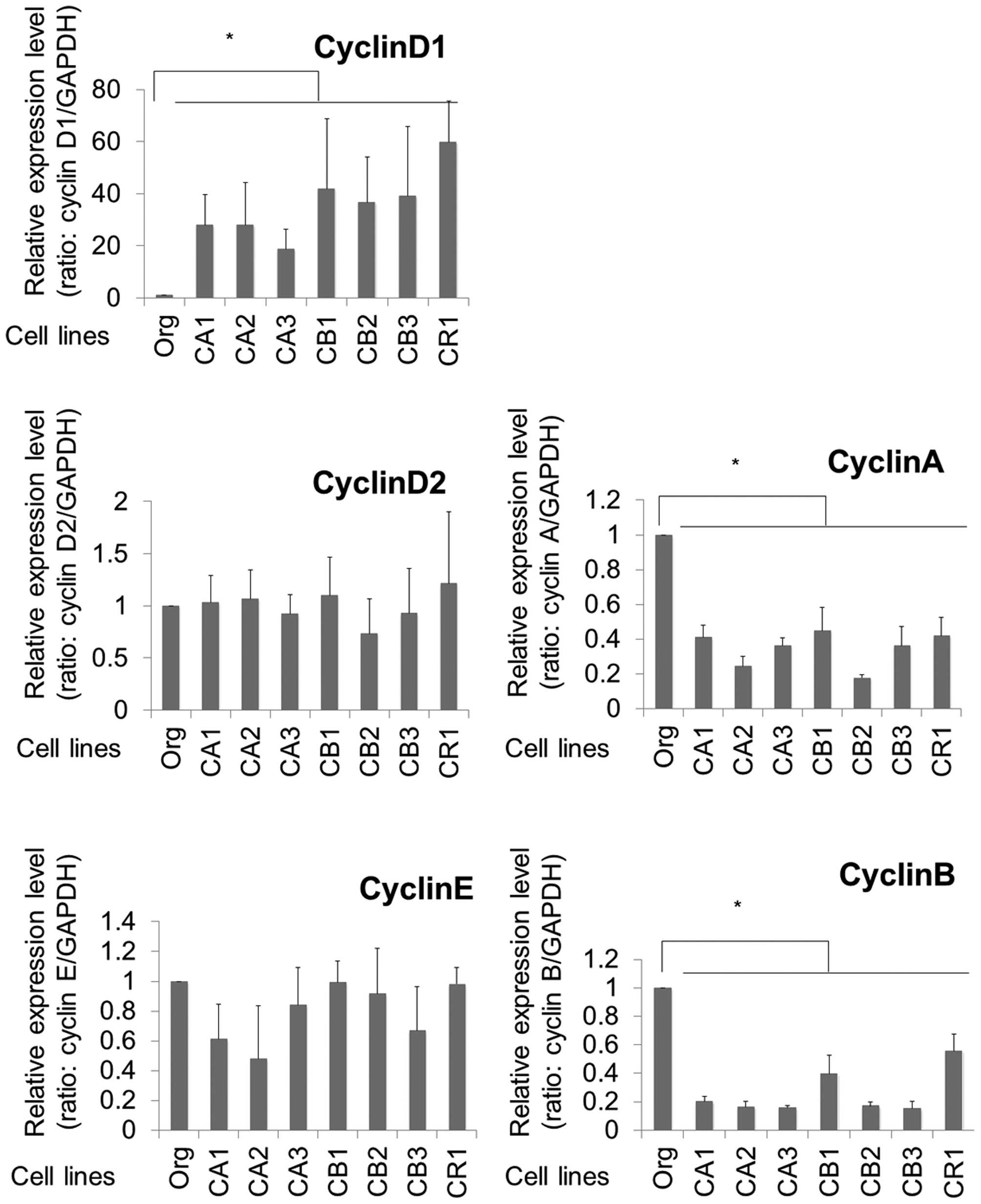
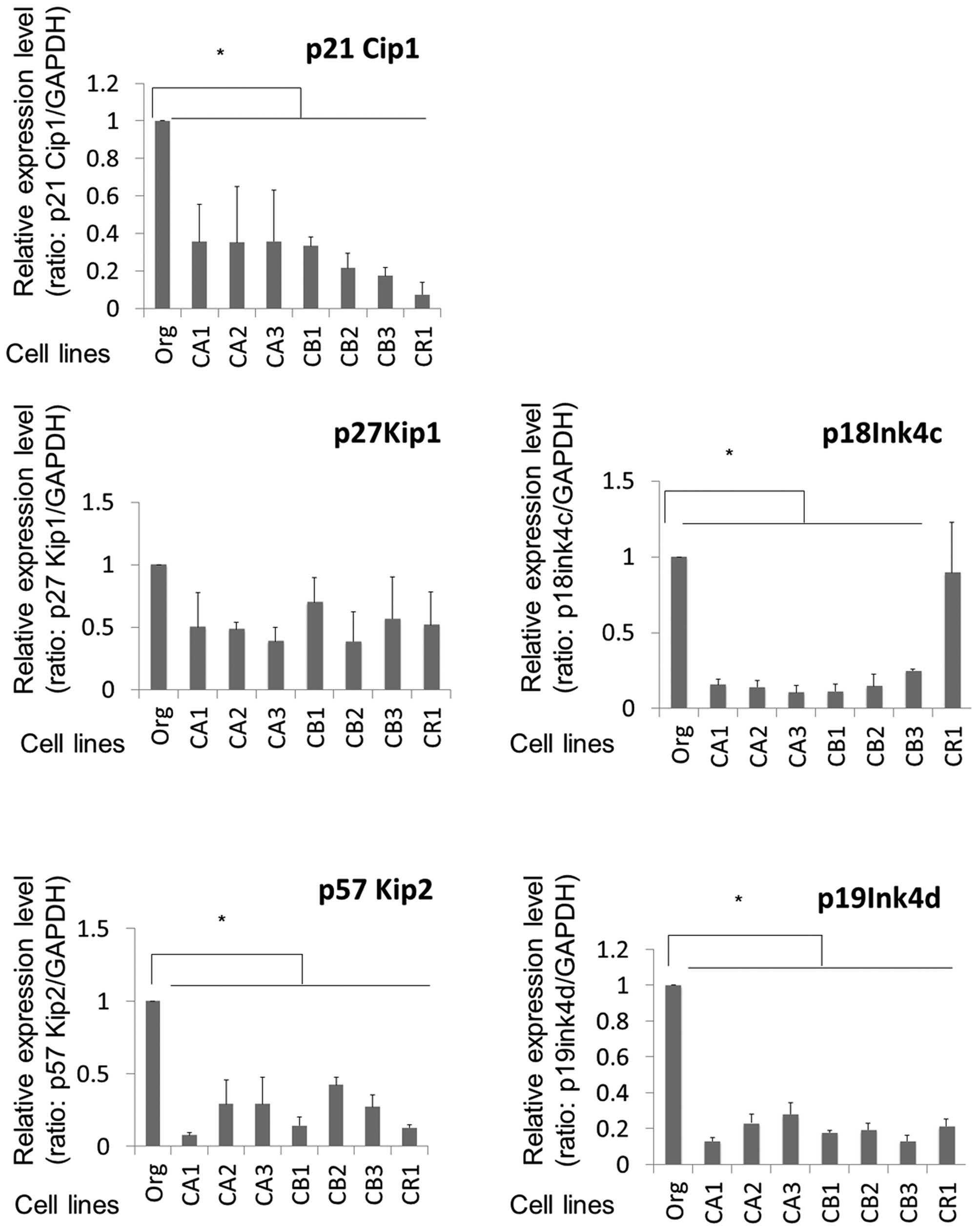
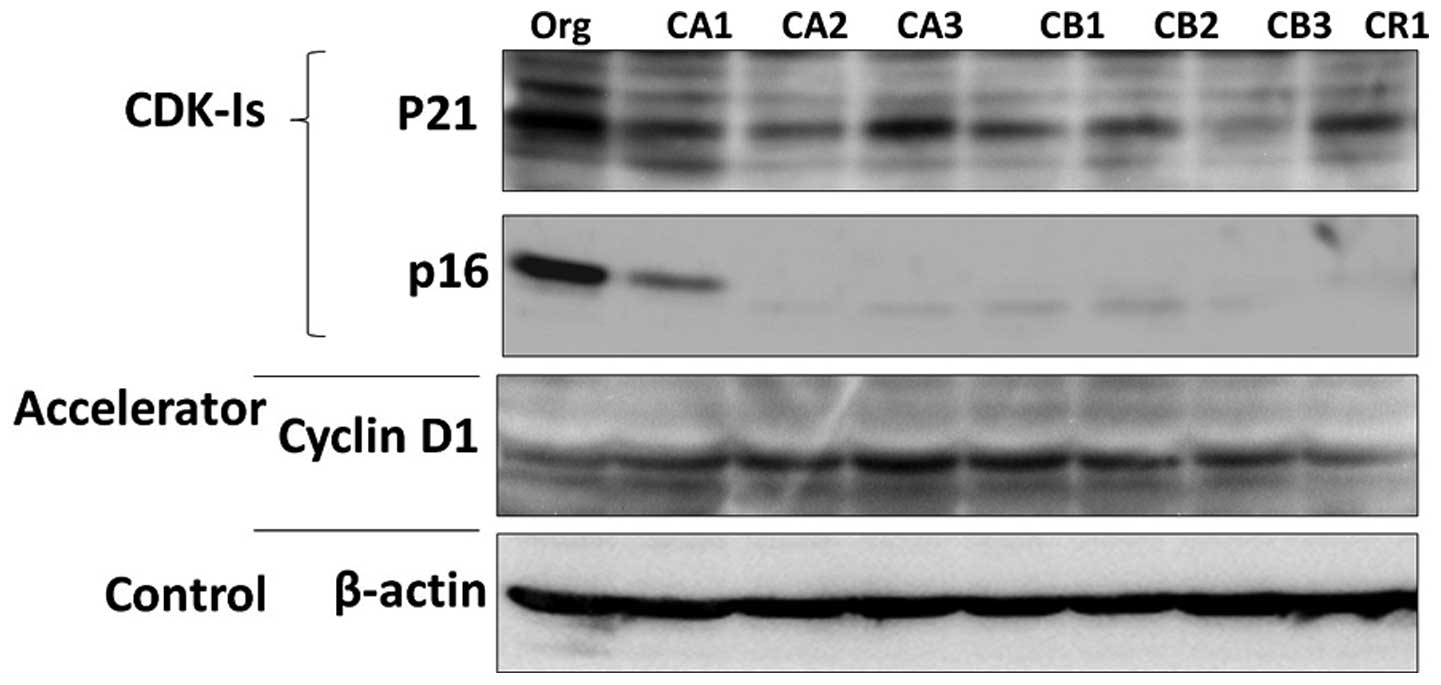
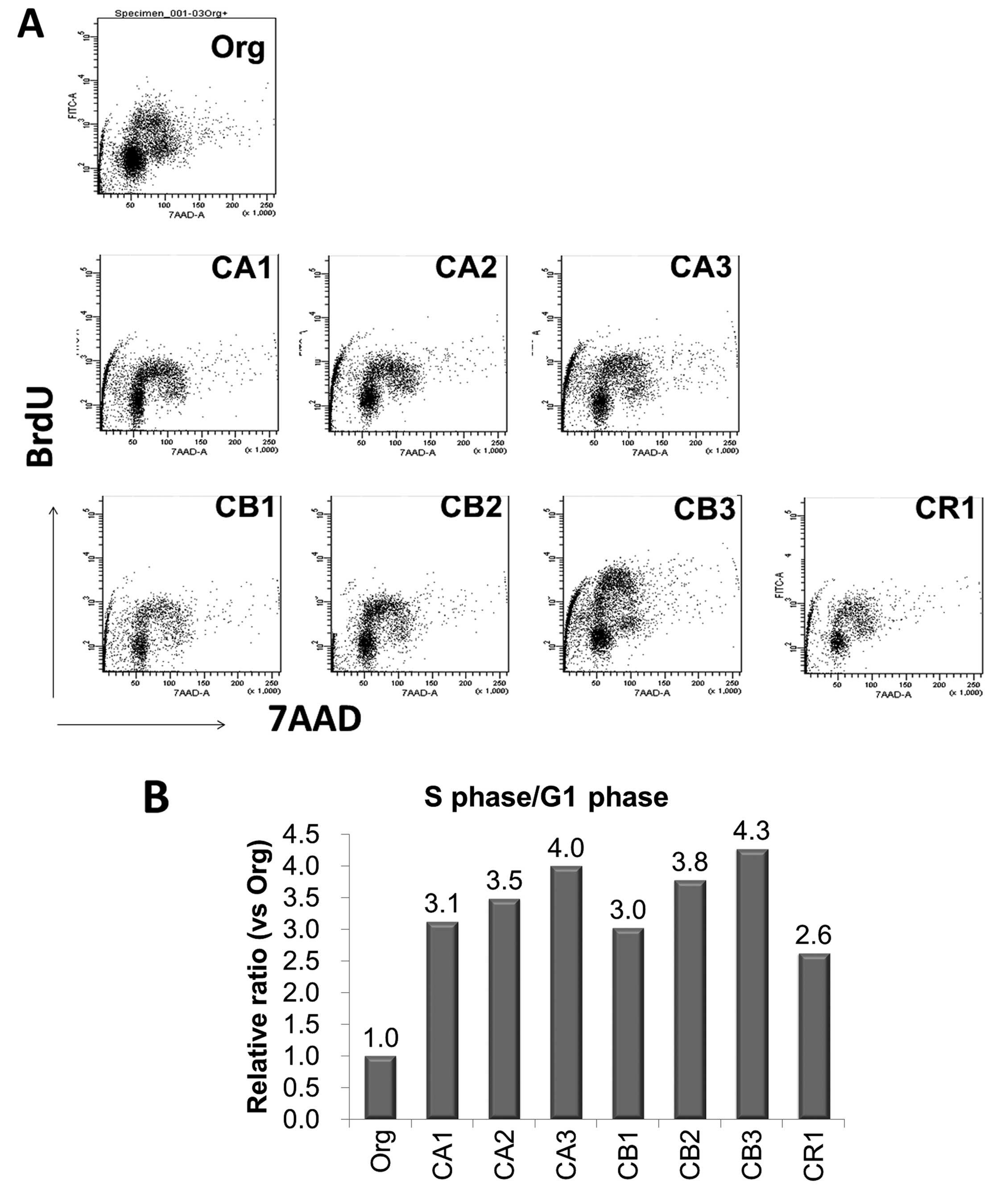
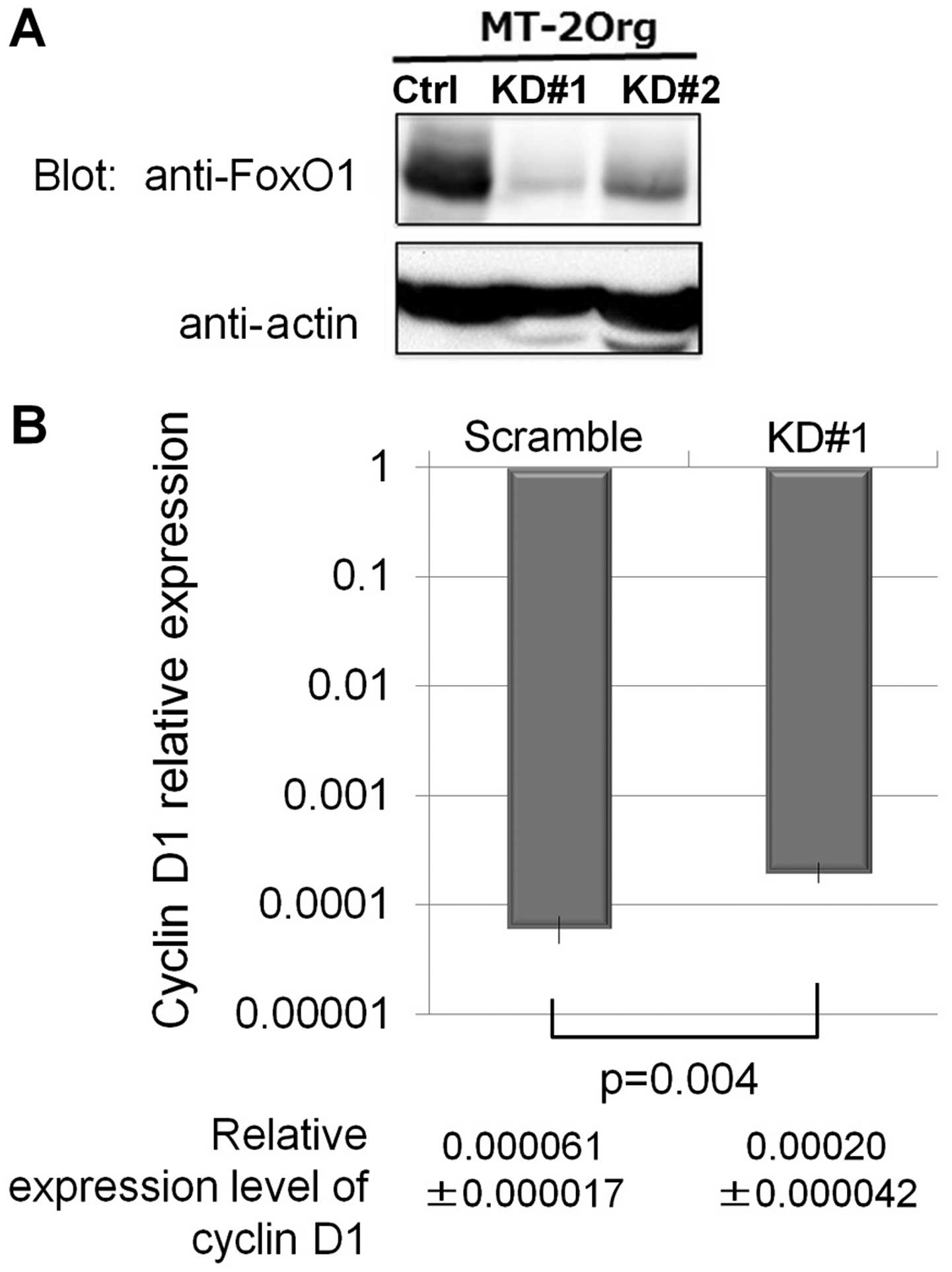
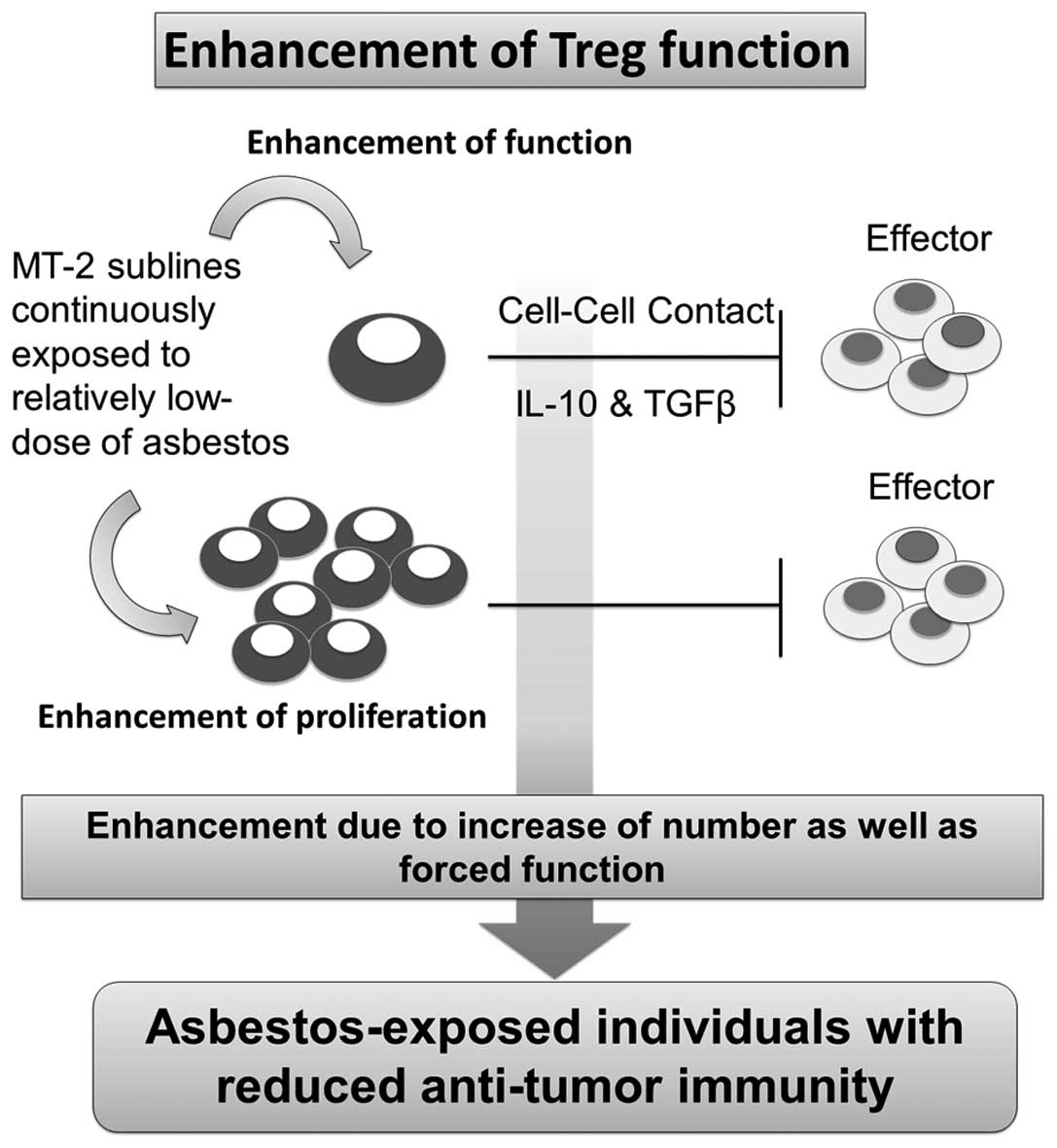
|
1
|
Parkes WR: Asbestos-related disorders. Br
