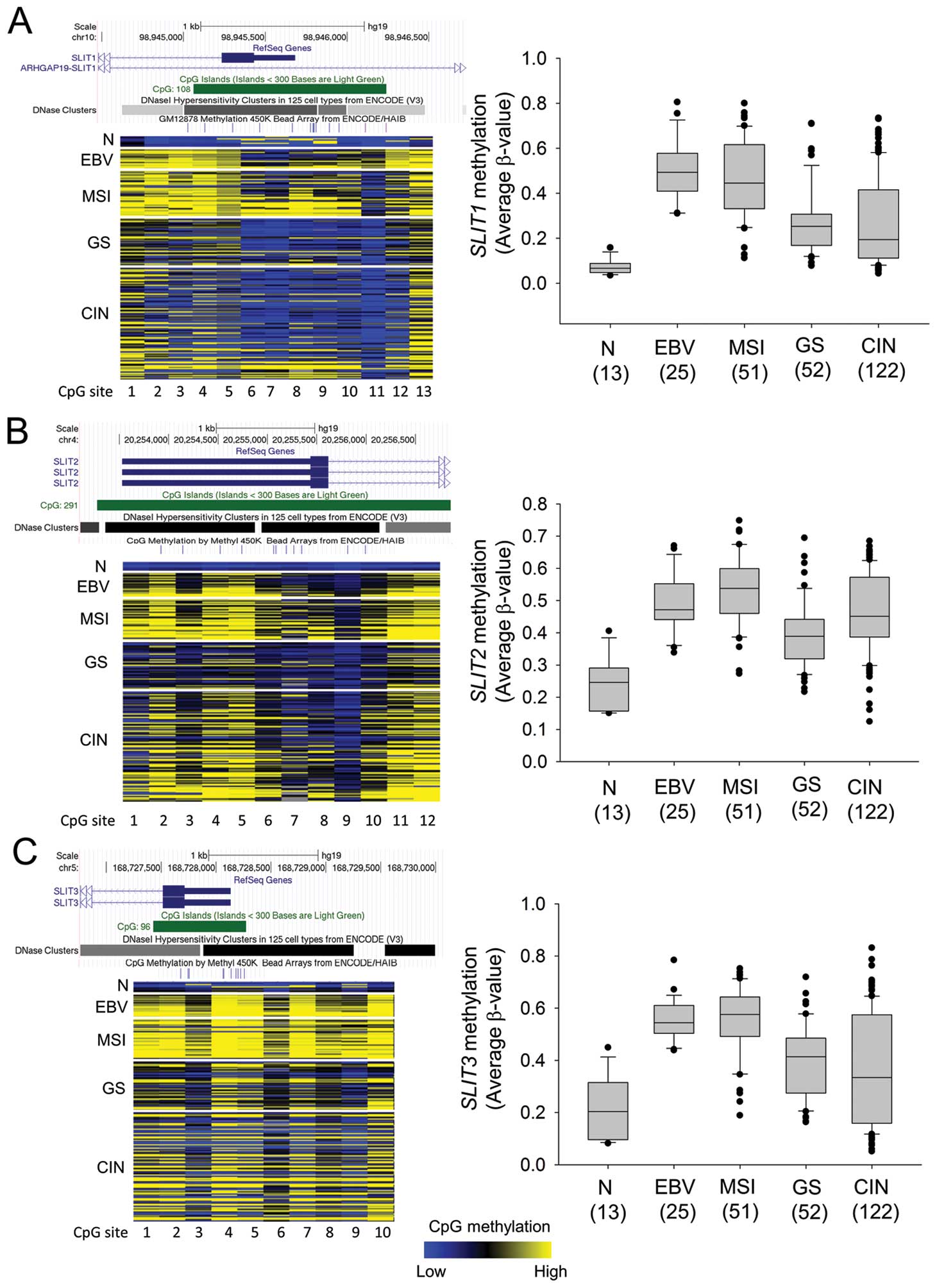
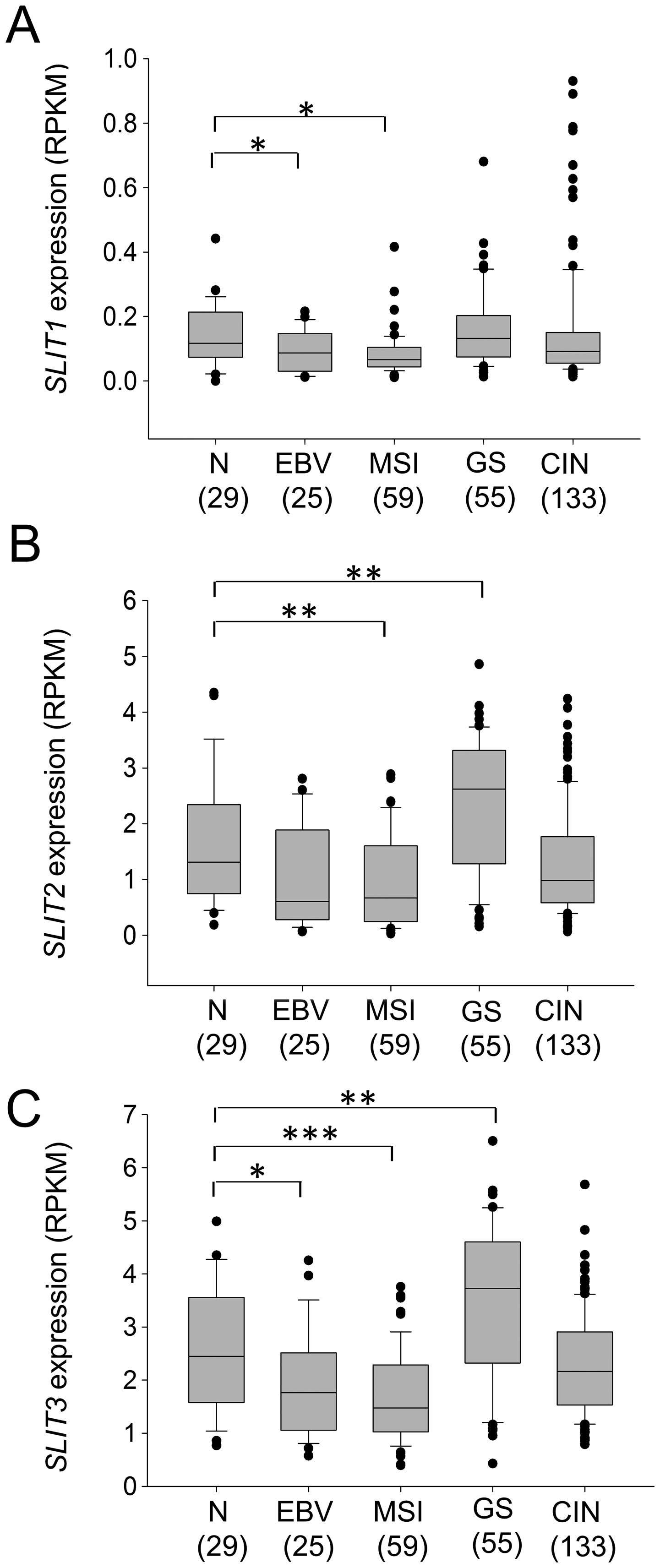
Subtype-specific expression and
methylation status of SLITs
To elucidate the specific expression and methylation
status of SLITs in gastric cancer subtypes (EBV-positive,
MSI, GS, and CIN), we analyzed RNA-seq data and Infinium 450K
methylation array data for gastric cancers provided by TCGA (2).
TCGA provides methylation array data for 250 gastric tumor samples
but only 2 normal samples, so we collected other public data for 10
normal gastric tissue samples (24,25)
and data for 1 sample in our laboratory. Fig. 4 shows the methylation profile of
the 13 normal gastric tissues and 25 EBV, 51 MSI, 52 GS, and 122
CIN subtype gastric cancer tissues in the SLIT1 CpG island
(13 CpG sites), SLIT2 CpG island (12 sites), and
SLIT3 CpG island (10 sites). SLIT1, SLIT2 and
SLIT3 showed similar subtype-dependent methylation patterns
(Fig. 5). As expected, the
EBV-positive and MSI subtypes had high levels of DNA methylation in
the SLIT CpG islands. Although the GS subtype had higher
SLIT methylation levels than normal gastric tissue, the
methylation differences were slight. The CIN subtype showed a broad
range of methylation levels of SLITs promoters (Fig. 5).
