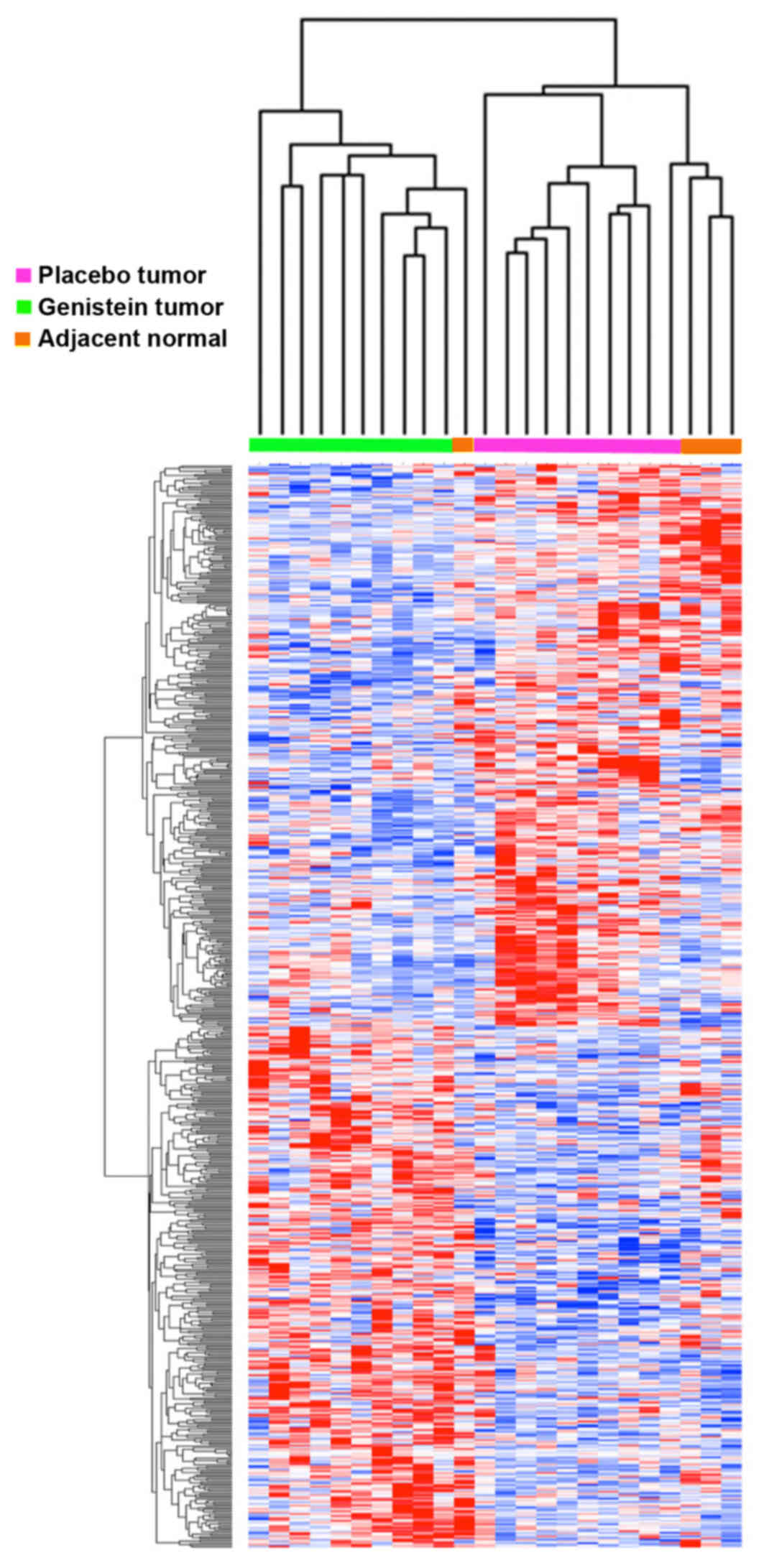
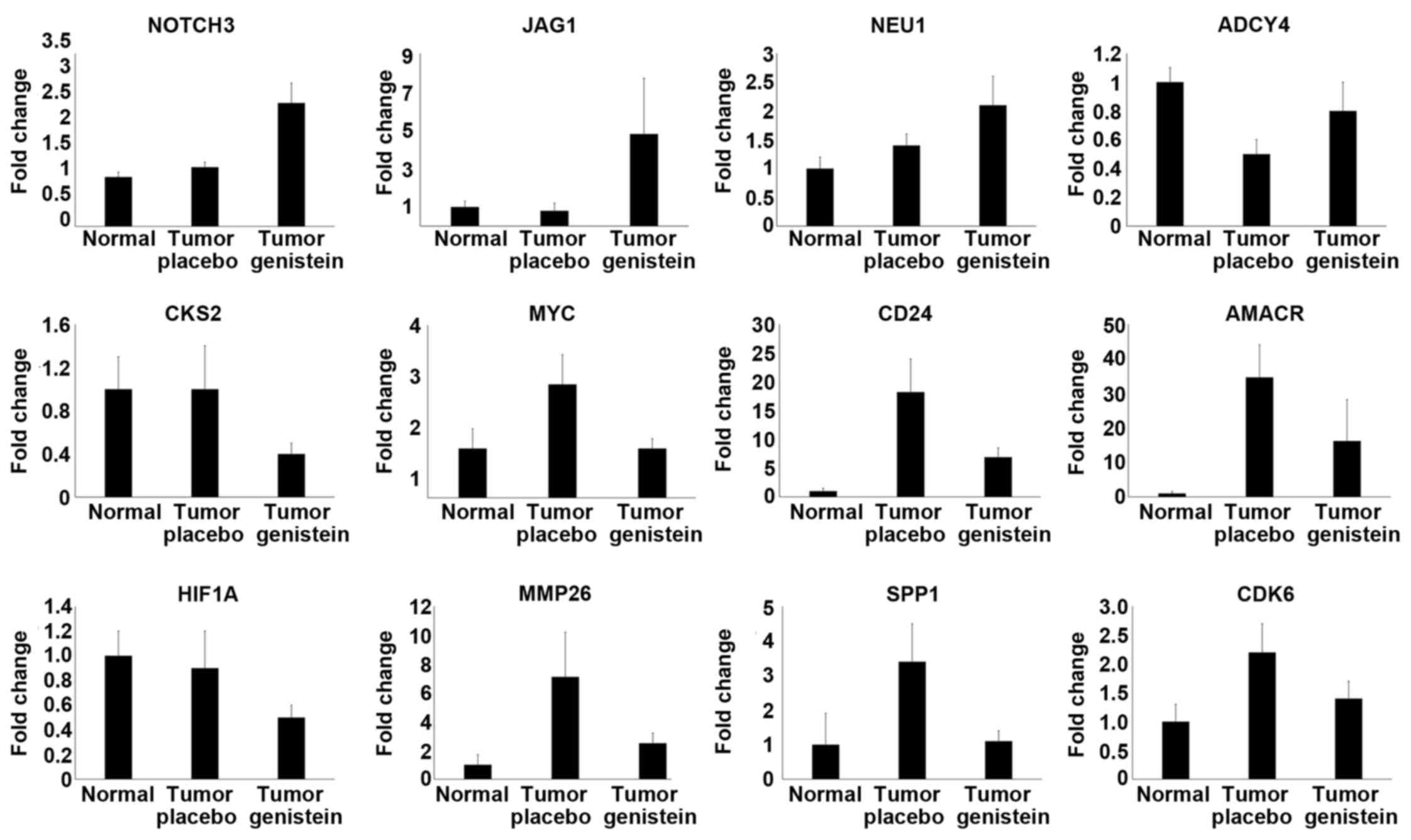
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Prostate Cancer Facts and Figures 2016.
American Cancer Society Inc; Atlanta, GA: 2016
|
|
3
|
Dunn MW and Kazer MW: Prostate cancer
overview. Semin Oncol Nurs. 27:241–250. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sartor AO: Progression of metastatic
castrate-resistant prostate cancer: Impact of therapeutic
intervention in the post-docetaxel space. J Hematol Oncol.