J Dis Chest. 67:261–300. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mossman BT and Gee JB: Asbestos-related
diseases. N Engl J Med. 320:1721–1730. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Peacock C, Copley SJ and Hansell DM:
Asbestos-related benign pleural disease. Clin Radiol. 55:422–432.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Morinaga K, Kishimoto T, Sakatani M, Akira
M, Yokoyama K and Sera Y: Asbestos-related lung cancer and
mesothelioma in Japan. Ind Health. 39:65–74. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
O'Reilly KM, Mclaughlin AM, Beckett WS and
Sime PJ: Asbestos-related lung disease. Am Fam Physician.
75:683–688. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lazarus A, Massoumi A, Hostler J and
Hostler DC: Asbestos-related pleuropulmonary diseases: Benign and
malignant. Postgrad Med. 124:116–130. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kamp DW, Graceffa P, Pryor WA and Weitzman
SA: The role of free radicals in asbestos-induced diseases. Free
Radic Biol Med. 12:293–315. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shukla A, Gulumian M, Hei TK, Kamp D,
Rahman Q and Mossman BT: Multiple roles of oxidants in the
pathogenesis of asbestos-induced diseases. Free Radic Biol Med.
34:1117–1129. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Toyokuni S: Mechanisms of asbestos-induced
carcinogenesis. Nagoya J Med Sci. 71:1–10. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Toyokuni S: Role of iron in
carcinogenesis: Cancer as a ferrotoxic disease. Cancer Sci.
100:9–16. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lemen RA, Dement JM and Wagoner JK:
Epidemiology of asbestos-related diseases. Environ Health Perspect.
