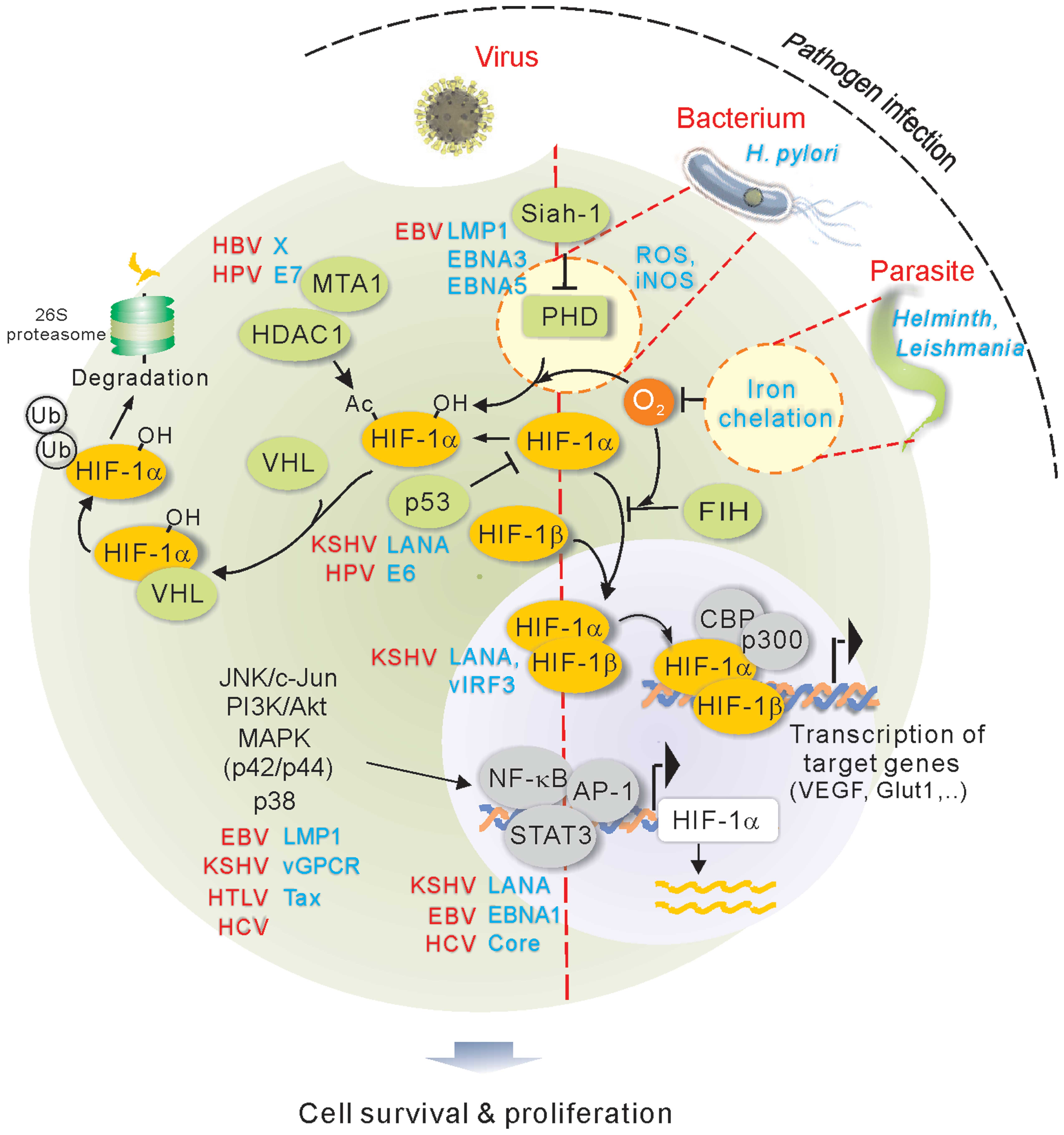
|
1
|
de Martel C, Ferlay J, Franceschi S,
Vignat J, Bray F, Forman D and Plummer M: Global burden of cancers
attributable to infections in 2008: A review and synthetic
analysis. Lancet Oncol. 13:607–615. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ackerman D and Simon MC: Hypoxia, lipids,
and cancer: Surviving the harsh tumor microenvironment. Trends Cell
Biol. 24:472–478. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Principles and
mechanisms of vessel normalization for cancer and other angiogenic
diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 10:417–427. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Minet E, Michel G, Remacle J and Michiels
C: Role of HIF-1 as a transcription factor involved in embryonic
development, cancer progression and apoptosis (Review). Int J Mol
Med. 5:253–259. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kurihara T, Westenskow PD and Friedlander
M: Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)/vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF) signaling in the retina. Adv Exp Med Biol.