4:182011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Skolarus TA, Wolf AMD, Erb NL, Brooks DD,
Rivers BM, Underwood W III, Salner AL, Zelefsky MJ, Aragon-Ching
JB, Slovin SF, et al: American Cancer Society prostate cancer
survivorship care guidelines. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:225–249. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hieronymus H, Schultz N, Gopalan A, Carver
BS, Chang MT, Xiao Y, Heguy A, Huberman K, Bernstein M, Assel M, et
al: Copy number alteration burden predicts prostate cancer relapse.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:11139–11144. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ferlay J, Bray F, Pisani P and Parkin DM:
Globocan 2000: Cancer Incidence, Mortality and Prevalence
Worldwide. IARC Press; Lyon: 2001
|
|
8
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kimura T: East meets West: Ethnic
differences in prostate cancer epidemiology between East Asians and
Caucasians. Chin J Cancer. 31:421–429. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Reinli K and Block G: Phytoestrogen
content of foods–a compendium of literature values. Nutr Cancer.
26:123–148. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Adlercreutz H, Markkanen H and Watanabe S:
Plasma concentrations of phyto-oestrogens in Japanese men. Lancet.
342:1209–1210. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Morton MS, Chan PS, Cheng C, Blacklock N,
Matos-Ferreira A, Abranches-Monteiro L, Correia R, Lloyd S and
Griffiths K: Lignans and isoflavonoids in plasma and prostatic
fluid in men: Samples from Portugal, Hong Kong, and the United
Kingdom. Prostate. 32:122–128. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hwang YW, Kim SY, Jee SH, Kim YN and Nam
CM: Soy food consumption and risk of prostate cancer: A
meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutr Cancer. 61:598–606.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Van Poppel H and Tombal B: Chemoprevention
of prostate cancer with nutrients and supplements. Cancer Manag
Res. 3:91–100. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Barnes S, Peterson TG and Coward L:
Rationale for the use of genistein-containing soy matrices in
chemoprevention trials for breast and prostate cancer. J Cell
Biochem (Suppl). S22:181–187. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Takimoto CH, Glover K, Huang X, Hayes SA,
Gallot L, Quinn M, Jovanovic BD, Shapiro A, Hernandez L, Goetz A,
et al: Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis of
unconjugated soy isoflavones administered to individuals with
cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 12:1213–1221.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gardner CD, Oelrich B, Liu JP, Feldman D,
Franke AA and Brooks JD: Prostatic soy isoflavone concentrations
exceed serum levels after dietary supplementation. Prostate.
69:719–726. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bloedon LT, Jeffcoat AR, Lopaczynski W,
Schell MJ, Black TM, Dix KJ, Thomas BF, Albright C, Busby MG,
Crowell JA, et al: Safety and pharmacokinetics of purified soy
isoflavones: Single-dose administration to postmenopausal women. Am
J Clin Nutr. 76:1126–1137. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yildiz F: Phytoestrogens in functional
foods. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL: 2005, https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420027594.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Morito K, Hirose T, Kinjo J, Hirakawa T,
Okawa M, Nohara T, Ogawa S, Inoue S, Muramatsu M and Masamune Y:
Interaction of phytoestrogens with estrogen receptors alpha and
beta. Biol Pharm Bull. 24:351–356. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chang WY and Prins GS: Estrogen
receptor-beta: Implications for the prostate gland. Prostate.
40:115–124. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kumar R, Verma V, Jain A, Jain RK,
Maikhuri JP and Gupta G: Synergistic chemoprotective mechanisms of
dietary phytoestrogens in a select combination against prostate
cancer. J Nutr Biochem. 22:723–731. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wang J, Eltoum IE and Lamartiniere CA:
Genistein chemoprevention of prostate cancer in TRAMP mice. J
Carcinog. 6:32007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Davis JN, Kucuk O and Sarkar FH:
Expression of prostate-specific antigen is transcriptionally
regulated by genistein in prostate cancer cells. Mol Carcinog.
