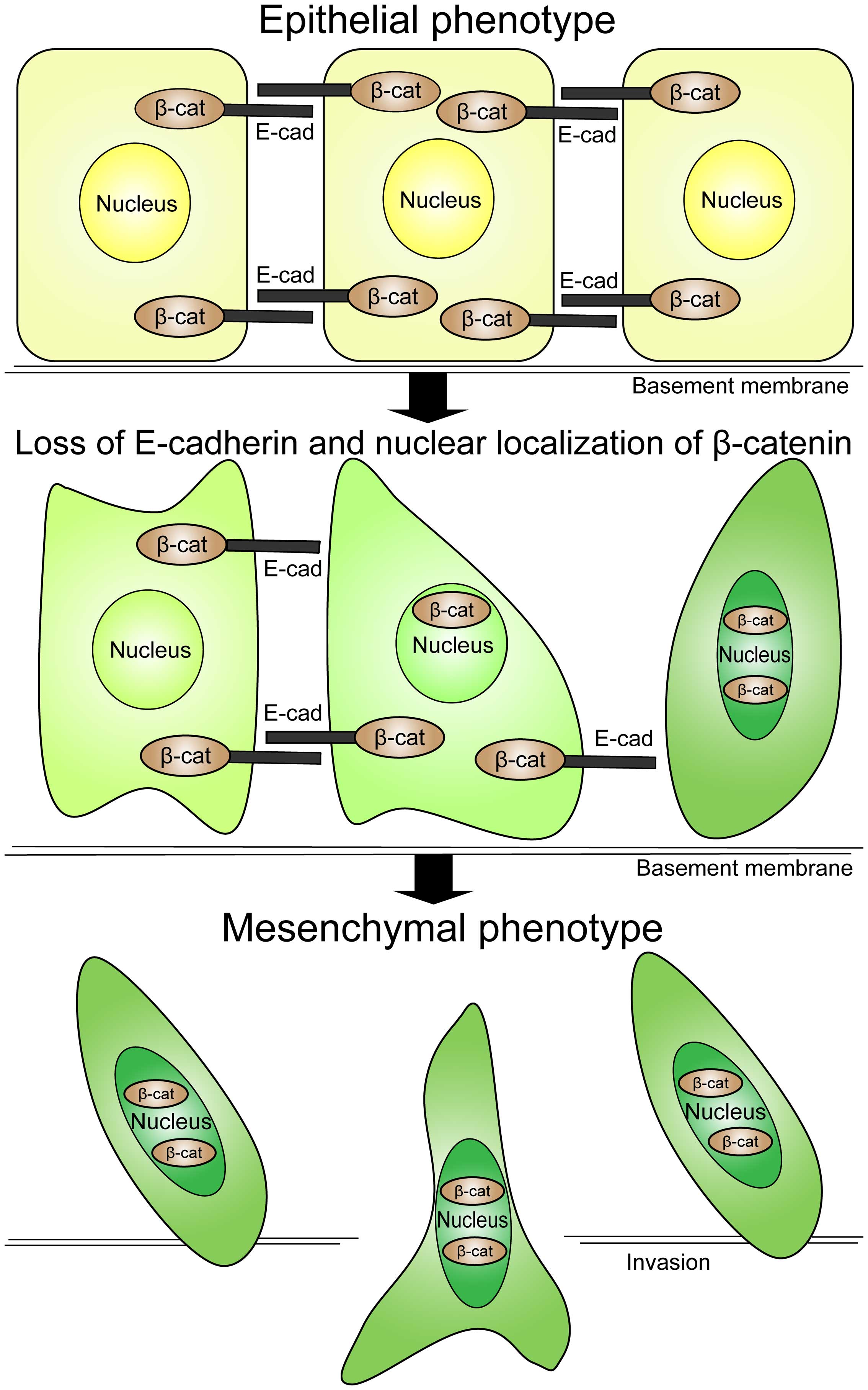
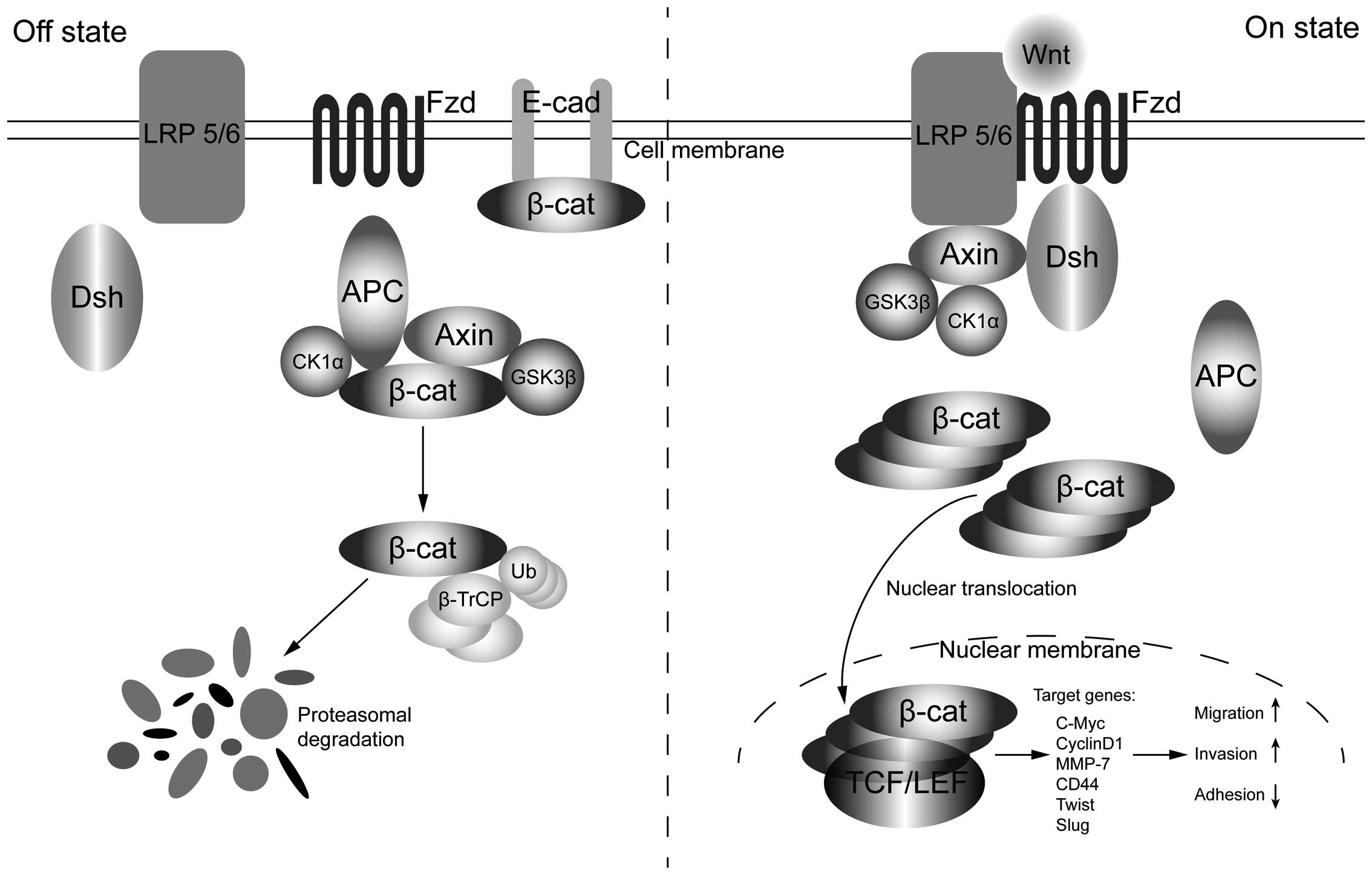
|
1
|
Guimarães RM and Muzi CD: Trend of
mortality rates for gastric cancer in Brazil and regions in the
period of 30 years (1980–2009). Arq Gastroenterol. 49:184–188.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shamir ER, Pappalardo E, Jorgens DM,
Coutinho K, Tsai WT, Aziz K, Auer M, Tran PT, Bader JS and Ewald
AJ: Twist1-induced dissemination preserves epithelial identity and
requires E-cadherin. J Cell Biol. 204:839–856. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pasquier J, Abu-Kaoud N, Al Thani H and
Rafii A: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in a clinical
perspective. J Oncol. 2015:7921822015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Heuberger J and Birchmeier W: Interplay of
cadherin-mediated cell adhesion and canonical Wnt signaling. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2:a0029152010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhao JH, Luo Y, Jiang YG, He DL and Wu CT:
Knockdown of β-catenin through shRNA cause a reversal of EMT and
metastatic phenotypes induced by HIF-1α. Cancer Invest. 29:377–382.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chang YW, Su YJ, Hsiao M, Wei KC, Lin WH,
Liang CL, Chen SC and Lee JL: Diverse targets of β-catenin during
the epithelial-mesenchymal transition define cancer stem cells and
predict disease relapse. Cancer Res. 75:3398–3410. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Moyret-Lalle C, Ruiz E and Puisieux A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition transcription factors and miRNAs:
‘Plastic surgeons’ of breast cancer. World J Clin Oncol. 5:311–322.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Greenburg G and Hay ED: Epithelia
suspended in collagen gels can lose polarity and express
characteristics of migrating mesenchymal cells. J Cell Biol.