801:275–281. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Calderwood MA, Venkatesan K, Xing L, Chase
MR, Vazquez A, Holthaus AM, Ewence AE, Li N, Hirozane-Kishikawa T,
Hill DE, et al: Epstein-Barr virus and virus human protein
interaction maps. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:7606–7611. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wakisaka N, Kondo S, Yoshizaki T, Murono
S, Furukawa M and Pagano JS: Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane
protein 1 induces synthesis of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha.
Mol Cell Biol. 24:5223–5234. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang L, Liu L, Xu Z, Liao W, Feng D, Dong
X, Xu S, Xiao L, Lu J, Luo X, et al: EBV-LMP1 targeted DNAzyme
enhances radiosensitivity by inhibiting tumor angiogenesis via the
JNKs/HIF-1 pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget.
6:5804–5817. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kondo S, Seo SY, Yoshizaki T, Wakisaka N,
Furukawa M, Joab I, Jang KL and Pagano JS: EBV latent membrane
protein 1 up-regulates hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha through
Siah1-mediated down-regulation of prolyl hydroxylases 1 and 3 in
nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 66:9870–9877. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
O’Neil JD, Owen TJ, Wood VH, Date KL,
Valentine R, Chukwuma MB, Arrand JR, Dawson CW and Young LS:
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA1 modulates the AP-1 transcription
factor pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells and enhances
angiogenesis in vitro. J Gen Virol. 89:2833–2842. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Darekar S, Georgiou K, Yurchenko M,
Yenamandra SP, Chachami G, Simos G, Klein G and Kashuba E:
Epstein-Barr virus immortalization of human B-cells leads to
stabilization of hypoxia-induced factor 1 alpha, congruent with the
Warburg effect. PLoS One. 7:e420722012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jiang JH, Wang N, Li A, Liao WT, Pan ZG,
Mai SJ, Li DJ, Zeng MS, Wen JM and Zeng YX: Hypoxia can contribute
to the induction of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) lytic cycle. J
Clin Virol. 37:98–103. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang X, Zhang Q, Nishitani J, Brown J, Shi
S and Le AD: Overexpression of human papillomavirus type 16
oncoproteins enhances hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha protein
accumulation and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in
human cervical carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2568–2576.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bodily JM, Mehta KP and Laimins LA: Human
papillomavirus E7 enhances hypoxia-inducible factor 1-mediated
transcription by inhibiting binding of histone deacetylases. Cancer
Res. 71:1187–1195. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
An J, Mo D, Liu H, Veena MS, Srivatsan ES,
Massoumi R and Rettig MB: Inactivation of the CYLD deubiquitinase
by HPV E6 mediates hypoxia-induced NF-kappaB activation. Cancer
Cell. 14:394–407. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Roman S, Jose-Abrego A, Fierro NA,
Escobedo-Melendez G, Ojeda-Granados C, Martinez-Lopez E and Panduro
A: Hepatitis B virus infection in Latin America: A genomic medicine
approach. World J Gastroenterol. 20:7181–7196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ali A, Abdel-Hafiz H, Suhail M, Al-Mars A,
Zakaria MK, Fatima K, Ahmad S, Azhar E, Chaudhary A and Qadri I:
Hepatitis B virus, HBx mutants and their role in hepatocellular
carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 20:10238–10248. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yoo YG, Na TY, Seo HW, Seong JK, Park CK,
Shin YK and Lee MO: Hepatitis B virus X protein induces the
expression of MTA1 and HDAC1, which enhances hypoxia signaling in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 27:3405–3413. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Holotnakova T, Tylkova L, Takacova M,
Kopacek J, Petrik J, Pastorekova S and Pastorek J: Role of the HBx
oncoprotein in carbonic anhydrase 9 induction. J Med Virol.