34:91–101. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bektic J, Berger AP, Pfeil K, Dobler G,
Bartsch G and Klocker H: Androgen receptor regulation by
physiological concentrations of the isoflavonoid genistein in
androgen-dependent LNCaP cells is mediated by estrogen receptor
beta. Eur Urol. 45:245–251; discussion 251. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shen JC, Klein RD, Wei Q, Guan Y, Contois
JH, Wang TT, Chang S and Hursting SD: Low-dose genistein induces
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors and G(1) cell-cycle arrest in
human prostate cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 29:92–102. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Davis JN, Singh B, Bhuiyan M and Sarkar
FH: Genistein-induced upregulation of p21WAF1, downregulation of
cyclin B, and induction of apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Nutr
Cancer. 32:123–131. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Raffoul JJ, Wang Y, Kucuk O, Forman JD,
Sarkar FH and Hillman GG: Genistein inhibits radiation-induced
activation of NF-kappaB in prostate cancer cells promoting
apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle arrest. BMC Cancer. 6:1072006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li Y and Sarkar FH: Down-regulation of
invasion and angiogenesis-related genes identified by cDNA
microarray analysis of PC3 prostate cancer cells treated with
genistein. Cancer Lett. 186:157–164. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guo Y, Wang S, Hoot DR and Clinton SK:
Suppression of VEGF-mediated autocrine and paracrine interactions
between prostate cancer cells and vascular endothelial cells by soy
isoflavones. J Nutr Biochem. 18:408–417. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li Y, Che M, Bhagat S, Ellis KL, Kucuk O,
Doerge DR, Abrams J, Cher ML and Sarkar FH: Regulation of gene
expression and inhibition of experimental prostate cancer bone
metastasis by dietary genistein. Neoplasia. 6:354–363. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang LL, Li L, Wu DP, Fan JH, Li X, Wu
KJ, Wang XY and He DL: A novel anti-cancer effect of genistein:
Reversal of epithelial mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer
cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 29:1060–1068. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kumi-Diaka JK, Hassanhi M, Merchant K and
Horman V: Influence of genistein isoflavone on matrix
metalloproteinase-2 expression in prostate cancer cells. J Med
Food. 9:491–497. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kazi A, Daniel KG, Smith DM, Kumar NB and
Dou QP: Inhibition of the proteasome activity, a novel mechanism
associated with the tumor cell apoptosis-inducing ability of
genistein. Biochem Pharmacol. 66:965–976. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kumi-Diaka J, Sanderson NA and Hall A: The
mediating role of caspase-3 protease in the intracellular mechanism
of genistein-induced apoptosis in human prostatic carcinoma cell
lines, DU145 and LNCaP. Biol Cell. 92:595–604. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lee J, Ju J, Park S, Hong SJ and Yoon S:
Inhibition of IGF-1 signaling by genistein: Modulation of
E-cadherin expression and downregulation of β-catenin signaling in
hormone refractory PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Nutr Cancer.
64:153–162. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Xu L and Bergan RC: Genistein inhibits
matrix metalloproteinase type 2 activation and prostate cancer cell
invasion by blocking the transforming growth factor beta-mediated
activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein
kinase 2-27-kDa heat shock protein pathway. Mol Pharmacol.
70:869–877. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Davis JN, Kucuk O and Sarkar FH: Genistein
inhibits NF-kappaB activation in prostate cancer cells. Nutr
Cancer. 35:167–174. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Li Y and Sarkar FH: Inhibition of nuclear
factor kappaB activation in PC3 cells by genistein is mediated via
Akt signaling pathway. Clin Cancer Res. 8:2369–2377.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Akiyama T, Ishida J, Nakagawa S, Ogawara
H, Watanabe S, Itoh N, Shibuya M and Fukami Y: Genistein, a
specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. J Biol
Chem. 262:5592–5595. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Park CE, Yun H, Lee EB, Min BI, Bae H,
Choe W, Kang I, Kim SS and Ha J: The antioxidant effects of
genistein are associated with AMP-activated protein kinase
activation and PTEN induction in prostate cancer cells. J Med Food.