95:333–339. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Steinestel K, Eder S, Schrader AJ and
Steinestel J: Clinical significance of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Clin Transl Med. 3:172014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Costabile V, Duraturo F, Delrio P, Rega D,
Pace U, Liccardo R, Rossi GB, Genesio R, Nitsch L, Izzo P, et al:
Lithium chloride induces mesenchymal-to-epithelial reverting
transition in primary colon cancer cell cultures. Int J Oncol.
46:1913–1923. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Logullo AF, Nonogaki S, Pasini FS, Osório
CA, Soares FA and Brentani MM: Concomitant expression of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition biomarkers in breast ductal
carcinoma: Association with progression. Oncol Rep. 23:313–320.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nozato M, Kaneko S, Nakagawara A and
Komuro H: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related gene expression
as a new prognostic marker for neuroblastoma. Int J Oncol.
42:134–140. 2013.
|
|
15
|
Nilsson GM, Akhtar N, Kannius-Janson M and
Baeckström D: Loss of E-cadherin expression is not a prerequisite
for c-erbB2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J Oncol.
45:82–94. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Moghbeli M, Moaven O, Memar B, Raziei HR,
Aarabi A, Dadkhah E, Forghanifard MM, Manzari F and Abbaszadegan
MR: Role of hMLH1 and E-cadherin promoter methylation in gastric
cancer progression. J Gastrointest Cancer. 45:40–47. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yu QM, Wang XB, Luo J, Wang S, Fang XH, Yu
JL and Ling ZQ: CDH1 methylation in preoperative peritoneal washes
is an independent prognostic factor for gastric cancer. J Surg
Oncol. 106:765–771. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hansford S, Kaurah P, Li-Chang H, Woo M,
Senz J, Pinheiro H, Schrader KA, Schaeffer DF, Shumansky K,
Zogopoulos G, et al: Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer syndrome:
CDH1 mutations and beyond. JAMA Oncol. 1:23–32. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li XJ, Zhao Y and Ren H: E-cadherin
expression and CDH1 promoter methylation in sporadic and hereditary
gastric cancer]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 35:125–127.
2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jun KH, Lee JE, Kim SH, Jung JH, Choi HJ,
Kim YI, Chin HM and Yang SH: Clinicopathological significance of
N-cadherin and VEGF in advanced gastric cancer brain metastasis and
the effects of metformin in preclinical models. Oncol Rep.
34:2047–2053. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kamikihara T, Ishigami S, Arigami T,
Matsumoto M, Okumura H, Uchikado Y, Kita Y, Kurahara H, Kijima Y,
Ueno S, et al: Clinical implications of N-cadherin expression in
gastric cancer. Pathol Int. 62:161–166. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Otsuki S, Inokuchi M, Enjoji M, Ishikawa
T, Takagi Y, Kato K, Yamada H, Kojima K and Sugihara K: Vimentin
expression is associated with decreased survival in gastric cancer.
Oncol Rep. 25:1235–1242. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shirahata A, Sakuraba K, Kitamura Y,
Yokomizo K, Gotou T, Saitou M, Kigawa G, Nemoto H, Sanada Y and
Hibi K: Detection of vimentin methylation in the serum of patients
with gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 32:791–794. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zeisberg M and Neilson EG: Biomarkers for
epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J Clin Invest. 119:1429–1437.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hu Z, Liu X, Tang Z, Zhou Y and Qiao L:
Possible regulatory role of Snail in NF-κB-mediated changes in
E-cadherin in gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 29:993–1000. 2013.