34:1–11. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee S, Matsuzaki H, Kumagai-Takei N,
Yoshitome K, Maeda M, Chen Y, Kusaka M, Urakami K, Hayashi H,
Fujimoto W, et al: Silica exposure and altered regulation of
autoimmunity. Environ Health Prev Med. 19:322–329. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hayashi H, Miura Y, Maeda M, Murakami S,
Kumagai N, Nishimura Y, Kusaka M, Urakami K, Fujimoto W and Otsuki
T: Reductive alteration of the regulatory function of the CD4(+)
CD25(+) T cell fraction in silicosis patients. Int J Immunopathol
Pharmacol. 23:1099–1109. 2010.
|
|
14
|
Lee S, Hayashi H, Maeda M, Chen Y,
Matsuzaki H, Takei-Kumagai N, Nishimura Y, Fujimoto W and Otsuki T:
Environmental factors producing autoimmune dysregulation - chronic
activation of T cells caused by silica exposure. Immunobiology.
217:743–748. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Otsuki T, Matsuzaki H, Lee S,
Kumagai-Takei N, Yamamoto S, Hatayama T, Yoshitome K and Nishimura
Y: Environmental factors and human health: Fibrous and particulate
substance-induced immunological disorders and construction of a
health-promoting living environment. Environ Health Prev Med.
21:71–81. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kumagai-Takei N, Maeda M, Chen Y,
Matsuzaki H, Lee S, Nishimura Y, Hiratsuka J and Otsuki T: Asbestos
induces reduction of tumor immunity. Clin Dev Immunol.
2011:4814392011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nishimura Y, Miura Y, Maeda M, Kumagai N,
Murakami S, Hayashi H, Fukuoka K, Nakano T and Otsuki T: Impairment
in cytotoxicity and expression of NK cell- activating receptors on
human NK cells following exposure to asbestos fibers. Int J
Immunopathol Pharmacol. 22:579–590. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nishimura Y, Maeda M, Kumagai N, Hayashi
H, Miura Y and Otsuki T: Decrease in phosphorylation of ERK
following decreased expression of NK cell-activating receptors in
human NK cell line exposed to asbestos. Int J Immunopathol
Pharmacol. 22:879–888. 2009.
|
|
19
|
Kumagai-Takei N, Nishimura Y, Maeda M,
Hayashi H, Matsuzaki H, Lee S, Hiratsuka J and Otsuki T: Effect of
asbestos exposure on differentiation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes in
mixed lymphocyte reaction of human peripheral blood mononuclear
cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 49:28–36. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kumagai-Takei N, Nishimura Y, Maeda M,
Hayashi H, Matsuzaki H, Lee S, Kishimoto T, Fukuoka K, Nakano T and
Otsuki T: Functional properties of CD8 (+) lymphocytes in patients
with pleural plaque and malignant mesothelioma. J Immunol Res.
2014:6701402014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hyodoh F, Takata-Tomokuni A, Miura Y,
Sakaguchi H, Hatayama T, Hatada S, Katsuyama H, Matsuo Y and Otsuki
T: Inhibitory effects of anti-oxidants on apoptosis of a human
polyclonal T-cell line, MT-2, induced by an asbestos, chrysotile-A.
Scand J Immunol. 61:442–448. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miura Y, Nishimura Y, Katsuyama H, Maeda
M, Hayashi H, Dong M, Hyodoh F, Tomita M, Matsuo Y, Uesaka A, et
al: Involvement of IL-10 and Bcl-2 in resistance against an
asbestos-induced apoptosis of T cells. Apoptosis. 11:1825–1835.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Maeda M, Yamamoto S, Chen Y, Kumagai-Takei
N, Hayashi H, Matsuzaki H, Lee S, Hatayama T, Miyahara N, Katoh M,
et al: Resistance to asbestos-induced apoptosis with continuous
exposure to crocidolite on a human T cell. Sci Total Environ.
429:174–182. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Maeda M, Chen Y, Hayashi H, Kumagai-Takei
N, Matsuzaki H, Lee S, Nishimura Y and Otsuki T: Chronic exposure
to asbestos enhances TGF-β1 production in the human adult T cell
leukemia virus-immortalized T cell line MT-2. Int J Oncol.