13:815–820. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Raschke M, Rowland IR, Magee PJ and
Pool-Zobel BL: Genistein protects prostate cells against hydrogen
peroxide-induced DNA damage and induces expression of genes
involved in the defence against oxidative stress. Carcinogenesis.
27:2322–2330. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Swami S, Krishnan AV, Moreno J,
Bhattacharyya RS, Gardner C, Brooks JD, Peehl DM and Feldman D:
Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis and actions by genistein in
human prostate cancer cells and by soy isoflavones in prostate
cancer patients. Int J Cancer. 124:2050–2059. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Adjakly M, Bosviel R, Rabiau N, Boiteux
JP, Bignon YJ, Guy L and Bernard-Gallon D: DNA methylation and soy
phytoestrogens: Quantitative study in DU-145 and PC-3 human
prostate cancer cell lines. Epigenomics. 3:795–803. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Vardi A, Bosviel R, Rabiau N, Adjakly M,
Satih S, Dechelotte P, Boiteux JP, Fontana L, Bignon YJ, Guy L, et
al: Soy phytoestrogens modify DNA methylation of GSTP1, RASSF1A,
EPH2 and BRCA1 promoter in prostate cancer cells. In Vivo.
24:393–400. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fang MZ, Chen D, Sun Y, Jin Z, Christman
JK and Yang C: Reversal of hypermethylation and reactivation of
16INK4a, RARbeta, and MGMT genes by genistein and other
isoflavones from soy. Clin Cancer Res. 11:7033–7041. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Majid S, Dar AA, Shahryari V, Hirata H,
Ahmad A, Saini S, Tanaka Y, Dahiya AV and Dahiya R: Genistein
reverses hyper-methylation and induces active histone modifications
in tumor suppressor gene B-Cell translocation gene 3 in prostate
cancer. Cancer. 116:66–76. 2010.
|
|
48
|
Kikuno N, Shiina H, Urakami S, Kawamoto K,
Hirata H, Tanaka Y, Majid S, Igawa M and Dahiya R: Genistein
mediated histone acetylation and demethylation activates tumor
suppressor genes in prostate cancer cells. Int J Cancer.
123:552–560. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li Y, Kong D, Ahmad A, Bao B, Dyson G and
Sarkar FH: Epigenetic deregulation of miR-29a and miR-1256 by
isoflavone contributes to the inhibition of prostate cancer cell
growth and invasion. Epigenetics. 7:940–949. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Rabiau N, Trraf HK, Adjakly M, Bosviel R,
Guy L, Fontana L, Bignon YJ and Bernard-Gallon DJ: miRNAs
differentially expressed in prostate cancer cell lines after soy
treatment. In Vivo. 25:917–921. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chen Y, Zaman MS, Deng G, Majid S, Saini
S, Liu J, Tanaka Y and Dahiya R: MicroRNAs 221/222 and
genistein-mediated regulation of ARHI tumor suppressor gene in
prostate cancer. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 4:76–86. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Chiyomaru T, Yamamura S, Fukuhara S,
Hidaka H, Majid S, Saini S, Arora S, Deng G, Shahryari V, Chang I,
et al: Genistein up-regulates tumor suppressor microRNA-574-3p in
prostate cancer. PLoS One. 8:e589292013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hillman GG, Forman JD, Kucuk O, Yudelev M,
Maughan RL, Rubio J, Layer A, Tekyi-Mensah S, Abrams J and Sarkar
FH: Genistein potentiates the radiation effect on prostate
carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 7:382–390. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li Y, Kucuk O, Hussain M, Abrams J, Cher
ML and Sarkar FH: Antitumor and antimetastatic activities of
docetaxel are enhanced by genistein through regulation of
osteoprotegerin/receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB
(RANK)/RANK ligand/MMP-9 signaling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res.