|
|
26
|
Zhang J, Zhou Y and Yang Y: CCR7 pathway
induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition through up-regulation of
Snail signaling in gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 32:4672015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shin NR, Jeong EH, Choi CI, Moon HJ, Kwon
CH, Chu IS, Kim GH, Jeon TY, Kim DH, Lee JH, et al: Overexpression
of Snail is associated with lymph node metastasis and poor
prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 12:5212012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Barnes RM and Firulli AB: A twist of
insight - the role of Twist-family bHLH factors in development. Int
J Dev Biol. 53:909–924. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu AN, Zhu ZH, Chang SJ and Hang XS:
Twist expression associated with the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in gastric cancer. Mol Cell Biochem. 367:195–203. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ru GQ, Wang HJ, Xu WJ and Zhao ZS:
Upregulation of Twist in gastric carcinoma associated with tumor
invasion and poor prognosis. Pathol Oncol Res. 17:341–347. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Qian J, Luo Y, Gu X, Zhan W and Wang X:
Twist1 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation through
up-regulation of FoxM1. PLoS One. 8:e776252013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang H, Gong J, Kong D and Liu HY:
Anti-proliferation effects of Twist gene silencing in gastric
cancer SGC7901 cells. World J Gastroenterol. 21:2926–2936. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Choi YJ, Kim N, Chang H, Lee HS, Park SM,
Park JH, Shin CM, Kim JM, Kim JS, Lee DH, et al: Helicobacter
pylori-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition, a potential role
of gastric cancer initiation and an emergence of stem cells.
Carcinogenesis. 36:553–563. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Okugawa Y, Toiyama Y, Tanaka K, Matsusita
K, Fujikawa H, Saigusa S, Ohi M, Inoue Y, Mohri Y, Uchida K, et al:
Clinical significance of Zinc finger E-box Binding homeobox 1
(ZEB1) in human gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 106:280–285. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Yabusaki N, Yamada S, Murai T, Kanda M,
Kobayashi D, Tanaka C, Fujii T, Nakayama G, Sugimoto H, Koike M, et
al: Clinical significance of zinc-finger E-box binding homeobox 1
mRNA levels in peritoneal washing for gastric cancer. Mol Clin
Oncol. 3:435–441. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Murai T, Yamada S, Fuchs BC, Fujii T,
Nakayama G, Sugimoto H, Koike M, Fujiwara M, Tanabe KK and Kodera
Y: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition predicts prognosis in
clinical gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 109:684–689. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jia B, Liu H, Kong Q and Li B:
Overexpression of ZEB1 associated with metastasis and invasion in
patients with gastric carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 366:223–229.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dai YH, Tang YP, Zhu HY, Lv L, Chu Y, Zhou
YQ and Huo JR: ZEB2 promotes the metastasis of gastric cancer and
modulates epithelial mesenchymal transition of gastric cancer
cells. Dig Dis Sci. 57:1253–1260. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Minn YK, Lee H, Hyung WJ, Kim JE, Choi J,
Yang SH, Song H, Lim BJ and Kim SH: MicroRNA-200 family members and
ZEB2 are associated with brain metastasis in gastric
adenocarcinoma. Int J Oncol. 45:2403–2410. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Brabletz T: To differentiate or not -
routes towards metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:425–436. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF and
Weissman IL: Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature.
414:105–111. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang C, Li C, He F, Cai Y and Yang H:
Identification of CD44+CD24+ gastric cancer
stem cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 137:1679–1686. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Han ME, Jeon TY, Hwang SH, Lee YS, Kim HJ,
Shim HE, Yoon S, Baek SY, Kim BS, Kang CD, et al: Cancer spheres
from gastric cancer patients provide an ideal model system for
cancer stem cell research. Cell Mol Life Sci. 68:3589–3605. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jiang J, Zhang Y, Chuai S, Wang Z, Zheng
D, Xu F, Zhang Y, Li C, Liang Y and Chen Z: Trastuzumab (herceptin)
targets gastric cancer stem cells characterized by CD90 phenotype.
