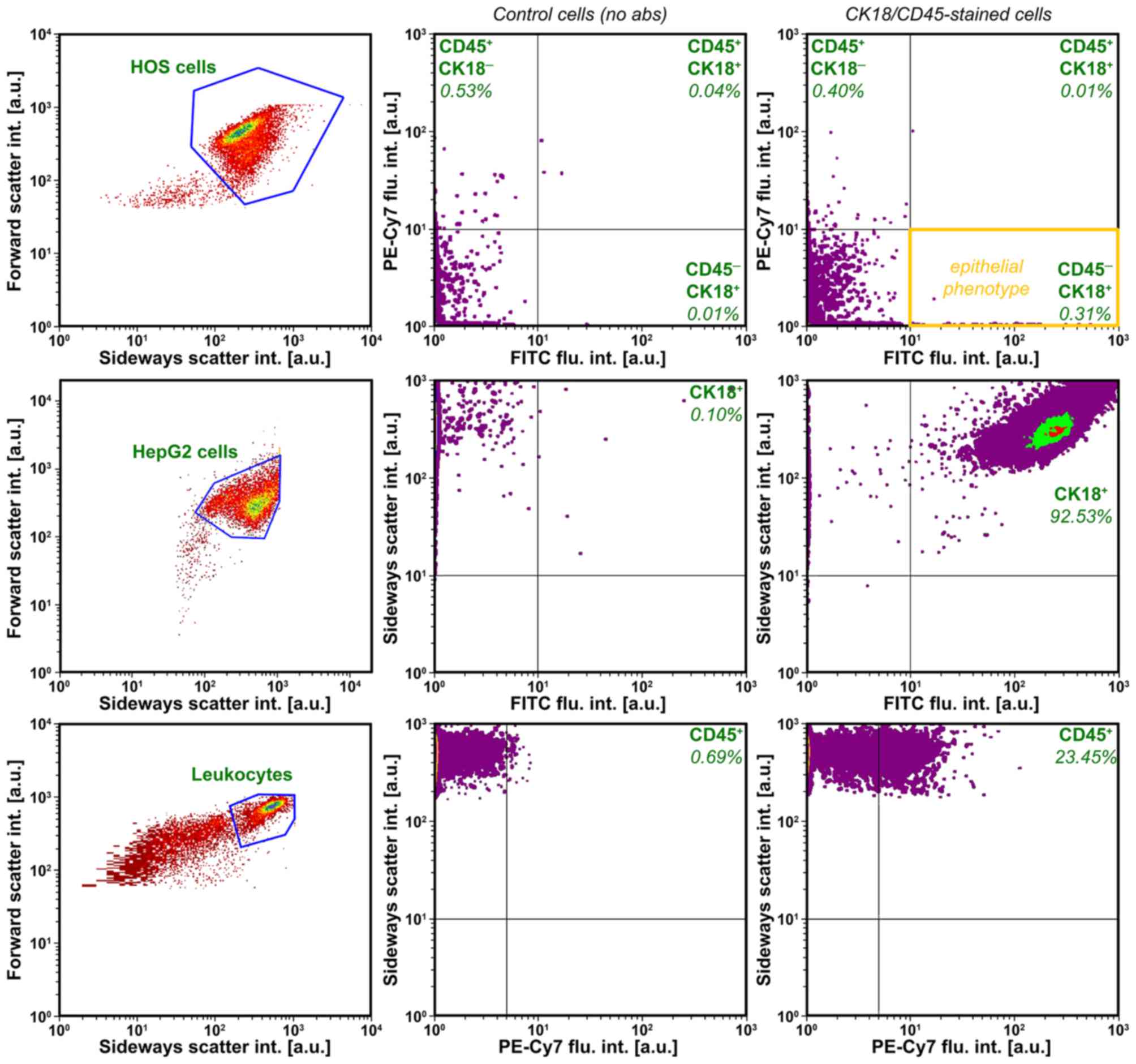
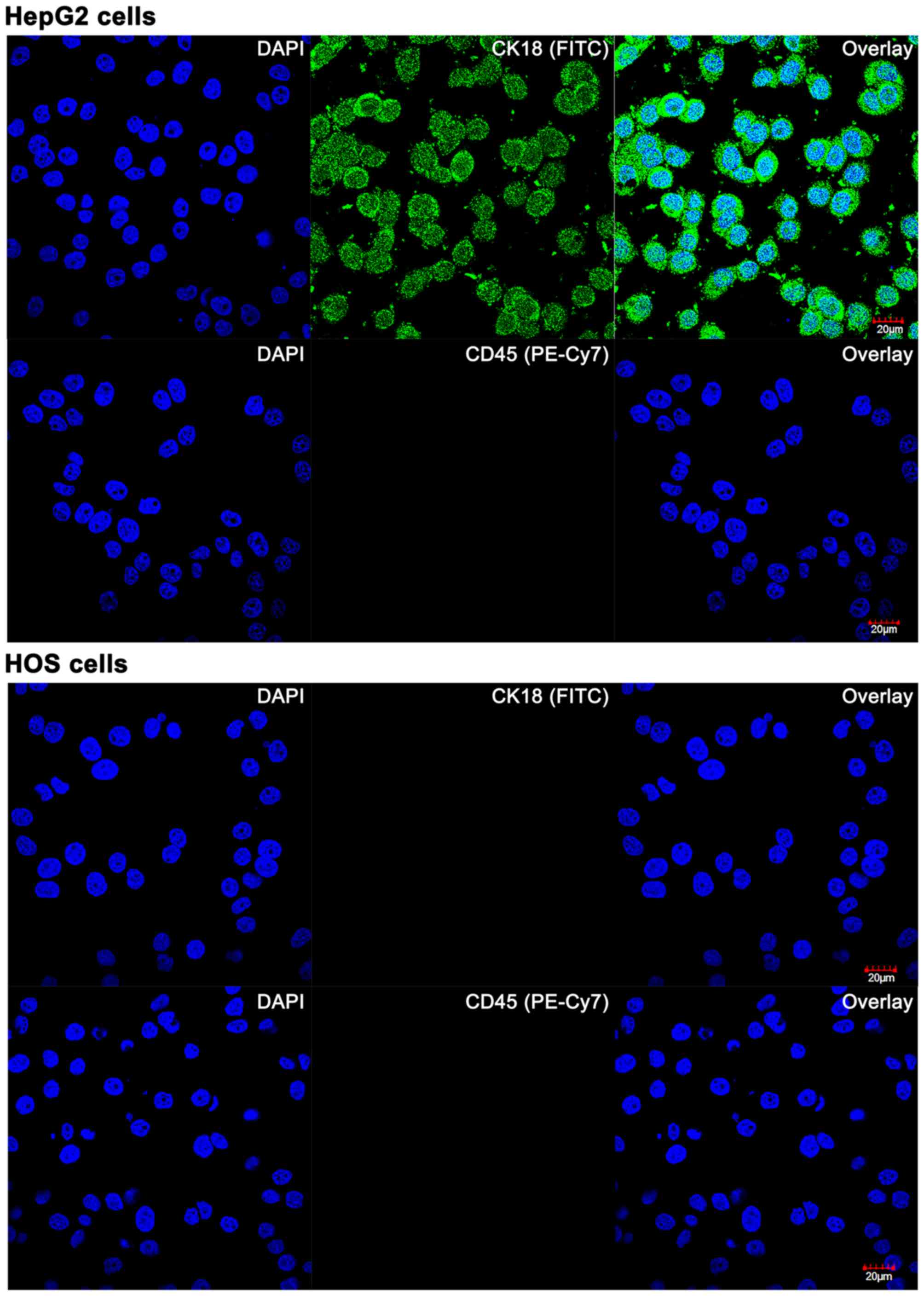
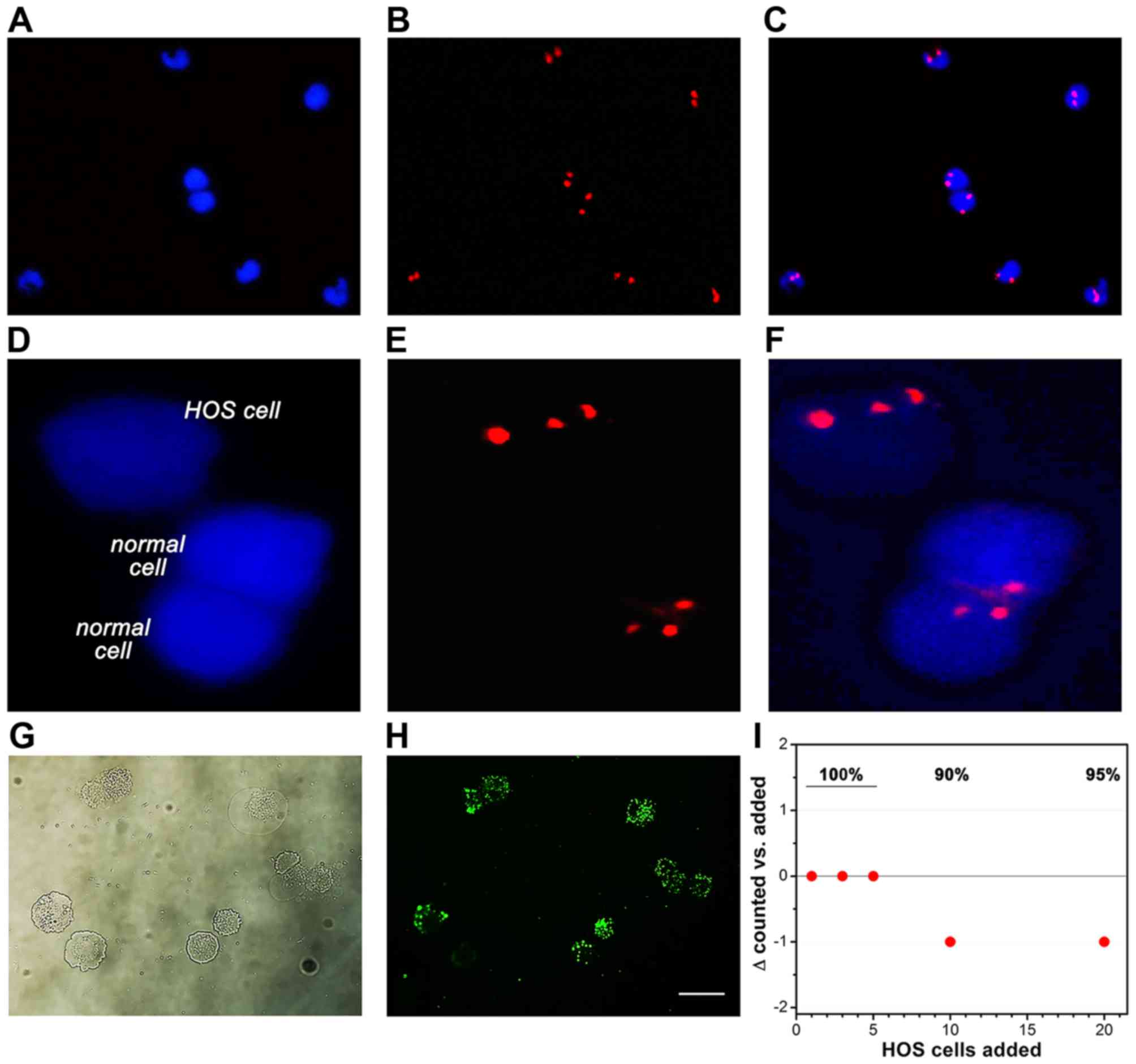
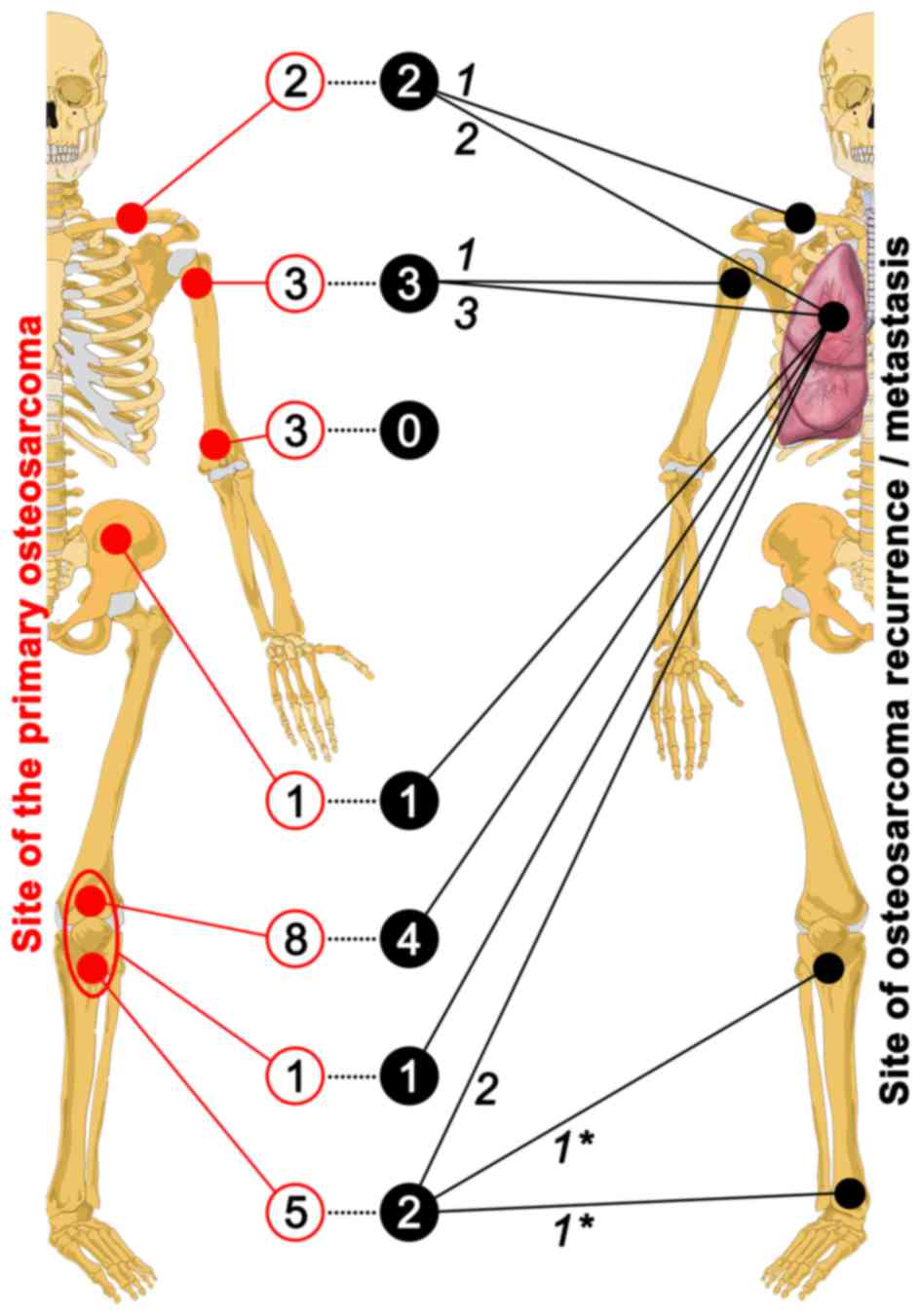
|
1
|
Burningham Z, Hashibe M, Spector L and
Schiffman JD: The epidemiology of sarcoma. Clin Sarcoma Res.
2:142012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferrari S and Palmerini E: Adjuvant and
neoadjuvant combination chemotherapy for osteogenic sarcoma. Curr
Opin Oncol. 19:341–346. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jaffe N: Adjuvant chemotherapy in
osteosarcoma: An odyssey of rejection and vindication. Cancer Treat
Res. 152:219–237. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chou AJ, Geller DS and Gorlick R: Therapy
for osteosarcoma: Where do we go from here? Paediatr Drugs.
10:315–327. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Haddox Cl, Han G, Anijar L, Binitie O,
Letson GD, Bui MM and Reed DR: Osteosarcoma in pediatric patients
and young adults: a single institution retrospective review of
presentation, therapy, and outcome. Sarcoma. 2014:4025092014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Serra M, Scotlandi K, Manara MC, Maurici
D, Benini S, Sarti M, Campanacci M and Baldini N: Analysis of
P-glycoprotein expression in osteosarcoma. Eur J Cancer.
31A:1998–2002. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Perissinotto E, Cavalloni G, Leone F,
Fonsato V, Mitola S, Grignani G, Surrenti N, Sangiolo D, Bussolino
F, Piacibello W, et al: Involvement of chemokine receptor 4/stromal
cell-derived factor 1 system during osteosarcoma tumor progression.