66:4816–4825. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Spagnuolo C, Russo GL, Orhan IE,
Habtemariam S, Daglia M, Sureda A, Nabavi SF, Devi KP, Loizzo MR,
Tundis R, et al: Genistein and cancer: Current status, challenges,
and future directions. Adv Nutr. 6:408–419. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Katoh M: Network of WNT and other
regulatory signaling cascades in pluripotent stem cells and cancer
stem cells. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 12:160–170. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Mori R, Wang Q, Danenberg KD, Pinski JK
and Danenberg PV: Both beta-actin and GAPDH are useful reference
genes for normalization of quantitative RT-PCR in human FFPE tissue
samples of prostate cancer. Prostate. 68:1555–1560. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Reich M, Liefeld T, Gould J, Lerner J,
Tamayo P and Mesirov JP: GenePattern 2.0. Nat Genet. 38:500–501.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Eisen MB, Spellman PT, Brown PO and
Botstein D: Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression
patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:14863–14868. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Saldanha AJ: Java Treeview - extensible
visualization of micro-array data. Bioinformatics. 20:3246–3248.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Barfield RT, Kilaru V, Smith AK and
Conneely KN: CpGassoc: An R function for analysis of DNA
methylation microarray data. Bioinformatics. 28:1280–1281. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
http://www.qiagen.com/ingenuity.
Qiagen's Ingenuity Pathway Analysis.
|
|
63
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for Annotation,
Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol. 4:32003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Wang Z and Chen H: Genistein increases
gene expression by demethylation of WNT5a promoter in colon cancer
cell line SW1116. Anticancer Res. 30:4537–4545. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Gao BN and Gilman AG: Cloning and
expression of a widely distributed (type IV) adenylyl cyclase. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 88:10178–10182. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Brikun I, Nusskern D, Gillen D, Lynn A,
Murtagh D, Feczko J, Nelson WG and Freije D: A panel of DNA
methylation markers reveals extensive methylation in histologically
benign prostate biopsy cores from cancer patients. Biomark Res.
2:252014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Monti E, Bonten E, D'Azzo A, Bresciani R,
Venerando B, Borsani G, Schauer R and Tettamanti G: Sialidases in
vertebrates: A family of enzymes tailored for several cell
functions. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 64:403–479. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Uemura T, Shiozaki K, Yamaguchi K,
Miyazaki S, Satomi S, Kato K, Sakuraba H and Miyagi T: Contribution
of sialidase NEU1 to suppression of metastasis of human colon
cancer cells through desialylation of integrin beta4. Oncogene.
28:1218–1229. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Kato T, Wang Y, Yamaguchi K, Milner CM,
Shineha R, Satomi S and Miyagi T: Overexpressing of lysosomal-type
sialidase leads to suppression of metastasis associated with
reversion of malignant phenotype in murine B16 melanoma cells. Int
J Cancer. 92:797–804. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Chang S, He S, Qiu G, Lu J, Wang J, Liu J,
Fan L, Zhao W and Che X: MicroRNA-125b promotes invasion and
metastasis of gastric cancer by targeting STARD13 and NEU1. Tumour
Biol. 37:12141–12151. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Haxho F, Neufeld RJ and Szewczuk MR:
Neuraminidase-1: A novel therapeutic target in multistage
tumorigenesis. Oncotarget. 7:40860–40881. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Liu L, Chen X, Wang Y, Qu Z, Lu Q, Zhao J,
Yan X, Zhang H and Zhou Y: Notch3 is important for TGF-β-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer
bone metastasis by regulating ZEB-1. Cancer Gene Ther. 21:364–372.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Danza G, Di Serio C, Ambrosio MR, Sturli
N, Lonetto G, Rosati F, Rocca BJ, Ventimiglia G, del Vecchio MT,
Prudovsky I, et al: Notch3 is activated by chronic hypoxia and
contributes to the progression of human prostate cancer. Int J
Cancer. 133:2577–2586. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Terada N, Shiraishi T, Zeng Y, Aw-Yong KM,
Mooney SM, Liu Z, Takahashi S, Luo J, Lupold SE, Kulkarni P, et al:
Correlation of Sprouty1 and Jagged1 with aggressive prostate cancer
cells with different sensitivities to androgen deprivation. J Cell
Biochem. 115:1505–1515. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Pedrosa AR, Graça JL, Carvalho S,
Peleteiro MC, Duarte A and Trindade A: Notch signaling dynamics in
the adult healthy prostate and in prostatic tumor development.