As expected from the high methylation levels of
SLIT promoters in the EBV and MSI subtypes, these two
subtypes had lower SLIT expression than the other subtypes
(Fig. 6). Interestingly,
expression of SLIT2 and SLIT3 was significantly
increased in the GS subtype (Fig.
6B; SLIT2, p=0.0062, Fig.
6C; SLIT3, p=0.0027). The CIN subtype had SLIT
expression levels similar to those of normal gastric tissue
(Fig. 6). These data suggested
that epigenetic inactivation of SLITs occurs in a
subtype-specific manner in gastric cancer.
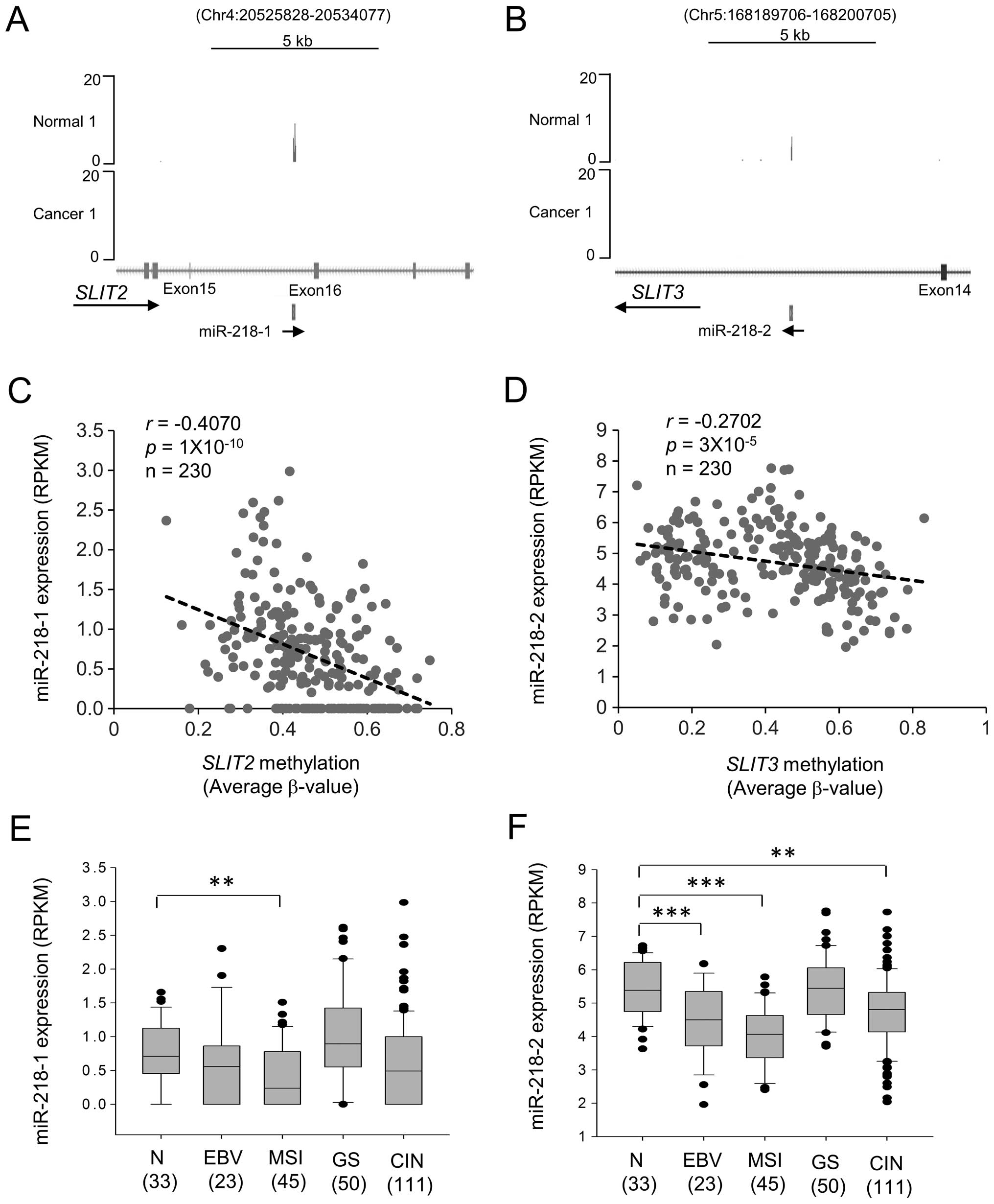
Downregulation of miR-218 through
methylation of SLIT2 and SLIT3 CpG islands
miR-218 is the mature form of miR-218-1 and
miR218-2, the intronic miRNAs that share the same promoter with
their host gene transcripts, SLIT2 and SLIT3,
respectively (15). miRNA-seq of
patient-derived gastric cancer cells and adjacent normal gastric
mucosa cells showed that expression of miR-218-1 and miR-218-2 was
silenced in gastric cancer cells (Fig.