82:32–40. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Matsuoka M and Jeang KT: Human T-cell
leukaemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infectivity and cellular
transformation. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:270–280. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Grassmann R, Aboud M and Jeang KT:
Molecular mechanisms of cellular transformation by HTLV-1 Tax.
Oncogene. 24:5976–5985. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jeong SJ, Dasgupta A, Jung KJ, Um JH,
Burke A, Park HU and Brady JN: PI3K/AKT inhibition induces
caspase-dependent apoptosis in HTLV-1-transformed cells. Virology.
370:264–272. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Peloponese JM Jr and Jeang KT: Role for
Akt/protein kinase B and activator protein-1 in cellular
proliferation induced by the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 tax
oncoprotein. J Biol Chem. 281:8927–8938. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tomita M, Semenza GL, Michiels C, Matsuda
T, Uchihara JN, Okudaira T, Tanaka Y, Taira N, Ohshiro K and Mori
N: Activation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in human T-cell
leukaemia virus type 1-infected cell lines and primary adult T-cell
leukaemia cells. Biochem J. 406:317–323. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Appel N, Schaller T, Penin F and
Bartenschlager R: From structure to function: New insights into
hepatitis C virus RNA replication. J Biol Chem. 281:9833–9836.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tan A, Yeh SH, Liu CJ, Cheung C and Chen
PJ: Viral hepatocarcinogenesis: From infection to cancer. Liver
Int. 28:175–188. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bergonzini V, Salata C, Calistri A,
Parolin C and Palù G: View and review on viral oncology research.
Infect Agent Cancer. 5:112010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Martin D and Gutkind JS: Human
tumor-associated viruses and new insights into the molecular
mechanisms of cancer. Oncogene. 27(Suppl 2): S31–S42. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Nasimuzzaman M, Waris G, Mikolon D,
Stupack DG and Siddiqui A: Hepatitis C virus stabilizes
hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and stimulates the synthesis of
vascular endothelial growth factor. J Virol. 81:10249–10257. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ripoli M, D’Aprile A, Quarato G,
Sarasin-Filipowicz M, Gouttenoire J, Scrima R, Cela O, Boffoli D,
Heim MH, Moradpour D, et al: Hepatitis C virus-linked mitochondrial
dysfunction promotes hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha-mediated
glycolytic adaptation. J Virol. 84:647–660. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liu XH, Zhou X, Zhu CL, Song H and Liu F:
Effects of HCV core protein on the expression of hypoxia-inducible
factor 1 alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor. Zhonghua Gan
Zang Bing Za Zhi. 19:751–754. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
32
|
Abe M, Koga H, Yoshida T, Masuda H,
Iwamoto H, Sakata M, Hanada S, Nakamura T, Taniguchi E, Kawaguchi
T, et al: Hepatitis C virus core protein upregulates the expression
of vascular endothelial growth factor via the nuclear
factor-κB/hypoxia-inducible factor-1α axis under hypoxic
conditions. Hepatol Res. 42:591–600. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mesri EA, Cesarman E and Boshoff C:
Kaposi’s sarcoma and its associated herpesvirus. Nat Rev Cancer.