Prostate. 76:80–96. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Pedrosa AR, Trindade A, Carvalho C, Graça
J, Carvalho S, Peleteiro MC, Adams RH and Duarte A: Endothelial
Jagged1 promotes solid tumor growth through both pro-angiogenic and
angiocrine functions. Oncotarget. 6:24404–24423. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Danza G, Di Serio C, Rosati F, Lonetto G,
Sturli N, Kacer D, Pennella A, Ventimiglia G, Barucci R, Piscazzi
A, et al: Notch signaling modulates hypoxia-induced neuroendocrine
differentiation of human prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res.
10:230–238. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Rampias T, Vgenopoulou P, Avgeris M,
Polyzos A, Stravodimos K, Valavanis C, Scorilas A and Klinakis A: A
new tumor suppressor role for the Notch pathway in bladder cancer.
Nat Med. 20:1199–1205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Hernandez Tejada FN, Galvez Silva JR and
Zweidler-McKay PA: The challenge of targeting notch in hematologic
malignancies. Front Pediatr. 2:542014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Giachino C, Boulay JL, Ivanek R, Alvarado
A, Tostado C, Lugert S, Tchorz J, Coban M, Mariani L, Bettler B, et
al: A tumor suppressor function for Notch signaling in forebrain
tumor subtypes. Cancer Cell. 28:730–742. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Jaskula-Sztul R, Eide J, Tesfazghi S,
Dammalapati A, Harrison AD, Yu XM, Scheinebeck C, Winston-McPherson
G, Kupcho KR, Robers MB, et al: Tumor-suppressor role of Notch3 in
medullary thyroid carcinoma revealed by genetic and pharmacological
induction. Mol Cancer Ther. 14:499–512. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Sriuranpong V, Borges MW, Ravi RK, Arnold
DR, Nelkin BD, Baylin SB and Ball DW: Notch signaling induces cell
cycle arrest in small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res.
61:3200–3205. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Liu YL, Zhang GQ, Yang Y, Zhang CY, Fu RX
and Yang YM: Genistein induces G2/M arrest in gastric cancer cells
by increasing the tumor suppressor PTEN expression. Nutr Cancer.
65:1034–1041. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Su SJ, Yeh TM, Chuang WJ, Ho CL, Chang KL,
Cheng HL, Liu HS, Cheng HL, Hsu PY and Chow NH: The novel targets
for anti-angiogenesis of genistein on human cancer cells. Biochem
Pharmacol. 69:307–318. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Jagadeesh S, Kyo S and Banerjee PP:
Genistein represses telomerase activity via both transcriptional
and posttranslational mechanisms in human prostate cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 66:2107–2115. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Mahmoud AM, Al-Alem U, Ali MM and Bosland
MC: Genistein increases estrogen receptor beta expression in
prostate cancer via reducing its promoter methylation. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 152:62–75. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Whirledge S, Senbanjo LT and Cidlowski JA:
Genistein disrupts glucocorticoid receptor signaling in human
uterine endometrial Ishikawa cells. Environ Health Perspect.
123:80–87. 2015.
|
|
88
|
Bhamre S, Sahoo D, Tibshirani R, Dill DL
and Brooks JD: Gene expression changes induced by genistein in the
prostate cancer cell line LNCaP. Open Prostate Cancer J. 3:86–98.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Ghaemi A, Soleimanjahi H, Razeghi S, Gorji
A, Tabaraei A, Moradi A, Alizadeh A and Vakili MA: Genistein
induces a protective immunomodulatory effect in a mouse model of
cervical cancer. Iran J Immunol. 9:119–127. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Korde LA, Wu AH, Fears T, Nomura AM, West
DW, Kolonel LN, Pike MC, Hoover RN and Ziegler RG: Childhood soy
intake and breast cancer risk in Asian American women. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 18:1050–1059. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Lee SA, Shu XO, Li H, Yang G, Cai H, Wen
W, Ji BT, Gao J, Gao YT and Zheng W: Adolescent and adult soy food
intake and breast cancer risk: Results from the Shanghai Women's
Health Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 89:1920–1926. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|