7A and B). To examine the relationship between miR-218-1 and
miR-218-2 expression and CpG island methylation of SLIT2 and
SLIT3, we performed regression analysis using TCGA data.
Decreasing miR-218-1 and miR-218-2 expression correlated with
increasing CpG methylation of SLIT2 (r=−0.4070,
p=1×10−10) and SLIT3 (r=−0.2702,
p=3×10−5), respectively (Fig. 7C and D).
The expression of miR-218-2 was higher than that of
miR-218-1 in both gastric normal and tumor tissues (Fig. 7E and F). miR-218-2 expression was
lower in EBV, MSI, and CIN subtypes (Fig. 7F), whereas miR-218-1 expression was
lower in MSI (Fig. 7E). These data
suggested that mature miR-218 is mainly derived from miR-218-2 in
gastric cancer, and CpG island methylation of SLIT3 reduces
miR-218 expression in EBV, MSI, and CIN subtypes of gastric
cancer.
Discussion
Recent studies indicated that the SLIT/ROBO pathway
has important roles in tumorigenesis, cancer progression, and
metastasis (8,9). Furthermore, large-scale genomic
studies discovered frequent mutations in SLIT/ROBO pathway genes in
gastric cancer (26), pancreatic
cancer (27), and small-cell lung
cancer (28). These studies
suggest that the SLIT/ROBO pathway is a master regulator for
multiple oncogenic signaling pathways and a promising target for
cancer therapy (8,9).
A methylation analysis of SLIT genes was
previously performed using only a few cancer cell lines and primary
tumor tissue samples (12,13). In this study, we analyzed
expression and methylation of SLITs in 11 gastric cancer
cell lines, 96 paired gastric tumors and adjacent normal gastric
tissues, and 250 gastric cancers provided by TCGA (2). We found
that all three SLIT genes were hypermethylated and
downregulated at early stages of gastric cancer (Fig. 3), and hypermethylation was even
detected in normal gastric tissues (Fig. 4). Interestingly, methylation of
SLIT1 and SLIT3 correlated significantly with age in
normal tissues (Fig. 4A and C).
These results suggest that loss of SLIT expression is an
early event in gastric cancer progression.
SLITs showed subtype-specific expression and
methylation. Inactivation of SLITs by CpG island methylation
mainly occurred in the EBV and MSI subtypes (Figs. 5 and 6). Interestingly, the GS subtype showed
significantly increased expression of SLIT2 and SLIT3
(Fig. 6B and C). The GS subtype is
considered as an aggressive, invasive, and stem-like gastric
cancer. Therefore, this result supports the idea that the SLIT/ROBO
pathway might inhibit cancer cell migration from the primary site.
However, in metastatic tumors, the SLIT/ROBO system might increase
cancer cell motility (9). More
basic research is required to better understand the complex
functions of these proteins during tumor progression.
The expression of miR-218 is significantly repressed
in gastric, colon, prostate, and pancreatic cancers (15). miR-218 suppresses cancer
progression by targeting the mRNAs encoding survivin (17), HOXB3 (29), Bmi1 (30), and components of the AKT/mTOR,
SLIT/ROBO, Wnt, and focal adhesion pathways (15). In this study, we found that
expression of miR-218-1 and miR-218-2 correlated negatively with
CpG island methylation in SLIT2 and SLIT3,
respectively (Fig. 7). According
to the expression pattern of their host genes, miR-218-1 and
miR-218-2 were expressed in a gastric cancer subtype-specific
manner. In particular, miR-218-2 expression was significantly
reduced in the EBV and MSI subtypes (Fig. 7F). However, miR-218 expression in
the GS subtype did not differ significantly from that in normal
tissue. We therefore propose a subtype-specific role for miR-218 in
gastric cancer.