Oncogene. 31:671–682. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Chen T, Yang K, Yu J, Meng W, Yuan D, Bi
F, Liu F, Liu J, Dai B, Chen X, et al: Identification and expansion
of cancer stem cells in tumor tissues and peripheral blood derived
from gastric adenocarcinoma patients. Cell Res. 22:248–258. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
46
|
Yoshida K, Tsujimoto H, Matsumura K,
Kinoshita M, Takahata R, Matsumoto Y, Hiraki S, Ono S, Seki S,
Yamamoto J, et al: CD47 is an adverse prognostic factor and a
therapeutic target in gastric cancer. Cancer Med. 4:1322–1333.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yang L, Ping YF, Yu X, Qian F, Guo ZJ,
Qian C, Cui YH and Bian XW: Gastric cancer stem-like cells possess
higher capability of invasion and metastasis in association with a
mesenchymal transition phenotype. Cancer Lett. 310:46–52.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bessède E, Staedel C, Acuña Amador LA,
Nguyen PH, Chambonnier L, Hatakeyama M, Belleannée G, Mégraud F and
Varon C: Helicobacter pylori generates cells with cancer stem cell
properties via epithelial-mesenchymal transition-like changes.
Oncogene. 33:4123–4131. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Ryu HS, Park J, Kim HH, Kim WH and Lee HS:
Combination of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem
cell-like phenotypes has independent prognostic value in gastric
cancer. Hum Pathol. 43:520–528. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Xu GF, Zhang WJ, Sun Q, Xu X, Zou X and
Guan W: Combined epithelial-mesenchymal transition with cancer stem
cell-like marker as predictors of recurrence after radical
resection for gastric cancer. World J Surg Oncol. 12:3682014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Jang YS, Sim JJ, Ji E, Jeong KY and Kim
HM: Investigation of lactate calcium salt-induced β-catenin
destabilization in colorectal cancer cells. Life Sci. 139:160–165.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Liu X, Yun F, Shi L, Li ZH, Luo NR and Jia
YF: Roles of signaling pathways in the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:6201–6206. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhang X and Hao J: Development of
anticancer agents targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Am J
Cancer Res. 5:2344–2360. 2015.
|
|
54
|
Yoshida GJ and Saya H: Inversed
relationship between CD44 variant and c-Myc due to oxidative
stress-induced canonical Wnt activation. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 443:622–627. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Mao J, Fan S, Ma W, Fan P, Wang B, Zhang
J, Wang H, Tang B, Zhang Q, Yu X, et al: Roles of Wnt/β-catenin
signaling in the gastric cancer stem cells proliferation and
salinomycin treatment. Cell Death Dis. 5:e10392014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Zhang H and Xue Y: Wnt pathway is involved
in advanced gastric carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology.
55:1126–1130. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Cheng XX, Wang ZC, Chen XY, Sun Y, Kong
QY, Liu J and Li H: Correlation of Wnt-2 expression and
beta-catenin intracellular accumulation in Chinese gastric cancers:
Relevance with tumour dissemination. Cancer Lett. 223:339–347.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kurayoshi M, Oue N, Yamamoto H, Kishida M,
Inoue A, Asahara T, Yasui W and Kikuchi A: Expression of Wnt-5a is
correlated with aggressiveness of gastric cancer by stimulating
cell migration and invasion. Cancer Res. 66:10439–10448. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kirikoshi H, Sekihara H and Katoh M:
Up-regulation of WNT10A by tumor necrosis factor alpha and
Helicobacter pylori in gastric cancer. Int J Oncol. 19:533–536.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Saitoh T, Kirikoshi H, Mine T and Katoh M:
Proto-oncogene WNT10B is up-regulated by tumor necrosis factor
alpha in human gastric cancer cell line MKN45. Int J Oncol.
19:1187–1192. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Figueiredo J, Söderberg O, Simões-Correia
J, Grannas K, Suriano G and Seruca R: The importance of E-cadherin
binding partners to evaluate the pathogenicity of E-cadherin
missense mutations associated to HDGC. Eur J Hum Genet. 21:301–309.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
62
|
Garziera M, Canzonieri V, Cannizzaro R,
Geremia S, Caggiari L, De Zorzi M, Maiero S, Orzes E, Perin T,
Zanussi S, et al: Identification and characterization of CDH1
germline variants in sporadic gastric cancer patients and in
individuals at risk of gastric cancer. PLoS One. 8:e770352013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Humar B, Blair V, Charlton A, More H,
Martin I and Guilford P: E-cadherin deficiency initiates gastric
signet-ring cell carcinoma in mice and man. Cancer Res.
69:2050–2056. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Humar B and Guilford P: Hereditary diffuse
gastric cancer: A manifestation of lost cell polarity. Cancer Sci.