45:2522–2532. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Maeda M, Chen Y, Kumagai-Takei N, Hayashi
H, Matsuzaki H, Lee S, Hiratsuka J, Nishimura Y, Kimura Y and
Otsuki T: Alteration of cytoskeletal molecules in a human T cell
line caused by continuous exposure to chrysotile asbestos.
218:1184–1191. 2013.
|
|
26
|
Maeda M, Nishimura Y, Hayashi H, Kumagai
N, Chen Y, Murakami S, Miura Y, Hiratsuka J, Kishimoto T and Otsuki
T: Reduction of CXC chemokine receptor 3 in an in vitro model of
continuous exposure to asbestos in a human T-cell line, MT-2. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 45:470–479. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Maeda M, Nishimura Y, Hayashi H, Kumagai
N, Chen Y, Murakami S, Miura Y, Hiratsuka J, Kishimoto T and Otsuki
T: Decreased CXCR3 expression in CD4+ T cells exposed to
asbestos or derived from asbestos-exposed patients. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 45:795–803. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Matsuzaki H, Maeda M, Lee S, Nishimura Y,
Kumagai-Takei N, Hayashi H, Yamamoto S, Hatayama T, Kojima Y,
Tabata R, et al: Asbestos-induced cellular and molecular alteration
of immunocompetent cells and their relationship with chronic
inflammation and carcinogenesis. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2012:4926082012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hamano R, Wu X, Wang Y, Oppenheim JJ and
Chen X: Characterization of MT-2 cells as a human regulatory T
cell-like cell line. Cell Mol Immunol. 12:780–782. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ying C, Maeda M, Nishimura Y,
Kumagai-Takei N, Hayashi H, Matsuzaki H, Lee S, Yoshitome K,
Yamamoto S, Hatayama T, et al: Enhancement of regulatory T
cell-like suppressive function in MT-2 by long-term and low-dose
exposure to asbestos. Toxicology. 338:86–94. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Matsuzaki H, Lee S, Maeda M, Kumagai-Takei
N, Nishimura Y and Otsuki T: FoxO1 regulates apoptosis induced by
asbestos in the MT-2 human T-cell line. J Immunotoxicol.
13:620–627. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Arden KC: FoxO: Linking new signaling
pathways. Mol Cell. 14:416–418. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Accili D and Arden KC: FoxOs at the
crossroads of cellular metabolism, differentiation, and
transformation. Cell. 117:421–426. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huang H and Tindall DJ: CDK2 and FOXO1: A
fork in the road for cell fate decisions. Cell Cycle. 6:902–906.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu P, Kao TP and Huang H: CDK1 promotes
cell proliferation and survival via phosphorylation and inhibition
of FOXO1 transcription factor. Oncogene. 27:4733–4744. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Eijkelenboom A and Burgering BM: FOXOs:
Signalling integrators for homeostasis maintenance. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 14:83–97. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kohyama N, Shinohara Y and Suzuki Y:
Mineral phases and some reexamined characteristics of the
International Union Against Cancer standard asbestos samples. Am J
Ind Med. 30:515–528. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gao FF and Oury TD: Other neoplasia.
Pathology of Asbestos-Associated Diseases. Roggi VL, Oury TD and
Sporn TA: 3rd ed. Springer; Berlin: pp. 177–192. 2014, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Craighead Je: Nonthoracic cancers possibly
resulting from asbestos exposure. Asbestos and its Diseases.
Craighead JE and Gibbs AR: Oxford University Press; New York, NY:
pp. 230–252. 2008, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Sakaguchi S, Ono M, Setoguchi R, Yagi H,
Hori S, Fehervari Z, Shimizu J, Takahashi T and Nomura T:
Foxp3+ CD25+ CD4+ natural
regulatory T cells in dominant self-tolerance and autoimmune
disease. Immunol Rev. 212:8–27. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nishikawa H and Sakaguchi S: Regulatory T
cells in tumor immunity. Int J Cancer. 127:759–767. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yamaguchi T and Sakaguchi S: Regulatory T
cells in immune surveillance and treatment of cancer. Semin Cancer
Biol. 16:115–123. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|