Clin Cancer Res. 11:490–497. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gill J, Geller D and Gorlick R: HER-2
involvement in osteosarcoma. Adv Exp Med Biol. 804:161–177. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jeffree GM, Price CH and Sissons HA: The
metastatic patterns of osteosarcoma. Br J Cancer. 32:87–107. 1975.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Moore DD and Luu HH: Osteosarcoma. Cancer
Treat Res. 162:65–92. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xing D, Qasem SA, Owusu K, Zhang K, Siegal
GP and Wei S: Changing prognostic factors in osteosarcoma: Analysis
of 381 cases from two institutions. Hum Pathol. 45:1688–1696. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dunn D and Dehner LP: Metastatic
osteosarcoma to lung: A clinicopathologic study of surgical
biopsies and resections. Cancer. 40:3054–3064. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Salah S, Ahmad R, Sultan I, Yaser S and
Shehadeh A: Osteosarcoma with metastasis at initial diagnosis:
Current outcomes and prognostic factors in the context of a
comprehensive cancer center. Mol Clin Oncol. 2:811–816.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hong Q, Fang J, Pang Y and Zheng J:
Prognostic value of the microRNA-29 family in patients with primary
osteosarcomas. Med Oncol. 31:372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang C, Yao C, Li H, Wang G and He X:
Serum levels of microRNA-133b and microRNA-206 expression predict
prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:4194–4203. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ma W, Zhang X, Chai J, Chen P, Ren P and
Gong M: Circulating miR-148a is a significant diagnostic and
prognostic biomarker for patients with osteosarcoma. Tumour Biol.
35:12467–12472. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cai H, Zhao H, Tang J and Wu H: Serum
miR-195 is a diagnostic and prognostic marker for osteosarcoma. J
Surg Res. 194:505–510. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang C, Yao C, Li H, Wang G and He X:
Combined elevation of microRNA-196a and microRNA-196b in sera
predicts unfavorable prognosis in patients with osteosarcomas. Int
J Mol Sci. 15:6544–6555. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chang L, Asatrian G, Dry SM and James AW:
Circulating tumor cells in sarcomas: A brief review. Med Oncol.
32:4302015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lapidot T, Sirard C, Vormoor J, Murdoch B,
Hoang T, Caceres-Cortes J, Minden M, Paterson B, Caligiuri MA and
Dick JE: A cell initiating human acute myeloid leukaemia after
transplantation into SCID mice. Nature. 367:645–648. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang ZF, Ngai P, Ho DW, Yu WC, Ng MN, Lau
CK, Li Ml, Tam KH, Lam CT, Poon RT, et al: Identification of local
and circulating cancer stem cells in human liver cancer.
Hepatology. 47:919–928. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schatton T, Murphy GF, Frank NY, Yamaura
K, Waaga-Gasser AM, Gasser M, Zhan Q, Jordan S, Duncan LM,
Weishaupt C, et al: Identification of cells initiating human
melanomas. Nature. 451:345–349. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sampieri K and Fodde R: Cancer stem cells
and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:187–193. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Budd GT, Cristofanilli M, Ellis MJ,
Stopeck A, Borden E, Miller MC, Matera J, Repollet M, Doyle GV,
Terstappen LW, et al: Circulating tumor cells versus imaging -
predicting overall survival in metastatic breast cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:6403–6409. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sheng Y, Wang T, Li H, Zhang Z, Chen J, He
C, Li Y, Lv Y, Zhang J, Xu C, et al: Comparison of analytic
performances of Cellsearch and iFISH approach in detecting
circulating tumor cells. Oncotarget. 2015:52015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Satelli A, Mitra A, Cutrera JJ, Devarie M,
Xia X, Ingram DR, Dibra D, Somaiah N, Torres KE, Ravi V, et al:
Universal marker and detection tool for human sarcoma circulating
tumor cells. Cancer Res. 74:1645–1650. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ran R, Li L, Wang M, Wang S, Zheng Z and
Lin PP: Determination of EGFR mutations in single cells
microdissected from enriched lung tumor cells in peripheral blood.
Anal Bioanal Chem. 405:7377–7382. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen Q, Ge F, Cui W, Wang F, Yang Z, Guo
Y, Li L, Bremner RM and Lin PP: Lung cancer circulating tumor cells
isolated by the EpCAM-independent enrichment strategy correlate
with cyto-keratin 19-derived CYFRA21-1 and pathological staging.
Clin Chim Acta. 419:57–61. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ning N, Zhan T, Zhang Y, Chen Q, Feng F,
Yang Z, Liu Z, Xu D, Wang F, Guo Y, et al: Improvement of specific
detection of circulating tumor cells using combined CD45 staining
and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Clin Chim Acta. 433:69–75.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Miller AB, Hoogstraten B, Staquet M and
Winkler A: Reporting results of cancer treatment. Cancer.
47:207–214. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Enneking WF: Musculoskeletal tumor
staging: 1988 update. Cancer Treat Res. 44:39–49. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Russell Wl, Sailors DM, Whittle TB, Fisher
DF Jr and Burns RP: Limb salvage versus traumatic amputation. A
decision based on a seven-part predictive index. Ann Surg.