100:1151–1157. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Mutoh H, Sakurai S, Satoh K, Tamada K,
Kita H, Osawa H, Tomiyama T, Sato Y, Yamamoto H, Isoda N, et al:
Development of gastric carcinoma from intestinal metaplasia in
Cdx2-transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 64:7740–7747. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kim HS, Lee JS, Freund JN, Min KW, Lee JS,
Kim W, Juhng SW and Park CS: CDX-2 homeobox gene expression in
human gastric carcinoma and precursor lesions. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 21:438–442. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Clements WM, Wang J, Sarnaik A, Kim OJ,
MacDonald J, Fenoglio-Preiser C, Groden J and Lowy AM: β-catenin
mutation is a frequent cause of Wnt pathway activation in gastric
cancer. Cancer Res. 62:3503–3506. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Yoda Y, Takeshima H, Niwa T, Kim JG, Ando
T, Kushima R, Sugiyama T, Katai H, Noshiro H and Ushijima T:
Integrated analysis of cancer-related pathways affected by genetic
and epigenetic alterations in gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer.
18:65–76. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Kim SJ, Shin JY, Cheong TC, Choi IJ, Lee
YS, Park SH and Chun KH: Galectin-3 germline variant at position
191 enhances nuclear accumulation and activation of β-catenin in
gastric cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis. 28:743–750. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Koo BK, Spit M, Jordens I, Low TY, Stange
DE, van de Wetering M, van Es JH, Mohammed S, Heck AJ, Maurice MM,
et al: Tumour suppressor RNF43 is a stem-cell E3 ligase that
induces endocytosis of Wnt receptors. Nature. 488:665–669. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Hao HX, Xie Y, Zhang Y, Charlat O, Oster
E, Avello M, Lei H, Mickanin C, Liu D, Ruffner H, et al: ZNRF3
promotes Wnt receptor turnover in an R-spondin-sensitive manner.
Nature. 485:195–200. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Jo YS, Kim MS, Lee JH, Lee SH, An CH and
Yoo NJ: Frequent frameshift mutations in 2 mononucleotide repeats
of RNF43 gene and its regional heterogeneity in gastric and
colorectal cancers. Hum Pathol. 46:1640–1646. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Lu H, Sun J, Wang F, Feng L, Ma Y, Shen Q,
Jiang Z, Sun X, Wang X and Jin H: Enhancer of zeste homolog 2
activates wnt signaling through downregulating CXXC finger protein
4. Cell Death Dis. 4:e7762013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Pandi NS, Manimuthu M, Harunipriya P,
Murugesan M, Asha GV and Rajendran S: In silico analysis of
expression pattern of a Wnt/β-catenin responsive gene ANLN in
gastric cancer. Gene. 545:23–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Qiu HB, Zhang LY, Ren C, Zeng ZL, Wu WJ,
Luo HY, Zhou ZW and Xu RH: Targeting CDH17 suppresses tumor
progression in gastric cancer by downregulating Wnt/β-catenin
signaling. PLoS One. 8:e569592013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
To KF, Chan MW, Leung WK, Yu J, Tong JH,
Lee TL, Chan FK and Sung JJ: Alterations of frizzled (FzE3) and
secreted frizzled related protein (hsFRP) expression in gastric
cancer. Life Sci. 70:483–489. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Kang W, Tong JH, Chan AW, Zhao J, Dong Y,
Wang S, Yang W, Sin FM, Ng SS, Yu J, et al: Yin Yang 1 contributes
to gastric carcinogenesis and its nuclear expression correlates
with shorter survival in patients with early stage gastric
adenocarcinoma. J Transl Med. 12:802014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Mo ML, Li MR, Chen Z, Liu XW, Sheng Q and
Zhou HM: Inhibition of the Wnt palmitoyltransferase porcupine
suppresses cell growth and downregulates the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
in gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. 5:1719–1723. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Cai C and Zhu X: The Wnt/β-catenin pathway
regulates self-renewal of cancer stem-like cells in human gastric
cancer. Mol Med Rep. 5:1191–1196. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Yu J, Tao Q, Cheng YY, Lee KY, Ng SS,
Cheung KF, Tian L, Rha SY, Neumann U, Röcken C, et al: Promoter
methylation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling antagonist Dkk-3 is
associated with poor survival in gastric cancer. Cancer. 115:49–60.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Than SS, Kataoka K, Sakaguchi M, Murata H,
Abarzua F, Taketa C, Du G, Yashiro M, Yanagihara K, Nasu Y, et al:
Intraperitoneal administration of an adenovirus vector carrying
REIC/Dkk-3 suppresses peritoneal dissemination of scirrhous gastric
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 25:989–995. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Gomceli I, Bostanci EB, Ozer I, Kemik AS,
Turhan N, Tez M, Kilic S, Demiriz B and Akoglu M: A novel screening
biomarker in gastric cancer: Serum Dickkopf-1.