In conclusion, we demonstrated that methylation of
CpG islands inactivated SLIT1, SLIT2 and SLIT3 during
early gastric tumor progression. SLITs were hypermethylated
and downregulated in the EBV and MSI subtypes of gastric cancer,
whereas SLIT2 and SLIT3 expression increased in the
GS subtype. We also showed that miR-218-1 and miR-218-2 expression
correlated negatively with CpG island methylation in SLIT2
and SLIT3, respectively. Although more basic research should
be conducted to understand the subtype-specific roles of SLITs and
miR-218, we suggest that a subtype-specific therapeutic strategy
targeting SLITs and miR-218 should be considered for treatment of
gastric cancer.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by National Research
Foundation of Korea (NRF) grants funded by the Korea government
(NRF-2012M3A9B4027954 and NRF-2013R1A1A2006621) and a KRIBB
research initiative grant.
References
|
1
|
Lauren P: The two histological main types
of gastric carcinoma: Diffuse and so-called intestinal-type
carcinoma. An attempt at a histo-clinical classification. Acta
Pathol Microbiol Scand. 64:31–49. 1965.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bass AJ, Thorsson V, Shmulevich I,
Reynolds SM, Miller M, Bernard B, Hinoue T, Laird PW, Curtis C,
Shen H, et al; Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive
molecular characterization of gastric adenocarcinoma. Nature.
513:202–209. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Fukayama M, Hino R and Uozaki H:
Epstein-Barr virus and gastric carcinoma: Virus-host interactions
leading to carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 99:1726–1733. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kaneda A, Matsusaka K, Aburatani H and
Fukayama M: Epstein-Barr virus infection as an epigenetic driver of
tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 72:3445–3450. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Velho S, Fernandes MS, Leite M, Figueiredo
C and Seruca R: Causes and consequences of microsatellite
instability in gastric carcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol.
20:16433–16442. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yamamoto H, Watanabe Y, Maehata T, Morita
R, Yoshida Y, Oikawa R, Ishigooka S, Ozawa S, Matsuo Y, Hosoya K,
et al: An updated review of gastric cancer in the next-generation
sequencing era: Insights from bench to bedside and vice versa.
World J Gastroenterol. 20:3927–3937. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kidd T, Bland KS and Goodman CS: Slit is
the midline repellent for the robo receptor in Drosophila. Cell.
96:785–794. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gara RK, Kumari S, Ganju A, Yallapu MM,
Jaggi M and Chauhan SC: Slit/Robo pathway: A promising therapeutic
target for cancer. Drug Discov Today. 20:156–164. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Mehlen P, Delloye-Bourgeois C and Chédotal
A: Novel roles for Slits and netrins: Axon guidance cues as
anticancer targets? Nat Rev Cancer. 11:188–197. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Prasad A, Paruchuri V, Preet A, Latif F
and Ganju RK: Slit-2 induces a tumor-suppressive effect by
regulating beta-catenin in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem.
283:26624–26633. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shi R, Yang Z, Liu W, Liu B, Xu Z and
Zhang Z: Knockdown of Slit2 promotes growth and motility in gastric
cancer cells via activation of AKT/β-catenin. Oncol Rep.
31:812–818. 2014.
|
|
12
|
Dallol A, Da Silva NF, Viacava P, Minna
JD, Bieche I, Maher ER and Latif F: SLIT2, a human homologue of the
Drosophila Slit2 gene, has tumor suppressor activity and is
frequently inactivated in lung and breast cancers. Cancer Res.
62:5874–5880. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dickinson RE, Dallol A, Bieche I, Krex D,
Morton D, Maher ER and Latif F: Epigenetic inactivation of SLIT3
and SLIT1 genes in human cancers. Br J Cancer. 91:2071–2078. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Narayan G, Goparaju C, Arias-Pulido H,
Kaufmann AM, Schneider A, Dürst M, Mansukhani M, Pothuri B and
Murty VV: Promoter hypermethylation-mediated inactivation of
multiple Slit-Robo pathway genes in cervical cancer progression.