213:473–480; discussion 480–481. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Detry MA and Lewis RJ: The
intention-to-treat principle: How to assess the true effect of
choosing a medical treatment. JAMA. 312:85–86. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xu SH, Yang YL, Han SM and Wu ZH:
MicroRNA-9 expression is a prognostic biomarker in patients with
osteosarcoma. World J Surg Oncol. 12:1952014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang J, Gao T, Tang J, Cai H, Lin L and Fu
S: Loss of microRNA-132 predicts poor prognosis in patients with
primary osteosarcoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 381:9–15. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tang M, Lin L, Cai H, Tang J and Zhou Z:
MicroRNA-145 downregulation associates with advanced tumor
progression and poor prognosis in patients suffering osteosarcoma.
Onco Targets Ther. 6:833–838. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mu Y, Zhang H, Che L and Li K: Clinical
significance of microRNA-183/Ezrin axis in judging the prognosis of
patients with osteosarcoma. Med Oncol. 31:8212014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhang H, Yin Z, Ning K, Wang L, Guo R and
Ji Z: Prognostic value of microRNA-223/epithelial cell transforming
sequence 2 signaling in patients with osteosarcoma. Hum Pathol.
45:1430–1436. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tian Z, Guo B, Yu M, Wang C, Zhang H,
Liang Q, Jiang K and Cao L: Upregulation of micro-ribonucleic
acid-128 cooperating with downregulation of PTEN confers metastatic
potential and unfavorable prognosis in patients with primary
osteosarcoma. Onco Targets Ther. 7:1601–1608. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jentzsch T, Robl B, Husmann M,
Bode-Lesniewska B and Fuchs B: Expression of MSH2 and MSH6 on a
tissue microarray in patients with osteosarcoma. Anticancer Res.
34:6961–6972. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sonaglio V, de Carvalho AC, Toledo SR,
Salinas-Souza C, Carvalho AL, Petrilli AS, de Camargo B and Vettore
AL: Aberrant DNA methylation of ESR1 and p14ARF genes could be
useful as prognostic indicators in osteosarcoma. Onco Targets Ther.
6:713–723. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhu H, Tang J, Tang M and Cai H:
Upregulation of SOX9 in osteosarcoma and its association with tumor
progression and patients' prognosis. Diagn Pathol. 8:1832013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhu Y, Zhou J, Ji Y and Yu B: Elevated
expression of AKT2 correlates with disease severity and poor
prognosis in human osteosarcoma. Mol Med Rep. 10:737–742.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hu F, Wang W, Zhou HC and Shang XF: High
expression of periostin is dramatically associated with metastatic
potential and poor prognosis of patients with osteosarcoma. World J
Surg Oncol. 12:2872014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhu H, Cai H, Tang M and Tang J:
Neuropilin-1 is overexpressed in osteosarcoma and contributes to
tumor progression and poor prognosis. Clin Transl Oncol.
16:732–738. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Kubo T, Shimose S, Fujimori J, Furuta T,
Arihiro K and Ochi M: Does expression of glucose transporter
protein-1 relate to prognosis and angiogenesis in osteosarcoma?
Clin Orthop Relat Res. 473:305–310. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
47
|
Wang X, Du J, Gu P, Jin R and Lin X:
Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor expression is correlated with
poor prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma. Mol Med Rep.
9:2105–2110. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dawood S, Broglio K, Valero V, Reuben J,
Handy B, Islam R, Jackson S, Hortobagyi GN, Fritsche H and
Cristofanilli M: Circulating tumor cells in metastatic breast
cancer: From prognostic stratification to modification of the
staging system? Cancer. 113:2422–2430. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hayes DF and Smerage J: Is there a role
for circulating tumor cells in the management of breast cancer?
Clin Cancer Res. 14:3646–3650. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liu MC, Shields PG, Warren RD, Cohen P,
Wilkinson M, Ottaviano YL, Rao SB, Eng-Wong J,
Seillier-Moiseiwitsch F, Noone AM, et al: Circulating tumor cells:
A useful predictor of treatment efficacy in metastatic breast
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:5153–5159. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Krawczyk N, Banys M, Hartkopf A, Hagenbeck
C, Melcher C and Fehm T: Circulating tumour cells in breast cancer.
E Cancer Med Sci. 7:3522013.
|