Hepatogastroenterology. 59:1661–1664. 2012.
|
|
83
|
Mühlmann G, Untergasser G, Zitt M, Zitt M,
Maier H, Mikuz G, Kronberger IE, Haffner MC, Gunsilius E and Ofner
D: Immunohistochemically detectable dickkopf-3 expression in tumor
vessels predicts survival in gastric cancer. Virchows Arch.
456:635–646. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Hu Y, Wan R, Yu G, Shen J, Ni J, Yin G,
Xing M, Chen C, Fan Y, Xiao W, et al: Imbalance of Wnt/Dkk negative
feedback promotes persistent activation of pancreatic stellate
cells in chronic pancreatitis. PLoS One. 9:e951452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Shin H, Kim JH, Lee YS and Lee YC: Change
in gene expression profiles of secreted frizzled-related proteins
(SFRPs) by sodium butyrate in gastric cancers: Induction of
promoter demethylation and histone modification causing inhibition
of Wnt signaling. Int J Oncol. 40:1533–1542. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Ebert MP, Fei G, Kahmann S, Müller O, Yu
J, Sung JJ and Malfertheiner P: Increased β-catenin mRNA levels and
mutational alterations of the APC and β-catenin gene are present in
intestinal-type gastric cancer. Carcinogenesis. 23:87–91. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Fang Z, Xiong Y, Li J, Liu L, Zhang W,
Zhang C and Wan J: APC gene deletions in gastric adenocarcinomas in
a Chinese population: A correlation with tumour progression. Clin
Transl Oncol. 14:60–65. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Pan KF, Liu WG, Zhang L, You WC and Lu YY:
Mutations in components of the Wnt signaling pathway in gastric
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 14:1570–1574. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Mazzoni SM and Fearon ER: AXIN1 and AXIN2
variants in gastrointestinal cancers. Cancer Lett. 355:1–8. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Howard S, Deroo T, Fujita Y and Itasaki N:
A positive role of cadherin in Wnt/β-catenin signalling during
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS One. 6:e238992011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Czyzewska J, Guzińska-Ustymowicz K,
Ustymowicz M, Pryczynicz A and Kemona A: The expression of
E-cadherin-catenin complex in patients with advanced gastric
cancer: Role in formation of metastasis. Folia Histochem Cytobiol.
48:37–45. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Yoshii T, Miyagi Y, Nakamura Y, Kobayashi
O, Kameda Y and Ohkawa S: Pilot research for the correlation
between the expression pattern of E-cadherin-β-catenin complex and
lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer. Tumori. 99:234–238.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Silva EM, Begnami MD, Fregnani JH, Pelosof
AG, Zitron C, Montagnini AL and Soares FA: Cadherin-catenin
adhesion system and mucin expression: A comparison between young
and older patients with gastric carcinoma. Gastric Cancer.
11:149–159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Wang L, Guo J, Wang Q, Zhou J, Xu C, Teng
R, Chen Y, Wei Q and Liu ZP: LZTFL1 suppresses gastric cancer cell
migration and invasion through regulating nuclear translocation of
β-catenin. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 140:1997–2008. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Guo J, Fu Z, Wei J, Lu W, Feng J and Zhang
S: PRRX1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the
Wnt/β-catenin pathway in gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 32:3932015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Li H, Wang Z, Zhang W, Qian K, Liao G, Xu
W and Zhang S: VGLL4 inhibits EMT in part through suppressing
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in gastric cancer. Med Oncol.
32:832015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Zha L, Zhang J, Tang W, Zhang N, He M, Guo
Y and Wang Z: HMGA2 elicits EMT by activating the Wnt/β-catenin
pathway in gastric cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 58:724–733. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Huang J, Xiao D, Li G, Ma J, Chen P, Yuan
W, Hou F, Ge J, Zhong M, Tang Y, et al: EphA2 promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
in gastric cancer cells. Oncogene. 33:2737–2747. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Cai J, Feng D, Hu L, Chen H, Yang G, Cai
Q, Gao C and Wei D: FAT4 functions as a tumour suppressor in
gastric cancer by modulating Wnt/β-catenin signalling. Br J Cancer.