10:707–719. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cesarman E, Chang Y, Moore PS, Said JW and
Knowles DM: Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA
sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas. N Engl J
Med. 332:1186–1191. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cai Q, Murakami M, Si H and Robertson ES:
A potential alpha-helix motif in the amino terminus of LANA encoded
by Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus is critical for nuclear
accumulation of HIF-1alpha in normoxia. J Virol. 81:10413–10423.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cotter MA II and Robertson ES: The
latency-associated nuclear antigen tethers the Kaposi’s
sarcoma-associated herpesvirus genome to host chromosomes in body
cavity-based lymphoma cells. Virology. 264:254–264. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cai Q, Lan K, Verma SC, Si H, Lin D and
Robertson ES: Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latent
protein LANA interacts with HIF-1 alpha to upregulate RTA
expression during hypoxia: Latency control under low oxygen
conditions. J Virol. 80:7965–7975. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cai QL, Knight JS, Verma SC, Zald P and
Robertson ES: EC5S ubiquitin complex is recruited by KSHV latent
antigen LANA for degradation of the VHL and p53 tumor suppressors.
PLoS Pathog. 2:e1162006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rivas C, Thlick AE, Parravicini C, Moore
PS and Chang Y: Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus LANA2 is a
B-cell-specific latent viral protein that inhibits p53. J Virol.
75:429–438. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Shin YC, Joo CH, Gack MU, Lee HR and Jung
JU: Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus viral IFN regulatory
factor 3 stabilizes hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha to induce
vascular endothelial growth factor expression. Cancer Res.
68:1751–1759. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sodhi A, Montaner S, Patel V, Zohar M,
Bais C, Mesri EA and Gutkind JS: The Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated
herpes virus G protein-coupled receptor up-regulates vascular
endothelial growth factor expression and secretion through
mitogen-activated protein kinase and p38 pathways acting on
hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Cancer Res. 60:4873–4880.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jham BC, Ma T, Hu J, Chaisuparat R,
Friedman ER, Pandolfi PP, Schneider A, Sodhi A and Montaner S:
Amplification of the angiogenic signal through the activation of
the TSC/mTOR/HIF axis by the KSHV vGPCR in Kaposi’s sarcoma. PLoS
One. 6:e191032011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Davis DA, Rinderknecht AS, Zoeteweij JP,
Aoki Y, Read-Connole EL, Tosato G, Blauvelt A and Yarchoan R:
Hypoxia induces lytic replication of Kaposi sarcoma-associated
herpesvirus. Blood. 97:3244–3250. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Samaras V, Rafailidis PI, Mourtzoukou EG,
Peppas G and Falagas ME: Chronic bacterial and parasitic infections
and cancer: A review. J Infect Dev Ctries. 4:267–281.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Nizet V and Johnson RS: Interdependence of
hypoxic and innate immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 9:609–617.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Dorer MS, Talarico S and Salama NR:
Helicobacter pylori’s unconventional role in health and disease.
PLoS Pathog. 5:e10005442009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Nardone G, Rocco A and Malfertheiner P:
Review article: Helicobacter pylori and molecular events in
precancerous gastric lesions. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 20:261–270.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Griffiths EA, Pritchard SA, Valentine HR,
Whitchelo N, Bishop PW, Ebert MP, Price PM, Welch IM and West CM:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression in the gastric
carcinogenesis sequence and its prognostic role in gastric and
gastro-oesophageal adenocarcinomas. Br J Cancer. 96:95–103. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Griffiths EA, Pritchard SA, McGrath SM,
Valentine HR, Price PM, Welch IM and West CM: Increasing expression
of hypoxia-inducible proteins in the Barrett’s
metaplasia-dysplasia-adenocarcinoma sequence. Br J Cancer.