Mol Cancer. 5:162006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lu YF, Zhang L, Waye MM, Fu WM and Zhang
JF: MiR-218 mediates tumorigenesis and metastasis: Perspectives and
implications. Exp Cell Res. 334:173–182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tatarano S, Chiyomaru T, Kawakami K,
Enokida H, Yoshino H, Hidaka H, Yamasaki T, Kawahara K, Nishiyama
K, Seki N, et al: miR-218 on the genomic loss region of chromosome
4p15.31 functions as a tumor suppressor in bladder cancer. Int J
Oncol. 39:13–21. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Alajez NM, Lenarduzzi M, Ito E, Hui AB,
Shi W, Bruce J, Yue S, Huang SH, Xu W, Waldron J, et al: MiR-218
suppresses nasopharyngeal cancer progression through downregulation
of survivin and the SLIT2-ROBO1 pathway. Cancer Res. 71:2381–2391.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tie J, Pan Y, Zhao L, Wu K, Liu J, Sun S,
Guo X, Wang B, Gang Y, Zhang Y, et al: MiR-218 inhibits invasion
and metastasis of gastric cancer by targeting the Robo1 receptor.
PLoS Genet. 6:e10008792010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim M, Kim JH, Jang HR, Kim HM, Lee CW,
Noh SM, Song KS, Cho JS, Jeong HY, Hahn Y, et al: LRRC3B, encoding
a leucine-rich repeat-containing protein, is a putative tumor
suppressor gene in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 68:7147–7155. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim M, Park YK, Kang TW, Lee SH, Rhee YH,
Park JL, Kim HJ, Lee D, Lee D, Kim SY, et al: Dynamic changes in
DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation when hES cells undergo
differentiation toward a neuronal lineage. Hum Mol Genet.
23:657–667. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Haam K, Kim HJ, Lee KT, Kim JH, Kim M, Kim
SY, Noh SM, Song KS and Kim YS: Epigenetic silencing of BTB and CNC
homology 2 and concerted promoter CpG methylation in gastric
cancer. Cancer Lett. 351:206–214. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim SK, Jang HR, Kim JH, Kim M, Noh SM,
Song KS, Kang GH, Kim HJ, Kim SY, Yoo HS, et al: CpG methylation in
exon 1 of transcription factor 4 increases with age in normal
gastric mucosa and is associated with gene silencing in
intestinal-type gastric cancers. Carcinogenesis. 29:1623–1631.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jones PA and Taylor SM: Cellular
differentiation, cytidine analogs and DNA methylation. Cell.
20:85–93. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lokk K, Modhukur V, Rajashekar B, Märtens
K, Mägi R, Kolde R, Koltšina M, Nilsson TK, Vilo J, Salumets A, et
al: DNA methylome profiling of human tissues identifies global and
tissue-specific methylation patterns. Genome Biol. 15:r542014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nazor KL, Altun G, Lynch C, Tran H,
Harness JV, Slavin I, Garitaonandia I, Müller FJ, Wang YC, Boscolo
FS, et al: Recurrent variations in DNA methylation in human
pluripotent stem cells and their differentiated derivatives. Cell
Stem Cell. 10:620–634. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wong SS, Kim KM, Ting JC, Yu K, Fu J, Liu
S, Cristescu R, Nebozhyn M, Gong L, Yue YG, et al: Genomic
landscape and genetic heterogeneity in gastric adenocarcinoma
revealed by whole-genome sequencing. Nat Commun. 5:54772014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Biankin AV, Waddell N, Kassahn KS, Gingras
MC, Muthuswamy LB, Johns AL, Miller DK, Wilson PJ, Patch AM, Wu J,
et al; Australian Pancreatic Cancer Genome Initiative. Pancreatic
cancer genomes reveal aberrations in axon guidance pathway genes.
Nature. 491:399–405. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Peifer M, Fernández-Cuesta L, Sos ML,
George J, Seidel D, Kasper LH, Plenker D, Leenders F, Sun R, Zander
T, et al: Integrative genome analyses identify key somatic driver
mutations of small-cell lung cancer. Nat Genet. 44:1104–1110. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li Q, Zhu F and Chen P: miR-7 and miR-218
epigenetically control tumor suppressor genes RASSF1A and Claudin-6
by targeting HoxB3 in breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
424:28–33. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tu Y, Gao X, Li G, Fu H, Cui D, Liu H, Jin
W and Zhang Y: MicroRNA-218 inhibits glioma invasion, migration,
proliferation, and cancer stem-like cell self-renewal by targeting
the polycomb group gene Bmi1. Cancer Res. 73:6046–6055. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|