113:1720–1729. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Qu Y, Ray PS, Li J, Cai Q, Bagaria SP,
Moran C, Sim MS, Zhang J, Turner RR, Zhu Z, et al: High levels of
secreted frizzled-related protein 1 correlate with poor prognosis
and promote tumourigenesis in gastric cancer. Eur J Cancer.
49:3718–3728. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Han R, Xiong J, Xiao R, Altaf E, Wang J,
Liu Y, Xu H, Ding Q and Zhang Q: Activation of β-catenin signaling
is critical for doxorubicin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in BGC-823 gastric cancer cell line. Tumour Biol.
34:277–284. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Zhao L, Li W, Zang W, Liu Z, Xu X, Yu H,
Yang Q and Jia J: JMJD2B promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition
by cooperating with β-catenin and enhances gastric cancer
metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 19:6419–6429. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Li A, Zhou T, Guo L and Si J: Collagen
type I regulates β-catenin tyrosine phosphorylation and nuclear
translocation to promote migration and proliferation of gastric
carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 23:1247–1255. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Su J, Zhang A, Shi Z, Ma F, Pu P, Wang T,
Zhang J, Kang C and Zhang Q: MicroRNA-200a suppresses the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by interacting with β-catenin. Int
J Oncol. 40:1162–1170. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Cong N, Du P, Zhang A, Shen F, Su J, Pu P,
Wang T, Zjang J, Kang C and Zhang Q: Downregulated microRNA-200a
promotes EMT and tumor growth through the wnt/β-catenin pathway by
targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1/ZEB2 in gastric
adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 29:1579–1587. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Song F, Yang D, Liu B, Guo Y, Zheng H, Li
L, Wang T, Yu J, Zhao Y, Niu R, et al: Integrated microRNA network
analyses identify a poor-prognosis subtype of gastric cancer
characterized by the miR-200 family. Clin Cancer Res. 20:878–889.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Kurashige J, Kamohara H, Watanabe M,
Hiyoshi Y, Iwatsuki M, Tanaka Y, Kinoshita K, Saito S, Baba Y and
Baba H: MicroRNA-200b regulates cell proliferation, invasion, and
migration by directly targeting ZEB2 in gastric carcinoma. Ann Surg
Oncol. 19(Suppl 3): S656–S664. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Tang H, Kong Y, Guo J, Tang Y and Xie X,
Yang L, Su Q and Xie X: Diallyl disulfide suppresses proliferation
and induces apoptosis in human gastric cancer through Wnt-1
signaling pathway by up-regulation of miR-200b and miR-22. Cancer
Lett. 340:72–81. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Zhang Z, Liu S, Shi R and Zhao G: miR-27
promotes human gastric cancer cell metastasis by inducing
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Genet. 204:486–491.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Zhao X, He L, Li T, Lu Y, Miao Y, Liang S,
Guo H, Bai M, Xie H, Luo G, et al: SRF expedites metastasis and
modulates the epithelial to mesenchymal transition by regulating
miR-199a-5p expression in human gastric cancer. Cell Death Differ.
21:1900–1913. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Yanaka Y, Muramatsu T, Uetake H, Kozaki K
and Inazawa J: miR-544a induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition
through the activation of WNT signaling pathway in gastric cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 36:1363–1371. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Xing AY, Wang YW, Su ZX, Shi DB, Wang B
and Gao P: Catenin-δ1, negatively regulated by miR-145, promotes
tumour aggressiveness in gastric cancer. J Pathol. 236:53–64. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Voon DC, Wang H, Koo JK, Nguyen TA, Hor
YT, Chu YS, Ito K, Fukamachi H, Chan SL, Thiery JP, et al: Runx3
protects gastric epithelial cells against epithelial-mesenchymal
transition-induced cellular plasticity and tumorigenicity. Stem
Cells. 30:2088–2099. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Tong X, Li L, Li X, Heng L, Zhong L, Su X,
Rong R, Hu S, Liu W, Jia B, et al: SOX10, a novel
HMG-box-containing tumor suppressor, inhibits growth and metastasis
of digestive cancers by suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
Oncotarget. 5:10571–10583. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Garzon R, Marcucci G and Croce CM:
Targeting microRNAs in cancer: Rationale, strategies and
challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 9:775–789. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|