96:1377–1383. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Park JH, Kim TY, Jong HS, Kim TY, Chun YS,
Park JW, Lee CT, Jung HC, Kim NK and Bang YJ: Gastric epithelial
reactive oxygen species prevent normoxic degradation of
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in gastric cancer cells. Clin
Cancer Res. 9:433–440. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bhattacharyya A, Chattopadhyay R, Hall EH,
Mebrahtu ST, Ernst PB and Crowe SE: Mechanism of hypoxia-inducible
factor 1 alpha-mediated Mcl1 regulation in Helicobacter
pylori-infected human gastric epithelium. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 299:G1177–G1186. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ohshima H and Bartsch H: Chronic
infections and inflammatory processes as cancer risk factors:
Possible role of nitric oxide in carcinogenesis. Mutat Res.
305:253–264. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Mannick EE, Bravo LE, Zarama G, Realpe JL,
Zhang XJ, Ruiz B, Fontham ET, Mera R, Miller MJ and Correa P:
Inducible nitric oxide synthase, nitrotyrosine, and apoptosis in
Helicobacter pylori gastritis: Effect of antibiotics and
antioxidants. Cancer Res. 56:3238–3243. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Metzen E, Zhou J, Jelkmann W, Fandrey J
and Brüne B: Nitric oxide impairs normoxic degradation of
HIF-1alpha by inhibition of prolyl hydroxylases. Mol Biol Cell.
14:3470–3481. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yuan C, Zhu C, Wu Y, Pan X and Hua X:
Bacteriological and molecular identification of Bartonella species
in cats from different regions of China. PLoS Negl Trop Dis.
5:e13012011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kempf VA, Lebiedziejewski M, Alitalo K,
Wälzlein JH, Ehehalt U, Fiebig J, Huber S, Schütt B, Sander CA,
Müller S, et al: Activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in
bacillary angiomatosis: Evidence for a role of hypoxia-inducible
factor-1 in bacterial infections. Circulation. 111:1054–1062. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Relman DA, Falkow S, LeBoit PE, Perkocha
LA, Min KW, Welch DF and Slater LN: The organism causing bacillary
angiomatosis, peliosis hepatis, and fever and bacteremia in
immunocompromised patients. N Engl J Med. 324:15141991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kaiser PO, Riess T, Wagner CL, Linke D,
Lupas AN, Schwarz H, Raddatz G, Schäfer A and Kempf VA: The head of
Bartonella adhesin A is crucial for host cell interaction of
Bartonella henselae. Cell Microbiol. 10:2223–2234. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Porta C, Riboldi E and Sica A: Mechanisms
linking pathogens-associated inflammation and cancer. Cancer Lett.
305:250–262. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Mostafa MH, Sheweita SA and O’Connor PJ:
Relationship between schistosomiasis and bladder cancer. Clin
Microbiol Rev. 12:97–111. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Vennervald BJ and Polman K: Helminths and
malignancy. Parasite Immunol. 31:686–696. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Araújo AP, Frezza TF, Allegretti SM and
Giorgio S: Hypoxia, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and vascular
endothelial growth factor in a murine model of Schistosoma mansoni
infection. Exp Mol Pathol. 89:327–333. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Wilson MS, Mentink-Kane MM, Pesce JT,
Ramalingam TR, Thompson R and Wynn TA: Immunopathology of
schistosomiasis. Immunol Cell Biol. 85:148–154. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Arrais-Silva WW, Paffaro VA Jr, Yamada AT
and Giorgio S: Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in the
cutaneous lesions of BALB/c mice infected with Leishmania
amazonensis. Exp Mol Pathol. 78:49–54. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Degrossoli A, Bosetto MC, Lima CB and
Giorgio S: Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in
mononuclear phagocytes infected with Leishmania amazonensis.
Immunol Lett. 114:119–125. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Singh AK, Mukhopadhyay C, Biswas S, Singh
VK and Mukhopadhyay CK: Intracellular pathogen Leishmania donovani
activates hypoxia inducible factor-1 by dual mechanism for survival
advantage within macrophage. PLoS One. 7:e384892012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Morsy TA: Cutaneous leishmaniasis
predisposing to human skin cancer: Forty years local and regional
studies. J Egypt Soc Parasitol. 43:629–648. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Suzuki H, Iwasaki E and Hibi T:
Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 12:79–87.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|